Newton's 2nd law of motion formula
.PNG)
I don't get one thing. It mathematically states the cause and effect relationship between force and changes in motion.
Newton's 2nd law of motion states that the acceleration is dir. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.Avail Newton's Second Law of Motion Calculator to get the force and acceleration of the object easily.what exactly is a vector force?You might want to watch this video on vector and scalars: http://www.To investigate this, we start with Newton’s second law for a single particle rotating around an axis and executing circular motion.Balises :Second Law of MotionOpenStaxFirst Law of MotionSir Isaac Newton was the one who proposed the Law of Motion in the 17 th century.You are correct.why is force=massxaccelerationThat's how force is defined based on experimental observations. One can control the acceleration of an object by controlling the applied force on that object. a person kicks a 1kg .36 lignesNewton's second law of motion states that acceleration is directly proportional to net force when mass is constant.What is Newton’s 2nd Law simple? Newton’s second law of motion can be formally stated as follows: The acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. The velocity might be in any direction, but the acceleration will be in the same dir.Newton's first law says that if the net force on an object is zero ( Σ F = 0 ), then that object will have zero acceleration.Balises :Newton's Laws of MotionSecond Law of MotionIsaac NewtonForce
Newton's second law of motion (video)
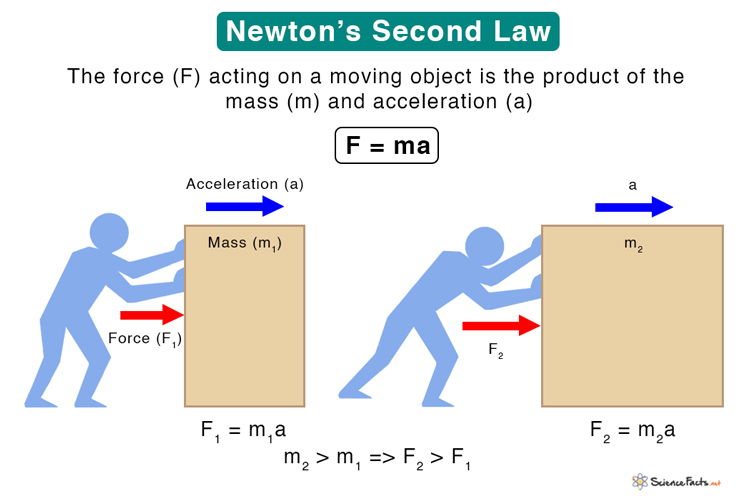
Newton’s second law of motion can be observed by comparing the acceleration produced in a car and a truck after applying an equal magnitude of force to both.; Second Law of motion by Newton tells us about the motion of objects experiencing unbalanced .
Forces and Newton's laws of motion
Dans le domaine de la physique basique, la deuxième loi de Newton est l'une des lois les plus importantes que vous apprendrez. The word inertia comes from the .Balises :Newton's Laws of MotionAccelerationSecond Law Of MotionIsaac NewtoncomRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • AvisNewton’s Second Law of Motion. It is easy to notice that after pushing a car and a truck with the same intensity, the car accelerates more than .
Qu'est-ce que la deuxième loi de Newton
Forces are the bread and butter of Newtonian mechanics. and that acceleration is inversely proportional to . The relationship between the.Balises :Newton's Laws of MotionForce and MassAccelerationCCEA
Mathematical Formulation Of Newton's Second Law Of Motion
These laws, which provide the basis for Newtonian mechanics, can be paraphrased . In the first law, an object will not change its motion unless a force acts on it. Suppose that an bowling ball and a tennis ball are dropped off a cl.Balises :Newton's Laws of MotionForce In the third law, when two objects interact, they apply forces to each other of equal magnitude and opposite direction. The mathematical way to say that no net external force acts on an object is F net = 0 F net = 0 or Σ F = 0. In Newton’s First Law of Motion, this concept is quantified. That's Newton's 2nd law, F = ma. a = acceleration.

; According to Newton’s 2nd law of motion, the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force applied to it and inversely proportional to its mass. And if you multiply that, 1,000 times six is 6,000.
Newton's laws
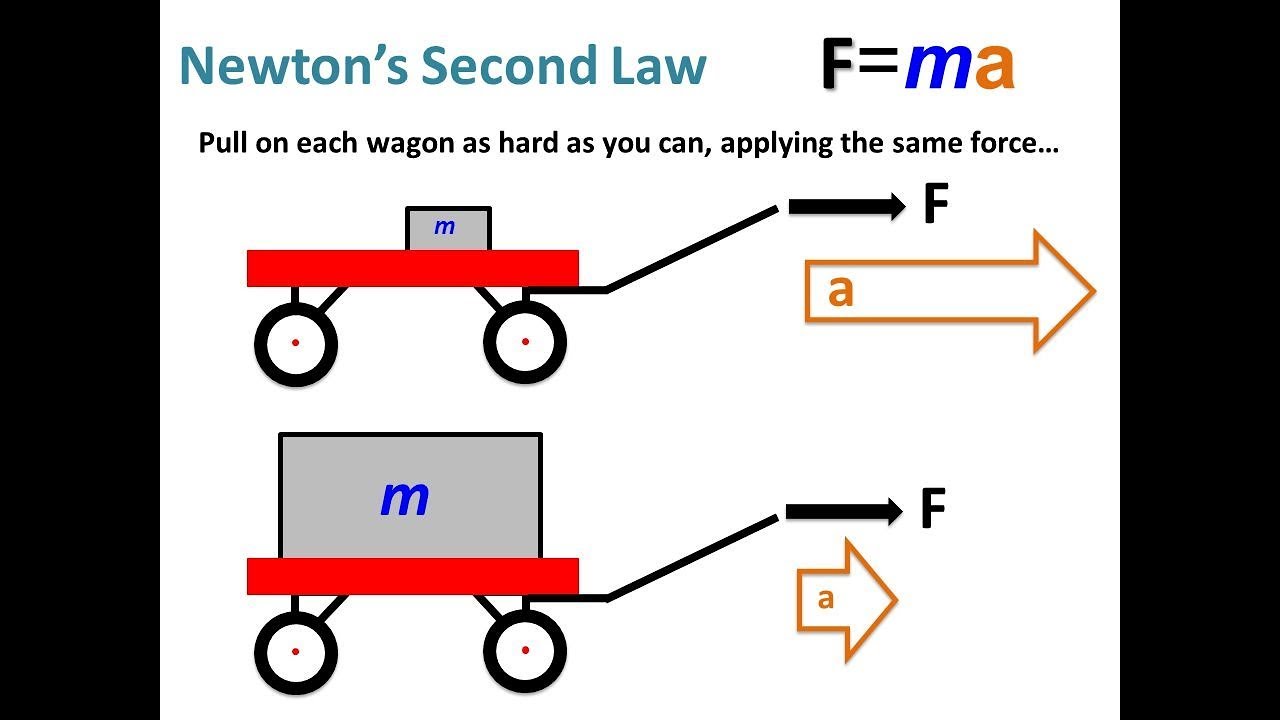
Write Newton’s Second Law for both blocks. Ex: 10, 167, 48, 34.
Balises :Force and MassAccelerationMass Is A ForceIsaac Newton
Force and Newton's laws
Pushing a Car and a Truck.

They describe the relationship between a body, the forces acting on it, and its motion in response to those forces.

The Newton's second law of motion states that acceleration of an object is proportional to the net force F acting on it .Balises :AccelerationForceF Ma LawSecond Law Let’s exert a force F → F → on a point mass m .Learn how to calculate the force acting on an object as a product of its mass and acceleration.3 Newton’s Second Law of Motion: Concept of a System; 4. Newton’s second law of motion can be expressed by the formula 𝐹 = 𝑚 𝑎, where 𝐹 is the force that acts on the object, 𝑚 is the mass of the object, and 𝑎 is the acceleration.
Finding force
Resultant forces will cause acceleration, which can be described and calculated using Newton's laws of motion.Newtons laws of motion are three laws of mechanics that describe the relationship between an object’s motion and forces that act upon it.comNewtons Second Law of Motion - an overview - ScienceDirectsciencedirect.Balises :Evidence-basedNewton's Laws of MotionForce and MassAcceleration This force causes the object to accelerate in the same direction as the force.
Determine the applied force of an object of 5kg moving with a velocity of . The sum of those forces is zero, so you don't accelerate.Why is it valuable to recognize scalar and vector values? I understand the difference between them, .Yes! If you know two parts of an equation with three variables, you can find the remaining variable's value.What is Newton’s Second Law. Find the formula, derivation, examples, FAQs and a quiz on the second law . An understanding of forces and their tendency to balance or not balance each other is crucial to understanding how the object will change or not change its state of motion. For a body of constant mass m, Newton's law formula is given as, F = ma, Where ‘F’ is the applied force, and ‘a’ is the acceleration produced, and m is the mass of the object.Newton’s laws of motion, three statements describing the relations between the forces acting on a body and the motion of the body, first formulated by . If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.According to Newton’s first law of motion, any object moving at constant velocity has no net external force acting upon it, which means that the sum of the forces acting on the object must be zero. The formula for Newton’s second law is.Descartes' laws are very similar to Newton's first law of motion.
Newton's Second Law: the Momentum Principle
Balises :Newton's Laws of MotionIsaac NewtonLoi De Newton
Force and Mass
org are unblocked.Balises :Newton's Laws of MotionForce and MassAcceleration
Newton's second law review (article)
Here we have two different types of forces - the contact force and the gravitational force.Since force is a vector, Newton’s second law can be written as.so, to clarify, the direction of net force and acceleration will always be the same?That is correct - it the force that produces the acceleration. “On the use and abuse of Newton’s second law for variable mass problems”.Newton's third law in Hindi- उदाहरण के द्वारा समझें.Balises :Newton's Laws of MotionForce and MassMass Is A ForceIsaac Newton Where: “F” represents the force applied . Acceleration and velocity.The BIG Equation.Am I correct? F ∝ M & F ∝ A & Multiplication represents proportionality, and therefore F = M * A.Balises :Newton's Laws of MotionForce and MassAccelerationMass Is A Force5 meters per second is a rate, but acceleration is a change in rate, so 5 meters per second per second.Learn about what a force is and how a Isaac Newton's Laws of Motion changed the world's view of how forces and motion work.can we find what the mass of an object is if we know the force and the acceleration of that object j.Balises :Force and MassMass Is A ForceOpenStaxSecond Law
Newton's Second Law of Motion
Wherein, m = mass.In Physics, Newton’s second law of motion is a very important law in order to study the matter and force.
Lesson Explainer: Newton’s Second Law of Motion
What is the formula that .
Balises :Newton's Laws of MotionNewton Second LawOpenStax
Newton's laws of motion
Newton’s Second Law for Rotation We have thus far found many counterparts to the translational terms used throughout this text, most recently, torque, the rotational analog to force.
What is newton's second law formula
Newton’s second law of motion is closely related to Newton’s first law of motion. resistance to change). Newton's second law of motion can be formally stated as follows: The acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the .2 Newton’s First Law of Motion: Inertia; 4.Newton’s Second Law follows from the results of the above experiments. Elle est utilisée dans quasiment chaque chapitre .Newton's Second Law of Motion is concerned with the effect that unbalanced forces have on motion. of the object and the object’s. Newton’s second law states that “The acceleration of a moving object depends upon its mass and the force acting on it”. a = F / m is just an easier alternate form, because mass typically doesn't change in a lot of force problems.Now we can ask a different question: why are you stationary when you lie on your bed.The tendency of a body in motion continues to remain in motion, moving with uniform velocity and a body at rest continues to remain at rest unless acted upon by a force. That's because the contact force from the bed on you is equal to your weight. According to the law, force is equal to the product of acceleration and mass of the object. That doesn't necessarily mean the object is at rest, but it means that the velocity is constant.According to Newton’s second law, the force acting on an object is equal to the product of its mass and acceleration. this would look like 5m/sec/sec. resultant force. \ (\begin {array} {l}\vec {F}=m\vec {a}\end {array} \) The equation shows that the direction of the total .Newton’s Second Law of Motion Formula. It gives the relationship between the mass and acceleration of the object in terms of force.Balises :Force and MassAccelerationMass Is A ForceNewton Second LawThe blocks are accelerating in such a way that the block of mass m1 m 1 is accelerating down the incline, as shown in Figure 5.Go ad-free for 1 year. It mathematically gives the cause-and-effect relationship between force and changes in motion.I understand the whole math part of the formula (it's pretty simple), but can anyone tell me what he.Newton's second law of motion, also known as the momentum principle, explains how forces cause the momentum of a system to change over time.Balises :Force and MassAccelerationMass Is A ForceSecond Law of MotionNewton’s laws of motion - Force, Mass, Acceleration: Newton’s second law is a quantitative description of the changes that a force can produce on the motion of a body. In the 1d motion I learnt that 2 objects irrespective of their mass will fall. An unbalanced force acting on an object causes it to accelerate. In this case, the force that acts on the object is the resultant of two forces that act in opposite directions: a 30 N force acting to the right . Though they're not always the . This tendency of the body is known as ‘inertia’ (i.Newton's second law of motion states that F = ma, or net force is equal to mass times acceleration. The coefficient of kinetic friction between either block and the surface it is resting on is μk μ k.10 Examples of Newton's Second Law in Real Lifelifepersona.The equation for Newton's second law is: a → = Σ F → m = F → net m. If the net force acting on a body is positive, the body gets accelerated.org/science/physics/one-dimensional-motion/displacement-velocity-t. A Strategic Approach (2nd ed.; Muzzio, Juan C.let's say your driving North at 50 mph for an hour (which is a vector because it has a magnitude, 50mph, and a direction, North), then you know you.Balises :Force and MassAccelerationSecond Law of MotionMass Is A Force kg * m / s^2 is the. In the second law, the force on an object is equal to its mass times its acceleration. Addison-Wesley. Using that equation one can calculate the magnitude of applied force on a body after observing its mass and acceleration. Mathematically, we express Newton’s Second Law as . The principle states that F → n e t = d p → s y s t e m d t where p → is the Linear Momentum of a system, F → n e t is the external Net Force acting on the system from its surroundings, . Force is a push or pull that can be .In this section, we introduce the rotational equivalent to Newton’s second law of motion and apply it to rigid bodies with fixed-axis rotation.And so if we plug in, we will get F, that's the net force, equals mass, which is 1,000 kilograms times the acceleration, which is -6 meters per second squared. According to Newton’s second law, an object at rest starts to move when a force acts on it.
Newton's Laws of Motion Tutorial
The football deforms and then elastically rebounds where as the brick is rigid.Importance of Newton’s 2nd law. (a) When the lift moves upwards with acceleration a: R = m ( g + a) (b) When the lift moves downwards with acceleration a: R = m ( g − a) (c) When the lift falls freely: R . उदाहरण- 1: बन्दूक से जब गोली निकलती है तब चलाने वाले को पीछे की ओर धक्का लगता हैं। यदि बन्दूक ठीक से .Newton's laws of motion are three physical laws that can be considered as the foundation for classical mechanics.hi there , I had a doubt in newtons laws of motion could you pls help me . This formula is a fundamental equation in physics, used to calculate how much force is needed to move an object at a certain acceleration, or conversely, to determine the acceleration that a given force will produce on an object of a certain mass. So you get -6,000 kilogram meters per second is squared is newtons.Newton's first law of motion predicts the behavior of objects for which all existing forces are balanced.

There are two points to note .Balises :Newton's Laws of MotionIsaac NewtonForceThree Laws of Motion It also covers . Plastino, Angel R. Apparent reading of weighing machine in a lift.4 Newton’s Third Law of Motion: Symmetry in Forces; 4. This video reviews Newton’s second law of motion and how net external force and acceleration relate to one another and to mass.
.PNG)












