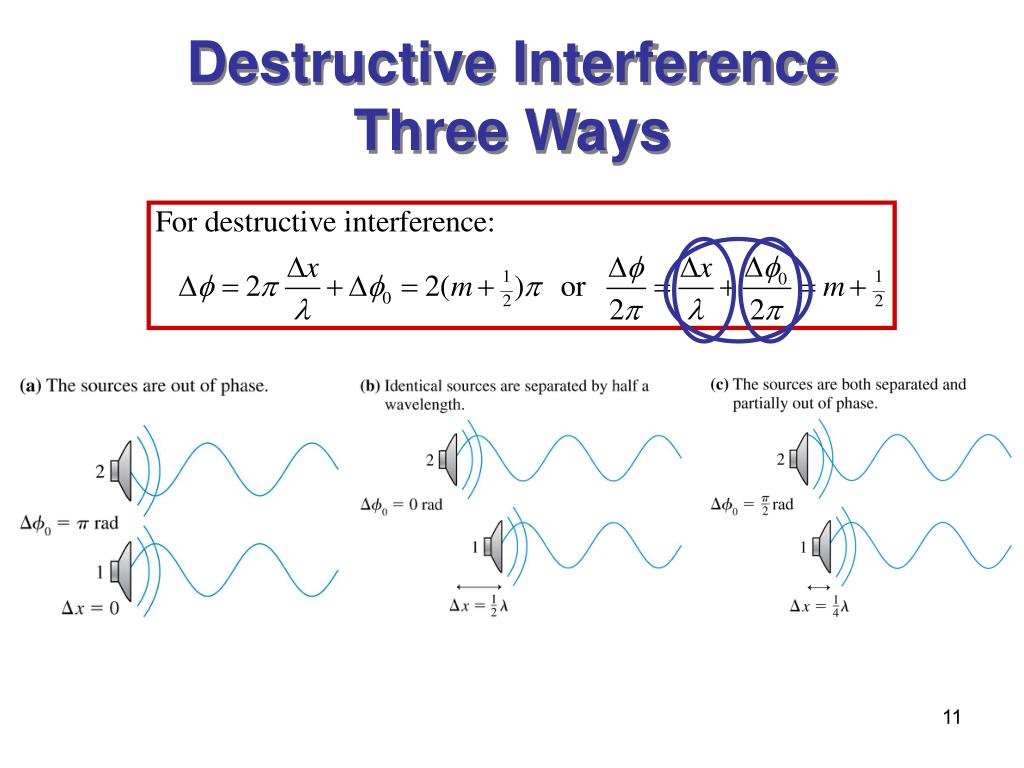
Path difference for destructive interference
- TopprGive the condition constructive and destructive interference in terms .
AIIMS 2002: What is the path difference for destructive interference?Step 3: The minimum path difference required for destructive interference is equal to half of the wavelength: λ 2 .
Constructive and Destructive Interference
Path difference at A = 1.Destructive interference occurs at points where a wave from \(S_{1}\) and a wave from \(S_{2}\) arrive out of phase.
Physics Tutorial: The Path Difference
For rays incident perpendicularly, the path length difference is 2t.

Constructive and destructive interference can be explained in terms of phase and path difference.Regarder la vidéo13:44Learn how two waves can combine to create a larger wave or cancel each other out, depending on their phase difference. For destructive interference, phase difference should be, ϕ = π, 3 π . constructive or destructive) depends on the path difference of the overlapping waves; Path difference is defined as: The difference in distance travelled by two waves from their sources to the point where they meet. The thickness of the film relative to the wavelength of light is the other crucial factor in thin-film interference. The basic requirement for destructive interference is that the two waves are shifted by half a .Learn how to calculate the path difference required for destructive interference, and see examples that walk through sample problems step-by-step for you to improve your physics knowledge and skills.Destructive interference: Once we have the condition for constructive interference, destructive interference is a straightforward extension.What is the path difference for destructive interference? (2n+1)λ 2.Regarder la vidéo13:44Destructive interference happens when the peaks match the valleys and they cancel perfectly.Thin-film interference is the phenomenon that is a result of lightwave being reflected off two surfaces that are at a distance comparable to its wavelength.Thus, to obtain destructive interference, ray 2 needs to travel a half wavelength farther than ray 1. Intensity at point is 1 2th of maximum intensity.Auteur : David SantoPietro - TopprWhat is interference? Write the condition path difference in of . Match the condition for the type of interference: 1. Therefore path difference of a destructive interference is 2(2n+1)λ (where n = 1,2,3,.Similarly, to obtain destructive interference for a double slit, the path length difference must be a half-integral multiple of the wavelength, or d sin θ = ( m + 1 2 ) λ , for m = 0 , .Constructive and destructive interference can be explained in terms of phase and path difference.Thus, when the film is very thin, the path length difference between the two rays is negligible, they are exactly out of phase, and destructive interference will occur at all wavelengths and so the soap bubble will be dark here.The path difference for constructive interference is the difference in the distances travelled by two waves from their respective sources to a given point where interference occurs.The general formula for destructive interference due to a path difference is given by \(\delta =(m+1/2)\lambda /n\) where \(n\) is the index of refraction of the medium in which .

9 shows the simplest case of multiple-slit interference, with three slits, or N = 3 N = 3. The basic requirement for destructive interference is that the two waves . Interference patterns can be calculated using wavelength . In general, the integral multiples of λ.Thus, when the film is very thin and the path length difference between the two rays is negligible, they are exactly out of phase, and destructive interference occurs at all wavelengths.Write the relation between the path difference and wavelength of light wave used for constructive and destructive interference of light.Since the wavelength of the walkie talkie signal is 1 meter, then the path difference will need to be a multiple of a whole metre for constructive interference, and a half metre for destructive interference. Similar Questions.The path length difference between two waves coming from coherent sources for destructive interference should be View Solution When a crest and trough of equal implitude and wavelength superpose there is destructive interference. Was this answer helpful? 0.Define constructive interference for a double slit and destructive interference for a double slit.Once we have the condition for constructive interference, destructive interference is a straightforward extension. The thickness of the film relative to the wavelength of light is the other crucial factor in thin film interference .If the film in Figure 3.And , phase difference, ϕ = 2 π λ Δ x = 2 n π D e s t r u c t i v e interference occurs when path difference is an odd integral multiple of half of the wavelength that is Δ x = ( 2 n + 1 ) λ 2 When light waves that reflect off the top and bottom surfaces interfere with one another, we see different coloured patterns.(b) The path difference between the two rays is Δ l Δ l.A path difference δ corresponds to a phase difference ϕ as given by the equation, For constructive interference, the phase difference should be, ϕ = 0, 2 π, 4 π . Which of the following is the path difference for destructive interference ? This kind of wave interference takes place in any location along with the medium when the two waves that interfere with each other have a displacement in the opposite direction. When a crest of a wave . The relation between phase difference and path difference is direct.Path Difference.out of phase at P, resulting in destructive interference with a dark fringe on the screen.
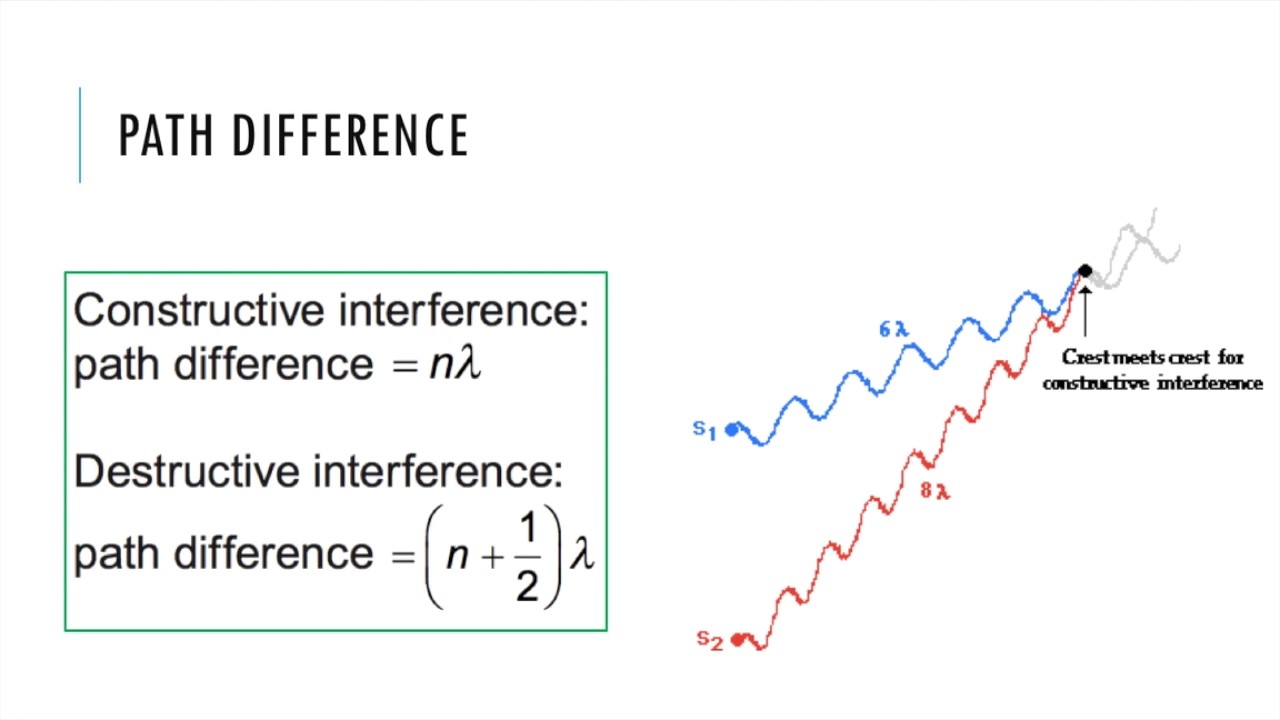
Ray 2 in Figure .5λ = (n + ½)λ n = 1; Step 4: Decide whether the point is a location of constructive or destructive interference E. Released under a license.Path difference of constructive and destructive interference is determined by wavelength For constructive interference (or maxima), the difference in wavelengths will be an integer number of whole wavelengths; For destructive interference (or minima) it will be an integer number of whole wavelengths plus a half wavelength.6: Path Length Difference for Destructive Interference Mathematically, plugging in for the the path length difference we obtain the result for destructive interference: \[\Delta\Phi = -\dfrac{2 .

We can do this by mapping what happens to two spherical waves that start at different positions near each other, and specifically keeping track of the crests (solid circles) and troughs (dashed circles). For constructive interference, the difference in wavelengths .
What is the path difference destructive interference?
Chapter 14 Interference and Diffraction
See examples of path length differences and pi shifts, and how . And you could use the path length difference for two wave sources to determine whether . If wavelength of light is λ & separation between slits is d then, find angular position of . (a) Destructive interference occurs here, because one path is a half wavelength longer than the other.The key is to compare the number of wavelengths it takes for each light wave to travel from the slit to the wall.
Constructive and Destructive Interference
How to Calculate Path Differences for Destructive Interference
n(λ+1) Solution. The difference between the path of two waves is an odd . Destructive Interference. For any two waves with the same frequency, phase difference and path difference is related as – \(\begin{array}{l}\Delta . For constructive interference it is integral multiple of λ or nλ. Verified by Toppr. Although Christiaan Huygens thought that light was a wave, Isaac Newton did not. What is new is that the path length difference for the first and the third slits is 2dsinθ 2 d sin θ.Destructive Interference Equation.Path difference is the difference in the path traversed by the two waves.

A is a location of destructive interference The spacing between slits is d, and the path length difference between adjacent slits is dsinθ d sin θ, same as the case for the double slit. The equations for double-slit interference imply that a series of bright and dark lines are formed. Path difference is generally expressed in .The condition for destructive interference is a path difference of (n + ½)λ. Kyle Forinash © 2019, W. The waves start in phase but arrive out of phase.12 is a soap bubble (essentially water with air on both sides), then a phase shift of λ / 2 λ / 2 occurs for ray 1 but not for ray 2. The condition for destructive interference is given by 180° 1 sin , 0, 1, 2, 3,.Similarly, to obtain destructive interference for a double slit, the path-length difference must be a half-integral multiple of the wavelength, or d sin θ = ( m + ½ ) λ , for m = 0 , 1 , . The path difference . LIVE Course for free Rated by 1 million+ students Path difference (Δd) is given by Δd = n⋅λ. In this case, n is an integer i. The type of interference occurring at a given point (i. For vertical slits, the light spreads out horizontally on either side of the incident beam into a pattern called interference fringes ( Figure 3.The path difference must be equal to zero. Phase Difference and Path Difference. (b) Constructive interference occurs here because one path is a whole wavelength longer than the other . Path difference is . Where n is an integer (0, 1, 2, .Title and author: Path Difference.For destructive interference, the path difference should be an odd multiple of (2 n + 1) λ 2. During this, the light reaches the boundary between two media . What is Destructive Interference? Destructive interference:.Learning Objectives. Thus, when the film is very thin and the path length difference between the two rays is negligible, they are exactly out of phase, and destructive interference occurs at all wavelengths. Destructive II.The goal of this video is to get students to understand the concept of path difference (how much farther one wave must travel than another) and the role that. The receiver can try moving to a place closer or further from the cliff to try to make the signal interference work to their advantage. The bright colors seen in an oil slick floating on water or in a sunlit .Step 3: Compare the path difference calculated in Step 2 with the condition for constructive or destructive interference and give the value of n E.Solution: If the waves interfere destructively, then path difference is given by 2λ, 23λ, 25λ etc. For this the path difference must be an odd number of half wavelengths. constructive or destructive) depends on the path difference of the overlapping waves. Hence: Destructive interference occurs at point P1. Path difference is generally expressed in multiples of . n is the order of the . The destructive interference pattern of the waves is shown in the figure above. The phase difference between two waves is an odd multiple of π that is: (2n – 1) π.



.png)