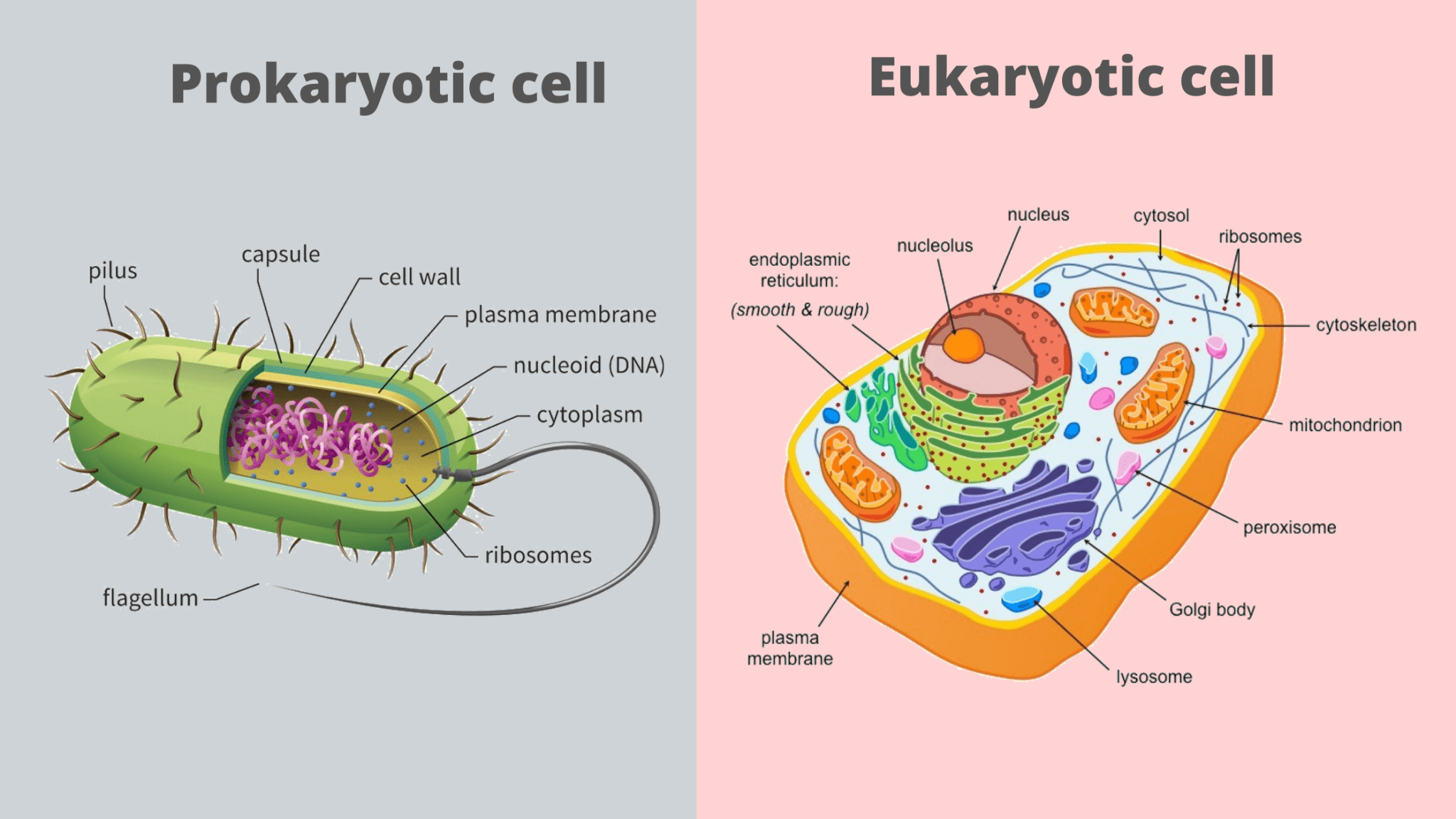
Organelles in eukaryotic and prokaryotic

It’s also been suggested that tiny organelles in eukaryotic cells – called mitochondria – may also be the descends of prokaryotic living-bacterium which were engulfed by other cells and .
Endosymbiosis and Eukaryotic Cell Evolution: Current Biology
A prokaryotic cell is a simple, single-celled (unicellular) organism that lacks a nucleus, or any other membrane . We’ll talk more about the nucleus and organelles in the next article on eukaryotic cells, but the main thing to .
Eukaryotic Cells
These are unicellular organisms and do not have membrane-bound cell organelles. Prokaryotes divide via using binary fission, while eukaryotic cells divide via mitosis. Reproduction happens through the process of .Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: a membrane-bound nucleus; numerous membrane-bound organelles—such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and others; several, rod-shaped chromosomes; Because a eukaryotic cell’s nucleus is surrounded by a membrane, it is often said to have a “true .0 μm in diameter, prokaryotic cells are significantly smaller than eukaryotic cells, which have diameters ranging from 10–100 μm ( Figure 5.Google Classroom. Their ribosomes are structurally smaller (70 S) in . Imarie uses a microscope to study different prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms.A prokaryote is a simple, single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.Eukaryotic cells are generally much larger than prokaryotic cells, frequently having a cell volume at least a thousandfold greater. Both, however, must carry out the same life processes. The small size of prokaryotes allows ions and organic molecules that enter them to quickly spread to other parts of the cell.
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells (video)
4 Years Ago Posted 4 Years Ago. Just like cells have membranes to hold everything in, . The difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells has to do with the little stuff-doing parts of the cell, called organelles.
Manquant :
organelles Differences in cellular structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes include the presence of mitochondria and chloroplasts, the cell wall, and the structure of chromosomal DNA. Cell structure - AQA Eukaryotes and prokaryotes.Symbioses, the living together of two or more species, involve varied metabolic interactions and diverse eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms (). Two of these organelles, mitochondria and chloroplasts, play critical roles in energy metabolism . All prokaryotic cells are encased by a cell wall. In most cases, this textbook categorization of eukaryotes and prokaryotes holds true. Their cells also hold much more DNA than prokaryotic cells do.Animal and plant cells are types of eukaryotic cells, whereas bacteria are a type of prokaryote.Eukaryotic cells are usually larger than prokaryotic cells, and they are found mainly in multicellular organisms. These are multicellular organisms and have membrane-bound .However, prokaryotes differ from eukaryotic cells in several ways. Organelles in animal cells include the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vesicles, and vacuoles.
However, decades . All of these features . Some features distinguishing prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are shown in Table \(\PageIndex{1}\). Learning Objectives.Prokaryotic cells have no organelles enclosed in plasma membranes; every eukaryotic cell has a nucleus and organelles, each enclosed in plasma membranes.
Prokaryotic cells (article)
However, the nature of .Eukaryotic cells are typified by the presence of intracellular organelles that compartmentalize essential biochemical reactions whereas their prokaryotic counterparts generally lack such sophisticated subspecialization of the cytoplasmic space. Prokaryotic cells are simpler and lack the eukaryote's membrane-bound organelles and nucleus, which encapsulate the cell's DNA. There are two primary types of cells: eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells.That is why eukaryotic cells require a variety of specialized internal organelles to carry out metabolism, provide energy, and transport chemicals throughout the cell.The organelle is the fourth example in history of primary endosymbiosis – the process by which a prokaryotic cell is engulfed by a eukaryotic cell and evolves beyond . Direct Link to Alex00hf's Post “Eukaryotic Cells They DoProkaryotes and Eukaryotes ReviewOrganelles in Eukaryotic CellsA typical eukaryotic cell is shown in Figurebelow. Eukaryotic cells also contain other organelles besides the nucleus.In addition to the nucleus, eukaryotic cells are characterized by numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, . Prokaryotic cells, however, have no true .Understanding the evolution of eukaryotic cellular complexity is one of the grand challenges of modern biology.The nucleus, which houses DNA, is contained within a membrane and separated from other cellular structures.Organelles are involved in many vital cell functions. It has now been firmly established that mitochondria and plastids, the classical membrane-bound organelles of eukaryotic cells, evolved from bacteria by endosymbiosis.Prokaryotes and eukaryotes share some similarities, but have many differences.Cell organelle that houses DNA and directs synthesis of ribosomes and proteins: No: Yes: Yes: Ribosomes: Protein synthesis: Yes: Yes: Yes: Mitochondria: ATP production/cellular respiration : No: Yes: Yes: Peroxisomes : Oxidizes and breaks down fatty acids and amino acids, and detoxifies poisons: No: Yes: Yes: Vesicles and vacuoles : Storage and . The word prokaryote comes from the Ancient Greek πρό (pró) 'before' and κάρυον (káruon) 'nut, kernel'. To hold up that big cell, eukaryotes have a cytoskeleton (Sy-toh-SKEL-eh-tun).state that the structures found in typical prokaryotic cells are chromosomal DNA/loop, plasmid DNA, cell membrane, cell wall, and flagella, describe a prokaryote as a unicellular organism that does not have a membrane-bound nucleus, describe the role of each of the structures and organelles listed,Key points: Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms belonging to the domains Bacteria and Archaea. The plasma membrane is a . Many also have a capsule or slime layer made of polysaccharide.Only eukaryotes have membrane-bound organelles and a nucleus. The nucleus stores DNA. Organisms with eukaryotic cells are called eukaryotes, and include fungi, animals, protists, and plants.
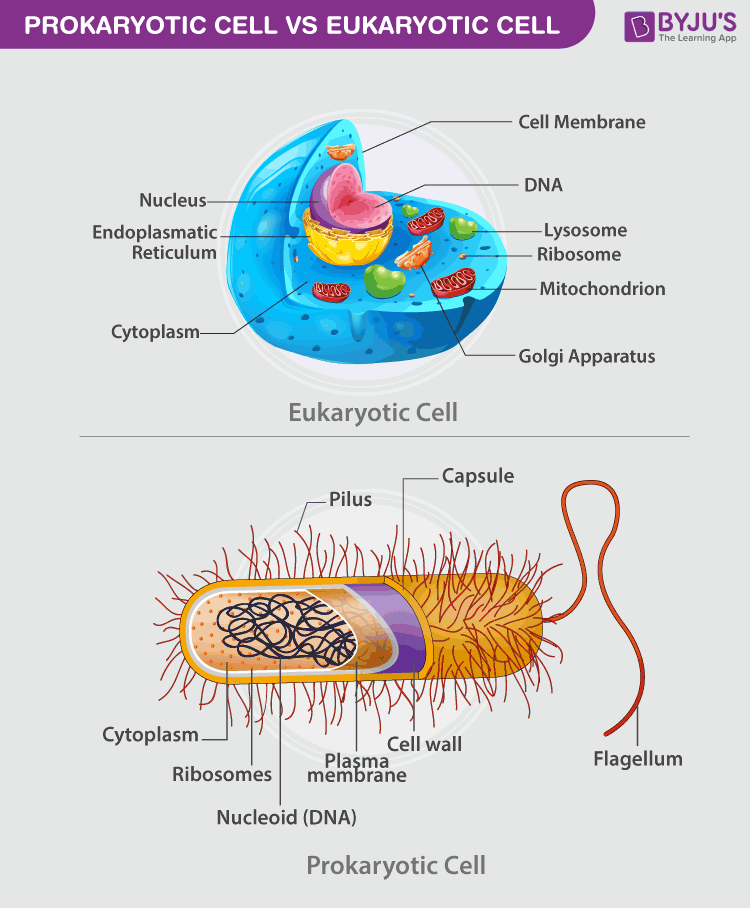
Organisms with eukaryotic cells are called eukaryotes, and they range from fungi to people. Most organisms are multicellular and have cells that are specialised to do a particular job.
Prokaryote structure (article)
What’s found inside a cell. The cell membrane is an extremely pliable structure composed primarily of two adjacent sheets of phospholipids.
Eukaryotic Cell: Definition, structure and organelles
Eukaryotic cells tend to be .Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic Cells .Eukaryotic cells are typified by the presence of intracellular organelles that compartmentalize essential biochemical reactions whereas their prokaryotic counterparts . 1: Eukaryotic Plasma Membrane: The eukaryotic plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with proteins and cholesterol embedded in it.Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles, such as the nucleus, while prokaryotic cells do not. Organisms are made up of cells. DNA in eukaryotic cells is found inside the .A eukaryotic cell is a cell that has a membrane-bound nucleus and other membrane-bound compartments or sacs, called organelles, which have specialized functions. Direct Link to Nesta's Post “What Makes Trichodina DIF5 Years Ago Posted 5 Years Ago. Over a long time, the .One thing in common, we all know that the Prokaryotes are those organisms that possess the prokaryotic cell.Organelles in Complex Eukaryotic Cells. Molecules that make up organelle membranes resemble those in prokaryotic membranes – and differ from those in .
Organelles in eukaryotic cells (video)
N 2 fixation in eukaryotes is only known to exist through diverse symbiotic partnerships with prokaryotic microbes capable of N 2 fixation.

Prokaryotes were the only form of life on Earth for millions of years . Prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells, have no nucleus, and lack organelles. Cholesterol, also present, contributes to the fluidity of the membrane. Eukaryotes have an enclosed nucleus, while prokaryote lack membrane . However, nonorganelle-associated ribosomes in eukaryotic cells are 80S ribosomes, composed of a 40S small subunit and a 60S large subunit. Components of Prokaryotic Cells. Which of the following statements describes how the prokaryotic cells appear .Eukaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles.
Prokaryote
The compartmentalization provided by cytoplasmic organelles is what allows eukaryotic cells to function efficiently.Like a prokaryotic cell, a eukaryotic cell has a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and ribosomes, but a eukaryotic cell is typically larger than a prokaryotic cell, has a true nucleus (meaning its DNA is surrounded by a membrane), and has other membrane-bound organelles that allow for compartmentalization of functions.
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells. In the case of mitochondria, evidence points very clearly to .
Lesson Plan: Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells
In terms of size and composition, this makes them distinct from the .
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes review (article)
In the two-empire system arising from the work of Édouard .
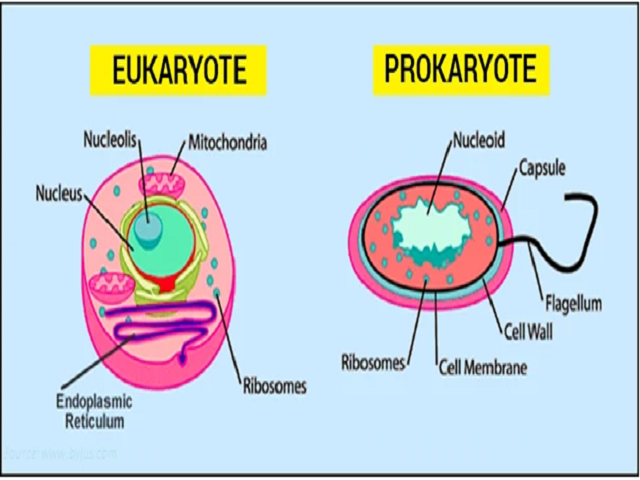
The other defining characteristic of prokaryotic cells is that it does not possess membrane-bound cell organelles such as a nucleus.It is made up of several types of organelles that allow the cell to function and reproduce. Made from a network of protein threads, it forms a scaffold inside the cell to give it strength and help it . Eukaryotic cells are usually larger than prokaryotic cells, and they are found mainly in multicellular organisms.
Eukaryotic Cell vs Prokaryotic Cell
On the other hand, Eukaryotes are those organisms that possess the Eukaryotic cells.