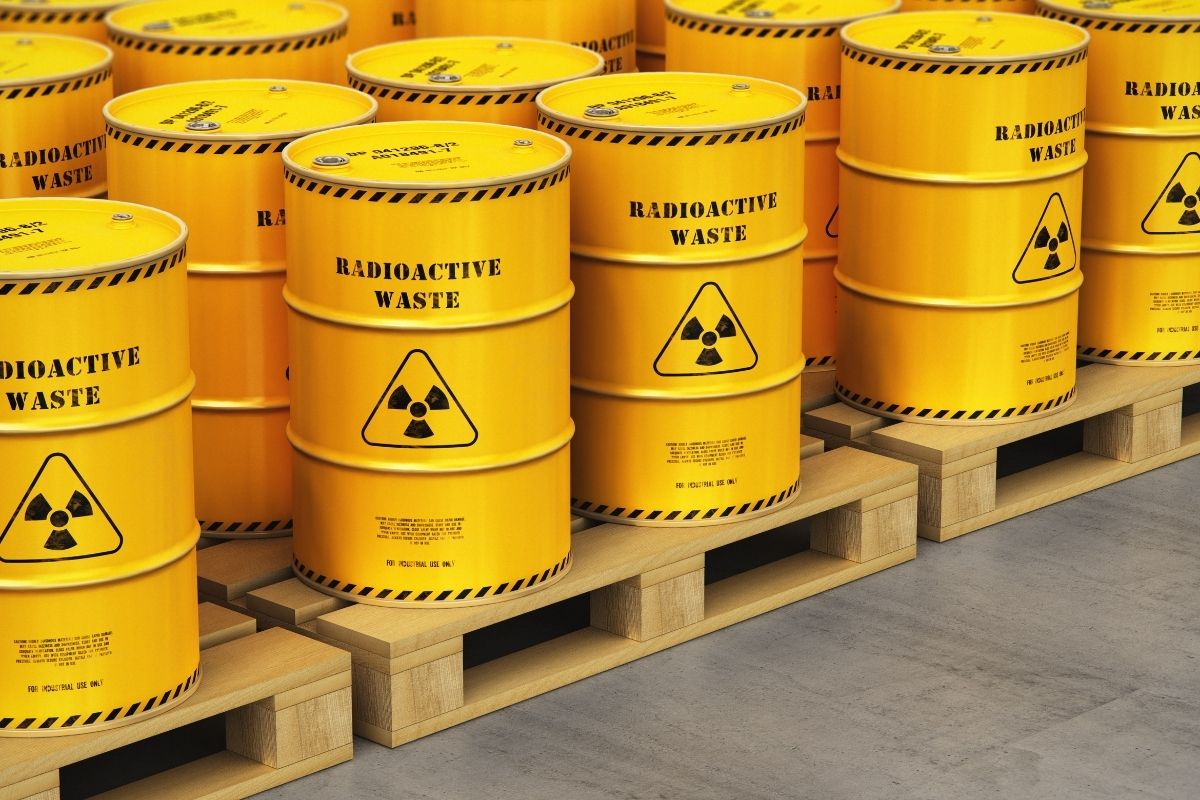
Radioactive waste disposal regulations

F1 [F2 13 Disposal of radioactive waste.
High-Level Waste
monitoring, verifying, checking including in-service Andra is in charge of disposal of radioactive waste, including those originating from dismantling operations (existing repositories and research/studies for .
Additionally, licensees may use 10 CFR 20.A special series of safety documents devoted to radioactive waste man-agement is being prepared within the framework of the IAEA's Radioactive Waste Safety Stand-ards .

Waste materials remaining after spent fuel is reprocessed. On this page: High-Level Waste; Federal Agency Roles; Yucca Mountain; The NRC has regulatory authority over storage and disposal of all commercially generated wastes in the .
Radioactive Substances Act 1993
Information was given for each of 15 countries against a standard template . Safe waste disposal is ensured by implementation of the Atomic Energy Safe Disposal of Radioactive Waste .With regard to regulatory development at the international level, the Safety Requirements WS-R-4 “Geological Disposal of Radioactive Waste” (issued in 2006 and jointly .Regulated Activities. These Rules and Regulations governing the disposal, concentration and storage of radioactive waste material are adopted pursuant to the Georgia Radioactive Control Act, as amended, i.1 Regulation Y FAR).The programmes should cover all types of spent fuel and radioactive waste under EU countries’ jurisdiction and all stages of spent fuel and radioactive waste management from generation to disposal.Radioactive waste is mainly generated from the production of electricity in nuclear power plants or from the non-power-related use of radioactive materials for medical, research, .In addition to containing nuclear substances, radioactive waste may also contain hazardous substances that are not radioactive, as defined in section 1 of the General Nuclear Safety and Control Regulations. The criteria do not apply to uranium and thorium recovery facilities already subject to appendix A to 10 CFR part 40 . 61, and 63), the criteria apply only to ancillary surface facilities that support radioactive waste disposal activities. If waste is shipped to . Radioactive waste is a devolved issue.101 Organization and Purpose 1/1. Most states have entered into compacts; however, only one .Radioactive waste can originate from research, the health sector and nuclear power and decommissioning.US Ecology is a disposal facility that is licensed by the state of Washington to receive commercial low-level radioactive waste. Safety aspects in mining and milling of prescribed substances are governed by the Mines Minerals Prescribed Substance Rules, 1984. Every 3 years since August 2015, EU countries submit national reports on the implementation of the directive to the Commission.
Radioactive Waste
1 Radioactive waste management: The general principles of radioactive waste management have been set initially by the December 30th 1991 Waste Act (called as .
Recognising that Scotland’s nuclear reactors generate radioactive waste, we aim to achieve a high level . The US Ecology site is a waste landfill that has been in operation since 1965.

The radioactivity of the wastes decays . They also plan how to manage waste before .At The European Level
Regulations (NRC, 10 CFR)
The Act encouraged the states to enter into compacts that would allow them to dispose of waste at a common disposal facility. For general information, see the How We Regulate page.
Regulatory and Guidance Information by Topic: Waste
Radioactive waste management and decommissioning in France
NRC Regulations .In France there are three major operators concerned with decommissioning activities: EDF, AREVA and CEA.The Environment Agency has an important part to play in regulating to protect the environment and supporting community involvement. • The limits on disposals given in Schedule 3 shall not be exceeded. It also regulates nuclear power plants and high-level radioactive waste storage and disposal.
Principles of radioactive waste management
Current regulations of CalRecycle and the State Water . If Class A waste also meets the stability requirements set forth in § 61. The Department of Transportation’s Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration regulates the transport of hazardous materials.Part 5Nondiscrimination on the basis of sex in .
Legislation and Regulation for control of Radioactive Waste
Under section 2 of the Nuclear Safety and Control Act (NSCA), radioactive waste in Canada is .

Check with your local waste .Various methodologies have been adopted within the framework of rules and regulation of government agencies for the disposal and management of radioactive . Located in the center of the Hanford site, the facility operates on 100 acres of land leased to the state by the federal government. High-level wastes take one of two forms: Spent ( used) reactor fuel when it is accepted for disposal. Hence, waste storage is by definition an interim measure and the term interim storage should not be used.PARTTITLEPart 1Statement of organization and general . February 22 2024, by Rosanna Xia, Los Angeles Times.Part 2Agency Rules of Practice and ProcedurePart 4Nondiscrimination in Federally assisted . ( ii) Class B waste is waste that must meet more rigorous requirements on waste form to .radioactive waste management in NEA member countries, with emphasis on waste disposal. The Hazardous Waste Program, under RCRA Subtitle C, establishes a system for controlling hazardous waste from the time it is generated until its ultimate disposal.
What We Regulate
1 ensures radioactive waste management and decommissioning activities, including transportation and disposal, are carried out in a comprehensive and integrated manner that prioritizes the health, safety and security of people and the environment, and ensures nuclear non-proliferation;
The Regulatory Function and Radioactive Waste Management
Learn more about Environmental Radiation Protection Standards for Management and Disposal of Spent Fuel, High Level and Transuranic .
Backgrounder on Radioactive Waste
Radioactive waste & spent fuel
It must be managed safely and in a way that avoids placing an undue burden on future generations.Storage (Radioactive Waste) The placement of radioactive waste in an appropriate facility with the intention of retrieving it at some future time.
How do we manage radioactive waste?
It's not just toxic chemicals: Radioactive waste was also dumped off Los Angeles coast, scientists conclude. Surveillance All planned activities, viz.There shall be no disposals of radioactive waste except of the types of radioactive waste and by the disposal routes specified in Schedule 3.High-level radioactive wastes are the highly radioactive materials produced as a byproduct of the reactions that occur inside nuclear reactors. For details, see the following: Low-Level Waste Disposal. (1)A licensee must provide for interim storage of radioactive waste prior to its clearance, discharge or disposal. Geological disposal is government policy for the long-term management of the UK’s most hazardous radioactive wastes. Export or import of radioactive waste for disposal is allowed only under strict conditions and requires an international agreement.Disposal of aqueous radioactive waste to sewer - patient excreta and compounds of uranium and thorium _____ 76 Disposal of low concentration aqueous radioactive waste to sewer, river or sea ___ 78 Disposal of gaseous radioactive waste _____ 82 Compliance with exemption conditions – universal provisions _____ 84 Technical . The Region III office near Chicago, Illinois, can be contacted at 800-522-3025.
Radiation Protection and Waste Disposal Regulations, 2011
1 NRC Licensing.(Updated January 2023) Radioactive wastes are stored so as to avoid any chance of radiation exposure to people, or any pollution.1 Overview of national policy The Korean government has strived to secure a disposal site for the safe management of . This means permanently placing radioactive waste in a specially designed .
Nuclear sites: environmental regulation
(1) Subject to section 15, no person shall, except in accordance with an authorisation granted in that behalf under this subsection, dispose of any radioactive waste on or from any premises which are used for the purposes of any .We have a duty through the Environmental Permitting Regulations (EPR) 2016 to make sure radiological protection is optimised in our regulation of activities that generate radioactive waste. (1982) The Nuclear Waste Policy Act (NWPA) supports the use of deep geologic repositories for the safe storage and/or disposal of radioactive waste.What We Regulate.NRC regulations (10 CFR Part 61) establish procedures, criteria, terms and conditions for licensing low-level waste disposal sites.

Most radioactive wastes are managed in the following way: Planning and preparation: Wherever possible, sites aim to reduce the amount of waste they produce. The producers of radioactive waste are responsible for its safe management, including permanent disposal.Navigate by entering citations or phrases (eg: 1 CFR 1.


For more information on how LLRW disposal facilities are regulated, see Low-Level Waste Disposal.
Wastes Banned From the Trash
The Low-level Radioactive Waste Policy Amendments Act of 1985 gave the states responsibility for the disposal of their low-level radioactive waste. The Act establishes procedures to evaluate and select sites for geologic repositories and for the interaction of state and federal governments.







