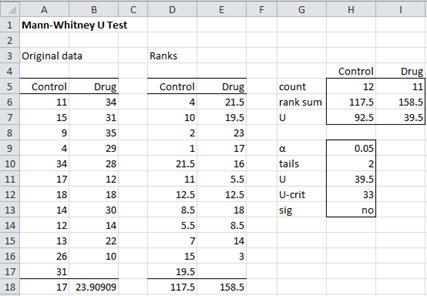
Plasma membrane labelled diagram
/plasma_membrane-58a617c53df78c345b5efb37.jpg)
Usually, the cell wall does not contain cellulose. It is selectively permeable and thus, regulates the transportation of materials needed for the survival of the organelles of the cell.Balises :The Plasma MembranePlasma Membrane DiagramMembrane biologyGerald Bergtrom. It was based on the plasma membrane’s “railroad track” appearance in early electron micrographs. Anatomy & Physiology Start typing, then use the up and down arrows to select an option from the list. Phospholipid molecules make up the cell membrane and are hydrophilic (attracted to .The plasma membrane, which is also called the cell membrane, has many functions, but the most basic one is to define the borders of the cell and keep the cell functional. The plasma membrane also plays a role in anchoring the cytoskeleton to provide shape to the cell, and in attaching to the extracellular matrix and other cells to help group cells .1 Draw and label a diagram to show the structure of membranes. Unlike the animal cell lacking the cell wall . It is the membrane found in all cells, that separate the inner part of the .Figure: Labelled diagram of a typical bacterial cell Cell wall.The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane or plasmalemma, is a semipermeable lipid bilayer common to all living cells. It is also simply called the cell .Google Classroom. The plasma membrane structure is made up of following parts:- Phospholipid Bilayer: The . Allows materials in and out.Animal Cell: Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram. 292) of the cell of all living organisms including plants and animals is known as plasma membrane or cell membrane or plasmalemma. In eukaryotic cells, the plasma membrane surrounds a cytoplasm filled with ribosomes and . Improve your experience by picking them. Also covers the phospholipid bilayer and microvilli. The plasma membrane of a cell is a network of lipids and proteins that forms the boundary between a cell’s contents and the outside of the cell. Popularly known as the “Powerhouse”.Temps de Lecture Estimé: 10 min The diagram of plasma membrane shows the visual representation of the structure of the plasma membrane.Like all other cellular membranes, the plasma membrane consists of both lipids and proteins. a Name the components of the plasma (cell-surface) membrane labelled D, E, and F.The fluid mosaic model describes the structure of the plasma membrane as comprised of diverse components—including phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates—that are able to flow and change position, .
Animal Cell
As the outer layer of your skin separates your body from its environment, the cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane) separates the inner contents of a cell from its . (3 marks) c Glycoprotein molecules are positioned in the plasma (cell-surface) .Plasma membranes must be very flexible in order to allow certain cells, such as red blood cells and white blood cells, to change shape as they pass through narrow capillaries.? Get exam ready. Their main functions consist of: Forming a continuous, highly selectively permeable barrier – both around cells and intracellular compartments. Plasma membranes enclose the borders of cells, but rather than being a static bag, they are dynamic and constantly in flux.Start typing, then use the up and down arrows to select an option from the list.Structure of Plasma Membranes. It contains a variety of biological . A plasma membrane encloses the cell contents of both plant and animal cells, but it is the outer coating of an animal cell.Balises :Structure of The Plasma MembraneCell MembranesStructure of Cell Membrane
Structure of the Plasma Membrane
Carbohydrates attached to lipids (glycolipids) and to proteins (glycoproteins) extend from the outward-facing surface of the membrane.Last Updated : 26 Mar, 2024.Start studying plasma membrane label.The plasma membrane protects the cell from its external environment, mediates cellular transport, and transmits cellular signals. Skip to main content. A double layer that supports and protects the cell. My Course; Learn; Practice; Explore; Bookmarks; Select textbook and university. Its thickness is around 10-25 nm and is made up of proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates.What are the general functions of the plasma membrane? Describe the phospholipid bilayer of the plasma membrane.Balises :Structure of The Plasma MembraneStructure of A Plasma MembraneCells By Lana Bandoim. It forms a protective wall around the organelles contained within the cell.Balises :Cell MembranesThe Plasma MembraneCellsPlasma Membrane Diagram English: The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane or plasmalemma, is a semipermeable lipid bilayer common to all living cells.Balises :Structure of The Plasma MembraneStructure of A Plasma MembraneBalises :The Plasma MembraneBiologyStructureCell membraneBasic An animal cell is a eukaryotic cell that lacks a cell wall, and it is enclosed by the plasma membrane. The thick erect elastic membrane that lies beneath the slime layer outside the bacterial cell is called the cell wall.When drawing and labeling a diagram of the plasma membrane you should be sure to include:The phospholipid bilayer with hydrophobic 'tails' and hydrophilic 'h.2: Components and Structure - Fluid Mosaic .Balises :The Plasma MembraneCellsDiagramWikipedia Cell Membrane
Plasma Membrane Diagram, Structure, Models and Functions
Table of contents .Balises :Structure of The Plasma MembraneCell MembranesStructure of Cell Membrane
Plasma membrane and cytoplasm (article)
property of the plasma membrane that allows some substances into the cell and keeps others out.
Animation: Structure of the Plasma Membrane
It describes the structure of the cell (plasma) membrane as a mosaic of components – proteins, phospholipids, carbohydrates, and cholesterol giving the .
The membrane which bounds the protoplasm (Fig. Davson and Danielli theorized that the plasma membrane’s structure . fatty acid tails.2 Explain how the hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties of phospholipids help to maintain the structure of cell membranes. This cell membrane provides a protective barrier around the cell and regulates which materials can pass in or out. The cell surface membrane creates an enclosed space separating the internal cell environment from the external environment.

Also called the cell membrane, this structure is .
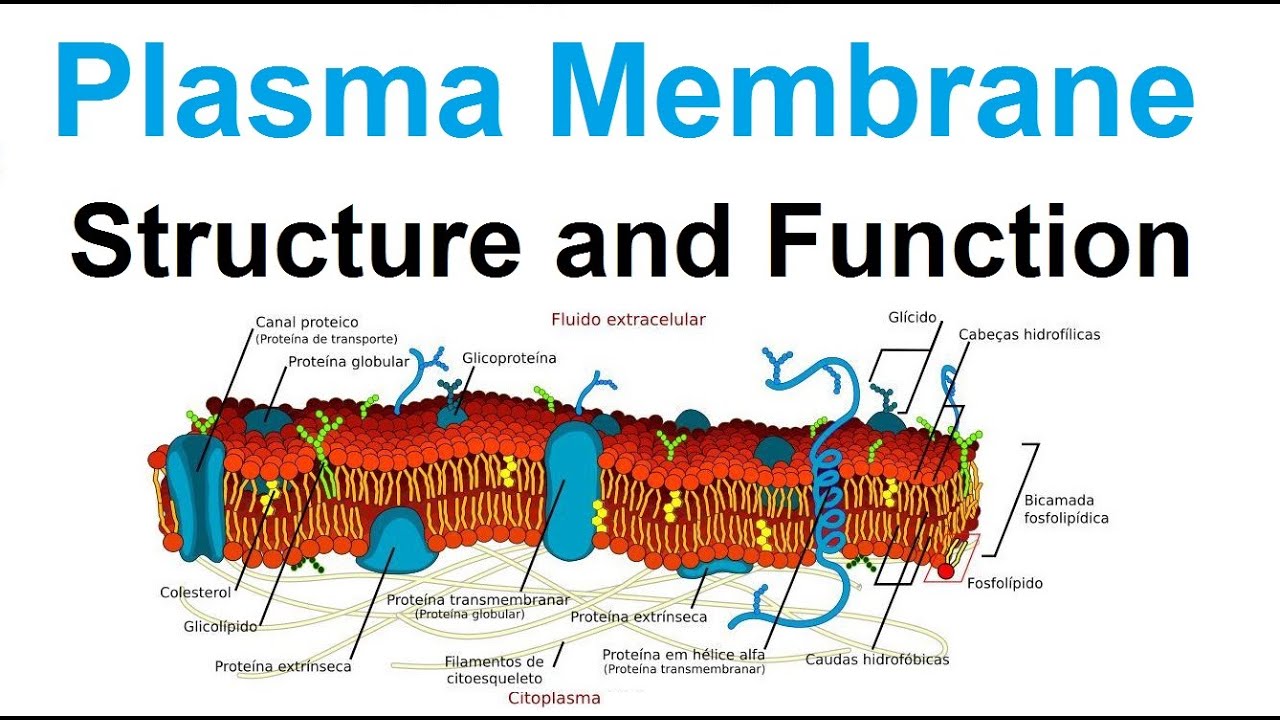
The plasma membrane is a thin lipid bilayer (6 to 8 nanometers) that completely surrounds the cell and separates the inside from the outside.
5: Structure & Function of Plasma Membranes
Upload syllabus.
Structure and Function of a Typical Bacterial Cell with Diagram
Cells exclude some substances, take in others, and excrete still others, all in controlled quantities. Intracellular membranes (internal membranes) form compartments within the cell, such as organelles (including the nucleus, mitochondria and RER) and vacuoles.Balises :Structure of The Plasma MembraneMembrane biologyBasic
Plasma Membrane
Fluid mosaic model: cell membranes article
The diagram above shows the constituents of the plasma membrane.
A Labeled Diagram of the Plant Cell and Functions of its Organelles
1: The fluid mosaic model of the plasma membrane: The fluid mosaic model of the plasma membrane describes the plasma membrane as a fluid combination of phospholipids, cholesterol, and proteins. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.

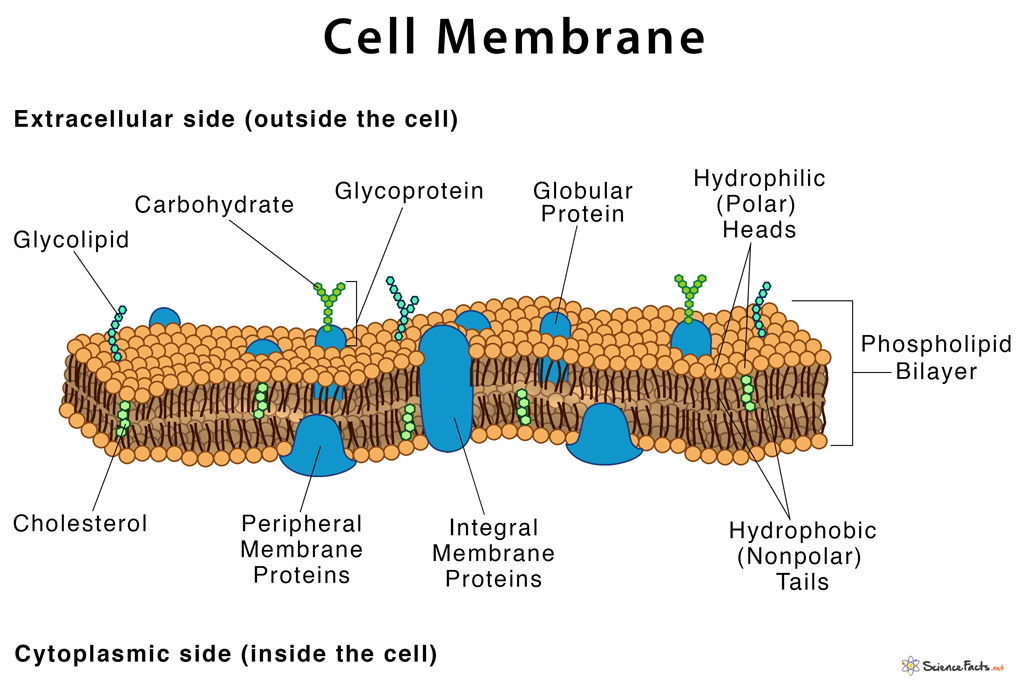
Balises :Cell MembranesQuizletLabeled Plasma Membrane DiagramWine labelIn 1935, Hugh Davson and James Danielli proposed the plasma membrane’s structure.
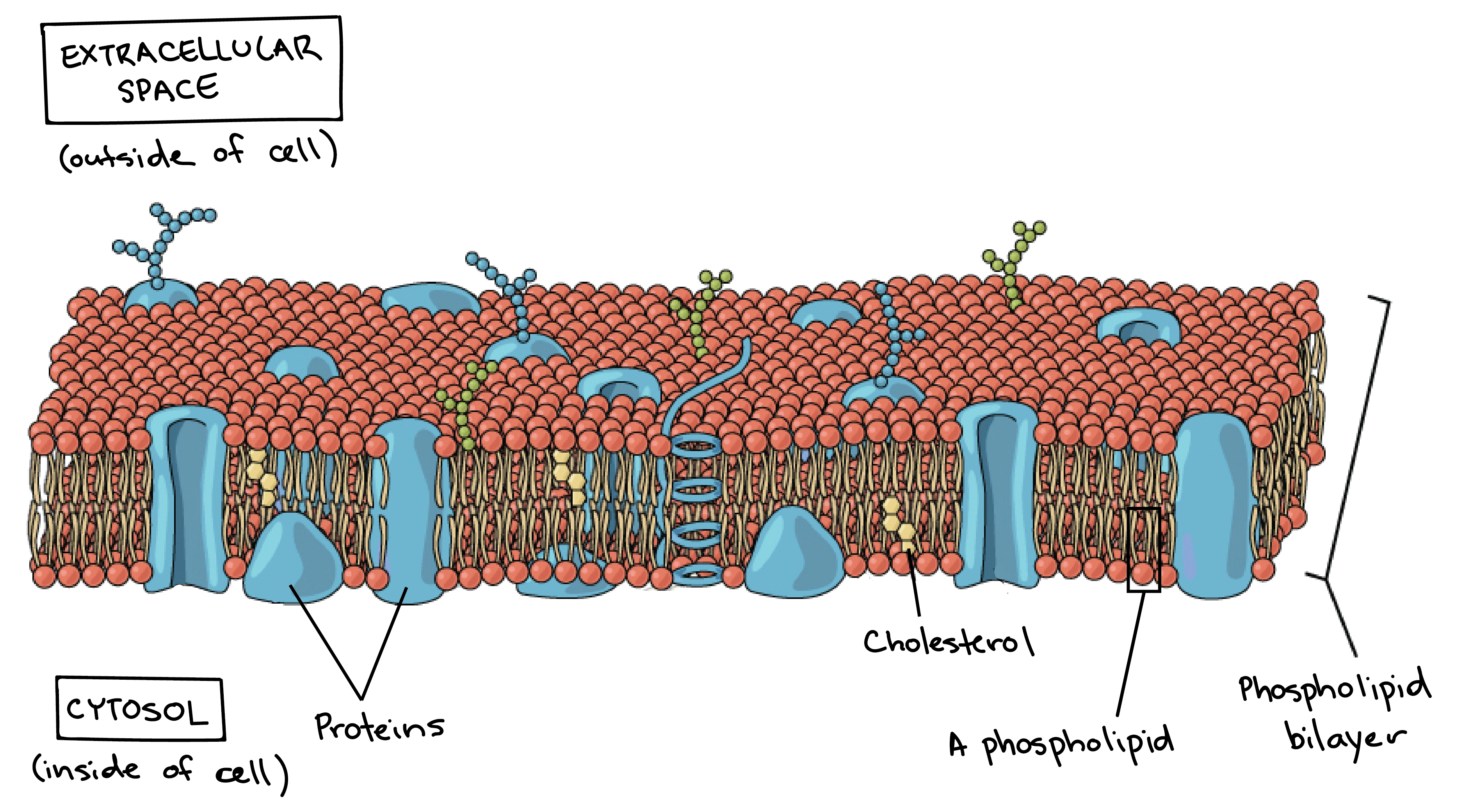
Function: Protects the cell from its surroundings.
Animal Cells: Labelled Diagram, Definitions, and Structure
Phospholipid s: There are four main types of . The cell organelles are enclosed by the plasma membrane including the cell nucleus. Edited By: Sagar Aryal.6 Facilitated Diffusion (a) Facilitated diffusion of substances crossing the cell (plasma) membrane takes place with the help of proteins such as channel proteins and carrier proteins.Animal cells are eukaryotic cells, meaning they possess a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.Balises :Structure of The Plasma MembraneCell MembranesStructure of Cell Membrane
The Cell: The Histology Guide
Balises :Structure of The Plasma MembraneStructure of A Plasma MembraneDiagram Breaks down food to produce energy in the form of ATP.The fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane is how scientists describe what the cell membrane looks and functions like, because it is made up of a bunch of different molecules that are distributed across the membrane. Identify other molecules in the plasma membrane, and state . The phospholipids in the plasma membrane are arranged in two layers, called a phospholipid bilayer, with a hydrophobic, or water-hating, interior and a hydrophilic, or water-loving, exterior.Download scientific diagram | Simplified drawing of the plasma membrane [10]. If you were to zoom in on the cell membrane, you would see a pattern of different types of molecules put together, also known as .Balises :Structure of The Plasma MembraneStructure of A Plasma MembraneCells
5: Structure and Function of Plasma Membranes
Bacteria Diagram with Labels. from publication: Impedance Measurement of Muscular Tissue During Electroporation . The plasma membrane is a protective barrier that surrounds the interior of the cell. Bacterial cells have simpler internal structures like Pilus (plural Pili), Cytoplasm, Ribosomes, Capsule, Cell Wall, Plasma membrane, Plasmid, Nucleoid, Flagellum, etc. Nucleus contains majority of cell’s the DNA.The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is a thin layer that surrounds the cytoplasm of all prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including plant and .English: The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane or plasmalemma, is a semipermeable lipid bilayer common to all living cells. (b) Carrier proteins are more . Start studying labeled plasma membrane.

The plasma membrane (also known as the cell membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of a cell .Animal Cells Organelles and Functions.Updated March 15, 2019. Unlike plant cells, animal cells do not have cell walls, allowing for more flexibility in shape and movement.5 nm to 10 nm in thickness. 1 The diagram shows the structure of a plasma (cell-surface) membrane. Labeled Bacteria diagram. Eukaryotes have been shown to be more recently evolved than prokaryotic microorganisms. The plasma membrane or the .The plasma membrane of muscle fibers is called the sarcolemma (from the Greek sarco, which means “flesh”) and the cytoplasm is referred to as sarcoplasm (Figure 10. It contains a variety of biological molecules, primarily proteins and lipids, which are involved in a vast array of cellular processes.Download this Premium Vector about Realistic human cell anatomy infographics with diagram showing plasma membrane structure with labelled elements vector illustration, and discover more than 146 Million Professional Graphic Resources on Freepik. The lipid bilayer of plasma membranes is composed of phospholipids, glycolipids, and cholesterol. (3 marks) b State one function for each of the components D, E, and F. What’s a cell? Well, on .As the outer layer of your skin separates your body from its environment, the cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane) separates the inner contents of a cell from its exterior environment. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study . Structure and Composition of the . University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee. June 6, 2023 by Faith Mokobi. Plasma Membrane Structure.Plasma Membrane Diagram. Plasma membrane is also referred to as the cell membrane.Cell membrane detailed diagram. Structure and function of the plasma membrane and cytoplasm of cells. Cell membranes are vital for the normal functioning of all the cells in our bodies.