Perfectly competitive market model

Due to its insignificant impact on the . If the ATC at 45 units is $8, the profit/loss amount at the profit-maximizing quantity is $________.
Perfect Competition(Short Run) Flashcards
Perfect Competition: The Theory and Why It Matters
No individual has enough power in a perfectly competitive market to have any impact on that price.
In a perfectly competitive market, price will be equal to the marginal cost of production.

Perfectly Competitive Market
Because there is freedom of entry and exit and perfect information, firms .One reason so few markets are perfectly competitive is that minimum efficient scales are so high that eventually the market can support only a few sellers.2 Operation of a Perfectly Competitive Market in the Short Run. Each of them has its own set of characteristics and assumptions, which in turn affect the decision-making of firms and the profits they can make. It is important to note that not all of . When a wheat grower, as we discussed . Competitors have good information about the product and sell identical products. If a perfectly competitive firm attempts to . Hence, when we describe a market as being perfectly competitive we do not mean that other market types are not competitive; all market structure are competitive in the sense that the suppliers wish to make profit, and they produce as efficiently as possible in order .A perfectly competitive market is a hypothetical extreme; however, producers in a number of industries do face many competitor firms selling highly similar goods, in which case they must often act as price takers. Explain why in long-run .
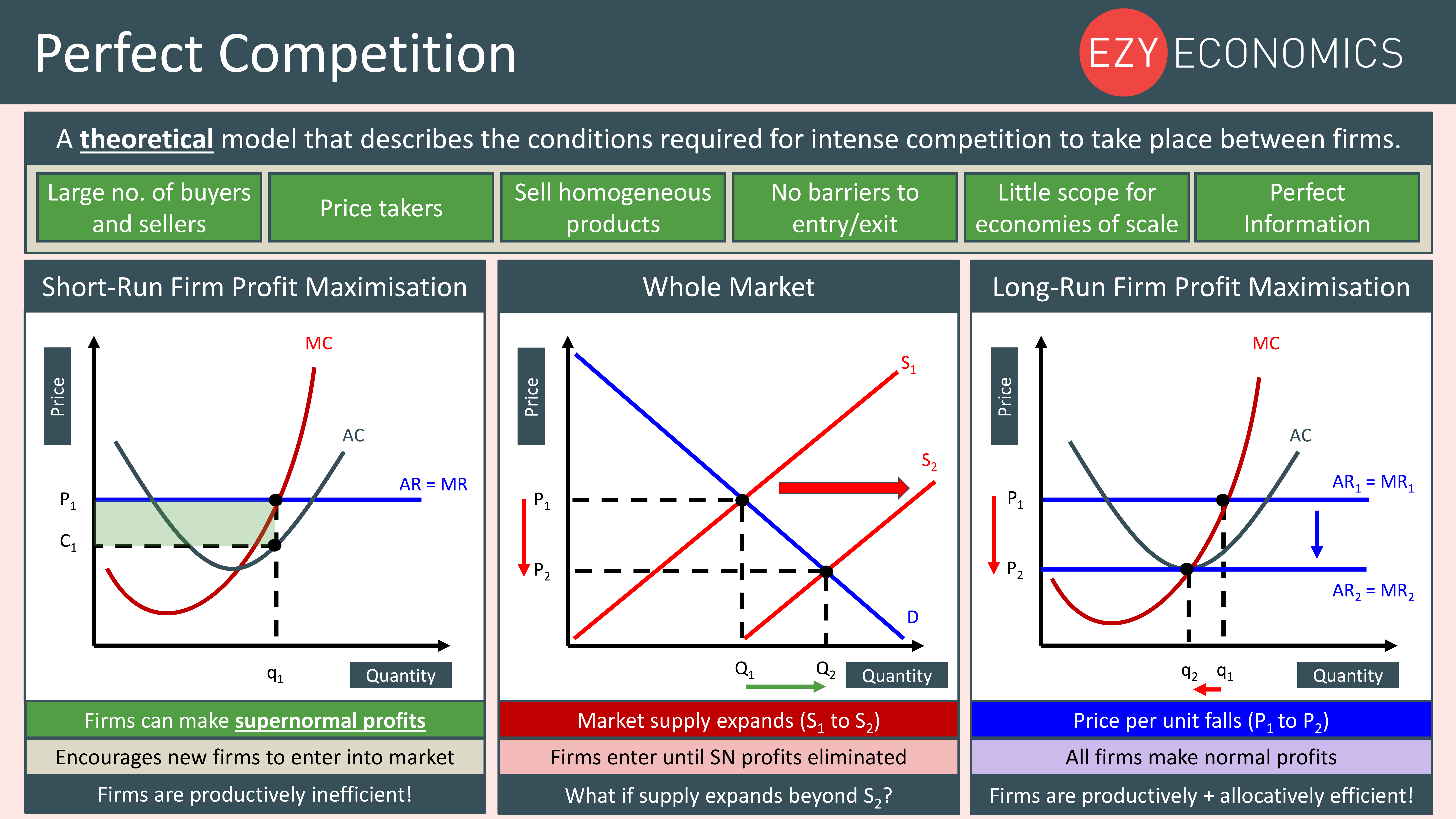
Perfect competition in the short run and . However, in practice, very few industries can be described as perfectly competitive.) In the real world, all markets are perfectly competitive, so this model .1 Flat Demand Curve as Seen by an Individual Seller in a Perfectly Competitive Market. 28 May 2019 by Tejvan Pettinger.3: Use the perfectly competitive market model to evaluate the decision to allow the consolidation of retail gas stations under fewer brands. Industries differ from one another in terms of how many sellers there are in a specific market, how easy or difficult . Economists often use agricultural markets as an example.3 Perfect Competition in the Long Run – Principles of Economics. Learning Objective 13.The generic drug industry is largely characterized by the attributes of a perfectly competitive market.Perfect competition is a model of the market based on the assumption that a large number of firms produce identical goods consumed by a large number of buyers.The perfect competition model is built on five assumptions: The market consists of many buyers. Firms in perfectly competitive markets aim to maximize profits by producing where marginal cost equals marginal revenue, which is equal to the market price.This chapter examines how profit-seeking firms decide how much to produce in perfectly competitive markets. Economists use it to study behavior and outcomes in highly competitive markets — highly .Perfectly Competitive Market | Model Answer A-level Economics.In the short run, the perfectly competitive firm will seek the quantity of output where profits are highest or, if profits are not possible, . When firms enter the market, prices fall and economic profit goes to zero. Because of this it serves as a natural benchmark against which to contrast other market structures.Overview
Perfect competition
Allocative efficiency means that among the points on the production possibility frontier, the chosen point is socially preferred—at least in a particular and specific sense.1: Describe the characteristics of a perfectly competitive market. Competitive Markets Supply and demand are the forces that make market economies work The terms supply and demand refer to the behaviour of people, as they interact with one another in markets o Buyers determine demand o Sellers determine supply A market is a group of . If a firm in a perfectly competitive market raises the price of its product by so much as a penny, it will lose all of its sales to competitors.Key Concepts and Summary.A perfectly competitive firm is known as a price taker, because the pressure of competing firms forces it to accept the prevailing equilibrium price in the market. The consequence of the preceding assumptions is that all exchanges in a perfectly competitive market will quickly converge to a single price.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Perfect-Competition-2de51ba3fa8a40e9bdfdc7b98a195ce0.png)
In neoclassical economics, perfect competition is a theoretical market structure in . Long-run equilibrium in perfectly competitive markets meets two important conditions: allocative efficiency and productive efficiency.
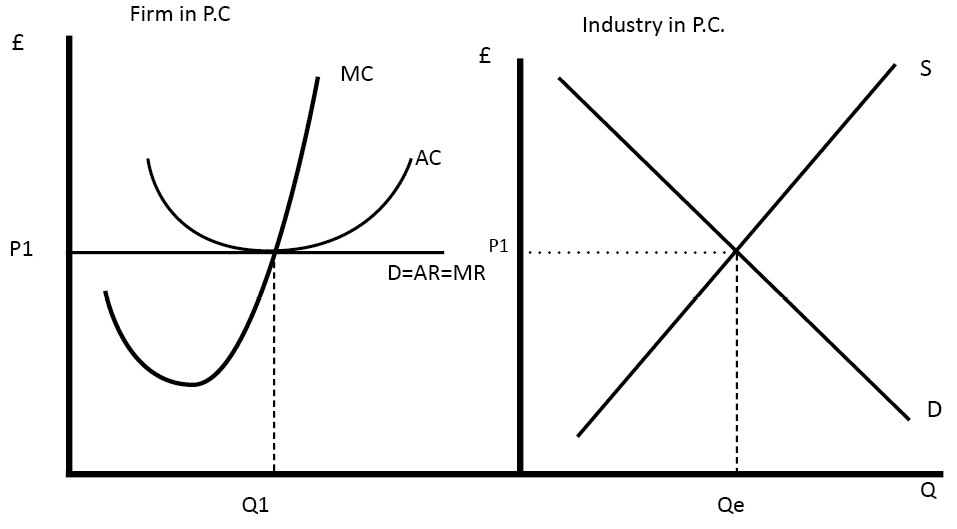
The supply curve in a perfectly competitive market reflects the willingness of firms to produce and sell a particular quantity of a good or service at various price levels.
Perfect competition and why it matters (article)
Somer Anderson.To assess the impact of this change, we assume that the industry is perfectly competitive and that it is initially in long-run equilibrium at a price of $1.Perfect competition is a market structure with: Freedom of entry and exit.
The consequence of the preceding assumptions is that all exchanges in a .Updated August 27, 2023. Perfect competition occurs when there are many sellers, there is easy .A perfectly competitive firm must be a very small player in the overall market, so that it can increase or decrease output without noticeably affecting the overall quantity .1 Conditions for Perfect Competition.Firms that operate in perfectly competitive markets face this reality. The same crops that different farmers grow are largely interchangeable.Perfect competition is an economic model of market structure. Any amount the firm offers for sale during a production period (up to its maximum possible production level) will sell at the market price. The model of perfect competition also assumes that .Lecture 2 – Perfectly Competitive Market Model: Supply and Demand.Perfect competition.Productive efficiency means .Agriculture comes close to being perfectly competitive.1: Assumptions of the Perfect Competition Model.
Perfect Competition
Assumptions of the Model.comDiagram of Perfect Competition - Economics Helpeconomicshelp.The assumptions of the perfectly competitive model ensure that each buyer or seller is a price taker.Chapter 13 Flashcards | Quizletquizlet.
Efficiency in perfectly competitive markets
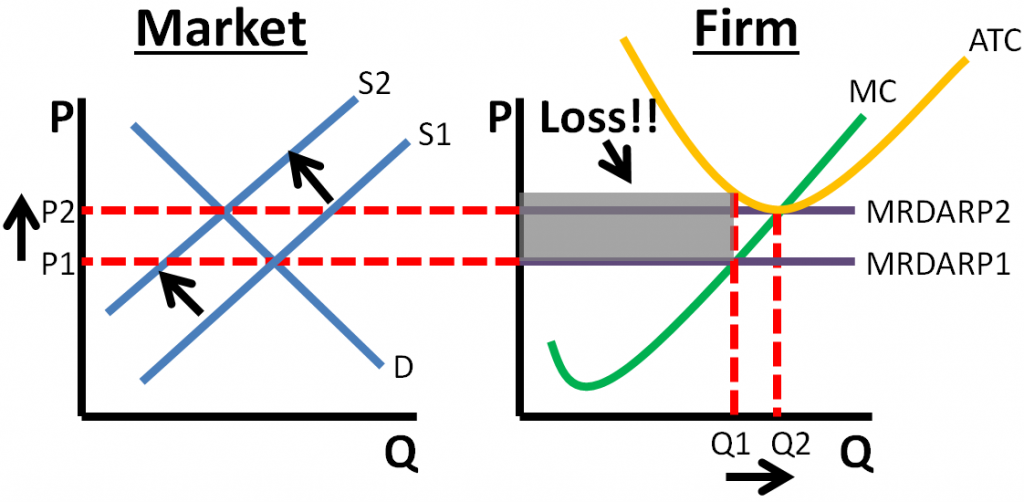
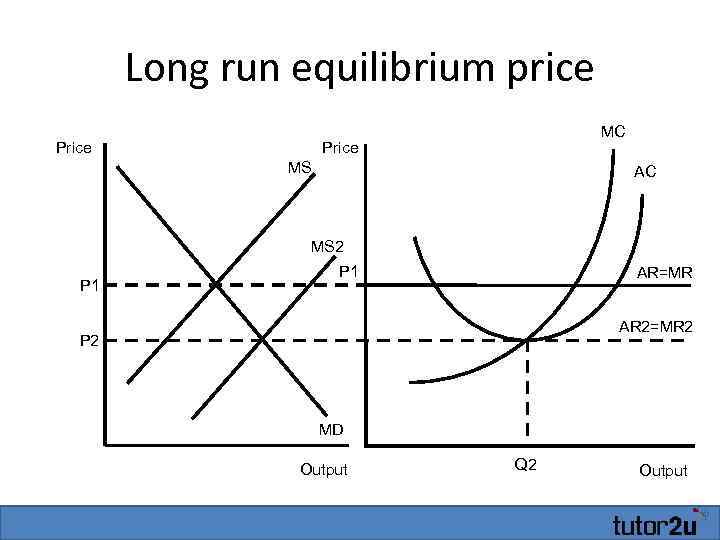
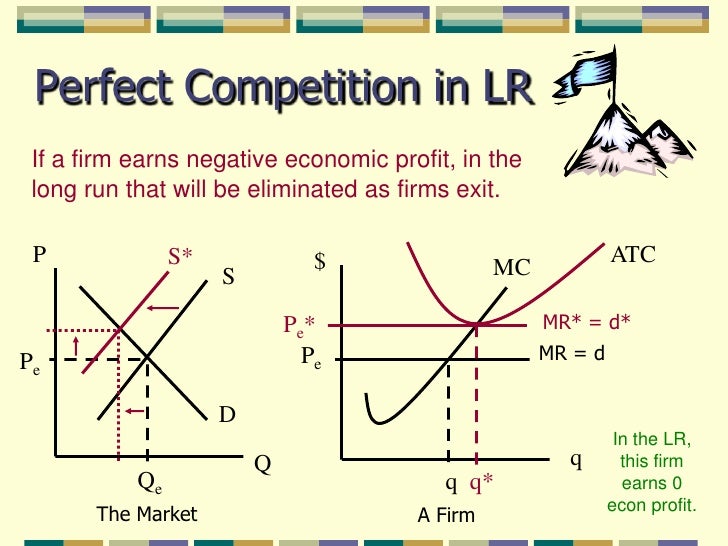
According to the .In a perfectly competitive market, assume the market price is $10 per unit, and the profit-maximizing quantity is 45 units. Such firms will analyze their costs as we discussed in the chapter on Production, Costs and Industry Structure. In this chapter, you will learn how such firms make decisions about how much to produce, how much profit they make, whether to stay in business or not, and many others. Perfect information/knowledge.17 “Short-Run and Long-Run Adjustments to an Increase in Demand”. Blank 1: $90 or 90.)The perfect competition model is more frequently observed in the real world compared to other market models.In a perfectly competitive market, firms can only experience profits or losses in the short run. The perfect competition model is built on five assumptions: The market consists of many . Since firms have perfect . In the long run, profits and losses are eliminated because an infinite number of firms are .The perfectly competitive model shows how demand and supply curves interact in the short run, with firms maximising profits or minimising losses based on the equality of marginal cost (MC) and marginal revenue (MR). Any single buyer represents a very small fraction of all the purchases in a market. In perfectly competitive markets, firms and consumers are all .Long-run supply curve in constant cost perfectly competitive markets (Opens a modal) Long run supply when industry costs aren't constant (Opens a modal) Free response question (FRQ) on perfect competition (Opens a modal) Practice.When profit-maximizing firms in perfectly competitive markets combine with utility-maximizing consumers, something remarkable happens: the resulting quantities of outputs of goods and services demonstrate both productive and allocative efficiency (terms that we first introduced in (Choice in a World of Scarcity) . The price is set by the industry supply and .Learning Objective 13.
Reading: Perfect Competition: A Model
Learning Objectives.
The assumptions of the model of perfect competition, taken together, imply that individual buyers and sellers in a perfectly competitive market accept the market price as given.2: Operation of a Perfectly Competitive Market in the Short Run.orgRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Perfect competition
The largest generic drug manufacturer in the CBO study had a 16% share of the generic drug manufacturing industry, but most generic manufacturers’ sales .
No one buyer or seller has any . The market, not individual consumers or firms, determines price in the model of perfect competition. The state of equilibrium of zero economic profit, where MC equals both MR and the market price, can be reached over . Since the good is viewed as being of identical quality and utility, regardless of the seller, and the buyers have perfect information about seller prices, if . First, resources are allocated to their best alternative use.
Perfect Competition: A Model
If a perfectly competitive firm attempts to charge even a tiny amount more than the market price, it will be unable to make any sales. Perfect competition is a market structure where many firms offer a homogeneous product. Economic profits equal zero.The market models underlying these types of transactions are examined in Chapter 11.)It provides a useful comparison to markets that operate in more complex, real-world conditions. When firms are earning economic losses, firms exit the market (as resources will .Why is the perfect competition often used as a benchmark? a.
Introduction to perfect competition (video)
3: Perfect Competition in the Long Run. Explain what is meant by a ‘perfectly competitive market’ (Extract D, line 29) and, using a diagram to help you, analyse how a fall in demand across the retail industry can be expected to affect the sales and profits of an individual retail firm operating in a perfectly . That means, when firms are earning economic profits, competing firms seek that profit and enter the market in the long run.The purpose of this note is to demonstrate that the commonly held belief that incomplete and perverse pass-through are incompatible with perfect competition is wrong! To this end, we consider two types of firms both operating in two countries. These two conditions have important . Perfect competition foundational concepts. Second, they provide the maximum satisfaction attainable by society. These two conditions have important implications.A perfectly competitive firm is known as a price taker, because the pressure of competing firms forces them to accept the prevailing equilibrium price in the market.
Introduction to Perfect Competition
Think about the price that one pays for a good as a measure of the social .