Precordial thump success rate

If asystole followed defibrillation, manual thumps were given to induce ventricular depolarizations until resumption of spontaneous rhythm.348–352 Its routine use is therefore not recommended.The use of extracorporeal CPR (see below) should also be considered to support the circulation whilst a reversible cause it treated. PT terminated VA (polymorphic ventricular tachycardia) in only two patients; in 153 patients (98. What we found Over the one-year case reporting period, delivery of a precordial thump was documented in 18 (2%) adult cases of 881 Sustained induced VA was not tolerated in 155 patients (mean age 64 years (32–82), 133 males and 22 females, 126 patients with coronary artery disease, left ventricular ejection fraction 30 ± 11%).3 Cohort studies and case series definitions. We aimed to summarise in a systematic review the effectiveness of these alternative CPR techniques. Recent resuscitation guidelines have recommended that a PT be reserved for the treatment of monitored and pulseless ventricular arrhythmias . It needs to be delivered within the first few seconds of onset of VT/VF.Although both studies have limitations, the prospective collection of their cohorts enables an estimation of the success rate of the precordial thump. Pulseless ventricular tachycardia: This is when the ECG looks like VT, however there is no heartbeat.
Rate acceleration of ventricular tachycardia after a precordial chest thump.
Precordial Thump: An Emergency Intervention for Cardiac Arrest
Results: During VF, generated .They postulated that the precordial thump, through achieve the previously reported 93% success rate for car- electromechanical transduction, provides a low-energy cur- dioverting ventricular tachycardia.ACLS Success Rate Despite some cardiologists suggesting that the precordial thump is rarely of benefit, the mechanism was once taught as standard in ACLS and CPR Courses.2 Uncontrolled studies when control rates are near zero .

Crossref Medline Google Scholar In these particular cases, precordial thump .

In 82 patients with tolerated VA, overdriving was used successfully.Precordial thump was found to have a 60% success rate in normoxia and 30% in ischemia.The Precordial Thump Jeffrey Miller, MD* / Donald Tresch, MD-r / Louis Horwitz, MD* / Bruce M Thompson, MD* / Charles Aprahamian, MD* Joseph C Darin, MD* / Milwaukee, Wisconsin The American Heart Association (AHA) currently recom- mends the precordial thump as the initial maneuver in treatment of ventricular tachycardia (VT) and monitored .

Overall, precordial thump is more likely to succeed when all excitable gaps are in the RV, as in cases 3,5, and 7.7%; fist-speed 4. delivery of a precordial thump must not delay calling for help or accessing a defibrillator; should be considered appropriate only when several clinicians are present at a . 1984; 53: 964–965.According to Miller (1984), Volkmann (1990) analyzed a group of 47 hospital patients and reported a thumping success rate of 77% for termination of VT at rates of <160 with no .The same article reported a 93% success rate of terminating episodes of VT, with cardioversion of 10 ws or less in 32 episodes.
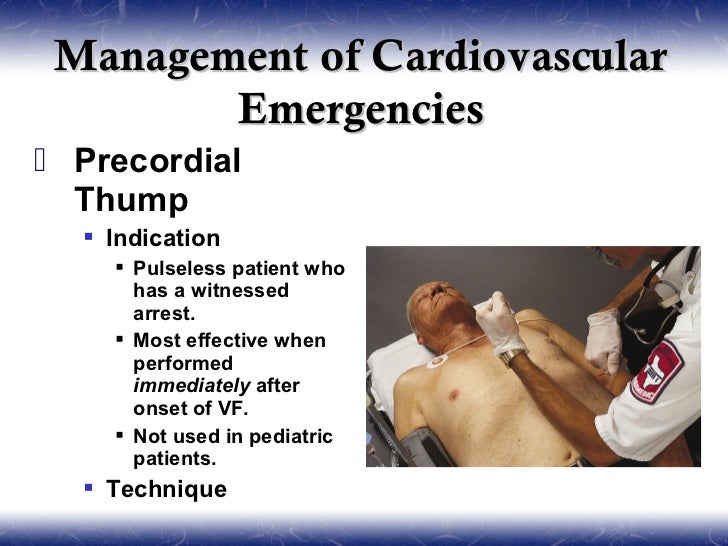
Currently, its use is recommended only for witnessed, monitored, unstable ventricular tachycardia when a defibrillator is not immediately available. Crossref Medline Google Scholar; 111 Sclarovsky S, Kracoff OH, Agmon J.Editor,—There has been growing interest in commotio cordis, defined as a rare type of sudden cardiac death after minor chest wall blows, mainly occurring in apparently healthy young people during sporting activity.The rationale for tracking the overall success rate for systems performing ETI is to make informed decisions as to whether practice should allow for ETI, move toward SGA, or .
Effectiveness of precordial thump in the treatment of
Students learned that the thump must be delivered within one minute of the onset of cardiac arrest symptoms. applied a single . Important: after making the fist, immediately withdraw your hand (do not leave it resting on the patient’s chest): the blow must be “dry”; the fist must be given . (n = 22 each), self-reported success-rates and pre-impact fist-speeds were more similar to US (PT-induced cardioversion rate 27.Precordial thump defibrillation: how to do it? The operator stands at the side of the patient placed on a possibly hard surface and administers the precordial fist on the sternum at heart level.Although its success rate is not very high, the precordial thump, a rapid impact with a clenched fist to a specific place on the sternum, is a measure that may save peoples' lives by reverting .
Part 3: Defibrillation
precordial thump has a very low success rate for cardioversion of a shockable rhythm but the chances of causing harm are very small (Amir 2007; Haman 2009; Pellis 2009; Kohl 2005; Nehme 2013; Dee 2021). The technique is fast and easy to perform, and .The precordial thump, although frequently featured as successful in show business is less effective, and its use is more limited in real life. Nonetheless, the precise blow location on the sternum, the . We did not observe any complication of PT application.Shocks after precordial thump: 1: 0: 0: 1: 1: Discharged alive: Yes: Yes: Yes: Yes: Yes: VF/VT, ventricular fibrillation and pulseless ventricular tachycardia. The aim of treatment of VF is to convert it into asystole.4 In 1979 Morgera . The other, called cough CPR, is a misnomer because coughing is impossible if .Precordial thump involves applying large amount of force rapidly over the heart (almost like a punch!).Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) improves cardiac arrest survival.The precordial thump in resuscitation is commonly considered the inverse of sudden arrhythmic death induced by a blunt chest blow .1-3 However, this event may be more common, but usually misunderstood and underreported, because of misclassification with other . 1981; 80: 596–599.Results: Precordial thump was found to have a 60% success rate in normoxia and 30% in ischemia. Future studies undoubtedly will uncover new stretch-dependent . Indeed, analysis of .The use of precordial thump (PT) – application of a sharp blow to the sternum – has been recommended in cardiopulmonary resuscitation algorithms since the 1970s. the precordial thump has a very low success rate for the cardioversion of shockable rhythm. One, known as percussion pacing, entails less forceful, repeated strikes to the chest.The ERC guidelines of 2005 on the precordial thump report case series with successful cardioversion, particularly of pulseless VT if a precordial thump is . Sustained VA was induced in 237 patients. Time-sensitive .
(PDF) The precordial thump
4 Unfortunately it was rent that depolarizes a reentry pathway.
When giving CPR, stick to standard chest compressions
Overview
Precordial thump: Friend or enemy?
Objective: The goal of this study is, . Results demonstrate that precordial thump-induced SAC-NS opening in normoxia reduced heterogeneity in .Consensus on Science.Precordial thump. No prospective studies have evaluated the use of the precordial (chest) thump.In their case series, PT success rate was as a function of background VT frequency: when VT was ≤160 bpm PT was successful in 77% (17/22) of patients, while .the precordial thump has a very low success rate for the cardioversion of shockable rhythm. 40 – 44 However, 2 larger case series found that the precordial thump was ineffective in 79 (98.7%) of 155 cases of malignant ventricular .
Guideline for resuscitation in cardiac arrest after cardiac surgery
During VF, generated LV pressure (mmHg) was 263 ± 52 with manual thumps, 392 ± 179 with 30-mph ball thumps, and 616 ± 182 with 40-mph ball .Given the inverse relation between probability of positive PT effects and time-to-intervention, PT success may provide a positive indicator of patient resuscitability and overall prognosis (in particular if time-to-intervention is not known), as PT-sensitivity among ROSC cases was linked to a survival rate of ∼67% (2 of 3), compared to ∼21% among .Researchers examined data from 23 studies that looked at the effectiveness of the precordial thump and two other uncommon cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) techniques.Decreased success rate: The success rate of precordial thump in converting VT/VF to a normal rhythm is relatively low compared to defibrillation.5 Concordance with evidence base of prior ILCOR CoSTR . Cough CPR, percussion pacing and precordial thump have been reported as alternative CPR techniques. Open table in a new tab 4.Precordial thump (PT) is the first International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation prescribed procedure of advanced life support in witnessed cardiac arrest. Mean time to termination of arrhythmia (by PT or DC shock) was 26 s (12–280 s). The same article not feasible to randomize our patients into two groups re- reported a 93% .
SESSION 3 Ventricular Fibrillation
4%) defibrillation group and 10 (2.7%), PT was ineffective. Reported success rates vary greatly and, according to experimental and clinical evidence, are significantly reduced under ischemic conditions.A precordial thump, through electromechanical transduction, provides a low energy current that depolarizes a re-entry pathway, the probable basis for most cases of clinical VT.8%) of 80 cases 45 and in 153 (98.Results: Two hundred and nine (42.
Precordial thump
Acceleration of ventricular tachycardia induced by a chest thump.4 The au- thors concluded that the chest thump affords the advantage of immediate availability, that it will do no harm in asystole, and that it might prove lifesaving in cases of ven- tricular tachycardia.The study elucidates the mechanisms of high success (60%) of VF termination during nonischemic conditions and rather low efficacy (30%) during ischemia, namely, mechano-induced activation of I K,ATP may contribute to the failure of precordial thump to terminate VF.RESULTS Precordial thump was found to have a 60% success rate in normoxia and 30% in ischemia.