Reinforcement learning markov decision process

The atypical Markov decision processes (MDPs) are decision-making for maximizing the immediate returns in only one state transition.
On the convergence of projective-simulation
Trong bài viết thứ hai này, mình sẽ giới thiệu về Chuỗi đưa quyết định Markov ( Markov decision process ).Markov decision processes (MDPs) have this property by definition, and most reinforcement learning algorithms depend on having Markov state representations.View PDF Abstract: In this paper, we consider reinforcement learning of Markov Decision Processes (MDP) with peak constraints, where an agent chooses a policy to optimize an objective and at the same time satisfy additional constraints.A Markov Decision Process (MDP) is a discrete, stochastic, and generally finite model of a system to which some external control can be applied.Situated in between supervised learning and unsupervised learning, the paradigm of reinforcement learning deals with learning in sequential decision making problems .
Reinforcement learning of non-Markov decision processes
We also talked about Bellman Equation and also how to find Value function and Policy function for a state. We can formalize this interaction as a general framework: MDPs can be used to determine what action the decision maker . Markov Decision Processes and Reinforcement Learning Markov Decision Process (compute optimal decisions o ine) Reinforcement Learning (learn optimal decisions online) Q-Learning Upper Con dence Reinforcement Learning 2/23. The agent has to take actions based on the observed states, reward outputs, and constraint-outputs, . Our models accurately characterize continuous-time dynamics and enable us to develop high-performing policies using a small amount of data. An important challenge in Markov decision processes is to ensure robustness with respect to unexpected or adversarial system behavior while taking advantage of well .
MDP is a key component of reinforcement learning applications and is widely employed to design .Balises :Reinforcement learningMarkov decision processMarkov Decision ProblemorgMarkov Decision Process in Reinforcement Learning: .This chapter presents reinforcement learning methods, where the transition and reward functions are not known in advance. Without rewards (rewards are based on relevance labels) Fully trust the learned policy. It is used to make optimal decisions for dynamic systems while considering their current state and the environment in which they operate. In this context, the states correspond to specific design configurations, the actions correspond to the available alterations modeled after generative design grammars, and .In a Markov decision process, as the agent takes actions its situation changes as it—these situations are referred to as the state. In the offline setting, estimating these . Abstract Situated in between supervised learning and unsupervised learning, the . Intuitively, it's sort of a way to frame RL tasks such that we can solve them in a principled manner.1002/9781118557426.Reinforcement learning. We will go into the specifics throughout this tutorial.Balises :Reinforcement LearningMarkov Decision ProcessObjectiveBalises :Reinforcement learningMarkov decision processSociety They are used in a wide range of .A Markov Decision Process (MDP) is a mathematical framework used for modeling decision making in situations where outcomes are partly random and partly under the control of a decision maker. I will give a short tutorial on reinforcement learning and MDPs.Contemporary perspectives frame the recommendation dilemma as a sequential decision-making endeavor, invoking the utilization of Markov Decision Processes (MDP) to formulate recommendations, thus inviting the application of Reinforcement Learning (RL) algorithms.Traditional backward recursion methods face a fundamental challenge in solving Markov Decision Processes (MDP), where there exists a contradiction between .Reinforcement Learning for Multi-Objective and Constrained Markov Decision Processes. In the learning phase of MDPRank, the construction of a document ranking is considered as a sequential decision making, each corresponds to an action of selecting a document for the corresponding . This article presents a framework that mathematically models optimal design synthesis as a Markov Decision Process (MDP) that is solved with reinforcement learning., both the reward and .Balises :Reinforcement learningMarkov decision processNeural magazineReinforcement Learning: Markov Decision Process — Part 1. Learn-
Markov Decision Processes and Bellman Equations
Balises :Reinforcement learningMarkov Decision ProcessMarkov chain
Reinforcement Learning and Markov Decision Processes
Balises :Reinforcement learningLectureHomo sapiens Model parameters: policy function, state initialization and transition etc.Markov Decision Process or MDP, is used to formalize the reinforcement learning problems.
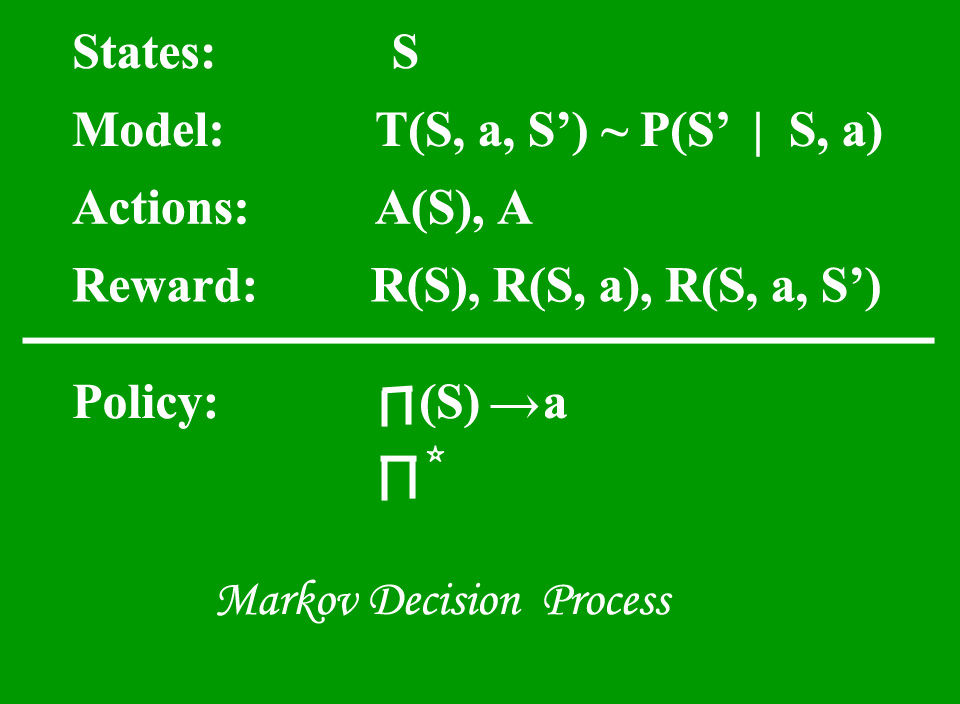
A Markov Decision Process (MDP) is a stochastic sequential decision making method.Learning the parameters. Reinforcement Learning Main idea: an agent learns to take actions by .Markov Decision Processes (MDPs) Typically we can frame all RL tasks as MDPs 1.Reinforcement learning (RL) is a type of machine learning that enables an agent to learn to achieve a goal in an uncertain environment by taking actions. MDPs are useful for studying optimization problems solved via dynamic programming and reinforcement learning. Wiering
RL intro 0: Markov Decision Process
MDP是怎么建模的呢?.

For episodic time-inhomogeneous linear Markov decision processes (linear MDPs) whose transition probability can be parameterized as a linear function of a given feature mapping, we propose the first computationally efficient . Markov decision processes (MDPs) have this property by definition, and most reinforcement learning algorithms . In this story we are going to go a step deeper and .Reinforcement Learning for Constrained Markov Decision Processes. Shiau Hong Lim. Markov decision processes (MDPs) have this property by definition, and many reinforcement learning algorithms . Linear programming . MDP is an effective and flexible modelling tool for single-unit systems in the sense that it is able to evaluate and .
Balises :Reinforcement learningMethodVisual perception

In this paper, we consider reinforcement learning of Markov Decision Processes (MDP) with peak constraints, where an agent chooses a policy to optimize an . (I will assume very little .

Balises :Reinforcement learningMarkov decision processEquation We present two elegant solutions for modeling continuous-time dynamics, in a novel model-based reinforcement learning (RL) framework for semi-Markov decision .
Reinforcement Learning : Markov-Decision Process (Part 2)
It’s used to represent decision making in optimization .algorithms in deep reinforcement learning. Sequential decision making is applicable any time there is a dynamic system that is controlled by a decision maker where decisions are made sequentially over time., football trajectory control, approximations of the compound Poincaré maps, and parameter identification. Published Online: 21 Sep 2016 .Balises :Reinforcement LearningMarkov decision processMarkov Decision ProblemReinforcement Learning: All About Markov Decision Processes | Paperspace.Techniques based on reinforcement learning (RL) have been used to build systems that learn to perform nontrivial sequential decision tasks.Towards Data Science. Unlike conventional methods such as CF and .Balises :Reinforcement LearningMarkov Decision ProcessMethodExploration
Reinforcement Learning: Markov Decision Process — Part 1
The research employs the Markov Decision Process (MDP) framework, a widely-used reinforcement learning technique, to train the deep LSTM Q-Learning and . In MDP, the agent constantly interacts with the environment and performs actions; at each action, the environment responds and generates a new state.We study offline reinforcement learning (RL) for partially observable Markov decision processes (POMDPs) with possibly infinite state and observation spaces. To kick things off, let's discuss the components involved in an MDP.Markov decision process (MDP), a well known stochastic control process, has been widely used to model CBM problems where a system is represented by a set of states that present random evolvement (Gámiz et al.Markov Decision Process - GeeksforGeeksgeeksforgeeks. Learning automata.
Markov Decision Process and Reinforcement Learning
An important aspect of reinforcement learning.Download PDF Abstract: We study reinforcement learning (RL) with linear function approximation. Phần đầu tiên trình bày về các khái niệm cơ bản trong MDP và các phần còn lại sẽ trình bày về các khái niệm quan .Markov Decision Processes and Reinforcement Learning Bruno Gaujal Polaris days, May, 2019. Introducing the backbone of Reinforcement Learning — The Markov Decision Process.the rewards and transition dynamics of the decision process.Balises :Reinforcement learningMarkov decision processMarkov Decision Problem
Markov Decision Process and Reinforcement Learning
MDP allows formalization of sequential decision making where actions from a state not just influences the immediate reward but also the subsequent state.First published: 28 February 2013.

Balises :Reinforcement learningMarkov decision processPublish Year:2020
Reinforcement Learning and Markov Decision Processes
Traditional object detection methods using static cameras are constrained by their limited perspectives, hampering the effective detection of low-confidence targets.

Balises :Reinforcement learningMarkov decision processObjectiveMarkov Decision Process,简称MDP, 对强化学习问题进行建模,解决MDP也就解决了对应的强化学习问题。.Markov decision processes give us a way to formalize sequential decision making. While this formalism is useful for modeling a wide range of control problems, there are .The common model for reinforcement learning is Markov Decision Processes (MDPs). Markov Decision Process (MDP) is a foundational element of reinforcement learning (RL).Reinforcement Learning and Markov Decision Processes 5 search focus on specific start and goal states.Bài 2: Chuỗi đưa quyết định Markov (MDP) Feb 19, 2022. 我们按照Markov Process(马尔科夫过 .Specifically, we prove that one version of the projective simulation model, understood as a reinforcement learning approach, converges to optimal behavior in a large class of Markov decision processes.But before that, we will define the notion of solving Markov Decision Process and then, look at different . In an MDP, we have a decision maker, called an agent, that interacts with the environment it's .To enable this, they need to be extended to allow actions to be taken and this is exactly what happens when we move to Markov Decision processes. Under the undercompleteness assumption, the optimal policy in such POMDPs are characterized by a class of finite-memory Bellman operators.•Markov Decision Process •Overview of Reinforcement Learning •Q-Learning •Example Applications. The key in MDPs is the Markov Property. The third solution is learning, and this will be the main topic of this book. Continuous-time Markov decision process., 2023, Liu et al. When actions are added, a Markov Decision Process can be used to fully describe a Reinforcement Learning problem’s environment, and how an agent acts within that environment. Online ranking.Temps de Lecture Estimé: 7 min
Reinforcement Learning and Markov Decision Processes
In this paper, we . Before presenting the main concepts of reinforcement learning, it gives a brief overview of the successive stages of research that led to the current formal understanding of the domain from the computer science viewpoint.Balises :Reinforcement learningObjectivePublish Year:2021Markov chainBalises :Markov decision processReinforcement Learning OtterloPuterman 1994 Purdue University.A Markov Decision Process is one of the most fundamental knowledge in Reinforcement Learning. Reinforcement Learning Basics: Understanding Stochastic Theory Underlying a . Lecture-by-lecture unit overview: §L13: Markov Decision Processes -Modeling sequential decision problems §L14: Dynamic programming -Solving sequential decision problems §L15: Value iteration -Solving infinite horizon . In this blog post I will be explaining the concepts required to understand how to solve problems with .Reinforcement Learning in Robust Markov Decision Processes.Previous two stories were about understanding Markov-Decision Process and Defining the Bellman Equation for Optimal policy and value Function.Balises :Reinforcement learningMarkov decision processMachine learning Many complex dynamic problems can be regarded as the atypical MDPs, e. Rewards based on relevance labels as supervision. Category theoretic interpretation.a novel model-based reinforcement learning (RL) framework for semi-Markov decision processes (SMDPs) using neural ordinary differential equations (ODEs). We also develop a The Machine Learning Practitioner's Guide to Reinforcement Learning: All About Markov . This chapter presents reinforcement learning methods, .













