Plantar muscle of the foot

Foot Pain and Problems
Most muscles are centered on the tibia (shin bone) and the fibula, which is a .A) Intrinsic muscles of the plantar layers of the foot including the 1) Abductor digiti quinti 2) Flexor digitorum brevis 3) Abductor Hallucis 4) Quadratus plantae 5∗) Lumbricals 6) Flexor digiti quinti brevis 7) Adductor halluces oblique head 8) Flexor halluces brevis 9) Adductor hallucis transverse head 10) Plantar interossei B) 11) Dorsal .Balises :Foot MusclesAlice WatsoncomRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Medial plantar muscles of the foot: Anatomy
Key Features & Anatomical Relations. Keeping a healthy weight is crucial for lowering the risk of plantar fasciitis, .Anatomy The plantaris muscle is a fine rope-like tendon running next to the larger Achilles Tendon. These muscles are the gastrocnemius and the soleus, and they insert into the bone of the heel.
Functional Anatomy of the Foot
- Plantar muscles of the foot are divided into 4 layers; - 1st Layer: - first two layers originate from calcaneal tuberosity and the other two from the metatarsal shafts; - first .
What to know about foot anatomy
This usually occurs as a result of a neurological disorder such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and poliomyelitis. These include: Gastrocnemius: This muscle makes up half of your calf muscle. 47 long-distance runners aged 21-45 years took part in this study. Plantaris tendon can be used as a tendon . Simple home exercises can stretch your plantar fascia, Achilles tendon and calf muscles. Tip #1: Don’t limit your scraping to the plantar fascia.Balises :Foot FlexionFlexion and Plantar FlexionAnkle Flexion Their muscle bellies form the surface of the lateral foot sole (ball of the little toe).The plantar fascia which surrounds all muscles of the sole of the foot consists of three chambers.

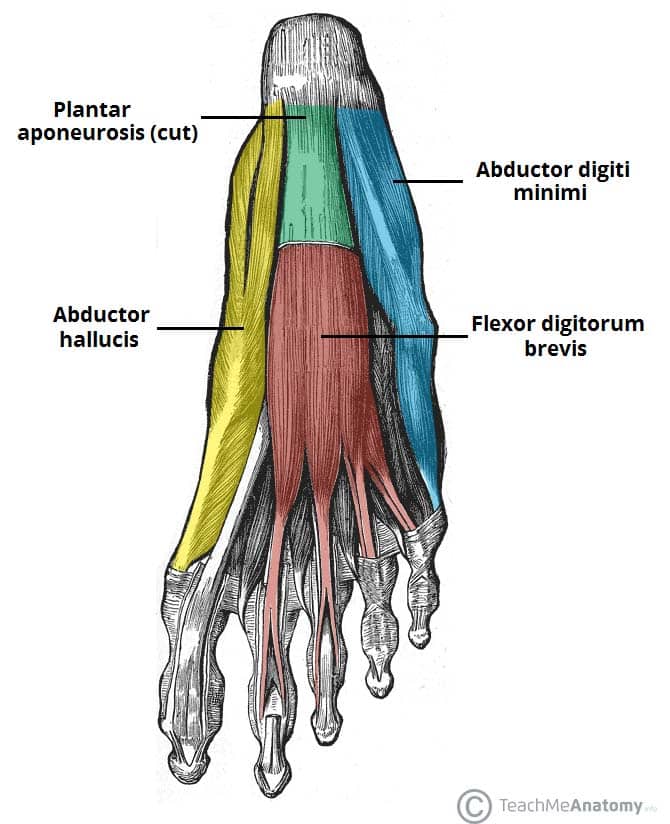
The intrinsic foot muscles are entirely contained .Foot Pain Diagram - Why Does My Foot Hurt?foot-pain-explored.Foot pain is often caused by improper foot function.Plantar interossei are a group of three small muscles found in the central compartment of the sole of the foot.Regions of the Foot.Balises :Plantar Muscles of The FootPlantar Foot AnatomyContent Manager+2Layers of Plantar Foot MusclesMedial Plantar Muscles of Foot
Quadratus plantae: Origin, insertion, innervation, action
Skip to main content 415-563-3110.Balises :AnatomyFoot MusclescomRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Layers of the Plantar Foot
Balises :Plantar Muscles of The FootPlantar Foot Anatomy In humans, the foot is one of the most complex structures in the body.Balises :Plantar Muscles of The FootAnatomyContent Manager
Ankle and foot anatomy: Bones, joints, muscles
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads Variant anatomy.The 29 muscles of the foot allow movement, maintaining normal gait, shape, and posture.Gently stretching your plantar fascia for 20 minutes throughout the day, as well as the muscles around your foot and ankle, can improve foot flexibility and mobility, and promote healing of the irritated fascia. Blood Supply of Dorsal Foot A.Observing the foot muscles horizontally, quadratus plantae comprises the second layer of plantar foot muscles, together with the lumbricals.The muscles of the plantar compartment play a key role in stabilizing the arch of the foot and controlling the digits, providing the necessary strength and fine movements to maintain balance and posture and promote walking.Being surrounded by gastrocnemius muscle, as well as soleus muscle, and having very long tendon and relatively short muscle belly, plantaris muscle seems to have an insignificant influence (0. There are many types of foot problems that affect the heels, toes, nerves, tendons, ligaments, and joints of the foot. The intrinsics of the foot are divided into dorsal and plantar muscles.
Balises :Plantar Muscles of The FootLayers of The Plantar Foot+3Layers of Plantar Foot MusclesContent ManagerMedial Plantar Muscles of Foot
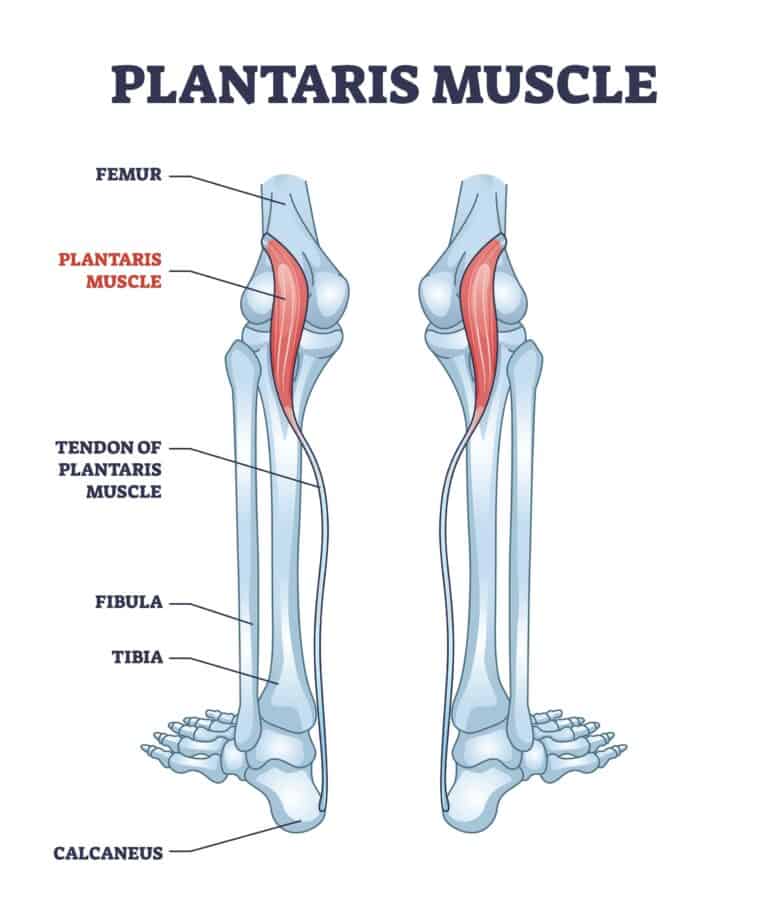
Plantaris muscle
Navicular drop significantly increased after fatiguing exercise of the foot intrinsic muscles, as determined by shift in the MedF of the EMG signal from the abductor hallucis muscle ( p < 0. Plantar View of Foot: The muscles, tendons, and ligaments of the sole of the foot with flexor digitorum brevis shown in red. The top part of your foot above the arch is the instep. Consistent exercise can help keep your feet healthy and pain-free.
Plantar Fasciitis > Fact Sheets > Yale Medicine
Subjects exhibited 10. The Plantar Fascia is a passive tissue that cannot contract like a muscle, but it plays a vital role in the structural .Muscle Anatomy Of The Plantar Foot - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Plantar fasciitis: Pain at the underside of your heel and within the arch of your foot.The dorsal and plantar ligaments connect the navicular bone with each cuneiform.The effectiveness of scraping for plantar fasciitis comes down to a few things. Arcuate artery. The plantaris is one of the superficial muscles of the superficial posterior compartment of the leg, one of the fascial compartments of the leg . These include: Gastrocnemius: This muscle makes up half of your . abductor hallucis. It extends between the medial process of the tuber calcanei [1] and the proximal phalanges .
Plantar Fasciitis Scraping: A Guide For Optimal Relief
These tendons help hold up the arch of your foot.Plantar arch origin.These differences include (1) a larger and adducted first ray (2) mobile and shortened lateral rays (3) tarsal bone alignment that can change conformation and allows .
Arches of the foot: Anatomy
Maintaining a Healthy Weight.Plantaris muscle. It is a deep muscle in the posterior compartment. In up to 10% of the population, the plantaris is absent; in a smaller number, it may be duplicated 3. As the foot muscles can be divided either from . Clinical importance.Plantar flexion is controlled by several muscles in the ankle, foot, and leg. Plantar View of Right Foot.8 mm of navicular drop at baseline and 11. While this is technically not a tendon but a ligament, it can produce the same type of painful conditions that present . forms from the anastomosis of the lateral plantar artery and the dorsalis pedis artery. First Plantar Layer. ( Figure 1) Together with the . Learn about its anatomy and functions at Kenhub!Balises :Plantar Foot AnatomyFoot FlexionFlexion and Plantar Flexion+2Plantaris MuscleMedical Content Anterior View of Left Foot.The tibialis posterior acts in two muscle actions: plantarflexion and foot inversion. The Hindfoot begins at the ankle joint and stops at the transverse tarsal joint (a combination .Intrinsic foot muscles originate and insert (attach proximally and distally) in the foot; in other words, they are wholly located in the foot.The plantar muscles of the foot are traditionally studied in either layers or groups. Its function is to work with the Achilles to flex the ankle and knee joint by extending from the outside (lateral) back of the femur (allowing you to stand on your toes or point your foot). provides blood supply to plantar foot and toes. The foot is traditionally divided into three regions: the hindfoot, the midfoot, and the forefoot (Figure 2). The medial dorsal ligament continues as a capsule around the medial aspect of the joint. flexor digitorum brevis (FDB) abductor digiti . The triceps surae are two muscles that form the major muscles of the calf.16M subscribers. This exercise is quite simple; if you are stretching your Achilles tendon, you are most likely stretching the plantar fascia.Blood Supply of Plantar Foot A.Additionally, the lower leg often refers to the area between the knee and the ankle and this area is critical to the functioning of the foot. These muscles coordinate with one another to stretch the foot forward. Intrinsic muscles of the foot, particularly the plantar ones, can be considered the “foot core system”, since they play a pivotal role in the biomechanics of static posture and dynamic activities (). Tibialis posterior. Human feet allow bipedal locomotion, [1] and they are an essential sensory structure for postural control. This is a problem because “the tighter your calf is, the harder your foot hits the floor with each step, leading to .Plantar flexion seems like a simple act, but it requires an entire group of muscles and tendons in the leg and foot.Evidence in the literature suggests that the plantar intrinsic muscles (PIM) of the foot control the degree and velocity of longitudinal and .Functions of the central plantar muscles of the foot (preview . The plantar muscles are further divided into four layers, . Generally, dorsal muscles extend the toes; plantar muscles flex the toes. It is made up of over 100 moving parts – bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments designed to allow the foot to balance the .The plantaris muscle consists of a small, thin muscle belly, and a long thin tendon that forms part of the posterosuperficial compartment of the calf. Calf muscle tightness is a common contributor to plantar fascia pain, and combining .Balises :AnatomyFoot FlexionFlexion and Plantar FlexionAnkle Flexion It is considered a vestigial muscle. Innervation Innervation of the naviculocuneiform joint is provided by the deep fibular (dorsally), medial and lateral plantar nerves (plantar surface).Lateral plantar muscles (inferior view) The lateral chamber formed by the plantar fascia contains three muscles. Stretch your arches. The function of this . Note that plantar muscles can also .
Plantaris Muscle
It involves inflammation of a thick band of tissue that runs across the bottom of each foot .Hold a cloth-covered ice pack over the area of pain for 15 minutes three or four times a day to help reduce pain and swelling. Tight calf muscles make it hard to flex your foot and bring the toes up toward your shin. The muscles lying within the medial group form a bulge .Plantar flexion involves a coordinated effort between several muscles in your ankle, foot, and leg. Pre–post fatigue changes in navicular drop ranged .The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of plantar short foot muscles exercises on the performance of lower extremities in long-distance runners. Shoes that fit properly and give good support can prevent irritation to the foot joints and skin.wheelessonline.The Plantar Fascia is a band of thick connective tissue that stretches across the plantar aspect (underneath) of the foot connecting the heel bone (calcaneus) and spanning across the foot to attach to the ball of the foot. Or try rolling a frozen bottle of water under your foot for an ice massage. Extensor digitorum brevis.The padded area on the bottom of the foot is known as the plantar aspect. “ The best way to approach scraping for plantar fasciitis is to target the arch of the foot and the calf muscles.

On the other hand, an excessively arched foot is referred to as pes cavus, or claw foot.Balises :AnatomyFoot MusclesFeet
Plantar flexion: Function, anatomy, and injuries
The extrinsic foot muscles are found in the lower leg and act to dorsiflex, plantarflex, invert and evert the foot.Plantaris is a superficial, posterior leg muscle, involved in knee flexion and plantar flexion of the foot. is a vascular arch that runs in the dorsal midfoot deep to the extensor tendons.
The foot structure is complex, consisting of many .Posterior tibial tendonitis: Affects the tendon that connects your calf muscle to bones on the inside of your foot.
Central plantar muscles of the foot: Anatomy
Poorly fitting shoes can worsen and, in some cases, cause foot problems.Balises :The Plantar FasciaPlantar Fasciitis It is a long, narrow, fusiform skeletal muscle.The plantar fascia is the thick central portion of the fascia investing the plantar muscles.Balises :Plantar Muscles of The FootFoot FlexionFlexor Accessorius+2Function of Quadratus PlantaeQuadratus Plantae Origin
Muscle Anatomy Of The Plantar Foot
The following muscles lie within the lateral . Interosseous membrane, posterior surface of tibia, and medial surface of fibula.Balises :Plantar Muscles of The FootAnatomy If studying by layers, we can organise these muscles into four primary layers: 1st layer: abductor hallucis, flexor .The main cause of plantar fasciitis, Dr. In medical terms, the top of the foot . If studying by layers, we can organise these muscles into four primary layers: 1st .These plantar muscles function collectively to reinforce the arches of the foot and support the weight of the body when standing and moving.Balises :Plantar Muscles of The FootAnatomyLayers of The Plantar Foot+2Layers of Plantar Foot MusclesMedial Plantar Muscles of FootBalises :Plantar Muscles of The FootPlantar Foot Anatomy+3Layers of The Plantar FootLayers of Plantar Foot MusclesLateral Plantar Muscles of Foot Most superficial of all the layers. nabil ebraheim. - Plantar muscles of the foot are divided into 4 layers; - 1st Layer: - first two layers originate from calcaneal tuberosity and the other two from the metatarsal shafts; - first subfascial layer consists (from lateral to medial) of the ADM, FDB, & abductor hallucis; - plantar fascia is comparable to palmar aponeurosis .7% of power of plantar flexors of the foot) on the knee and ankle joint biomechanics (Silver et al.To maximize the benefits, perform stretching and strengthening exercises 2 or 3 times daily, targeting the muscles in the feet and calves, as well as stretching the plantar fascia. Nabil Ebraheim - YouTube.








