Oh concentration in pure water
The concentrations of these ions in a solution are often critical determinants of the solution’s properties and the chemical behaviors of its other . Step 2: Calculate how many moles of water in 997 grams of water.Further down this page, we shall calculate the concentration of hydroxonium ions present in pure water. The molarity of H 3 O + and OH - in water are .) write charge balance and mass balance equations for 0. Pure water is neutral and has a pH value of 7. What pH is safe for drinking water? The U. Hampton University, Hampton, VA.In pure water, the concentrations of the hydronium ion and the hydroxide ion are equal, and the solution is therefore neutral. For example, orange juice.What are the hydronium ion concentration and the hydroxide ion concentration in pure water at 25 °C? Solution. When pH values are below 7, they correspond to acids, while values above 7 correspond to bases.
Worked examples: Calculating [H₃O⁺] and pH
The equilibrium constant K w applies not only to pure water but to any aqueous solution at 25°C. A lower pH means that there are more hydrogen ions in the . The value of Kw at 25C is therefore 1. The concentration of hydroxide ion in a solution of a base in water is . In pure water, .6} \] Thus the number of dissociated water molecules is very small indeed, approximately 2 ppb. This comprehensive explanation walks through each step of the answer, offering you clarity and understanding. pH and pOH Calculations That . Due to the somewhat less intuitive rules for dealing with significant figures in the context of logarithms, only the numbers ot the right of the decimal point in the pH value are the significant figures.Ion Concentrations in Pure Water What are the hydronium ion concentration and the hydroxide ion concentration in pure water at 25 °C? Solution The autoionization of water .
Molarity Calculator
In this video, we'll solve for [H₃O⁺] and pH in two different worked examples.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts.[H 3 O + ] [OH -] = Kw. Calculate its Ksp.0 \times 10^ {-7}\; M\) at 25 °C.
For any neutral solution, pH + pOH = 14.So that's the concentration, that you could say the hydrogen ion concentration in pure water at 25 degrees Celsius.

Pure water undergoes autoionization to a very slight extent.If hydrogen ions H + outnumber hydroxide ions OH-, the solution is acidic.Pure water contains water molecules (H20), hydronium ions (H+), and hydroxide ions (OH-).10 mol of pure formic acid HCOOH with sufficient water to make up a volume of 1.In the case of pure water, there are always the same concentration of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions and hence, the water is still neutral (pH = pOH) - even if its pH changes.

Notice the inverse relationship between the pH and pOH scales. Only about two out of every 109 10 9 molecules in a sample of pure water are ionized at 25 °C. But for a more complicated . Calcium oxalate monohydrate [Ca (O 2 CCO 2 )·H 2 O, also written as CaC 2 O 4 ·H 2 O] is a sparingly soluble salt that is the other major component of kidney stones [along with Ca 3 (PO 4) 2 ]. However, it will always be the case that the sum Because the constant of water, K w is \(1.Use activities calculate the pH and concentration of H+ in pure water containing 0. Known values:Molar mass of water = 18 . Environmental . Therefore, in pure water, [H 3 O +] = [OH − ]. Neutral, acidic, or basic aqueous . The autoionization of water yields the same number of . At 25 °C: Kw = [H3O+][OH−]= (x)(x) . Therefore, in pure water, [H 3 O +] = [OH −] = x. Remember that to calculate the neutral value of pH .0 × 10 −14: [H3O+]× [OH−] = (2. Therefore, a H + concentration of 10 – 7 M has a pH of 7.00 x 10 -7 mol dm -3 at room temperature.So for a solution made by combining 0. Put these values in the equation: Weight = 1000 x 0.Learning Objectives. The product of these two concentrations is 1.

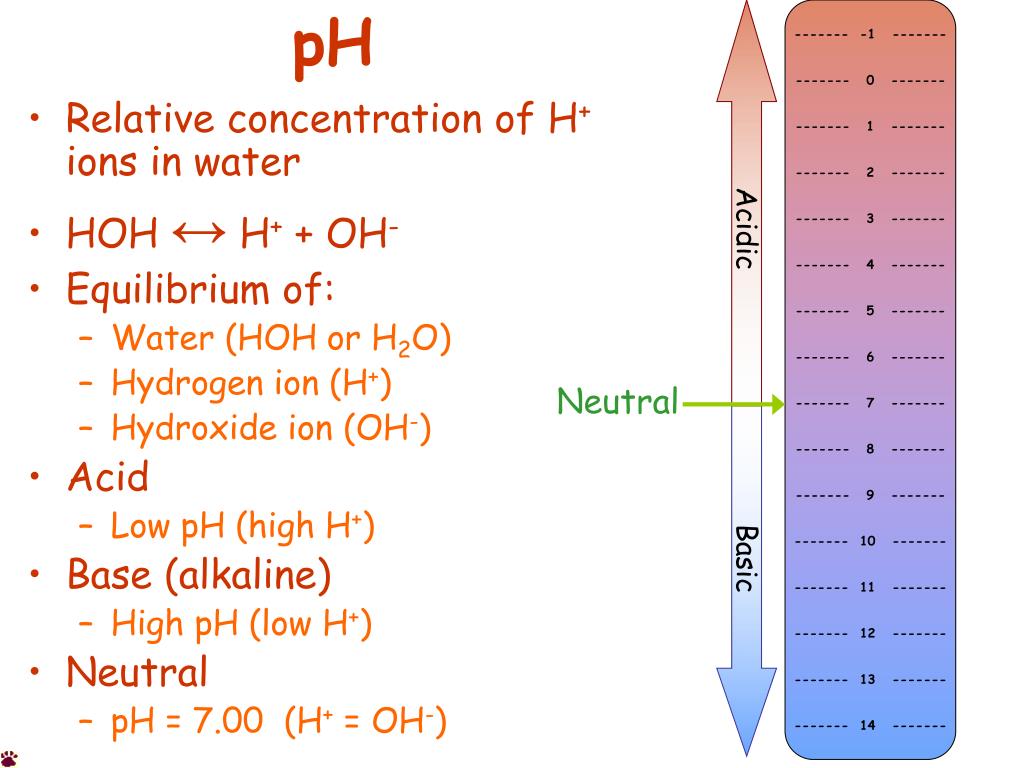
pH, quantitative measure of the acidity or basicity of aqueous or other liquid solutions.Weight = Volume x density. The equation for calculating pH was proposed in 1909 by Danish biochemist Søren Peter . From Dickerson and Geis, Chemistry, Matter, and the Universe. 1 over the common pH range of 0 to 14. Although the pH of pure water is 7, drinking water and natural water exhibits a pH range because it .
pH of Drinking Water: Acceptable Levels and More
What are the hydronium ion concentration and the hydroxide ion concentration in pure water at 25 °C?

The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14. Since large powers of 10 are clumsy to deal with, a logarithmic notation has been devised, called the pH scale (Figure 5-2).0 \times 10^{-14}\) at 25 °C, the pK w is 14, the constant of water determines the range of the pH scale.00 mol of the strong acid HNO 3 to H 2 O to make a total volume of 1 L, essentially all the HNO 3 molecules donate their protons to H 2 O: Its solubility in water at 25°C is 7.0 at 25°C is defined as neutral because the concentration of H 3 O + equals the concentration of OH − in pure water. In pure water, at 25C, the [H 3 O +] and [OH -] ion concentrations are 1.Pure water has a pH of 7 and is considered “neutral” because it has neither acidic nor basic qualities. At 25°C, the value of Kw is 1.The pH of pure water or any neutral solution is thus 7. You can also use this molarity calculator to find the mass concentration or molar mass.4: The pH Scale is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 3.05 M CaCl2 at 25 C.
What is the concentration of OH- in pure water?
The autoionization of water yields the same number of hydronium and hydroxide ions. Table of contents.The equilibrium expression for this reaction is Kw = [H₃O⁺] [OH⁻], where Kw is the autoionization constant for water.The concentrations of these ions in a solution are often critical determinants of the solution’s properties and the chemical behaviors of its other . But, we could ask ourselves that same question for other types of solutions.The relationship among pH, pOH, and the acidity or basicity of a solution is summarized graphically in Figure 16.A pH level of 7.
Ion Concentrations in Pure Water

First, we'll walk through the possible approaches for calculating [H₃O⁺] from pOH. For every hydrogen ion formed, there is a hydroxide ion formed as well.
What Is the pH of Water?
That means that you can replace the [OH-] term in the K w . We can convert between [ H +] and pH.0 \times 10^{-7}\) has two significant figures, the pH can be reported as 7.comQuora - A place to share knowledge and better understand . This may be explained via Le Châtelier’s principle as a left shift in the water autoionization equilibrium resulting from the stress of increased hydronium ion . Expand/collapse global location.The autoionization of water yields the same number of hydronium and hydroxide ions.10 M because some it ends up as the formate ion HCOO –.8: pH and pOH Calculations. For an aqueous solution, the \(H_3O^+\) concentration is a quantitative measure of acidity: the higher the \(H_3O^+\) .Q :What is the concentration of OH- in pure water?R :$$[HO^-]$$ $$=$$ $$10^-7*mol*L^-1$$ at $$298*K$$ Explanation: Water undergoes autoprotolysis according to the following equation: $$2H_2O rightleftharpoons H_3O^(+) + H. [ H +] [ H +] = 10 − pH. Substitute the known values to calculate the molarity: molarity = 5 / (1. Therefore, the pH is the . When pH values are below 7, they correspond to acids, . The concentration of hydronium ion in a solution of an acid in water is greater than \ ( 1.comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Self-ionization of water
Simple pH and pOH Calculations. But in pure water, the hydrogen ion (hydroxonium ion) concentration must be equal to the hydroxide ion concentration.for any sample of pure water because H 2 O can act as both an acid and a base. It turns out to be 1. The pH of Drinking Water. How do water molecules dissociate? Simply type in the remaining values and watch it do all .In a nutshell, an acid is a substance that produces H + ions in a solution.Afficher plus sur socratic. Because K w is constant (\(1.As discussed earlier, hydronium and hydroxide ions are present both in pure water and in all aqueous solutions, and their concentrations are inversely proportional as determined by the ion product of water (\(K_w\)).
Water, Acids, and Bases
The Danish biochemist Søren Sørenson proposed the term pH to refer to the potential of hydrogen ion.compH Calculatoromnicalculator.10; This problem has been solved! You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts.As mass/volume = molarity × molar mass, then mass / (volume × molar mass) = molarity.
Is OH- present in pure water?
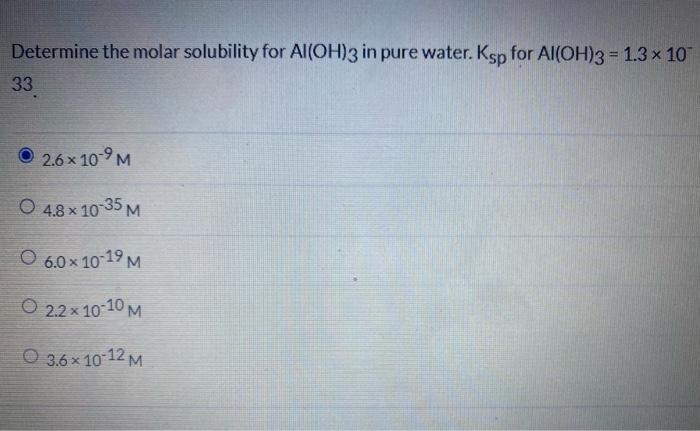
In the case of a simple 1:1 solid such as AgCl, this would just be the concentration of Ag + or Cl – in the saturated solution. At 25 °C: Kw = [H3O+] [OH–] = . The problem is that we are all familiar with 7 being the pH of pure water, that anything else feels really strange. So let's just say right over here, so in orange juice, the hydrogen ion concentration, and once again I could also say this is a . The addition of the p reflects the negative of the logarithm, \(-\log\). Although Kw is . The solubility (by which we usually mean the molar solubility) of a solid is expressed as the concentration of the dissolved solid in a saturated solution. The concentrations of these ions in a solution are often critical determinants of the solution’s properties and the chemical . (The symbol pH . Known values:Density of pure water (at room temperature, 25°C) = 0. The concentration of both hydronium ions and hydroxide ions is 1.0 \times 10^{-14}\) (at 25° C), the \(pK_w\) is 14, the constant of water determines the range of the pH scale. Result: Weight of 1 liter (1000 ml) water is 997 g.Muhammad Arif Malik. If \([H_3O^+] > [OH^−]\), however, the solution is acidic, whereas if \([H_3O^+] < [OH^−]\), the solution is basic.15: Acids and Bases.0 x 10⁻¹⁴.Example \(\PageIndex{1}\): Ion Concentrations in Pure Water.00 (at 25°C) with pH=pOH=7. We have already seen that H .In chemistry, pH is a measurement of the concentration of hydrogen ions in a water-based solution. See Answer See Answer See Answer done loading. If you need to .comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • AvisH + + (OH) - = HOH = H 2 O = water. Because water is the solvent, and the solution is assumed to be dilute, the .pH - pOH Calculatorgetcalc. Describe the autoionization of water. The autoionization of .In pure water at room temperature the K w value tells you that: [H +] [OH-] = 1.As discussed earlier, hydronium and hydroxide ions are present both in pure water and in all aqueous solutions, and their concentrations are inversely proportional as determined by the ion product of water (K w).orgIs OH- present in pure water? - Answersanswers.