Monetary policy refers to

Check here Highlights of RBI’s first bi-monthly policy statement for FY’25: RBI holds the Repo rate unchanged at 6. The ECB Blog looks at a recent high-level conference that analysed the . Price stability refers to a condition of low and stable inflation.Monetary policy refers to the Federal Reserve's actions and communications to promote maximum employment, stable prices and moderate long-term interest rates. The BSP's main responsibility is to formulate and implement policy in the areas of money, banking and credit with the primary objective of preserving price stability. It aims to prevent inflation, reduce unemployment, and promote . Learn how central banks such as the Fed and the Bank of . The equation for the demand for money is: Md = P × L(R, Y) M d = P × L ( R, Y).Tight monetary policy is a course of action undertaken by the Federal Reserve to constrict spending in an economy that is seen to be growing too quickly or to curb inflation when it is rising too .
How Does It Work?
Monetary Policy. B) Federal Reserve takes to manage the money supply and interest rates to pursue its macroeconomic policy objectives.Monetary policy is the responsibility of a central bank, such as the Federal Reserve, to pursue its dual mandate of price . What is monetary policy and why is it important? Central banks use monetary policy to manage economic fluctuations and achieve price stability, which means .Monetary policy actions take time - usually between six and eight quarters - to work their way through the economy and have their full effect on inflation. What happens to the money supply when the FED buys securities on the open market?
What Is Monetary Policy?
Governments and central banks can shield the economy from shocks with their decisions.Monetary policy refers to changes made by a central bank to interest rates and/or the quantity of money in order to achieve changes in aggregate demand . Monetary policy consists of decisions and actions taken by the Central Bank to ensure that the supply of money in the economy is consistent with growth and price objectives set by the government.Monetary policy is the use of interest rates and other tools to achieve maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates. For this reason, monetary policy is always forward looking and the policy rate setting is based on the Bank’s judgment of where inflation is likely to be in the future, not what it is today. The _____ market is a market in which the demand for and supply of money determine an interest rate or opportunity cost of holding money balances. For example, policymakers manipulate . the fed is pursuing an expansionary monetary policy. Learn about the tools of .
Monetary Policy: Stabilizing Prices and Output
Monetary policy is a central bank's actions and communications that manage the money supply.The Demand for Money.
Monetary Policy and Central Banking
How Does It Work? – Forbes .The Federal Reserve conducts the nation's monetary policy to promote maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates in the U.
From the central bank's role as lender of last resort, to the Fed's dual mandate of price stability and maximum employment, to new policy tools devised .
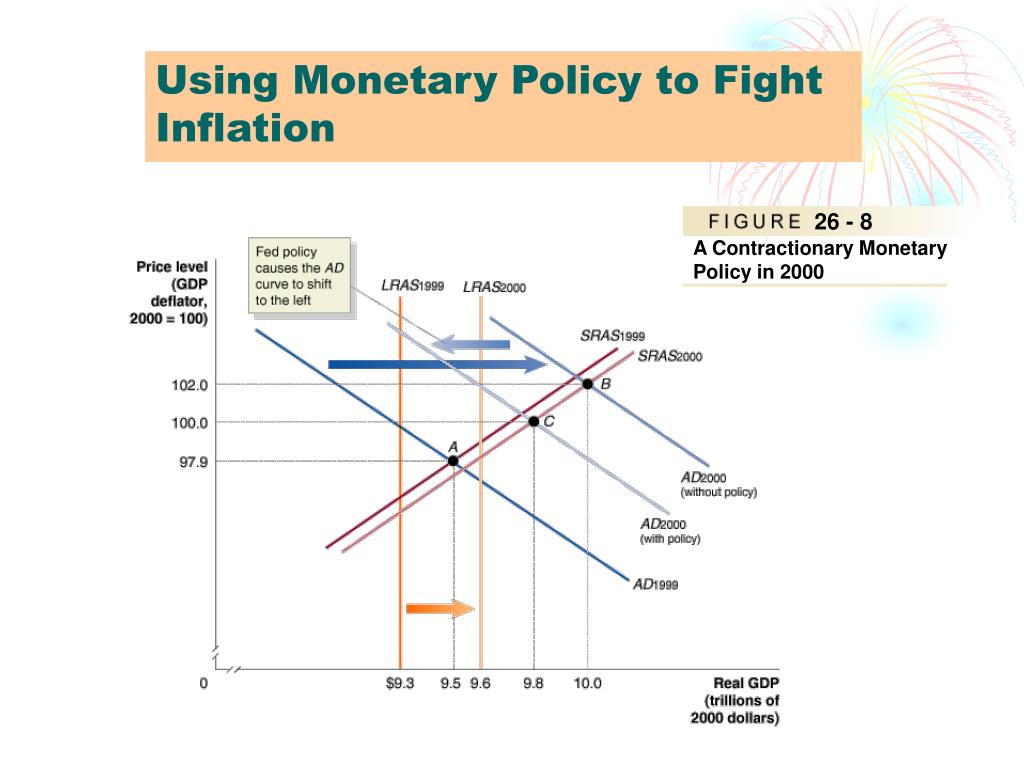
Price stability refers to maintenance of a low and . In the euro area, the European Central .
![]()
The repo rate is so called because banks give the SARB an asset, such as a Government bond, in exchange for cash. monetary policy and economic developments in 2020, with excerpts and select figures from the Monetary Policy Report published in February .Monetary and fiscal policy are two ways in which governments attempt to achieve or maintain high levels of employment, price stability, and economic growth.5% which is lower than 5. Generally, the nominal demand for money increases with the level of nominal output and decreases with the nominal interest rate. Fiscal policy typically is established legislatively and addresses issues such as tax rates and government .Monetary policy is how a central bank (also known as the bank's bank or the bank of last resort) influences the demand, supply, price of money, and credit to direct a nation's economic objectives.The term monetary policy refers to actions taken by central banks to affect monetary and other financial conditions in pursuit of the broader objectives of sustainable growth of real output, high employment, and price stability.comWhat are the types of Monetary Policy? - Business Jargonsbusinessjargons. federal reserve.

Monetary policy is the central bank's management of the money supply to achieve economic goals.Monetary policy refers to the steps taken by a country’s central bank to control the money supply for economic stability. Refers to changes in the money supply (by the Federal Reserve System) of a nation in order to influence its economy. This section reviews U.

The objective of monetary policy is to maintain price stability in the economy.Price Stability., money supply, and credit to influence economic .
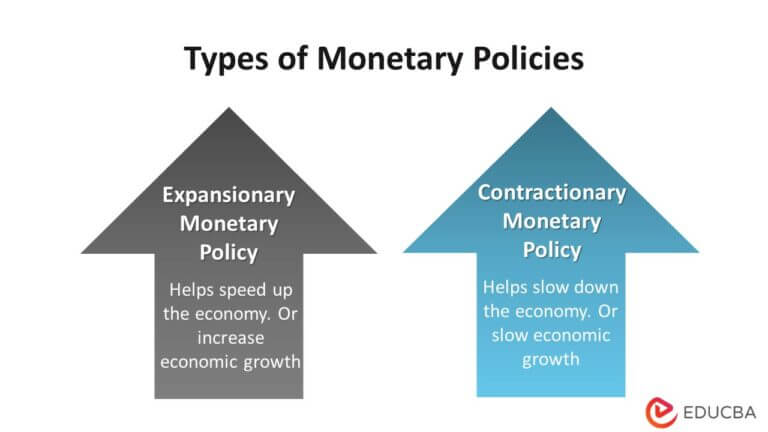
Monetary policy refers to the actions taken by a central bank or monetary authority to manage the supply of money and interest rates in an economy, with the aim of promoting economic growth and .Monetary policy is an economic policy that manages the size and growth rate of the money supply in an economy. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Monetary policy refers to the actions the, The federal reserve's .Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Monetary policy refers to the actions the A) President and Congress take to manage the money supply and interest rates to pursue their economic objectives. It involves management of money supply and interest rate and is the demand side economic policy used by the government of a country to achieve macroeconomic objectives like inflation, consumption, growth and liquidity. But however it may appear, it generally boils down to adjusting the supply of money in the economy to achieve some combination of . It is a crucial tool used to stabilize and manage the overall economic conditions, including inflation, unemployment, and economic growth.Monetary policy refers to the action of the _____ to influence the supply of money and credit in the U.Monetary policy is the macroeconomic policy laid down by the central bank. What Is Monetary Policy? The average rate of growth of the stock of money in circulation has been viewed for centuries as the decisive . While central banks are given the mandate to .comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Monetary policy
Monetary policy involves decisions by central banks on issues such as interest rates. Learn how monetary policy affects the global economy and why it matters for you . . actions taken by a government to control the amount of money in an economy and how easily available it is, for example by . If the fed lowers its target for the federal funds rate, this indicates that.monetary policy, Measures employed by governments to influence economic activity, specifically by manipulating the money supply and interest rates.Monetary policy refers to the measures and actions employed by a monetary authority or country's central bank to manage the economy's interest rates, money supply, and credit conditions.Transferable Underwriting Facility - TRUF: A type of underwriting facility that deals in Euro notes. Interest rate changes and adjustments to bank reserve requirements are examples of monetary policy strategies.noun [ U ] uk us.With monetary policy, a central bank increases or decreases the amount of currency and credit in circulation, in a continuing effort to keep inflation, growth and employment on track.Monetary policy is implemented by setting a short-term policy rate – the repo rate. Monetary policy primarily .Monetary policy is the use of money supply and interest rates to influence economic activity.Monetary policy refers to a change in the cost of borrowing (the rate of interest) or the quantity of money in circulation, in order to achieve the objective of low and stable inflation .Monetary policy.The RBI’s MPC’s two-day meeting, which began on April 3, wraps up on 5th April 2024.
Monetary policy
Fiscal policy refers to a . Description: In India, monetary policy of the .Monetary policy refers to a central bank’s moves to achieve macroeconomic policy objectives such as price stability, full employment, and stable economic growth. Learn how central banks such as the Federal Reserve System implement .The Atlanta Fed's latest Fed Explained video hits both marks. Generally classified as either expansionary or contractionary, Money Policy is utilized to achieve objectives including inflation, consumption, growth .Monetary policy refers to the actions and strategies implemented by a central bank or monetary authority to control and regulate the money supply and interest rates in an economy. Learn how it works, what tools it uses, and how it differs from .5-minute show traces 102 years of monetary policy through engaging animation and voiceovers tailored for the layperson. In economics, the demand for money is generally equated with cash or bank demand deposits. Monetary policy in the United States comprises the Federal Reserve's actions and communications to promote maximum employment, stable prices, and .The term monetary policy refers to actions taken by central banks to affect monetary and other financial conditions in pursuit of the broader objectives of sustainable . The Central Bank of a . It involves the regulation of interest rates Refer to the cost of borrowing money or the return on investment for lending money, usually expressed as a percentage.The monetary policy of a nation involves the overall set of laws and practices that control the quantity and quality of money in an economy.
Role of Monetary Policy in the Economy
The term monetary policy refers to the actions undertaken by a central bank, such as the Federal Reserve, to influence the availability and cost of money and credit to .
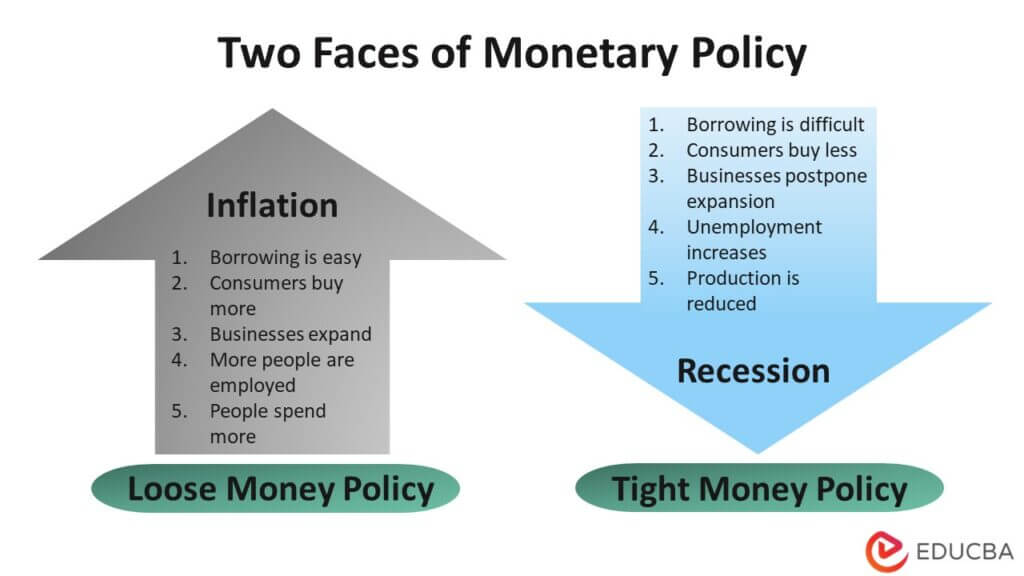
A reduction in the money supply designed to slow down .5% for the 7th consecutive time.” From these definitions, it is clear that a monetary policy is related to the availability and cost of money supply in the economy in order to attain certain broad objectives.
What is monetary policy?
They can later repurchase (repo) that .








