Reactions of carboxylic acids chemguide
William Reusch.The LibreTexts libraries are Powered by NICE CXone Expert and are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis...
William Reusch.The LibreTexts libraries are Powered by NICE CXone Expert and are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot.
Alcohols Menu
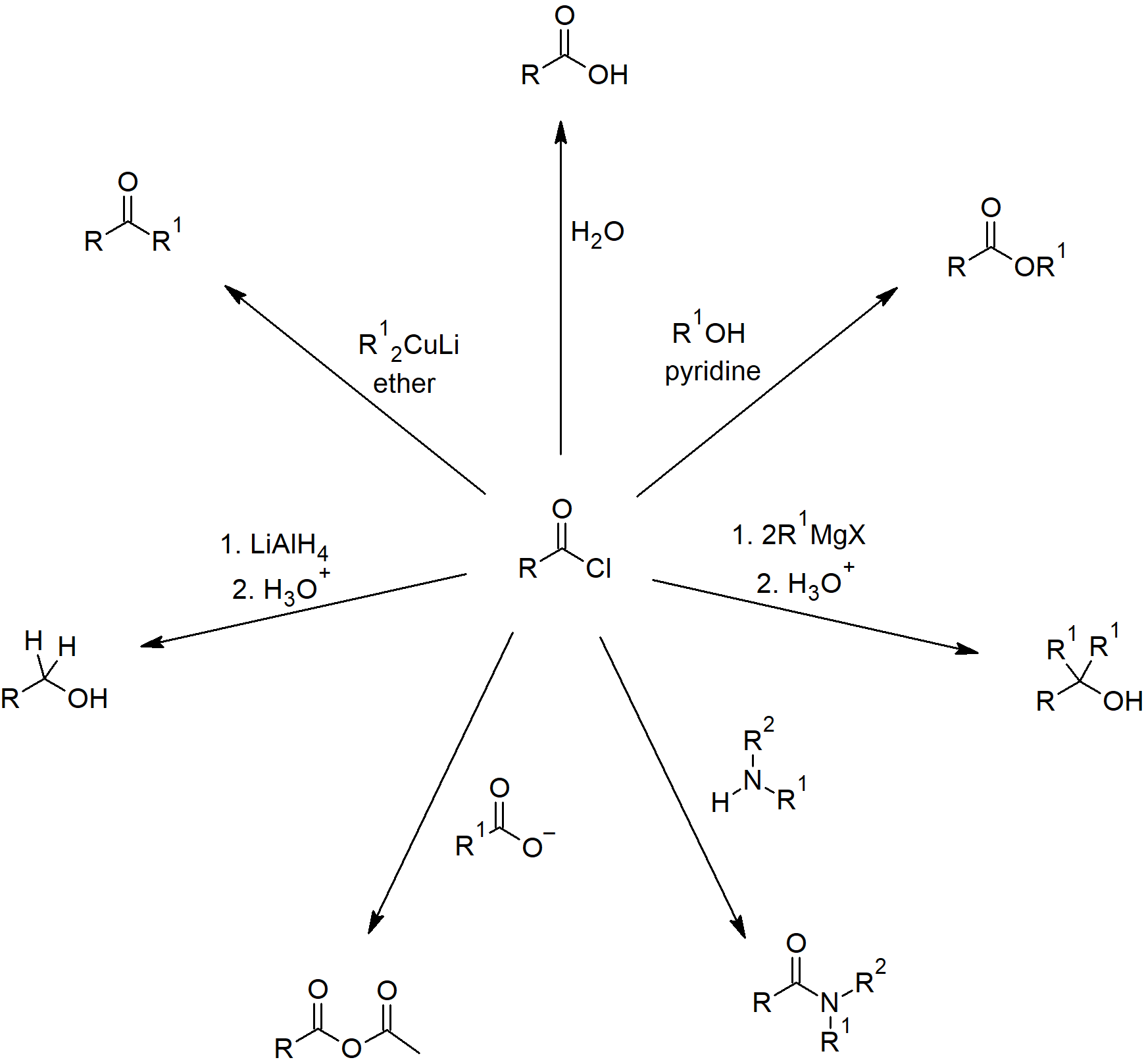
Simple reactions of carboxylic acids as acids . We prepare carboxylic acids by the oxidation of aldehydes or . The carboxylic acid is first converted into an ammonium salt which then produces an amide on heating. Sydenham and H. The video uses the symbol 1M for the concentrations of the two acids. Revision notes in exam days is one of the best tips recommended by teachers during exam days. Reduction to a 1º-alcohol takes place rapidly on treatment with the powerful metal hydride reagent, lithium aluminum hydride, as . Of the three major kinds of alcohol reactions, which are summarized in Figure 14.Making esters from alcohols . It also considers their simple physical properties such as solubility and boiling points., 2021, 23, 6405 DOI: 10.Carboxylic acids are weak acids (see the chapter on acids and bases), meaning they are not 100% ionized in water.1: Prelude to Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. The revision notes help you revise the whole chapter 12 in minutes.3: Reactions of Carboxylic Acids - Ester and Amide Formation. It leaves a liquid mixture of the acyl chloride and a phosphorus compound, phosphorus trichloride oxide (phosphorus oxychloride) - POCl 3. Carboxylic acids belong to a class of organic compounds in which a carbon (C) atom is bonded to an oxygen (O) atom by a double bond and to a hydroxyl .The sulphur dichloride oxide reacts with carboxylic acids to produce an acyl chloride, and sulphur dioxide and hydrogen chloride gases are given off. The organic acids are weak in the sense that this ionisation is very incomplete. 2) Removal of Cl leaving group. During the reaction the hydroxyl group of the carboxylic acid is converted to a . This shows in their .This page describes the preparation of amides from carboxylic acids, acyl chlorides (acid chlorides) and acid anhydrides. The triiodomethane (iodoform) reaction .Learning outcome 33: Carboxylic acids and derivatives. All of these particular cases contain a very electronegative element with an active lone pair of electrons - either oxygen or nitrogen.2(c): Reactions as acids.You will probably remember that you can make esters from alcohols by reacting them with carboxylic acids. This statement is about the oxidation of methanoic and ethanedioic . Step 2: Nucleophilic attack by the carboxylate.William Reusch.Carboxylic Acid - Definition, Structure, Properties with Uses .Reactions of carboxylic acids.5: Polyamides and Polyesters. 5) Deprotonation.2: Acidity of Carboxylic Acids.ukCarboxylic Acid: Examples & Uses – StudiousGuystudiousguy. The reactions (of both acyl chlorides and acid anhydrides) involve things like water, alcohols and phenols, or ammonia and amines.The reduction of a carboxylic acid. In common names of aldehydes, carbon atoms near the carboxyl group are often designated by Greek letters.A carboxylic acid first adds to the DCC molecule to form a good leaving group, which can then be displaced by an amine during nucleophilic substitution to form the corresponding amide.
The most common . 1, two—dehydration and oxidation—are considered here. The use of this reaction to detect the presence of the CH 3 CH (OH) group .Reaction type: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution. When carboxylic acids react with alcohols an ester is formed; Esters are compounds with an -COOR functional group and are characterised by their sweet and fruity smells; They are prepared from the condensation reaction between a carboxylic acid and alcohol with concentrated H 2 SO 4 as catalyst. Michigan State University. Download Revision Notes as PDF. Almost all of the basic types of reactions now have been covered: addition, elimination, substitution, and rearrangement by polar, radical, and concerted mechanisms. Obviously, if you have got an ester like the one in .
comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
making carboxylic acids
Reactions of Carboxylic Acids. The direct conversion of a carboxylic acid to an amide is difficult because amines are basic and tend to convert carboxylic acids to their highly unreactive carboxylates. Note: You can find .4: Hydrolysis of Esters and Amides. Reactions with metals, sodium hydroxide, carbonates and hydrogencarbonates, ammonia and amines. In principle, all carboxylic acids derivatives can be made from the parent carboxylic acid see above. (2) Nucleophilic acyl substitution reactions allow substitution of the hydroxyl group which .A solvent-reagent selection guide for Steglich-type esterification of carboxylic acids A.1: Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives- Properties and Names. Organic Chemistry II.
an introduction to acid anhydrides
Carboxylic acids can undergo reduction reactions. For instance, acetic acid (the one that you find in table vinegar) has pKa=4. The carboxyl functional group that characterizes the carboxylic acids is unusual in that it is composed of two functional groups: (1) the carboxyl group and (2) of a hydroxyl group bonded to a carbonyl group. 4) Leaving group removal. These statements are about reactions of carboxylic acids as acids. It is often written in condensed form as –CO 2 H or –COOH. 1) Nucleophilic attack on Thionyl Chloride.Hydrogen ions are always attached to something during chemical reactions.Chemical reactions in alcohols occur mainly at the functional group, but some involve hydrogen atoms attached to the OH -bearing carbon atom or to an adjacent carbon atom.
carboxylic acids
Acid Chlorides react with carboxylic acids to form anhydrides. Carboxylic acids react with Thionyl Chloride ( SOCl2 S O C l 2) to .So ethanoic acid solution (and solutions of the other carboxylic acids) contain hydrogen ions, but not as many as hydrochloric acid of the same concentration.1039/D1GC02251B This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3. Steven Farmer ( Sonoma State University) Conversion of carboxylic acids to acid chlorides is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4. In the bit of video below, it shows how you can make nylon-6,10 as a simple demonstration in the lab. If you count them, there are now 10 carbon atoms in the acyl . The video shows a simple comparison between the two acids with magnesium ribbon and with solid sodium carbonate.Simple reactions. Note: If you aren't sure about esters, you would probably do better to skip the next bit and instead read the page about making esters (which includes esters made from .Carboxylic acids are considered relatively weak acids with typical pKa values between 4 and 6. Hydrogen atom in the -OH of carboxylic acid positively charged and has the acidic property.comCarboxylic acid | Structure, Properties, Formula, Uses, & Factsbritannica. Generally only about 1% of the molecules of a carboxylic acid dissolved in water are ionized at any given time. OH - provided from NaOH is like to attack that acidic H +. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2000 , 122 (11) , 2621-2627.Conversion of Carboxylic acids to amide using DCC as an activating agent.Acyl chlorides are far more reactive than carboxylic acids.comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
an introduction to carboxylic acids
Carboxylic acids are reduced to alcohols with LiAlH 4.
17: Carboxylic Acids and their Derivatives
Examples of aldehydes.0 Unported Licence.1: Carboxylic acids.
preparation of acyl chlorides (acid chlorides)
Primary alcohols and aldehydes are normally oxidised to carboxylic acids . This is also called . So, your typical strong acid is over ten million times more acidic than a typical carboxylic acid.
Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Class 12 Notes Chemistry
These compounds can be synthesized from carboxylic acids using a reaction called Fischer esterification. For example: The . Dilute ethanoic acid reacts in the same way as acids like hydrochloric acid - just slower. For example:
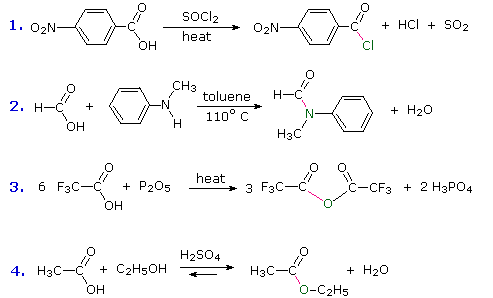
Conversion of carboxylic acids to acid chlorides
Making esters . The materials used are: ClOCCH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 COCl. They are simple in the sense that they don't have other reactive groups like -OH or -Cl attached directly to the carbon atom in the carbonyl group - as you might find, for example, in carboxylic acids containing -COOH.
Cheat Sheet: Aldehydes and Ketones Free Study Guide
Making a chain with ester links. For example, ethanoic acid (CH 3 COOH) can be formed by the oxidation of .CDI performance was moderate for reactions 1, 3, 4 but was very poor in reaction 2, a trend which was similarly observed in the authors’ earlier work employing thiol substrates with carboxylic acids. There is an internal transfer of a hydrogen ion from the -COOH group to the -NH 2 group to leave an ion with both a negative charge and a positive charge.
REDUCTION OF CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
Phosphorus(V) chloride is a solid which reacts with carboxylic acids in the cold to give steamy acidic fumes of hydrogen chloride. Some comments: Don't worry about the relative strengths of these . Learning outcome 33. For example, ethanoic acid (CH 3 COOH) can be . Details of the chemical reactions . It would be a carboxylic acid. Carboxylic acids undergo reactions to produce derivatives of the acid. Carboxylic acids react with Thionyl Chloride to form acid chlorides. The carbon atom of a carboxyl group is in a relatively high oxidation state. The ammonium salt is formed by adding solid ammonium carbonate to an excess of the acid. The acyl chloride can be separated by fractional distillation.Reactions of Carboxylic Acids. You will find everything . Mainly the reaction between alcohols and carboxylic acids to produce esters, together at a brief look at making esters from the reactions between alcohols and acyl chlorides or acid anhydrides.
Carboxylic acids Reactions of carboxylic acids
Aldehydes and ketones are simple compounds which contain a carbonyl group - a carbon-oxygen double bond. Because of their enhanced acidity, carboxylic acids react with bases to form . Reduction is the opposite of oxidation.Making carboxylic acids by oxidising primary alcohols or aldehydes.This page explains what carboxylic acids are, and looks at the ions that they form in their salts.
We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under . If you haven't done any chemistry calculations yet .This reaction occurs by a nucleophilic acyl substitution pathway in which the carboxylic acid is first converted into an acyl chlorosulfite intermediate, thereby replacing the –OH .
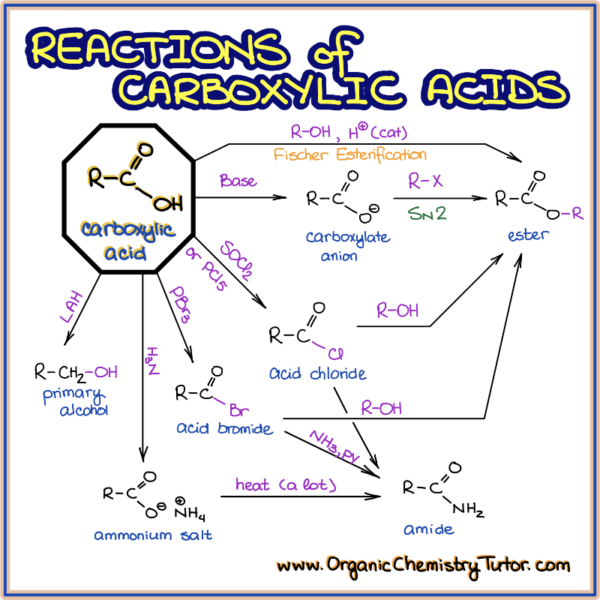
At any one time, most of the acid will be present in the .6: Phosphoric Acid Derivatives.
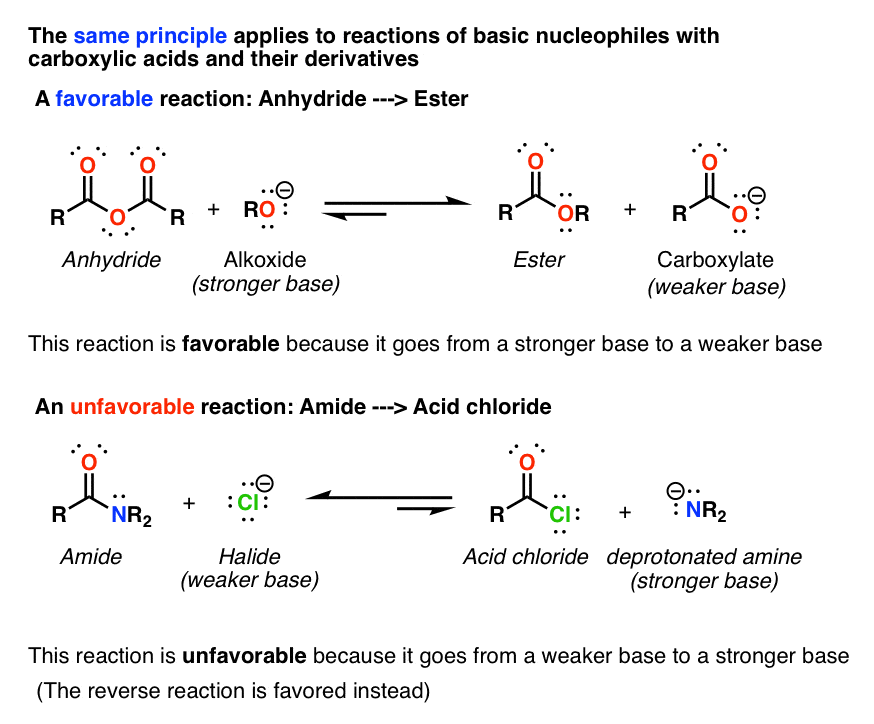
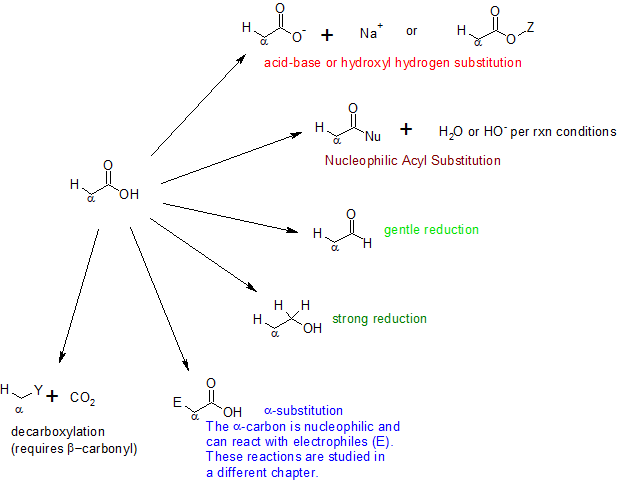
Carboxylic Acids Menu
An amino acid has both a basic amine group and an acidic carboxylic acid group. Reactions 2–4, conducted using COMU, generally showed moderate to good conversion, though yields for reaction 1 were lower. Step 3: Nucleophilic attack by the amine. In practice, there . Because lithium tetrahydridoaluminate reacts .Four general reaction categories are represented here: (1) As carboxylic acids are easily deprotonated, they readily form a carboxylate salt which can then potentially be reacted with an electrophile to complete a substitution of the hydroxyl hydrogen. Indeed, if you have been looking for similarities, you will have seen that most of the reactions discussed in the preceding . The reaction steps are shown below: Step 1: Deprotonation of the acid. Reactions of Carboxylic Acids and Carboxylic Acid Derivatives. Read the individual statements as you go along. Spectroscopy How to Solve IR Problems in 3 steps; NMR Spectroscopy – 3 pages that include; Chemical Shift and Integration; Number of NMR signals Spin-Spin Splitting (Multiplicity) of the NMR signal; I am working on covering all the topics of Org I and II and the list is ever-growing.Google Classroom.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. These names were chosen by chemists to usually describe a source of where the compound is found.These are the Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids class 12 Notes prepared by team of expert teachers. This is called a zwitterion.A carboxylic acid such as ethanoic acid has the structure: .













