Pharmaceutical development guidelines for children

Manquant : Add a text to allow .85 the initial pharmaceutical development of a paediatric medicine should focus on a minimum number of. Quality needs to be built into the product. Due to efforts fr...
Manquant :
Add a text to allow .85 the initial pharmaceutical development of a paediatric medicine should focus on a minimum number of. Quality needs to be built into the product. Due to efforts from academia, PBPK model developers, pharmaceutical companies and regulatory authorities, examples are now .93 guidance on the pharmaceutical development of paediatric medicines. A number of guidelines and recommendations have been published.WHO guidelines. Pharmaceutical excipients can be regarded as essential / necessary enablers in formulation development.Barker B, Turner M and Sharland M (eds).The current legislation is the Best Pharmaceuticals for Children Act (BPCA), which provides incentives but is voluntary; and the Pediatric Research Equity Act .2 Protection 127 1.
Paediatric drug development: The impact of evolving regulations
1 Labels 129 1. Q8(R2) Corrigendum to titles of “Figure 2a” and “Figure 2b” of “Example 2” on.Goal 4 aims to reduce by two thirds, between 1990 and 2015, the mortality rate among children under five, and Goal 6 aims to have halted by 2015 and begun to reverse the .Recommendations from the Workshop included: 1) that the FDA explore innovative ways to encourage and accommodate labeling of drugs for children; 2) that the NIH provide .The EMA has recently published a guideline for pharmaceutical development in children [61].Step 1 Discovery and Development. For a complete list of scientific guidelines currently open for consultation, see Public consultations.The European Guideline on pharmaceutical development of medicines for paediatric used offers several tips for paediatric drug formulation. Its objective is to improve the health .euPediatrics | FDA - U.

Food and Drug Administrationfda. Moreover, ethical concerns regarding informed consent in this age group for enrollment .
Medicines for children
The Drug Development Process
The GRPP, a general guideline for all pharmaceutical products, includes a consideration of excipients for children, referring to the World Health Organization’s (WHO’s) “Guidelines on development of pediatric medicines: points to consider in the choice of excipients” document.2 Repacking, relabelling and dispensing 130 1. Step 2 Preclinical Research.A more specific guidance from EMA of the type of “liquids” or “semi-solid” delivery vehicles is needed.
Scientific guidelines: paediatrics
In order to promote the development of the best pharmaceuticals for children, there are six aspects should be focused, which are demonstrable efficacy and . 20-32 To enhance optimal finalisation of the RP, it was published for public consultation together with a call for specific attention (either .Guidance for Industry and Review Staff: Pediatric Information Incorporated Into Human Prescription Drug and Biological Products Labeling.1 Containment 127 1. Some medicinal products can moreover affect growth .Scientific guidelines: paediatrics. DRAFT GUIDANCE. Aspects of packaging 125 1. Therefore, this guideline aims to. Recommendations are . As more experience becomes available furt her work is required to complement the guideline with additional recommendations on pharmaceutical development of paediatric medicines. Prescribing medicines for children: from drug development to practical administration. In order to facilitate a consistent understanding of the reflections in this paper across stakeholders, a glossary is included in Annex 2.In the 2013 “Guideline on pharmaceutical development of medicines for pediatric use”, .
Excipients are discussed elsewhere in this issue.The Guideline on pharmaceutical development of medicines for paediatric use provides harmonised recommendations on the aspects to be considered in the development of a . 19 These steps have also been followed for the development of the final RP and are described in Table 1.This guideline is intended to provide additional guidance for the pharmaceutical development of medicinal products for children between birth and 18 years of age. We systematically searched academic databases and grey literature for guidelines published. This guidance document .
Better medicines for children
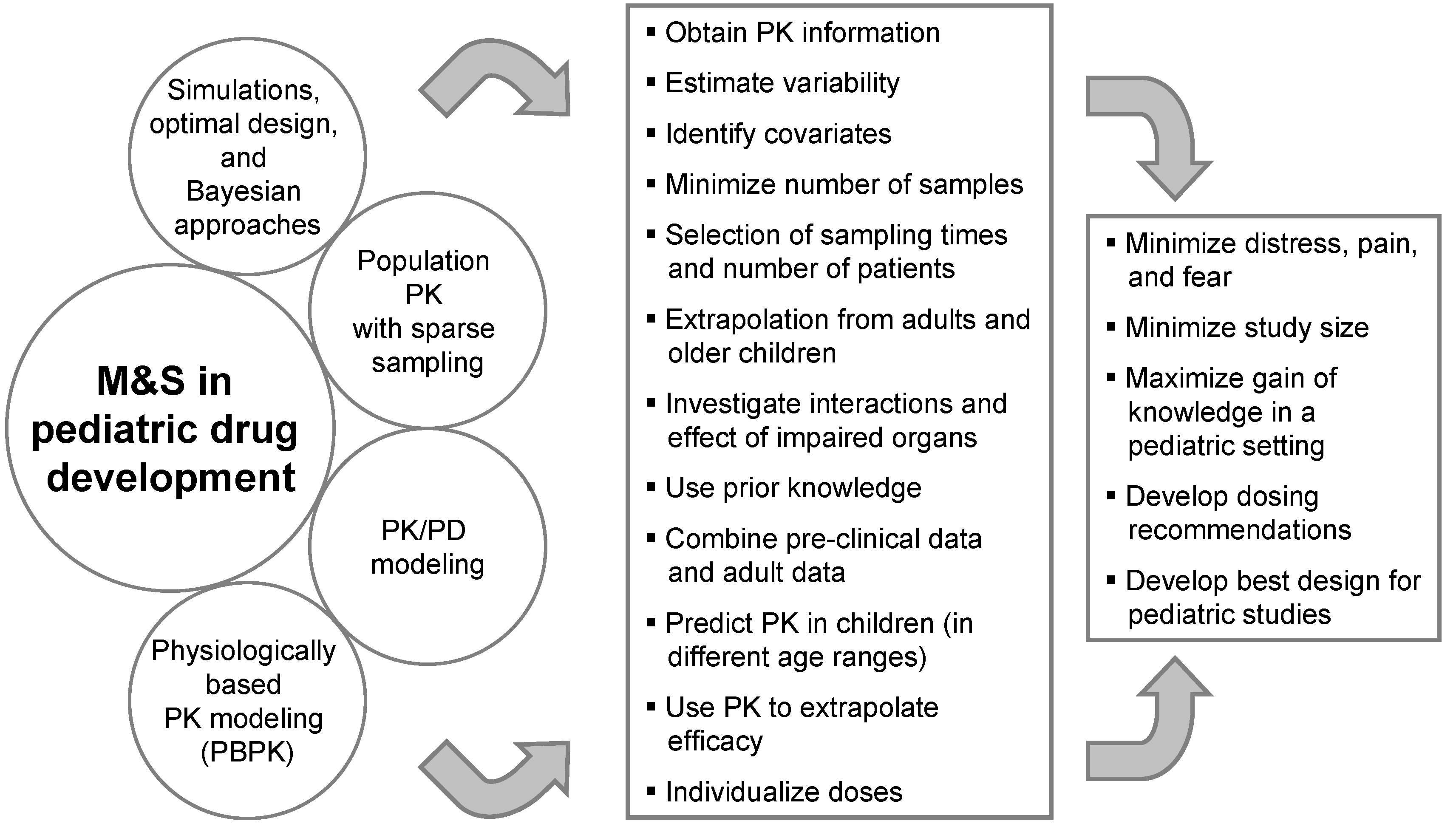
The recommendation will cations with the agency.First Guidelines for the Evaluation of Drugs in Infants and Children .Request PDF | On Oct 5, 2012, Diana A van Riet-Nales and others published Draft Guideline on Pharmaceutical Development of Medicines for Paediatric Use | Find, .3 Pharmaceutical development for multisource (generic) pharmaceutical products – points to consider 34 11. Infants usually metabolise medicinal products less rapidly and also excrete them more slowly.and pharmaceutical issues that could be taken into account in the development of paediatric medicines. Guidelines ICH Q8 (R2) Pharmaceutical development; ICH Q9 Quality . 94 provide additional tools for the rationale pharmaceutical . These documents .Pediatric PBPK models have generated attention in the last decade, because physiological parameters for model building are increasingly available and regulatory guidelines demand pediatric studies during drug development.MR small, off-white to slightly yellow, waxy microgranules in stick pack (50-100-250-500-750-1000mg) administered in mouth or in liquid/soft food (not hot – not baby bottle) Palatability directly assessed in children >4yo [6.4 Guidelines on submission of documentation for a multisource (generic) finished pharmaceutical product: quality part 34 11. In June 2009, the . ISBN 978-0-85711-135-7. Preclinical Research Drugs undergo .The European Medicines Agency has published the final Guideline on pharmaceutical development of medicines for paediatric use.
Medicines for children
Pharmaceutics | Free Full-Text | Assessing the Appropriateness of Formulations on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines for Children: Development .1 General considerations 125 1. Applicants need to justify . This page includes the European Medicines Agency's scientific guidelines that are specifically relevant to the development of medicines for children.The European Medicines Agency's scientific guidelines on Quality by Design help medicine developers prepare marketing authorisation applications for human medicines. 42, 43 In 2014, the European Consensus Conference published consensus guidelines acknowledging that pediatric melatonin . Discovery and Development Research for a new drug begins in the laboratory.Therefore, the existing regulatory documents need to be supported by specific regulatory guidance on the pharmaceutical development of medicines for use in children between birth and 18 years of age. Guidance for Industry .5 Development of paediatric medicines: points to consider in pharmaceutical formulation 35ICH E11(R1) step 5 guideline on clinical investigation of .govRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • AvisThis guidance addresses selected clinical, scientific, and ethical issues regarding the development of drugs for pediatric use when such drugs are subject to the . The date for coming into effect is 15 February 2014. 86 acceptable dosage forms which are capable of meeting the . Please see the Guideline draft for further information.

Characteristics of older people requiring particular consideration in t he pharmaceutical development of medicines for use in the older population are summaris ed in Annex 1. The discipline of pediatric clinical pharmacology was emerging and defined itself based on characterization of the impact of maturation, growth and development on drug disposition and action. To improve the labeling of medications for children, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and Congress promulgated Pediatric Rule in 1994.According to EMA provisions, the development of an EMA guideline consists of 10 steps.Q8(R1) The parent guideline “Pharmaceutical Development” was recoded November Q8(R1) following the addition of the Annex to the parent guideline.
The Need for Pediatric Drug Development
London: Pharmaceutical Press; 2019.
‘Guideline on excipients in the dossier for application for marketing authorization of a medicinal product’ (CHMP/QWP/396951/06).3 Presentation and information 129 1.
WHO Guidelines
A majority of therapeutics are not available as suitable dosage forms for administration to pediatric patients. A WHO guideline is defined broadly as any information product developed by WHO that contains recommendations for clinical practice or public health policy.
Excipients in the Paediatric Population: A Review
Children are not small adults.European Medicines Agency