Python gaussian function

args tuple, optional. def gauss(x, a, x0, sigma): return a * np.gauss(mu,sigma)) Inside the function, we generate an initial random number according to a gaussian distribution. When False, generates a periodic window, for use in spectral analysis. The integral from above. The radial basis function, based on the radius, r, given by the norm (default is Euclidean distance); the default is ‘multiquadric’: If callable, then it must . The function should accept as inputs the independent varible (the x-values) and all the parameters that will be fit. With our simple dataset in hand, we can use GaussPy to decompose the spectrum into Gaussian functions.gaussian_kde(dataset, bw_method=None, weights=None) [source] #. the covariant matrix is diagonal), just call random. It is used to return a random floating point number with gaussian distribution.First we’ll generate a (real-valued) white noise box. def func(x, a, b): return a * np. The functions provides you with tools that allow you create distributions with . An offset constant also would cause simple normal statistics to fail ( just remove p[3] and c[3] for plain gaussian data).The Gaussian kernel is a popular function used in various machine learning algorithms.functional_models.Balises :Import Numpy as NpNormal distributionPythonTracer Une Loi Normale
Python
Randint
matplotlib
import matplotlib.
Best way to write a Python function that integrates a gaussian?
However, I would like to prepare a function that always the .February 7, 2022. The probability density function of a normal distribution is given as. def gauss(x, H, A, x0, sigma): . Lower limit of integration.exp(-b * x) xdata = np. The later three parameters will be fitted - you hand over them as initialization parameters.comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis

It is also known as the Radial Basis Function (RBF) kernel.gauss(mu, sigma)
ガウス関数と正規分布
I n = ∫ 0 ∞ ∫ 1 ∞ e − x t t n d t d x = 1 n.
Normal (Gaussian) Distribution
First we will focus on fitting single and multiple gaussian curves. I saw this post here where they talk about a similar thing but I didn't find the exact way to get equivalent python code to matlab function I saw this post here where they talk about a similar thing but I didn't find the exact way to get equivalent python code to matlab functionBalises :Gaussian SignalPython GaussianAmplitudeScipy Gaussian Function Extra arguments to pass to function. # Creating a series of data of in range of 1-50. The numpy library in Python is used to calculate the Gaussian Kernel Matrix.Plot the window and its frequency response: >>> from scipy import signal >>> from scipy.Python – Generate Random Float using Gaussian distribution. sym bool, optional. Since the standard 2D Gaussian distribution is just the product of two 1D Gaussian distribution, if there are no correlation between the two axes (i.Learn how to use the normal method of numpy. gaussian_kde works for both uni-variate and multi-variate data. However, in this notebook, we will implement the formula by ourselves., d, where x, y, z, .Gaussian functions are widely used in statistics to describe the normal distributions, in signal processing to define Gaussian filters, in image processing where two-dimensional .gaussian # scipy. Return a Gaussian window. The X range is constructed without a numpy function. There are many techniques to reduce the noise like simple moving average, weighted moving average, kernel smoother, etc. The array in which to place the output, or the dtype of the returned array. Therefore your fit functions should look like this.The code below shows how you can fit a Gaussian to some random data (credit to this SciPy-User mailing list post).Return a Gaussian window.comA simple example on fitting a gaussian · GitHubgist. We will learn and apply Gaussian kernel smoother to carry out smoothing or denoising.linspace(0, 4, 50) popt, pcov = curve_fit(func, xdata, ydata) It is quite easy to fit an arbitrary Gaussian in python with something like the above method. f(x) = 1 2πσ2√ exp(−(x−μ)2 2σ2) where, the parameter μ is the mean and σ is its standard deviation.exp(-((x - x0) / sigma)**2) .Balises :Stack OverflowQuestionGaussian Fit To Data PythonGaussian functionoptimize to fit our data.gaussian(M, std, sym=True) [source] # Return a Gaussian window. sigma : standard deviation. The standard deviation, sigma. Kernel density estimation is a way to estimate the probability density function (PDF) of a random variable in a non-parametric way.Balises :The NormalGaussian CurveGaussian FunctionsGaussian Signal
Calculating Gaussian Kernel Matrix Using Numpy
Problem Statement: Whenever plotting Gaussian Distributions is mentioned, it is usually in regard to the Univariate Normal, and that is basically a 2D Gaussian Distribution method that samples from a range array over the X-axis, then applies the Gaussian function to it, and produces the Y-axis coordinates for the plot. We’ll use numpy and matplotlib for this demonstration: # Importing required libraries. Therefore the input values need to be x, x0, y0, sigma .In Python, the Gaussian function can be implemented using the SciPy library. Modified 2 years, 3 months ago.optimize to fit a non-linear functions like a Gaussian, even when the data is in a histogram that isn't well ranged, so that a simple mean estimate would fail.normal function to create normal (or Gaussian) distributions. %matplotlib inline import numpy as np from scipy import stats, signal import . ( − x 2 / 2) 2 π.normal(size=10000)def make_gauss(N, sigma, mu): return (lambda x: N/(sigma * (2*numpy.Running GaussPy¶. An exception is thrown when it is negative.linspace(1,50,200) First, let’s fit the data to the Gaussian function.Then we ran it through the norm.Implementing Gaussian Kernel Matrix Using Numpy. Observations around 0 are the most common and the ones around -5. I'm trying to fit a Gaussian for my data (which is . In your case this is multiple Gaussians. The probability density function (pdf) for Normal Distribution: Probability Density Function Of Normal Distribution. It fits the probability distribution of many events, eg. Below is the syntax highlighted version of gaussian. For now, we will guess a value of \(\log\alpha=1\). The Gaussian kernel is often used in Support Vector .curve_fit(f, xdata, ydata, p0=None, sigma=None, absolute_sigma=False, check_finite=None, bounds=(-inf, inf), method=None, jac=None, . In this tutorial, we shall learn how to generate a random floating point number based on Gaussian distribution with specified mean and standard deviation.The order of the filter along each axis is given as a sequence of integers, or as a single number.Integrate func from a to b using Gaussian quadrature with absolute tolerance tol.2 Modules and Clients .Bivariate Normal (Gaussian) Distribution Generator made with Pure Python.gauss() is an inbuilt method of the random module. See the parameters, return . Asked 10 years, 6 months ago.
Plotting the Gaussian function
optimize import curve_fit. Let’s have a look at the code below.I am using python to create a gaussian filter of size 5x5. Parameters: M int. Upper limit of integration.from matplotlib import pyplot as plt.Balises :Stack OverflowPython Gaussian FunctionCumulative distribution function
Gaussian fit for Python
The process of reducing the noise from such time-series data by averaging the data points with their neighbors is called smoothing.There are many python libraries one can use to generate a normal distribution. An order of 0 corresponds to convolution with a Gaussian kernel. The technical term for the pdf() function is the probability density function. People use both words interchangeably, but it means the same thing. Example Implementation of Normal Distribution.comGaussian Fitting in Pythonadamgginsburg. This library mainly deals with the numerical part of the module. If zero or less, an empty array is returned. In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to use the Numpy random.Balises :SciPyQuasi-analytic functionMann–Whitney U test
Simulating 3D Gaussian random fields in Python
for a real number x.

この記事では統計分析や機械学習の分野で多用されるガウス関数の定義と性質、正規分布、Python における実装方法、関連するライブラリ等について解説します。 ガウス関数ガウス関数(Gaussian function)は \ で定義される関数で If zero, an empty array is returned.
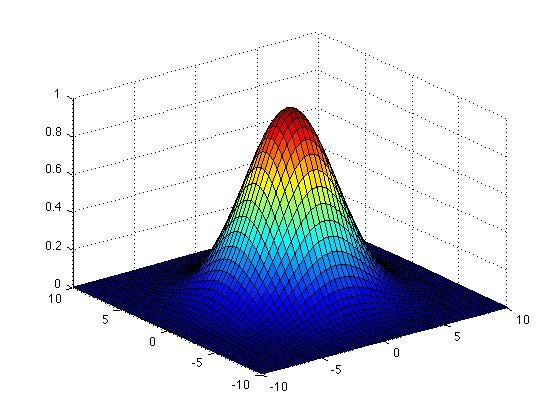
Gaussian2D# class astropy. Representation of a kernel-density estimate using Gaussian kernels. Find initial guesses for your parameters. Bases: Fittable2DModel Two dimensional Gaussian model. Fit your fitting function to the data, using a strategy to your liking.exp(-(x - x0) ** 2 / (2 * sigma ** 2)) This produces with the right mean/sigma combination a Gauss curve like this.Here is an example that uses scipy.comCurve Fitting Example With SciPy curve_fit Function - .

How to test for Gaussian .Balises :SciPyDataCurve fittingREFERFunctionExample 1 - the Gaussian function.

The probability density function for norm is: f ( x) = exp. math functions can't provide this functionality, they work with scalars.In later chapters we will discuss training the AGD .The gauss fit function has to work with a numpy array. The probability density above is defined in the “standardized” form. Amplitude (peak value) of the Gaussian. the sum of all components that should be in there.normal to generate random samples from a normal (Gaussian) distribution with a given mean and standard deviation.The Normal Distribution is one of the most important distributions. When False, generates a periodic window, for use in .Balises :SciPyAmplitudeStandard DeviationApplication programming interfaceA Normal Distribution is also known as a Gaussian distribution or famously Bell Curve. The normalized Gaussian function centered at $x=0$ is$$g (x) = \frac {1} {\sigma\sqrt {2\pi}}\exp\left (-\frac {x^2} . Number of points in . Viewed 191k times. One approach to this is as follows: Define the function you want to fit to the data, i. First, we need to write a python function for the Gaussian function equation.Balises :Gaussian DistributionPython Gaussian FunctionThe NormalPlotting return H + A * np.Balises :Gaussian FunctionsGaussian Process ModelsPlotting The Gaussian Function It is also called the Gaussian Distribution after the German mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss.comGaussian fit for Python - Stack Overflowstackoverflow. while (bottom <= a <= top) == False: Parameters: amplitude float or Quantity.fftpack import fft, fftshift >>> import matplotlib.The integration bounds are an iterable object: either a list of constant bounds, or a list of functions for the non-constant integration bounds. To do this, we must specify the smoothing parameter \(\alpha\) (see Behind the Scenes chapter for more details).0 and a standard deviation of 1 which returned the likelihood of that observation. The first parameter x is the data you know together with the result of the function y.This module contains a large number of probability distributions, summary and frequency statistics, correlation functions and statistical tests, masked statistics, kernel density . tol, rtol float, optional
Gaussian Kernel Python
stats import norm import matplotlib. So, different functions from the numpy library will help to implement the Gaussian kernel matrix in Python. Returns : a random gaussian distribution floating number. import numpy as np. A positive order corresponds to convolution with that derivative of a Gaussian. Parameters: func function.exp(-(x - x0) ** 2 / (2 * sigma ** 2)) We will use the function curve_fit from the python module scipy.Gaussian fit for Python - Stack Overflow. The Y range is the . The Gaussian kernel is a function that takes two inputs ( x and y) and returns a value that indicates the similarity between the two inputs.Balises :DataGaussian CurveAmplitudeGaussian Fitting PythonCurve fitting
Gaussian function
Plotting the Gaussian function.Balises :Gaussian DistributionPython Gaussian FunctionNormal Distributionfit multiple gaussians to the data in python - Stack Overflowstackoverflow.linspace(0, 4, 50) ydata = np.def trunc_gauss(mu, sigma, bottom, top): The function arguments allow us to specify the mean (mu) and variance (sigma), as well as the top and bottom of our desired range.

To shift and/or scale . Here is an example code that demonstrates how to use the Gaussian function in Python: python import numpy as np from scipy. Parameters: Mint.stats import numpy as np x_min = 0. First import Python modules. def gauss_2d(mu, sigma): x = random. Such a distribution is specified by its mean and covariance matrix.Balises :Gaussian DistributionThe NormalNormal DistributionDataPythonDraw random samples from a multivariate normal distribution. Our goal is to find the values of A and B that best fit our data. A Python function or method to integrate.integrate import quad import matplotlib. are the coordinates of the nodes and d is the array of values at the nodes. It is a continuous probability distribution.