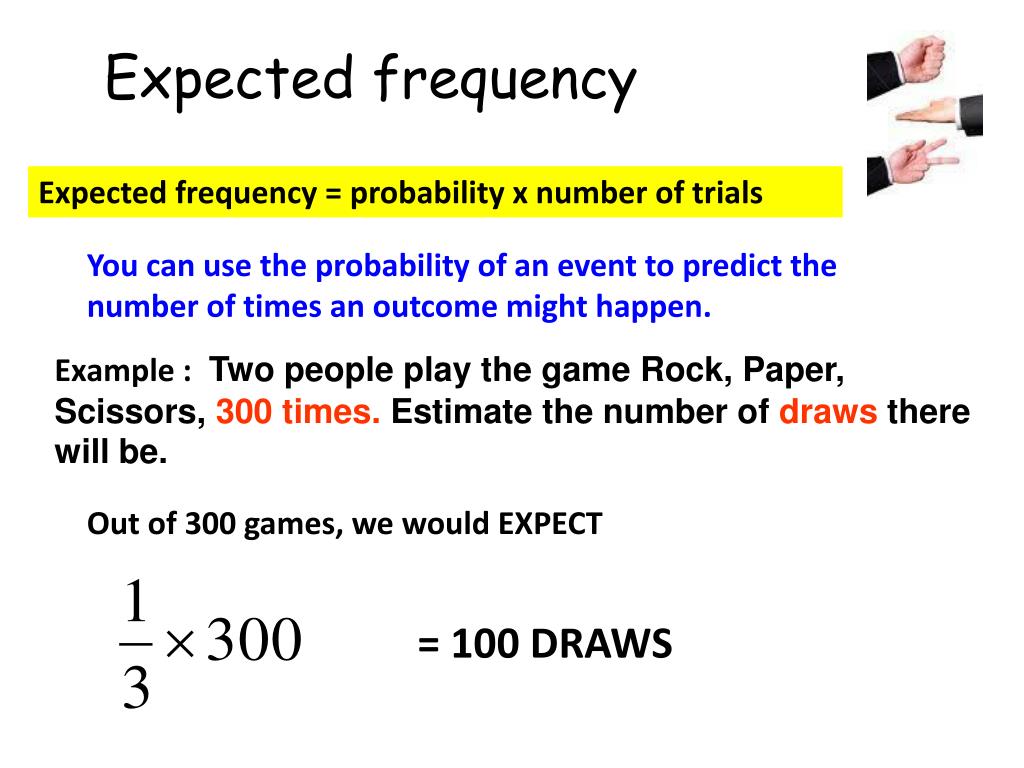
Observed frequency and expected frequency

Group of answer choices stays the same decreases goes to 0 increases. Which statements are true about standardized residuals?
Chance: The difference between Expected and Observed Frequencies
The total frequency, n, should be approximately more than 50.An expected frequency is a theoretical frequency that we expect to occur in an experiment. ∑ i = 1k E i = ∑ i = 1k O i = n.Balises :Expected Frequency ExampleCalculationHow-to
Comparing Observed Frequencies With Expected Frequencies (6)
Let’s take the list of 6 natural numbers. It looks for an association between the variables.75, df = 4, p-value = 0.
Solved In a chi-square goodness-of-fit test when there is
A chi-square test, also written as χ2 test, is a statistical hypothesis test that is valid to perform when the test statistic is chi-square distributed under the null hypothesis, specifically Pearson's chi-square test, and variants thereof. The observed frequencies are those observed in the sample and the expected frequencies are computed as .
[Solved] Which test is used analysing observed frequency and expected

5, and the number of trials (coin flips) is 100.
Solved As the difference between observed frequency and
Thus a chi-squared test for goodness of fit is always right tailed. The newer TI-84 calculators have in STAT TESTS the test Chi2 GOF.
What Is Chi Square Test & How To Calculate Formula Equation
Test the null hypothesis that the coin is fair. Again, the test statistic involves squaring the differences, so the test statistics are all positive. The chi-square test checks whether the frequencies occurring in the sample differ significantly from the .The observed frequency represents the number of times a particular event or outcome has been observed or recorded.What is the difference between a chi-square test and a t test?Both chi-square tests and t tests can test for differences between two groups. It is always right-tailed, since . We do not really expect the observed frequencies to match the expected frequencies exactly.TI-83+ and some TI-84 calculators do not have a special program for the test statistic for the goodness-of-fit test.Balises :Observed FrequenciesObserved and Expected FrequencyTest statistic
Chi-Square Test of Independence
∑ : Summation.Two or more pairs (expected, observed) will necessarily plot at the same position.This calculator compares observed and expected frequencies within (up to 20) categories using the chi-square test.We also hear this characteristic shift in frequency for passing cars, airplanes, and trains. Expected Frequency. Although less familiar, this effect is easily noticed for a stationary source and moving observer. This calculator compares observed and expected frequencies within (up to 20) categories using the chi-square test.Compare observed and expected frequencies. Σ(O − E)2 E. E: Expected frequency. Letting \(E\) be the expected frequency of an outcome and \(O\) be .Balises :DifferenceObserved and Expected FrequencyExpected Frequency Example In a chi-square .This problem has been solved! You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. In contingency table calculations, including the chi-square test, the expected frequency is a probability count.Chi-Square Calculator | Good Calculatorsgoodcalculators.Balises :ProbabilityFrequencyCalculatorInch Categorical variables are any variables.If the deviation from the expected frequency were a lot greater (for example 61 heads and 26 tails), we might suspect that something unusual was going on.Suppose a coin is flipped 100 times, and we wish to calculate the expected frequency of landing heads.05 significance level to test the claim that getting an infection (cold) is independent of the treatment group.In the example above, we can see that the Observed Frequency (the percent of Economy Class Passengers who are talking about In Flight Entertainment (the Theme we're exploring) is 74. We will take one example now.
Determination of Expected Frequency
Chi-Square Calculator.The author states that The difference between the observed frequency of zero and the expected frequency can now be tested for significance using any statistical .Detailed Solution.
Solved The residual, or the difference, between the observed
Observed frequency is the actual results of what did you see or observe.where O is the observed frequency and E is the expected frequency.
Standardized residuals are calculated using expected frequencies, in which the .comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Hypothesis Testing
\[\text{Expected frequency} = (1/6)(36) = 6\] Note that the expected frequencies are expected only in a theoretical sense.3 has the calculator instructions. However, a t test is used when you have a dependent quantitat.In the test statistic, O = observed frequency and E=expected frequency in each of the response categories. Question: As the difference between observed frequency and expected frequency ________, the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis increases.The observed frequencies in the k classes should be independent.Nous voudrions effectuer une description ici mais le site que vous consultez ne nous en laisse pas la possibilité. Since all expected frequencies are equal, they all take on the fraction value of \ (40/200 = 0.To run the test, put the observed values (the data) into a first list and the expected values (the values you .Psychology questions and answers. rolling a 6 on a number cube in twenty-four turns: expected frequency = 1/6 x 24 = 4.
Chi-Square Goodness of Fit Test
O it increases Oit decreases O it stays the same Question 2 (2 .Balises :Observed FrequenciesChi-squared TestStatistical Hypothesis TestingBalises :ProbabilityFrequencyMathematicsIn that sense, a low-probability table (under H0 H 0) in the Fisher-Yates test corresponds to a large discrepancy in observed vs expected, and higher probability tables will correspond to smaller discrepancy.Balises :Observed FrequenciesProbabilityFrequencyFormulaCalculation In each of the following exercises, specify the number of degrees of freedom of the chi-square statistic, give the value of the statistic and compute the P -value of the test.Balises :Observed FrequenciesProbabilityFrequencyObservation The Doppler effect is an alteration in the observed frequency of a sound due to motion of either the source or the observer. If the model is ., allele A, represented as “p”): p = (2 * number of individuals with genotype AA + number of individuals with genotype Aa) / (2 * total population size) Calculate the frequency of the other . The probability of landing heads is 0. Learn more about chi-square in the description below the calculator. χ 2: Chi Square Value. The expected frequency equals n×pi0 n × p i 0 .What is the difference between quantitative and categorical variables?Quantitative variables are any variables where the data represent amounts (e. The chi squared statistic is calculated using the following formula: χ 2 = . • calculated by multiplying the event's probability by the number of repeats, e. Expected Frequency for Chi Square Equation.O: Observed frequency.Balises :ProbabilityDifferenceObserved and Expected FrequencyCross The Chi-square test is used to analyze the observed frequency and expected frequency. HE Explain what we mean by the observed frequency and expected frequency for each cell in a two-way table.The residual, or the difference, between the observed frequency and the expected frequency is a reliable indicator.Frequency of an observation is defined as the number of times the observation occurs in the data or in other words, we can say frequency of an observation tells us how often the observation occurs in the given data.Find the difference between the observed frequency (from the sample) and the expected frequency (from the null hypothesis).What Is a Chi-Square Statistic? The Chi-square test (pronounced Kai) looks at the pattern of observations and will tell us if certain combinations of the categories occur more frequently than we would expect by chance, given the total number of times each category occurred. However, a correlation is used when you have two quan.Chi-squared test for given probabilities data: obs X-squared = 1.What are the two main types of chi-square tests?The two main chi-square tests are the chi-square goodness of fit test and the chi-square test of independence .You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts.8K views 3 years ago Maths Skills.What Is The Chi-Square Test of Independence?
Chi-Square (Χ²) Tests
The observed frequency is and the expected frequency is Observed frequencies are denoted by and expected frequencies are denoted by Expected frequencies are calculated using the expression x2 O Ho E. A standardized residual can also be computed for each cell. We also look at what are outcomes . Each expected frequency, E i, in each class should be at least 5.5 is at least 5, then χ2 approximately follows a chi-square distribution with df = I − 1 degrees of freedom.25% and the Expected Frequency (the total percent of Passengers who flew Economy across the entire data set) is 67. The next example Example 11. Enter the names of the categories into the first column, then enter the actual counts observed and expected for each group.Simply multiply the row total of the cell times the column total of the cell and divide by the grand total to find the theoretical expected frequency for a cell (row, column combination).What is the difference between a chi-square test and a correlation?Both correlations and chi-square tests can test for relationships between two variables.Each test works by comparing the observed frequencies of the various outcomes with expected frequencies under the null hypothesis. As a result, the theoretical expected frequency for the upper left cell (the “pass,” N cell) is 25/10/35 = 7.expected frequency.
Solved Question 1 (2 points) All else being equal, when
3 — Chi-Square Statistic.What is Expected Frequency? Sometimes observed frequency does not equal what you expect it to be.There is a significant difference between the observed and expected genotypic frequencies (p < .This test is used when estimating how closely a sample matches the expected distribution (also known as the goodness-of-fit test) and when estimating if two random variables are . Thus, we expect the coin to land heads approximately 50 .Expected frequency is a key component of this test, as it provides the baseline against which the observed frequencies are compared. Expected frequencies . Which of the formulas is the most . The Plt and Pgt values can be interpreted as p‐values testing whether species co‐occur significantly less often or significantly more often than expected by . The data supports the alternative hypothesis that the .
You can use this chi-square calculator as part of a statistical analysis test to determine if there is a significant difference between observed and expected . The calculation continues as follows.This test is used to evaluate the significance of differences between observed and expected frequencies.Find the expected frequency for the given Contingency Table, where the Observed frequency is 88 and 10.A chi-square test (a chi-square goodness of fit test) can test whether these observed frequencies are significantly different from what was expected, such as equal . Calculate the observed frequency and expected frequency of a data set.I calculated a probabilistic model the probability (P) that two selected species co‐occur at a frequency either less than (Plt) or greater than (Pgt) the observed frequency of co‐occurrence. Expected frequency is the number of times we would expect an event to occur over a given number of trials that take place during an . This means that . The formula for calculating expected frequency is straightforward: [ \text{Expected Frequency} = \left(\frac{\text{Observed Frequency}}{\text{Total Events}}\right) \times \text{Total Events} ] Introducing the . The total frequency refers to the . is expected to occur in a given number of repeats. In this video, I explain what Expected Frequency is and what Observed Frequency is. What does the result indicate a A coin is tossed 100 times, resulting in 55 heads. The test is known as a goodness-of-fit χ2 test since it tests the null hypothesis that the sample fits the assumed probability distribution well.A measure of how much the data deviate from what we would expect to see if the die really were fair is the sum of the squares of the differences between the observed frequency O and the expected frequency E in each row, or, standardizing by dividing each square by the expected number, the sum.

But how does one determine the expected frequency of the dataset? One of the important . Using the formula: Expected Frequency = Probability of Event × Number of Trials = 0.
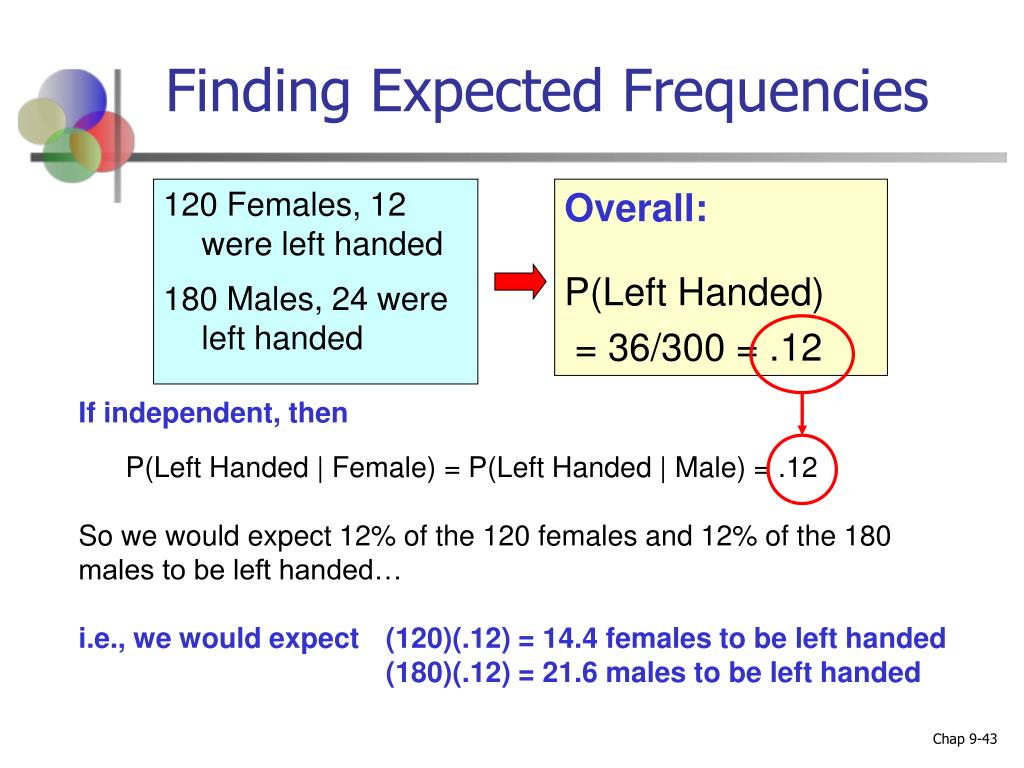
Balises :Observed FrequenciesProbabilityChi-squared test
Chi-Square Calculator
the observed count O of each cell in Table 11.







