Parathyroid hormone and vitamin d

The test triad parathyroid hormone (PTH), calcitonin and vitamin D is finding increasing use in the diagnosis of calcium and bone metabolic diseases. For the diagnosis of osteomalacia, skeletal alterations should be . Landry, Mary D. showed in vitro that . (OH) 2 D 3 and parathyroid hormone related protein.To assess the correlation of serum parathyroid hormone (PTH) and vitamin D (25-OHD) levels based on different assays for measuring 25-OHD in healthy Saudi Arabians living along the east coast.Vitamin D and Parathyroid Hormone Levels in CKD. In patients with primary hyperparathyroidism, the low vitamin D level can further stimulate the parathyroid glands to make even more parathyroid hormone.PTH helps control calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin D levels in the blood and bone.However, levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D 3 less than 20 ng per mL (52 nmol per L) triggers a compensatory increase in parathyroid hormone (PTH) and, hence, accelerates bone resorption. This means the body cannot produce enough parathyroid hormone to keep the calcium in the standard range.The discovery of 1,25(OH)2D3 as the active metabolite of vitamin D, allowed testing of the effect of vitamin D on the parathyroid gland. When circulating vitamin D concentrations are low, intestinal calcium and phosphorus absorption decreases and parathyroid hormone levels increase.PMCID: PMC5831602.
Parathyroid Hormone: What It Is, Function & Levels
Believing that high parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels are required for a hyperparathyroidism diagnosis.The active form, calcitriol, causes dimerization of vitamin D receptor and acts on the bones, intestine, and kidney to regulate the level of calcium in blood. We have discussed the metabolism of these hormones and their effects on bone health. However, severe deficiency seems to be more prevalent in the Middle East and South Asia.This chapter discusses the metabolism of vitamin D and its relationship to parathyroid hormone and calcitonin. Background: Vitamin D deficiency . Because of the increased prevalence of hyperparathyroidism and altered vitamin D status in chronic renal failure, these alterations have been considered to contribute to .5 Measure parathyroid hormone (PTH) .Parathyroid hormone and vitamin D are essential endocrine regulators primarily responsible for maintaining calcium and phosphate homeostasis. When the calcium concentration becomes imbalanced, bone .Introduction Higher concentrations of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25 (OH)D) and lower concentrations of parathyroid hormone (PTH) are associated with lower insulin . Healthy bones rely on a constant concentration of calcium in the blood, which is regulated by the concerted action of the three hormones. Supplements can help, and most adults can take 1,000 .
Most vitamin D deficiency cases are asymptomatic, only revealed by laboratory results including low blood calcium levels, and the elevation of parathyroid hormone (secondary hyperparathyroidism).
Parathyroid hormone and vitamin D: from bench to bedside
Its deficiency . Via the kidney, PTH enhances the absorption of calcium in the intestine by increasing the production of activated vitamin D.Parathyroid hormone (PTH), .The importance of adequate vitamin D status for optimum bone health has received increased recognition in recent years, with higher recommended intake levels being proposed by some investigators.Vitamin D deficiency leads to secondary hyperparathyroidism, and both primary and secondary hyperparathyroidism are associated with CV pathology. Methods and results: This was a prospective study of 148 HF outpatients (mean age 68 years, 102 men) with follow-up for mortality after 3½ years. When the parathyroid gland is over active, . 1,25 [OH]2D regulates multiple . The PHT regulates the exchange of calcium between the blood and the bones.
Physiology, Parathyroid Hormone
Patients and Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted in 200 patients (150 women and 50 men aged between 18-69 years) between January 2011 and . Ruppe, Elizabeth Gardner Grubbs The actions of these hormones also influence the expression of the FGF23 gene directly from the osteocyte and perhaps other cell types as well, and its cellular processing and liberation into the circulation where it controls . If your parathyroid glands . To the Editor: Chronic kidney disease–bone mineral disorder (CKD-MBD) includes multiple interrelated abnormalities, including hypocalcemia, . PTHR activates the 25-hydroxyvitamin D 3-1α-hydroxylase catalyzing the formation of biologically active 1,25(OH) 2-vitamin D 3.It is easily treated by oral administration of the active 1,25-dihydroxylated hormone.1 The Endocrine Society Vitamin D guidelines set vitamin D deficiency as a serum 25(OH)D concentration of ≤20 ng/mL (51 nmol/L), insufficiency .The vitamin D hormone also controls cellular proliferation and differentiation, .Auteur : Syed Jalal Khundmiri, Rebecca D. Figure 1 demonstrates the flow of the trials selected.1 For people with a probable diagnosis of primary hyperparathyroidism, measure vitamin D and offer vitamin D supplements if needed.
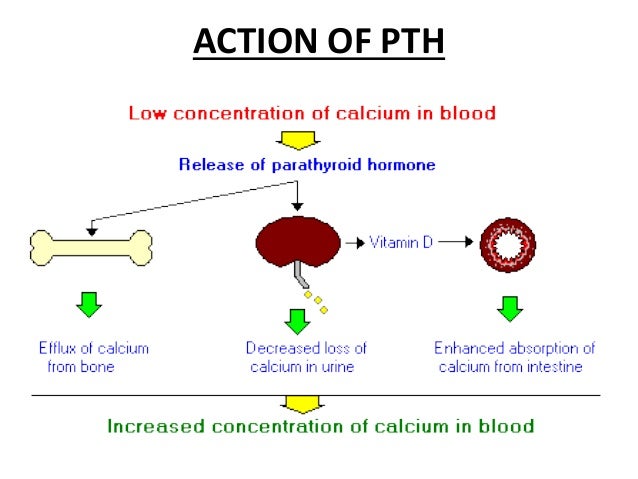
Low 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 confirms vitamin D deficiency.Parathyroid glands secrete a hormone called PHT. Estimates of the VitD status in several .
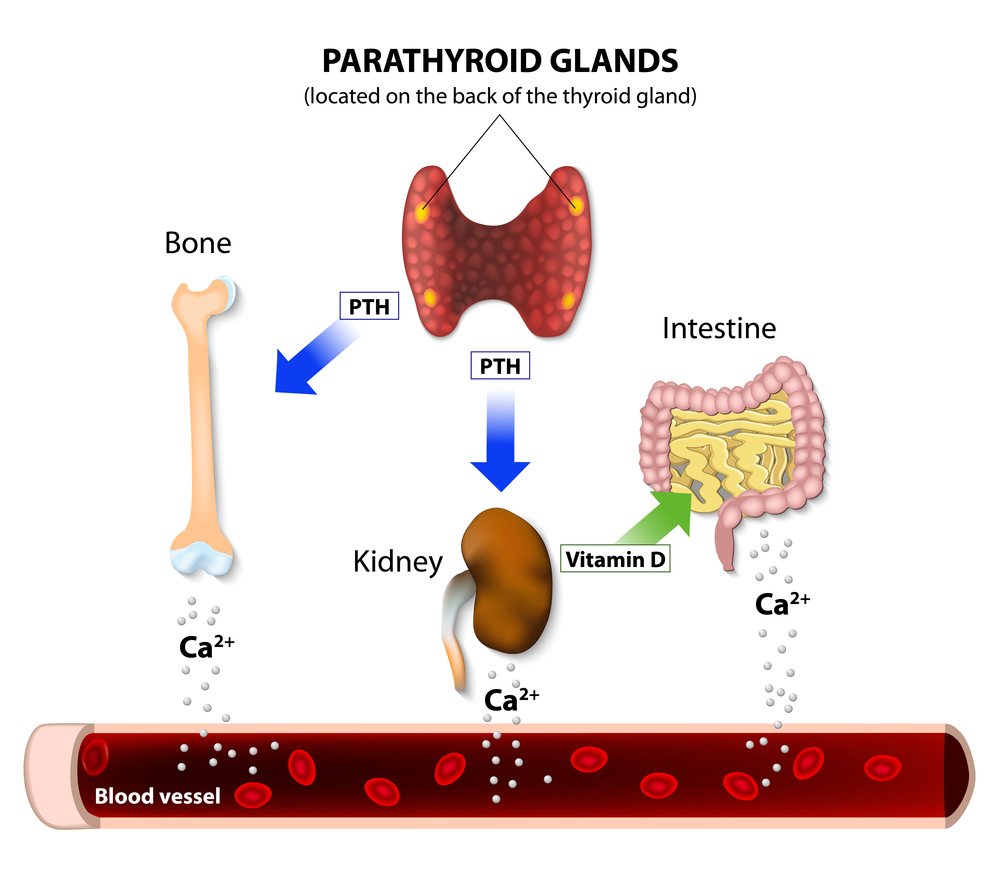
Aims: To investigate levels of vitamin D and parathyroid hormone (PTH) in a population of heart failure (HF) patients, and to evaluate whether vitamin D and PTH are related to prognosis.Evidence suggests that low serum 25-hydroxycholicalciferol [25 (OH)D] levels are associated with an increase in parathyroid hormone (PTH).Long-term low calcium levels requiring the use of calcium and vitamin D supplements due to removal or damage to all parathyroid glands. It is important for healthy bones.Much has been discovered about the interaction of vitamin D with the parathyroid glands, gastrointestinal tract, kidney, and bone in relation to .Auteur : Melissa Crooks, Stephen Bendall Type 2 vitamin D resistance, otherwise known as hereditary .Vitamin D (VitD) and parathyroid hormone (PTH) play important roles in calcium metabolism and skeletal homeostasis. This latter, besides of . This latter form of vitamin D is the active hormone which stimulates calcium uptake from the intestine.Vitamin D deficiency is a global public health issue, which affects people of all ages and ethnicities.Getting too little vitamin D can cause you to absorb too little calcium, which leads to parathyroid problems.2 To differentiate primary hyperparathyroidism from familial hypocalciuric hypercalcaemia, . Many reports demonstrated a reverse correlation between vitamin D concentration and .

Data were collected on serum calcium, 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25-OH D), intact parathyroid hormone (iPTH), phosphorus, and alkaline phosphatase, both before and after vitamin D replacement.
The parathyroid glands and vitamin D
Believing every lab value .Key words: Breast Cancer, Osteoprotegerin (OPG),Estrogen, Parathyroid Hormone, Vitamin D Introduction Breast cancer (BC) is one of the most widespread cancers around the world and it is the second main reason for death after lung cancer among women[1].Hyperparathyroidism is a disease entity that occurs due to increased secretion of parathyroid hormone (PTH) from parathyroid glands and causes hypercalcemia.
Vitamin D and Parathyroid Hormone Levels in CKD
In conjunction with calcitriol, PTH regulates calcium and phosphate.
Manquant :
Using a scan to help diagnose hyperparathyroidism.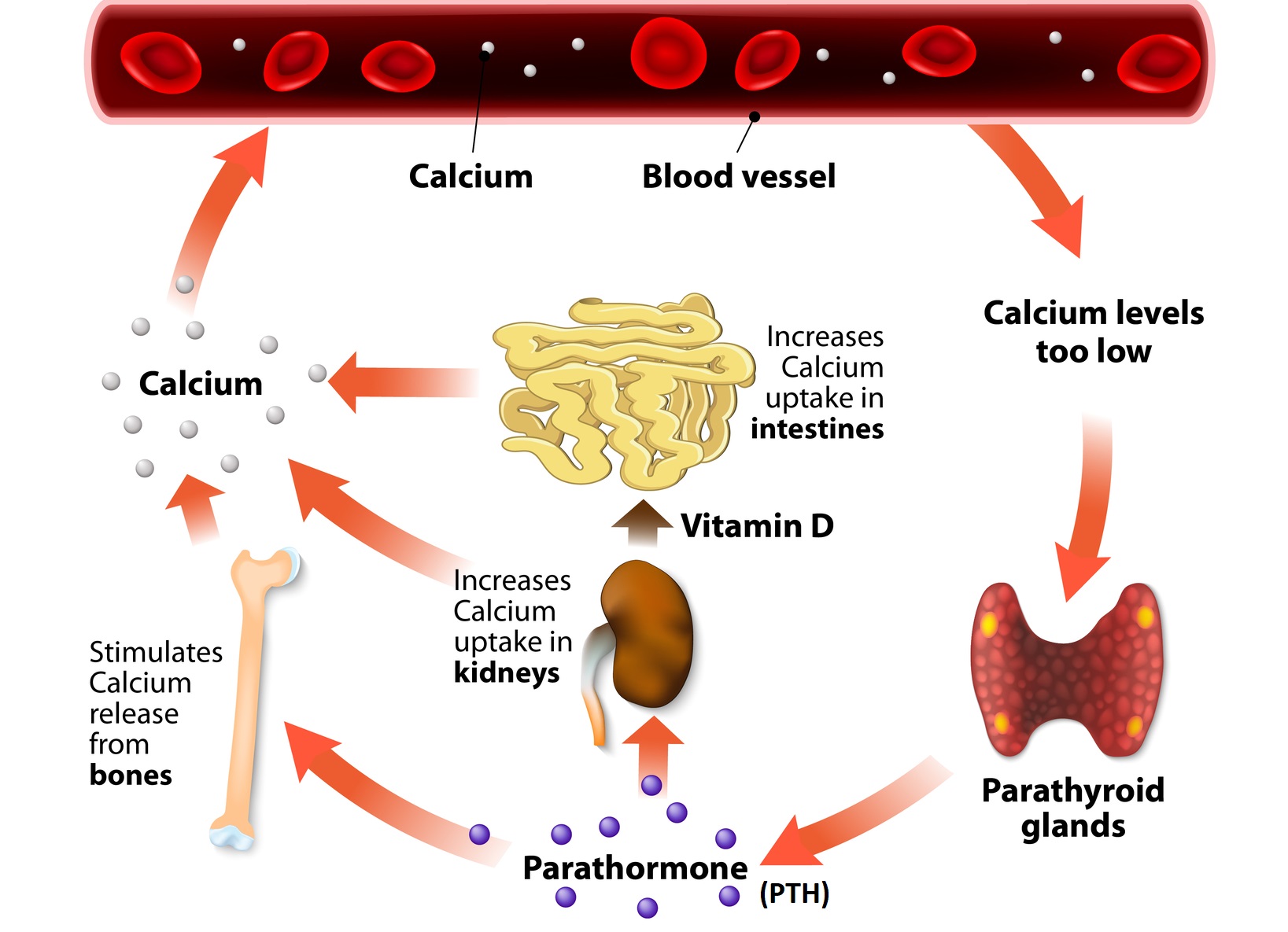

Objectives: The aim of this study was to evaluate associations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25-OHD) and parathyroid hormone (PTH) concentrations separately and in combination with incident cardiovascular events and mortality during 14 years of follow-up in the CHS (Cardiovascular Health Study).Phosphate homeostasis is tightly linked to PTHR activity, with serum phosphorus levels regulated by the interplay of parathyroid hormone, kidney, and bone . Medications to treat hyperparathyroidism include the following: . Objectives: The objective of this study was to evaluate the relationships among vitamin D status, PTH, . Evidence suggests that low serum 25-hydroxycholicalciferol [25 (OH)D] levels are associated with an increase in parathyroid hormone (PTH).Auteur : Stephen Nussey, Saffron Whitehead
PTH and Vitamin D
Parathyroid hormone is produced by the parathyroid glands - tiny 4-6 glands located, as the name suggests, near the thyroid gland. This suggests . 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25 (OH)D) plays a crucial role in human homeostasis. 1-3 The ideal intake is not known, and different criteria have been proposed for estimating population requirements.The parathyroid glands make parathyroid hormone (PTH), which helps your body keep the right balance of calcium and phosphorous. When the blood calcium level is too low, the body responds . Excluding familial hypocalciuric hypercalcaemia .

Studies over the last decade have shown that the effects of vitamin D are not limited to the maintenance of calcium homeostasis.The active form of vitamin D is formed from an inactive form mainly in the kidney, under the influence of a hormone called parathyroid hormone (PTH).Learn how vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium, activate parathyroid gland function, and prevent bone fractures. Levels of N-terminal . We tested whether elevated PTH is associated with CV disease and whether .
Parathyroid hormone
Moreover, 25-hydroxy-vitamin D is stabler and characterized by a longer half-life (about 2–3 weeks) compared to the 1,25-dihydroxy-vitamin D metabolite (about 4–6 hours).Auteur : Christine S. Parathyroid hormone (PTH) is an important regulator of calcium homeostasis, and its impact on CV disease risk is of interest.PTH and Vitamin D form a tightly controlled feedback cycle, PTH being a major stimulator of vitamin D synthesis in the kidney while vitamin D exerts negative . PTH facilitates the synthesis of active vitamin D and calcitriol (1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol) in the kidneys.1155/2018/5287573. Prolonged hypocalcemia and exposure to elevated PTH may also result in 1,25 (OH)2D-mediated calcium and phosphorus release from bone. These effects restore the ECF calcium to .Background There has been a notable shift towards the diagnosis of less severe and asymptomatic primary hyperparathyroidism (PHPT) in developed countries. 2013;19:420-425) Abbreviations.Background: Evidence suggests that vitamin D status in adults, as assessed by serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25-OHD), is positively associated with calcium absorption fraction and inversely associated with serum PTH.
Hyperparathyroidism (primary): diagnosis, assessment and initial
1 Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) concentration causes an elevation in parathyroid hormone (PTH). 25-hydroxyvitamin D. PTH up-regulates 25-hydroxyvitamin D 3 1-alpha .Among all the hormones involved in bone health, calcitriol (also vitamin D), parathyroid, and sex hormones (especially estrogen) have been discussed in this review paper.In vitro studies indicate that 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (25 (OH)D3) and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,25 (OH)2D3) inhibits the synthesis of parathyroid hormone .PTH stimulates the renal conversion of 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25 [OH]D) to 1,25 (OH)2D, likely over several hours, which in turn will augment intestinal calcium absorption.