Nerve cell structure

Anatomically, a nerve cell consists of several parts mentioned above. Their main function is to send electrical signals over short and long distances in the body, and they are electrically and chemically excitable.Learn about nerve cells, the basic functional units of the nervous system, and their anatomy, types, and functions.0, via Wikimedia Commons. To be able to do this, the cell body contains organelles or really tiny organs in the nucleus.Nerve cells can also be classified into four types based on their structure. The nervous system monitors the changes that occur inside and outside the body, carries the obtained information from one part of the body to .Nerve cells (neurones) – these form the functional basis of the nervous system, responsible for transmitting signals as electrical or chemical signals. The function of the neuron is dependent on the structure of the neuron. They use electrical and chemical signals to send information between different areas of .Overview
Aperçu de la structure et de la fonction du neurone
orgRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Neuron
In the PNS, a cluster of neuron cell bodies is referred to as a ganglion. Nerve ending] 1. Updated on October 15, 2023.What is a neuron?
Activité : Medical Content
Nerve Cell
Nerve Cells
Medically reviewed by Smita Patel, DO.The cell body . Neurons (or nerve cells) are specialized cells that transmit and receive electrical signals in the body. Neurons are unique in their ability to receive and transmit information. The impulses from the axon cross a synapse (the junction between 2 nerve cells) to the dendrite of another cell. At the end of the axon, we find the axon terminals. Dendrites typically receive signals while the axon passes on the signals to other cells, such as other .Neuron structure is variable, but the main components of cell body (shown in black), dendrites (shown in brown), and axon (shown in blue) are common among all neurons.Typical Structure of a Nerve Cell. A nerve cell (neuron) consists of a large cell body and nerve fibers—one elongated extension (axon) for sending impulses and usually many branches (dendrites) for receiving impulses.What Are Neurons? By Sarah Jividen, RN.Also known as the soma, the cell body is a ball-like structure. Identifier les divisions anatomiques et fonctionnelles du système nerveux. Usually, the size of nerve cells varies depending on how long the electrical impulses are to be transmitted.Structure and Function of Neurons.
Nervous system: Structure, function and diagram
At the end of the axon, or the axon terminals, special chemicals called neurotransmitters pass the signal on to the target cell, which may be a nerve cell, a muscle cell, or a gland cell. Each nerve cell receives input from another nerve cell or cells and sends output to the other nerve cell or cells.
Histology of nervous tissue: neurons, nerves and ganglia
wetcake / Getty Images. Extending from the cell body are thin structures that are specialized for receiving and sending signals.
Find out how they receive, process, and transmit information to the brain and body. Objectifs d'apprentissage.Expand/collapse global location. La cellule nerveuse (neurone) est constituée d’un grand corps cellulaire et de fibres nerveuses, dont un prolongement (axone) qui transmet les impulsions et, en général, de . The structure of nerve cells is highly specialized. Cell body The (soma) is the factory of the neuron. Other synapses are electrical; in these synapses, ions flow directly between cells.Structure of Nerve Cell. Glial cells – .Neuronal membrane][3. Neurons, also called nerve cells, are electrically excitable cells that are the main functional units of the nervous system. 1: Interneurons of Adult Visual Cortex. The myelin sheath prevents the nerve cells from being able to undergo cell division.
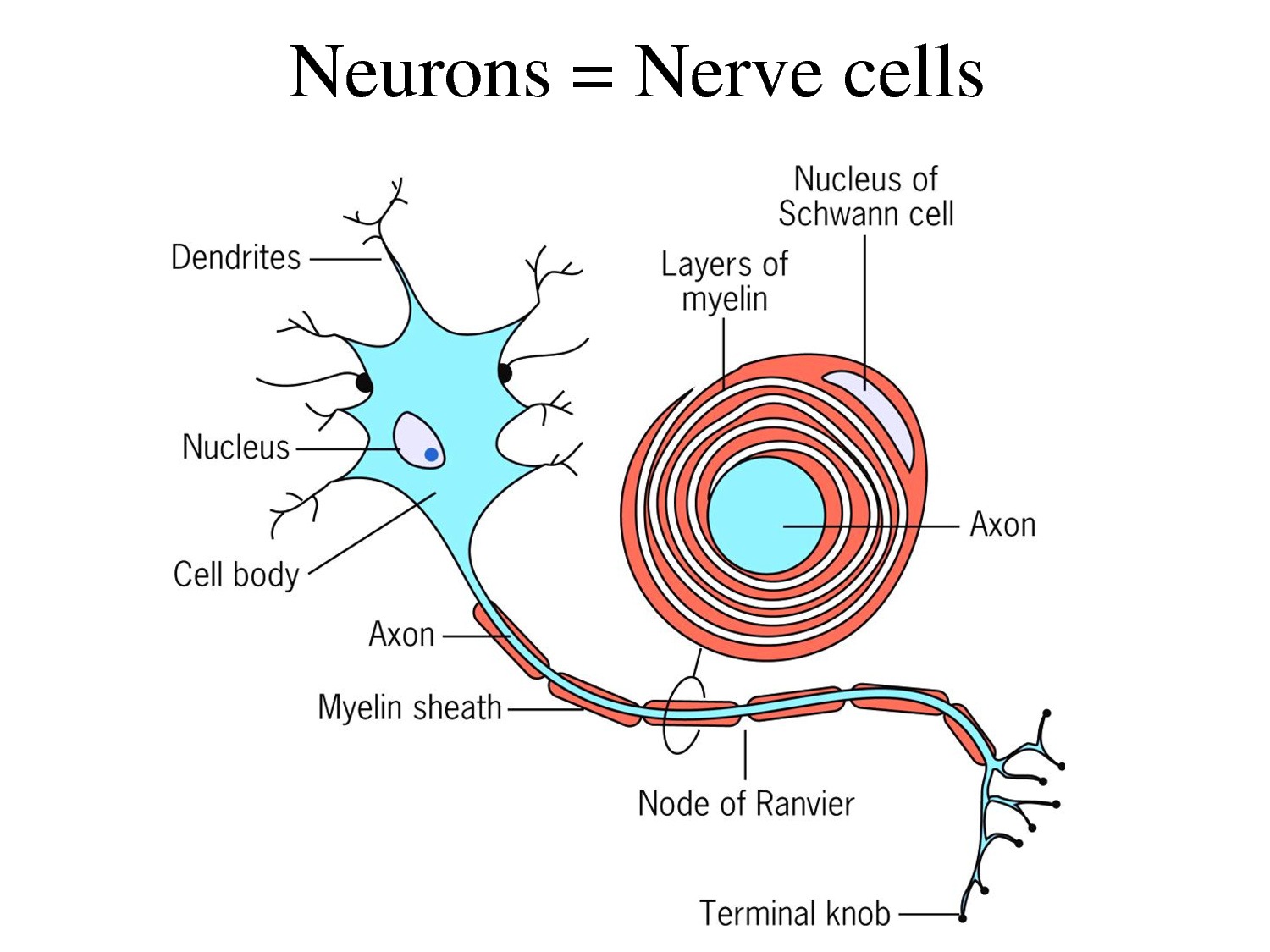
Figure: Structure d’une cellule nerveuse
Les neurones et leurs différents types et morphologiesneuromedia. Find out how neurons communicate with each other . They enable the passage of electrical impulses within the brain and between the brain and the . Unipolar neurons have a single structure extending from the cell body which contains . The impulses from the axon cross a synapse (the junction between two nerve cells) to the dendrite of another cell. The nerve cell is a specialized individual cell that forms our nervous system.
![[DIAGRAM] Diagram Of Nerve Cell Organelles - MYDIAGRAM.ONLINE](https://what-when-how.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/04/tmp14261.jpg)
0 International License. Nerve cells consist of a cell body (soma), dendrites, an axon and a specialized cytoskeleton. Together, the cell body and the nucleus control the functions of the nerve cell.A nerve consists of many structures including axons, glycocalyx, endoneurial fluid, endoneurium, perineurium, and epineurium. It produces all the proteins for the dendrites,axons and synaptic terminals and contains specialized organelles such asthe mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, . Most synapses are chemical; these synapses communicate using chemical messengers. The message then moves through the axon to the other end of the neuron, then to the tips of the axon and then into the space between neurons. They need to respond and provide information quickly. Structural features of a motor neuron include the cell body, nerve fibres, and dendrites. However, they can stretch for meters and meters.Cell body: In the cell body, neurons store genetic material and produce energy to function.
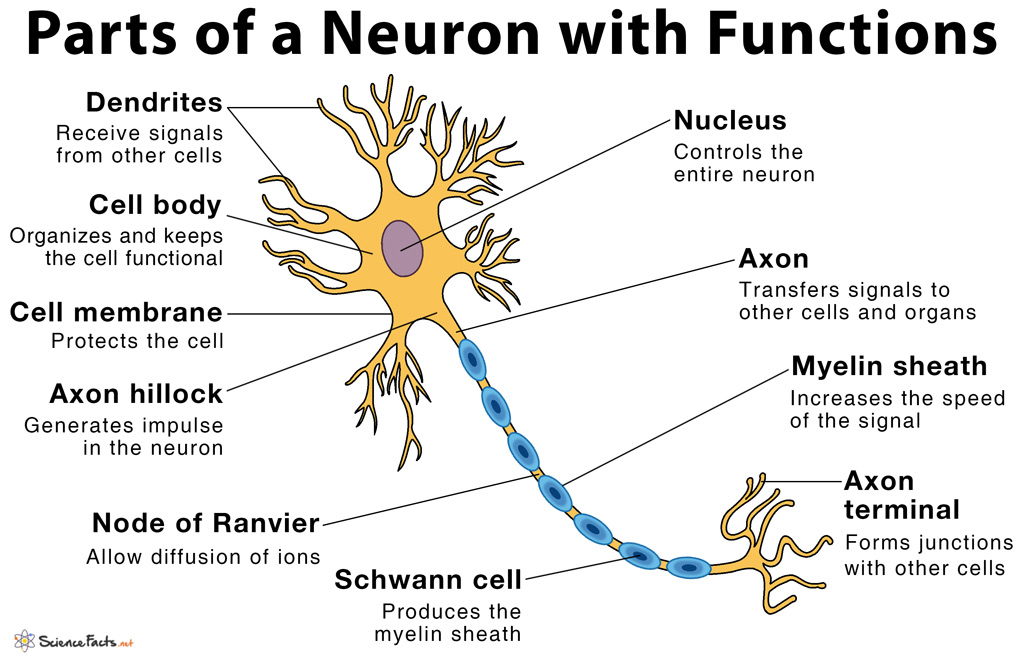
Those names are specific to whether the structure is central or peripheral. They may possess some or all of these structures depending on their specific function.Neurons are electrically excitable cells that transmit signals throughout the body.2 – Nervous Tissue: Nervous tissue is made up of neurons and neuroglia. To overcome this issue, the body has developed clever ways to produce rapid .
Figure: Typical Structure of a Nerve Cell
Anatomy of a nerve cell.

Celles-ci incluent les cellules nerveuses (ou neurones) et les cellules .Nerves are the functional and structural units of the peripheral nervous system (PNS). An individual nerve cell (neuron) is made up of small branching extensions called dendrites, a cell body (soma), and an axon which is one single, long branch.18: Nerve Cells.The neon green structures in the picture are neurons. The myelin sheath helps slow down the speed of electrical conduction. While different types of nerve cells make up the nervous system, they all contain these primary structures: .Changes in the structure of the myelin sheath initiate a nervous impulse.Their function is to receive stimuli and transmit nerve impulses to the target organ.Learn about the parts and functions of neurons, the nerve cells that transmit information in the nervous system. Neurons are specialized in transmitting . Neurons are similar to other cells in the human body in a number of ways, but there is one key difference between neurons and other cells.
Lesson Explainer: Nerve Cells
Structure Of The Neuron. Every neuron consists of a body (soma) .The nerve cell, also called the neuron, is a specialized cell capable of transmitting electrical signals.As such, neurons typically consist of four main functional parts which include the: Receptive part (dendrites), which receive and conduct electrical signals toward the . From there the message can move to the next neuron. The neuronal cell body—the soma— houses the nucleus and organelles vital to cellular function.They are the cells in the brain that transmit and receive signals to enable processes such as thought. It contains the control center of the neuron, also known as the nucleus. Compared to the other sections of the cell, the cell body is larger and may . The axons are bundled together into groups called fascicles, and each fascicle is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the perineurium.Comme le cœur, les poumons et l'estomac, le système nerveux est composé de cellules spécialisées.

Neurons are connected to other neurons at synapses and connected to effector organs or cells at neuroeffector junctions. The cells of nervous tissue are specialized to transmit and . The function of axons is to transmit information in the form of electrical impulses between neurons.A neuron (nerve cell) is a specialized cell that conveys electrochemical impulses throughout the body. A close-up view of a spider web? Some sort of exotic bacteria? What do you think this is? This is actually a nerve cell, the .
Parts of a neuron: Structure and functions
Nerve cells (neurons) form the structural and functional units of the central and peripheral nervous systems.

Magnetic resonsance neurography is a technology used to detect nerve .caLe neurone - Fédération pour la Recherche sur le Cerveau .
Lesson Explainer: Specialized Cells
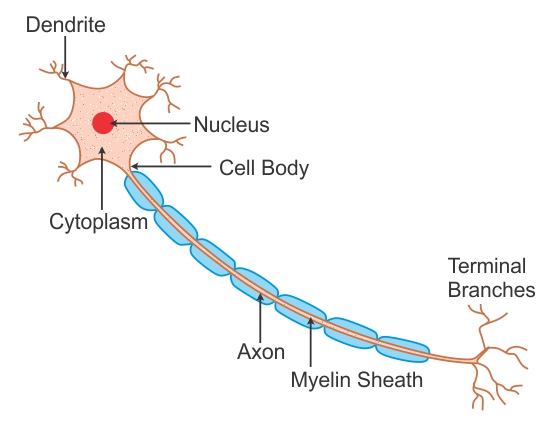
A typical multipolar neuron is comprised of .
Brain Basics: The Life and Death of a Neuron
Neurons are composed of three main .Neurons, or nerve cell, are the main structural and functional units of the nervous system. A localized collection of neuron cell bodies in the CNS is referred to as a nucleus. ‘Neuron Types‘ by Casey Henley is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial Share-Alike (CC-BY-NC-SA) 4.Nerve Cell: Dendrites receive messages from other neurons. Neurons are the basic units of the brain. Each organelle has a unique job.Parts of the Nerve Cell and Their Functions Silvia Helena Cardoso, PhD [1.
2 Cells of the Nervous System: The Neuron
Neuron Diagram & Types
These signals are transmitted across junctions called synapses by . The shape, size, and structure of nerve cells depend on their position and function in the body. The neuron is one of two basic types of cells in the nervous system, the other type being the glial cell. The myelin sheath is a lipid-rich layer formed by Schwann cells. A nerve cell (neuron) consists of a large cell body and nerve fibers—1 elongated extension (axon) for sending impulses and usually many branches (dendrites) for receiving impulses. At a chemical synapse, an action potential triggers the presynaptic neuron to release neurotransmitters. The only exception to this rule is nerve cells that are connected to sensory receptors and .Axons are thin fibers that enable communications between neurons (nerve cells). A neuron is a nerve cell that is the basic building block of the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. A neuron consists of two major parts: a cell body and nerve processes. Usually, the size of nerve cells varies depending on . BruceBlaus, CC BY 3.Neurons and Their Role in the Nervous System. While different types of nerve cells make up the nervous system, they all contain these primary structures: Cell body (Soma) The soma is the cell body of the nerve cell that contains the nucleus. Table of Contents. Neurons contain the same cellular components as other body cells.