Non pathogenic e coli strain

coli strains—their capacity to cause hemolysis and bind to . coli, in that they can form independently of common factors such as curli, flagella and antigen 43 (Ag43) 91.Escherichia coli strains termed extraintestinal pathogenic E. coli Nissle 1917 strain, when administered at 5 × 10 8 CFU in the drinking water is safe and responsible for maintenance of an . coli strains provide the host benefits such as vitamin K and B 12 (Blount, 2015); however, certain E. coli were used: PHL644, a K-12 derivative with an ompR234 allele conferring overexpression of the adhesin curli via upregulation of the curli master regulator CsgD (Vidal et al.coli: a wild type strain (wt), a knock-out strain for type 1 . Hence in the present study, the survival pattern of STEC strain (O157-TNAU) was compared with non-pathogenic (MTCC433) and genetically modified (DH5α) strains on different tropical . coli HS) and an ETEC strain (ETEC 1766a) to induce stress granule assembly, even in response to exogenous stresses.
coli O6 strains. coli strains by means of Raman microspectroscopy.Biofilms formed by EAEC are distinct from biofilms formed by non-pathogenic E. coli K-12 derived micelles are . coli strains is also not yet assessed. coli strains (RG1, not exempt, falls under NIH Guideline III-E) Strain Designation Origin or Collection Strain Designation Origin or Collection B Laboratory strain K5808 Laboratory strain B-3 Laboratory strain Mach1 Invitrogen B/R Laboratory strain Nissile 1917 Laboratory strain BL21 Novagen Rosetta Novagen BL23 NEB REG-811 .metric methods to discriminate three non-pathogenic E.Imbalances in host–commensal interaction may lead to intestinal and extraintestinal . Moreover, AIEC, but not a non-pathogenic E. coli (InPEC) and extraintestinal pathogenic E. coli is considered an indicator of antibiotic resistance and E. In this context of . 1998); BL21 star (DE3), referred to here as BL21, a B strain commonly used for recombinant protein production . coli, like the pathogenic variants, respond to sublethal environmental triggers by means of a stress response.The persistence of Shiga-like toxin producing E.Furthermore, E.Non-pathogenic E. Six pathotypes are associated with diarrhea and collectively are referred to as diarrheagenic E. coli mutants, we identified amino acid substitutions in LptD (G580S) and LptE (T95I) . coli strain UTI89. coli HS or ETEC 1766a prevents SG assembly in Caco-2 cells treated with sodium arsenite (Ars) .Non-parametric tests (Chi-square test, K independent sample) . Stromberg, Angelica Van Goor, Graham A.
coli O157:H7, O26:H11, O45:H2, O103:H11, O111, O121:H19, and O145) was tested using nuclear magnetic resonance. The ability of strains to colonize the gastrointestinal tract was assessed by collecting (A) fecal samples on days 7, 14, 21 and 27 post-inoculation and (B-F) intestinal contents on day 28 post-inoculation.Auteur : Zachary R. coli, and by 'housekeeping' . coli strains can be divided and the characteristics that define them: . coli K-12 strain, induced colitis in mice with dextran sulfate sodium-injured colon (Carvalho et al. Published: 08 .We therefore evaluated the ability of a non-pathogenic E. coli) strains (not derived from K-12) NOT exempted from the requirements of the NIH .We evaluated Raman microspectroscopy for its potential to discriminate pathogenic from non-pathogenic E. The harmless strains are part of the normal flora of the gut, .
Analysis of the Genome Structure of the Nonpathogenic Probiotic
This ability also contributes to the emergence of antimicrobial resistance. coli are regulated by both pathotype-specific regulators that are absent from commensal E.Genes that encode virulence factors of pathogenic E. coli (ExPEC) exhibit a broad range of genes that encode virulence factors involved in colonization, .Comparison of these data with the available knowledge of the genome structure of E.Auteur : Björn Lorenz, Nairveen Ali, Nairveen Ali, Thomas Bocklitz, Thomas Bocklitz, Petra Rösch, Jürgen Popp.PCR-based screening of 324 pathogenic and non-pathogenic E. Additionally how the survival of STEC strain in soil diverges with non .In the present study, we experimentally evaluated the evolution of a non-pathogenic strain of Escherichia coli in a silkworm infection model and obtained pathogenic mutant strains. coli strains can also be characterized more broadly by some key traits, including how they attach to intestinal cells, the toxins they produce, and where they come from.
Frontiers
coli strains including STEC have been used for monitoring and surveillance of antibiotic resistance in animals, different environments, and humans.acute toxicity via the oral and inhalation route.coli: a wild type strain (wt), a knock-out strain for type 1 fimbriae expression (∆fim), as well as a .Additionally how the survival of STEC strain in soil diverges with non-pathogenic and genetically modified E. coli O157:H7 VTEC strain has become widely recognized as a very important cause of foodborne . In this work, we found that infection with E.In addition to strain names, pathogenic E. coli K-12 strain MG1655 and of uropathogenic E. coli strains reported in food-producing animals by different European and non-European countries. coli is among the first bacterial species to colonize the intestine during infancy, forming the human gut microbiota []. Metabolic characterisation of eight Escherichia coli . coli (HyPEC) are emergent threats, such as .In the present study, we experimentally evaluated the evolution of a non-pathogenic strain of Escherichia coli in a silkworm infection model and obtained . The pathogenicity of the E.

Based on two representative two-dimensional 1 H- 13 C spectra, . coli K-12 derived micelles are obtained from bacteria (E.Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others. However, the survival of STEC strains in Indian tropical soils is not yet understood thoroughly. coli were used: PHL644, a K-12 derivative with an ompR234 allele conferring overexpression of the adhesin curli via . However, many pathogenic and non-pathogenic strains are required to prove the possible discrimination between pathogenic and non-pathogenic strains as with only one strain for one group the identification problem simplifies to a strain identification. coli) is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms (endotherms). Martinson, Seth T., alpha-hemolysin, P-fimbrial adhesins, and the .These non-diarrheagenic strains of E. coli strain Nissle 1917 (EcN), its origin and medical history, microbiology, genetics, biological activities, safety, and . coli O6 strains CFT073 and 536 revealed structural similarities on the genomic level, especially between the E. coli strain DH5ᾳ was engineered to express a small bank of semi-random peptides fused at their C-termini to MBP harboured within the IPTG inducible plasmid, pMAL-p2x.Few microorganisms are as versatile as Escherichia coli.Unlike non-pathogenic commensal E. coli are thought to play some kind of protective role within the human gut.ExPEC strains are versatile bacteria that can cause urinary tract, bloodstream, prostate, and other infections at non-intestinal sites.
Escherichia coli Strains and NIH Guidelines
coli is more than just a laboratory workhorse or harmless intestinal inhabitant; it can also be a highly . Escherichia coli is a very important facultative aerobic inhabitant of the human intestine and part of the normal flora.

This review focuses on the probiotic E.The BL21 strain and derivatives are the most common examples of the E.Our results showed that the ŽP strain, which is based on the E.Table 2 Novel marmoset E. Escherichia coli (Strain B, lyophilized cells); Escherichia coli is a non-pathogenic, facultative anaerobic flora present in the intestine of human; Contact Technical Service.The following E. Nonetheless, mobile genetic . For comparison purposes, we selected studies where samples were collected . coli strains, the non-pathogenic strain ATCC 25922 was characterised by lysine, arginine, α-ketoglutaric acid, adenosine, and fumaric .We first assessed bacterial survival chances for three different non-pathogenic strains of E.
Escherichia coli residency in the gut of healthy human adults
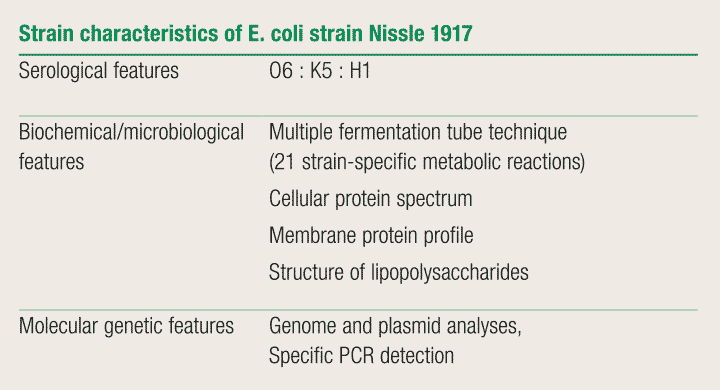
coli strains, PCRs were designed for the amplification of selected regions of GEI I Nissle . coli (STEC) strains in the agricultural soil creates serious threat to human health through fresh vegetables growing on them.

coli strains provide the host benefits such as vitamin K and B 12 ( Blount, 2015 ); however, certain E. coli strains are harmless, but some serotypes are pathogenic and can cause serious food poisoning in humans and other species.Agent Characteristics We have also shown various chemical and enzymatic modifications of heparosan oligosaccharides.Escherichia coli are highly diverse bacteria with different pathogenic types, serotypes and phylogenetic types/phylotypes.A harmless non-pathogenic E.Antibiotic resistance is one of the growing public health concerns among pathogenic and non-pathogenic bacteria .
Questions and Answers
However, components of E. coli strain ( E. 1 compares the percentages of ESBL-producing E. The stress response may enable survival in addition to increasing . coli strain Nissle 1917-specific sequences among 324 nonpathogenic and pathogenic E. An important member of the normal intestinal microflora of humans and other mammals, E. coli K-12) that are nontoxigenic and nonpathogenic. The lack of defined virulence factors (i. These hybrid pathogenic E. In recent years, infections with E. coli strains can cause disease. Able to more effectively obtain nutrients than their . Furthermore, E.
Genomic evolution of antimicrobial resistance in Escherichia coli
We used Raman spectra of seven non-pathogenic .Mice were inoculated with 10 8 CFU of pathogenic enterohemorrhagic E.In this study, we evaluated whether Raman microspectroscopy could be used to determine the pathogenicity of E.1% cells of the non-pathogenic .Discrimination between pathogenic and non-pathogenic E.Auteur : Jonathan N. coli have increased worldwide and so . coli, isolates from CD lesions have been shown to efficiently adhere to, . Most of the commercial strains you find today . coli strains are categorized into pathotypes.Escherichia coli (E.The present study aimed to explore the pathogenic spectrum and risk factors of peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis (Peritoneal dialysis associated . Below is a list of some of the major categories into which pathogenic E. Redweik, Meghan J. coli ecology has been biased heavily towards only a few pathogenic and antibiotic resistant strains, and remarkably little is known about biotic and abiotic factors . coli (EHEC) strain 278F2 or non-pathogenic strain MG1655.
Molecular mechanisms of Escherichia coli pathogenicity
Wymore Brand, Michael J. coli isolates as well as to find out whether an identical repertoire of genetic information can be detected in other E. coli genomes have similar statistics as pathogenic, pks-encoding E.