Newton definition physics
Newton's Third Law of Motion states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. Première loi de Newton : un objet au repos reste au .Newton's second law describes the affect of net force and mass upon the acceleration of an object.Auteur : The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica
Newton (unit)
This is the most common and useful definition of weight in physics.Newton's Third Law of Motion.
If a car is at rest, the only forces acting on the car are weight and the contact force of the pavement pushing up on the car (Figure 5. It is easy to understand that a nonzero net force is . It is used to predict how an object will accelerated (magnitude and direction) in the presence of an .
Weight and mass
Definitions of Newton. Learning Objectives.
Qu'est-ce que la première loi de Newton
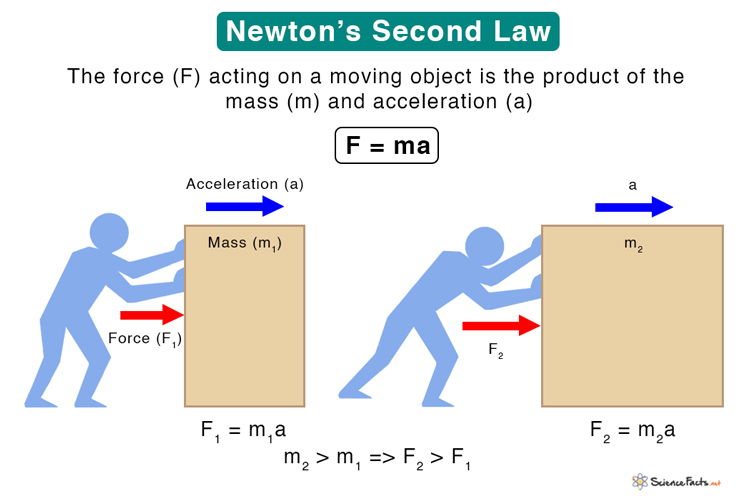
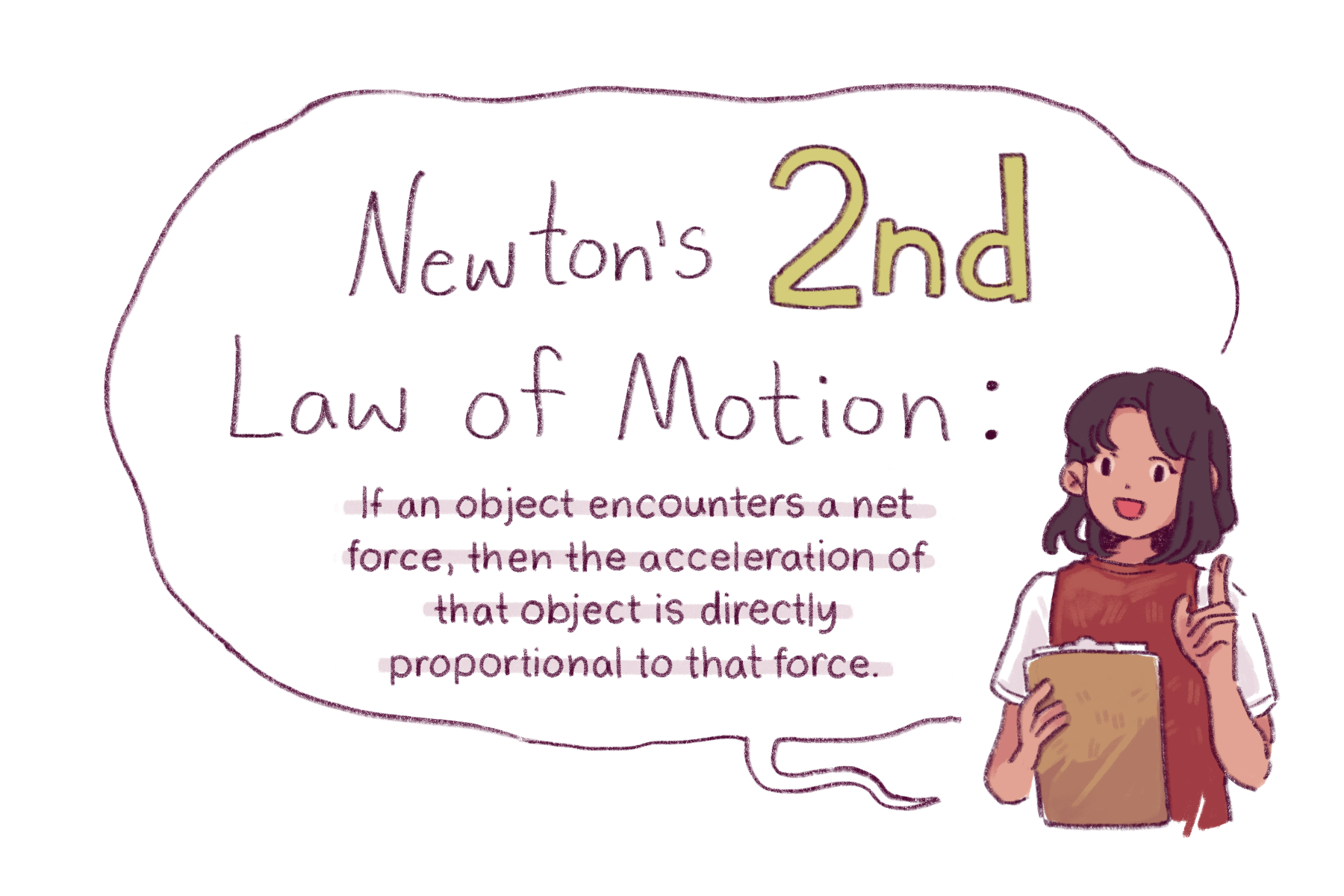
Il y a 3 lois de Newton : la première, . This measurement was improved in 1889 by redefining the meter to be the distance between two engraved lines on a platinum-iridium bar. According to Newton’s first principle, a body that is at rest or moving at a uniform rate in a . Your body is held to Earth by force and held together by the . This means that when acceleration is not zero, the object can be either speeding up, slowing down, or changing direction. Newton's laws became a fundamental foundation of physics, while his discovery that white light is made up of a rainbow of .Learn about what a force is and how a Isaac Newton's Laws of Motion changed the world's view of how forces and motion work.Inclined plane force components.Newton's laws of motion are three laws that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it.The most convenient way to do this is to choose an area that is one “unit” squared in your chosen measurement system, which is what “per unit area” means in the definition.Le newton est l'unité de mesure de la force dans le Système international d'unités (SI), c'est-à-dire que le newton est l'unité utilisée pour quantifier les forces en .Dans le domaine de la physique basique, la deuxième loi de Newton est l'une des lois les plus importantes que vous apprendrez. Parcourez les vidéos, les articles et les exercices par thème. The newton is represented by the symbol . Les lois de Newton. Force of friction keeping the block stationary. Mathematically, you can define pressure as: P = \frac {F} {A} P = AF.It is defined as 1 kg⋅m/s 2, the force which gives a mass of 1 kilogram (kg) an acceleration of 1 meter (m) per second (s 2) squared (per second (s) per second (s)). Often the word deceleration is used to describe the act of slowing down, but in physics we will always refer to any kind of velocity change as . They describe the relationship between a body, the forces acting on it, and its motion in response to those forces. Inertia is the tendency of an object to remain at rest or remain in motion. Often expressed as the equation a = Fnet/m (or rearranged to Fnet=m*a), the equation is probably the most important equation in all of Mechanics.Axiom 1 (Newton’s first law of motion). For example, when you are standing on the ground, you are pushing .
Manquant :
physics Le terme s' emploie à la fois dans les domaines de la physique et de la métrologie . The newton is the unit of force in the International System of Units (SI). If object A exerts a force on object B, because of the law of symmetry, object B will exert a force on object A that is equal to the force acted on it: FA = −FB (4.force, in mechanics, any action that tends to maintain or alter the motion of a body or to distort it. Ice accelerating down an incline.Le newton (unité) : définition, équivalences et multiples
1 N is the force of Earth’s gravity on a mass of about 102 g.
Newton (N) Unit Definition
Phrases like ‘a bag of sugar weighs 1 kg’ are not scientifically correct.6) F A = − F B. See video transcript. To be clear, a is the acceleration of the object, Σ F is the net force on the object, and m is the mass of the object.Home All Definitions Unit Newton (N) Unit Definition. a unit used to measure force, equal to the force that moves a mass of one kilogram one metre in.
NEWTON definition: 1.
Newton : Définition simple et facile du dictionnaire
Newton’s laws of motion
What Are Newton's Three Laws of Motion?
Définition
Temps de Lecture Estimé: 2 min
Forces et lois de Newton
Système de masses reliées entre elles et plan incliné.
Newton
A Newton is abbreviated by an N.
Newton Definition & Meaning
Newton désigne une unité de force du système SI, force qui communique à un corps, dont la masse est de un kilogramme, une accélération de 1 m/s² ; le symbole de Newton est N.Newton definition, the standard unit of force in the International System of Units (SI), equal to the force that produces an acceleration of one meter per second per second on a mass of one kilogram.

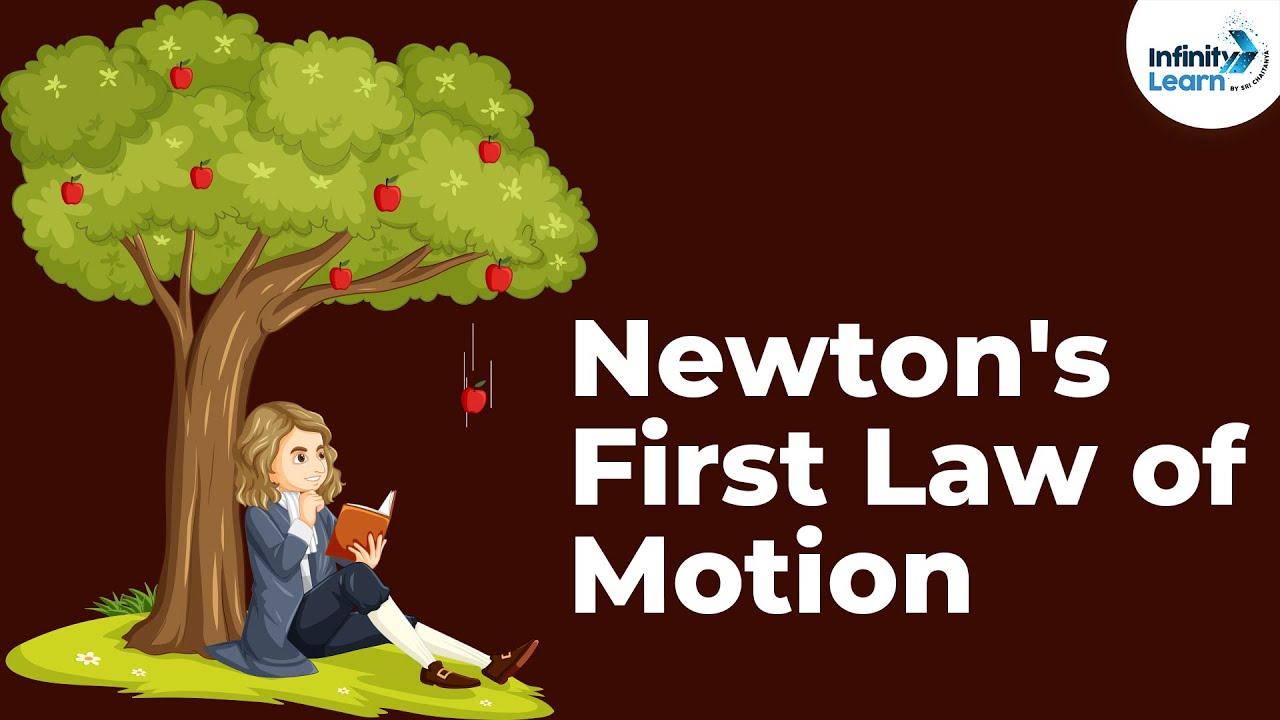
Where P is pressure, F is the force on the surface and A is area. The viscosity of water at 20 °C is 1. This is also known as the law of inertia. Tout corps persévère dans son état de repos ou de mouvement rectiligne uniforme dans lequel il se trouve si et seulement si les forces extérieures appliquées sur lui se compensent. Identify simple free-body diagrams. Correction to force of friction keeping the block stationary. The idea that objects only change their velocity due to a force is encapsulated in Newton's first law.Troisième loi de Newton : Si un objet A exerce une force sur un objet B, alors l'objet B exerce une force de même valeur et de sens opposé sur l'objet A.Force is a quantity that is measured using the standard metric unit known as the Newton. A newton is how much force is required to make a mass of one kilogram accelerate at a rate of one metre per second squared. Another major branch of physics is thermodynamics, which includes the study of thermal energy and the transfer of heat. Most ordinary liquids have viscosities on the order of 1 to 1000 mPa s, while gases have viscosities on the order of 1 to 10 μPa s.Viscosity is first and foremost a function of material.We know objects can only accelerate if there are forces on the object.Newton's laws of motion are three physical laws that can be considered as the foundation for classical mechanics. Understand the definition of force.In physics, the proper definition of acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. Logiquement, le nom de Newton rend hommage à l'illustre physicien Isaac Newton, qui a posé les bases de la mécanique, la partie de la physique qui étudie l'effet . It differs dramatically, however, from the definition of weight used by NASA and the .The broadest definition of weight in this sense is that the weight of an object is the gravitational force on it from the nearest large body, such as Earth, the Moon, the Sun, and so on.Newton, absolute unit of force in the International System of Units (SI), abbreviated N.Newton’s rings are a series of concentric circular rings consisting of bright- and dark-colored fringes.Isaac Newton (1642-1727) was an English mathematician and physicist widely regarded as the single most important figure in the Scientific Revolution for his three laws of motion and universal law of gravity.The terms weight and mass are often used incorrectly.A newton is the SI unit of force.La première loi de Newton, aussi appelée principe d’inertie, peut être définie de la manière suivante : —. Parcourez les .

We will define the general ‘external action’ as a force, therefore a force is now anything that can change the velocity of a particle. These laws were the standard for studying kinematics and dynamics even today. Forces affect every moment of your life. These laws, which provide the basis for . James Prescott Joule, an English .Nous allons voir dans ce chapitre les lois de Newton, du nom du célèbre mathématicien et physicien anglais Isaac Newton. Elle est utilisée dans quasiment chaque . When a plano-convex lens lies on top of a plane lens or glass sheet, a small layer of air is formed . English mathematician and physicist; remembered for developing the calculus and for his law of gravitation and his three . The concept of force is commonly explained in terms of Isaac Newton ’s three laws of motion set forth in his Principia Mathematica (1687).Newton’s first law is deceptively simple. Newton's first law: An object at rest remains . Forces are the bread and butter of Newtonian mechanics.0020 millipascal seconds (which is conveniently close to one by coincidence alone).The newton (symbol: N) is the SI unit of force.Une théorie de la physique classique qui permet de décrire le mouvement des objets.La Première loi de Newton décrit le fait que la vitesse d'un objet ne peut être modifiée que par la présence d'une force. Newton’s first law of motion states that a body at rest remains at rest, or, if in motion, remains in motion at a constant velocity unless acted on by a net external force.
Traduction en anglais : newton.
5: Newton's Laws of Motion
Note that the first law includes particles at rest, i.
Isaac Newton
Passez au niveau supérieur sur toutes les compétences relevant de ce chapitre et gagnez jusqu'à 300 points ! Ce chapitre fait partie de la bibliothèque de physique. Ce chapitre fait partie de la bibliothèque de physique. Often expressed as the equation a = Fnet/m (or rearranged to Fnet=m*a), . It is named after Sir Isaac Newton because of his work on classical mechanics. Abbreviation: N See more. As long as there is no external action, a particle’s velocity will remain constant. Lorsque ces objets sont à l'échelle . (The bar is now housed .Newton’s third law basically states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Qu'est-ce que la troisième loi de Newton
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.The definition of the meter has changed over time to become more accurate and precise.Newton’s laws of motion, three statements describing the relations between the forces acting on a body and the motion of the body, first formulated by .Le newton est l'unité de mesure de la force dans le Système international d'unités (SI), c'est-à-dire que le newton est l'unité utilisée pour quantifier les forces en physique.Isaac Newton discovered the laws of motion that describe these situations. Though they're not always the easiest way to think about .