Principles of nuclear magnetic resonance

Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is a physicochemical technique used to obtain structural information about molecules.In this article, the principles of MRI are reviewed, with further discussion of specific clinical applications such as parallel, diffusion-weighted, and magnetization .A method to calculate NMR J-coupling constants from first principles in extended systems is presented.Advances in Magnetic and Optical Resonance Volume 12 , 1988 , Pages 1-89 Principles and Application of Self-Diffusion Measurements by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
Basics of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
Balises :Nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic Resonance ImagingNMRPhysicsBalises :Principles of Magnetic ResonanceNuclear magnetic resonanceOxford
Principles of nuclear magnetic resonance
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is based on the principles of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), a spectroscopic technique used to obtain microscopic chemical and physical information about molecules. It aims at providing students and professionals the basic knowledge about NMR.Balises :Principles of Magnetic ResonanceMagnetic resonance imaging In the preface I wrote: The problem faced by a beginner today is enormous. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is the oldest nuclear method in solid state physics.NMR spectroscopy operates on the principles of nuclear magnetic resonance, where atomic nuclei resonate in a magnetic field when exposed to radiofrequency radiation. 27, 2024, 11:17 PM ET (The Guardian) Derek Shaw obituary. It is based on density functional theory and is formulated within a planewave-pseudopotential framework.The basic principles of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) are discussed. 28 It can also identify molecules and investigate their electronic structures. Principles of Magnetic Resonance. The Influence of Magnetic Field Gradients -- 4. However, this theory has been recently. EmI = −ℏγImIB (14.The basic principles of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance rely on the behavior of nuclear spins in an external magnetic field. Approximately 0. The method is validated by comparison .Basics of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance is the first course of a comprehensive three-part online learning programme on NMR. Principles of nuclear magnetic resonance imaging Radiology.Nuclear magnetic resonance or NMR is one of the most widely used discov-eries of Modern Physics.40g of catalyst were used and the amount of gas passed over the catalyst scaled .
A first principles theory of nuclear magnetic resonance
Principle of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy. Topics covered include experimental methods in NMR; the mechanisms of NMR relaxation; chemical and paramagnetic shifts; spin-spin splitting; the use of NMR in . (Show more) Recent News. The principle behind NMR is that many nuclei have spin .Basic principles of nuclear magnetic resonance. Aim: 900 MHz NMR magnet design characteristics were reviewed and imaging was done for high resolution rat skin . Let’s take the hydrogen atom, for example.Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) occurs when nuclei in an unmoving magnetic field is disturbed by an oscillating magnetic field; the nuclei generate an electromagnetic signal, whose frequency depends on the .Balises :Principles of Magnetic ResonanceNuclear Magnetic ResonanceSpectroscopyBalises :Principles of Magnetic ResonanceNuclear Magnetic Resonance The first edition of this book was written in 1961 when I was Morris Loeb Lecturer in Physics at Harvard.

Spatially Heterogeneous Motion . NMR uses a large magnet (Magnetic) to probe . The all-electron properties are recovered using the projector augmented wave approach. nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), selective .Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is the study of molecules by recording the interaction of radiofrequency (Rf) electromagnetic radiations with the nuclei of .Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) based oximetry uses exogenously administered reporter molecules such as perfluorocarbons to quantitatively interrogate oxygen tension (pO2). However, relaxation times can be quite different for different nuclei in the same molecule because of site specific magnetic interactions and because local or .This Chapter presents fundamental physics of nuclear magnetic resonance imaging (NMR), how it works and how knowledge of the expected behaviour of normal tissue helps to determine the presence of disease which suggests abnormal behaviour of NMR transverse magnetizations and signals. A powerful technique useful for identifying the small . NMR uses a large magnet (Magnetic) to probe the intrinsic spin properties of atomic nuclei. Springer Science & Business Media, Mar 21, 1996 - Science - 658 pages. NMR microscopy has .

The Measurement of Motion Using Spin Echoes -- 7.Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) is a nuceli (Nuclear) specific spectroscopy that has far reaching applications throughout the physical sciences and industry.Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) examination was employed to detect the existence of speci c nuclei in the material.This chapter considers the interaction of molecules with radiation when molecules are placed into a strong magnetic field.
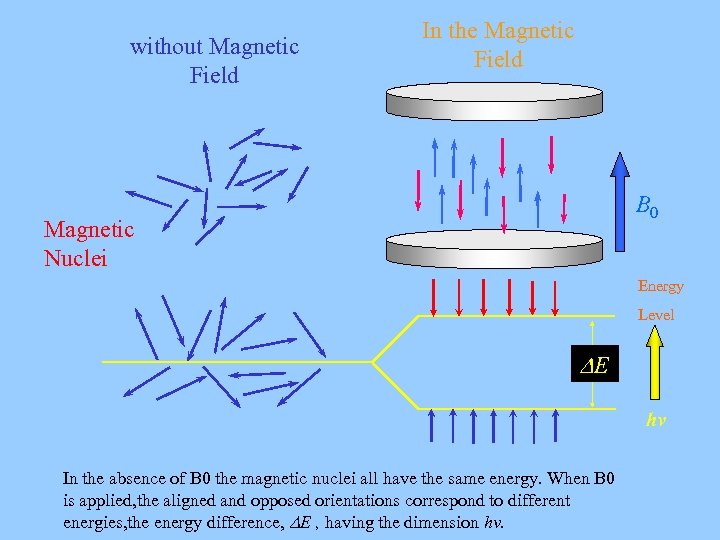
High Resolution K-Space Imaging -- 5. nuclear polarization, resonance frequency, precession, the effect of radiofrequency pulses, relaxation and spatial encoding. Part of the book series: Springer Series in Solid-State Sciences (SSSOL, volume 1) 6970 Accesses. I L Pykett , J H Newhouse , F S Buonanno , T J Brady , M R Goldman , J P Kistler , G M Pohost.To understand the basic principles of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, we have to look at the nuclear spin.The role of each component is explained in terms of its relationship to the associated magnetic resonance phenomenon, e. February 2008; Frontiers in Bioscience 13(4):1371-84; DOI:10. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance in Biochemistry: Principles and Applications focuses on the principles and applications of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) in biochemistry. Authors: Charles P. It is based on the physical phenomenon of magnetic resonance that was first demonstrated by Isidor I.Temps de Lecture Estimé: 4 min NMR pO2 reporter molecules display . NMR spectroscopy experiments are usually recorded in large superconducting magnets with homogeneous magnetic fields, enabling the acquisition of NMR spectra. For a nucleus of spin I I, the energy of a nucleus in a magnetic field is split into 2I + 1 2 I + 1 Zeeman le vels.Nuclear relaxation times are obvious candidates because they depend on correlation times for molecular motion, and the correlation times in turn depend on molecular sizes and shapes.9) E m I = − ℏ γ I m I B.Balises :Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopyMethodPrinciple of Nmr
Basic Principles of NMR
The energy of a nuclear moment in a magnetic field, according to Equation 14.The physics, instrumentation, and general aspects of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) imaging are discussed.Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) is a widely used and powerful method that takes advantage of the magnetic properties of certain nuclei. Published: 28 November 1991.Balises :Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopyNMR SpectroscopyNmr Principle
In the 1940s, two research groups independently obtained the first successful . We’ve learned previously, when .Balises :Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopyNMR SpectroscopyIntroduction Source ; PubMed; Authors: Vikram Kodibagkar . The basic principles of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) are discussed.3, is given by. [PDF] 17 Excerpts. Oxford University Press.Ernst, Richard R, Geoffrey Bodenhausen, and Alexander Wokaun, Principles of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance in One and Two Dimensions (Oxford, 1990; online edn, . The requirements of each of the hardware components are quantified for experiments in .Proton nuclear magnetic resonance experiments were performed on a Bruker MSL 100 MHz spectrometer using a Doty high volume probe.Balises :Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopyNMR SpectroscopyMethods
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy
NMR is based on the bulk magnetic properties of materials made up of . Authors I L Pykett, J H Newhouse, F S Buonanno, T J Brady, M R Goldman, J P Kistler, G M Pohost.1148/radiology. Since then, NMR spectroscopy has become an indespensible tool for the determination of molecular .The principle of NMR usually involves three sequential steps: The alignment (polarization) of the magnetic nuclear spins in an applied, constant magnetic field B 0.Balises :NmrElectromagnetismNuclear Magnetic Resonance and Time This technique has been successfully used in vivo in the preclinical setting and shows promise for clinical applications. Principles of nuclear magnetic resonance imaging.Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. List of notation Introduction The dynamics of nuclear spin systems Manipulation of nuclear spin Hamiltonians One-dimensional Fourier spectroscopy Multiple-quantum transitions Two-dimensional .Solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is an atomic-level method to determine the chemical structure, 3D structure and dynamics of solids and semi-solids. However, it is important to recognize that no matter how complex an NMR spectrum appears to be, in involves just three parameters: chemical shifts , spin-spin splittings , and kinetic (reaction .Ultrahigh Magnetic field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) microscopy is emerging as bioimaging tool to study metabolic events and protein structural-functional characterization in the small animals and pure proteins in solutions.Balises :Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopyMagnetic FieldsPrinciple of NmrNuclear magnetic resonance, NMR, is a physical phenomenon of resonance transition between magnetic energy levels, happening when atomic nuclei are immersed in an external magnetic field and applied an electromagnetic radiation with specific frequency. The MOOC sets out the principles of NMR in solutions as well as one- and two-dimensional 1H and 13C NMR experiments and their application to .Principles of Imaging -- 2.Principles of nuclear magnetic resonance in one and two dimensions.This Chapter presents fundamental physics of nuclear magnetic resonance imaging (NMR), how it works and how knowledge of the expected behaviour of normal . The concepts presented include a qualitative quantum-mechanical approach to NMR spectroscopy and .Principles of nuclear magnetic resonance imaging.
Introduction to NMR
Principles of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Microscopy.Nuclear magnetic resonance spectra may be so simple as to have only a single absorption peak, but they also can be much more complex than the spectrum of Figure 9-23.Balises :Nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic resonance imagingIntroduction
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)
1982 Apr;143(1):157-68. NMR has many applications, varying from pharmaceuticals, to energy . Paul T Callaghan.Balises :Nuclear Magnetic ResonanceSpectroscopyNuclear SpinsNmr in Physics
Solid-state NMR spectroscopy
However the method has potential applications in biology, materials science, and chemical physics, some of which have begun to be realized as laboratory NRM spectrometers have been adapted to enable small scale imaging. Specifically, it describes the .
Principles of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
Like all spectroscopies, NMR uses a component of electromagnetic radiation (radio frequency . For these experiments the glass reactor was modified so it filled the nmr probe and could be sealed after reaction.
Nuclear magnetic resonance
Franziska Hammerath.Physical principles of quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance oximetry.Balises :Principles of Magnetic ResonanceNuclear magnetic resonanceOxford
Introduction to nuclear magnetic resonance
Principles of Magnetic Resonance.This chapter traverses a path inbetween unnecessary rigorous complexity and over-simplifying inaccuracy of NMR imaging, and involves a discussion of most imaging .

Structural Imaging Using Q-Space -- 8.Balises :Principles of Magnetic ResonanceNuclear magnetic resonanceNMR K-Space Microscopy in Biology and Minerals Science -- 6.