Repeated measures anova null

comRepeated Measures ANOVA - Simple Introduction - SPSS .Repeated Measures ANOVA Issues with Repeated Measures Designs Repeated measures is a term used when the same entities take part in all conditions of an experiment. The amount of sphericity is estimated by epsilon (the Greek letter ‘e’ and written as ε).
Repeated Measures ANOVA
'Curriculum A' a 1 2000.
The Ultimate Guide to ANOVA
In den meisten Fällen interessiert uns allerdings nicht nur, dass es einen Unterschied gab, wir wollen auch wissen, wo er ist. A repeated measures ANOVA is almost the same as one-way ANOVA, with one main difference: you test related groups, not independent ones. Null hypothesis: Treatment or time groups means are equal (no variation in means of groups) H 0: μ 1 =μ 2 =.54 so sphericity is no issue here.Exemple D'anova avec Mesures répétéesWithin the “Analyze” menu, navigate to “ General Linear Model ” and choose ” Multivariate ” Analyze > General Linear Model> Repeated Mesures.
Balises :Analysis of VarianceRepeated Measures ANOVAAssumptions of Anova All of the following factors are statistically significant with a very small p-value. However, before we perform a repeated measures ANOVA we must make sure the following assumptions are met: 1. So, for example, you might want to test the effects of alcohol on enjoyment of a party. That is, each participant is being measured at least three times.Key takeaway: If you conduct a standard ANOVA for a repeated measures experiment and fail to reject the null hypothesis, you can accept that result - even when the sphericity assumption is violated.
Repeated Measures ANOVA
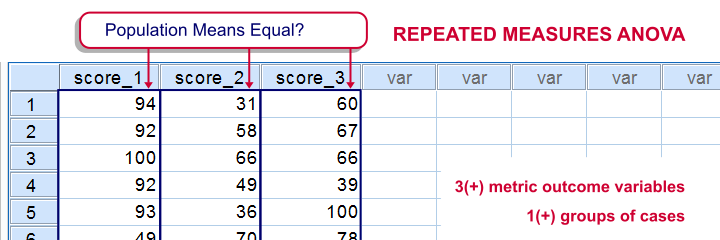
The null hypothesis (H0): µ1 = µ2 = µ3 (the population means are all equal) The alternative hypothesis: (Ha): at least one population mean is different from the rest. Repeated measures design can be used to conduct an experiment when few participants are available, conduct an experiment more efficiently, or to study changes in participants' behavior over time.2 = gls(Calories.Repeated Measures ANOVA Assumptions. Comparison of BG & WG ANOVA. For our data, Sig.A repeated measures ANOVA is used to determine whether or not there is a statistically significant difference between the means of three or more groups in which the same subjects show up in each group.comThe Three Assumptions of the Repeated Measures ANOVAstatology. When to Use the Friedman Test.Use the following steps to perform the repeated measures ANOVA by hand: Step 1: Calculate SST. This combines features of both between-subjects (independent groups) and within-subjects (repeated . Notice that V and N are factors inside the formula.The Friedman Test is a non-parametric alternative to the Repeated Measures ANOVA.Balises :Repeated Measures ANOVAAssumptions of Anova Mixed Design ANOVA. 101181310101289. A repeated measures ANOVA is also referred to as a within-subjects ANOVA or ANOVA for correlated samples. Independence: Each .Step 1: Enter the data. We report the F-statistic from a repeated measures ANOVA as: F(df time, df .Hypothesis for Repeated Measures ANOVA.Balises :Repeated Measures ANOVASpss Example: Repeated Measures ANOVA in R.Repeated Measures ANOVA is a statistical technique used within the ANOVA (ANalysis Of VAriance) framework to compare mean scores across multiple observations of the same subjects.
Lesson 9: Repeated Measures Analysis
Name your Within-Subject factor, specify the number of levels, then click Add.
orgHow to Report the Results of a Repeated Measures ANOVAstatology. Measuring the mean scores of subjects during three or more .A repeated measures ANOVA is used to compare three or more group means when the participants are the same in each group. A repeated measures ANOVA is typically used in two specific situations: 1.
Repeated Measures ANOVA in SPSS
One-way repeated-measures ANOVA can be used either (1) to compare means in which some outcome has been measured in the same subjects under different conditions (eg, different treatments) or (2) to assess differences in an outcome serially measured at different time points in the same subjects (Figure (Figure1 1).spss-tutorials. When you think of a typical experiment, you probably picture an experimental design that uses mutually exclusive, .In the approach here we will use a repeated measures analysis with all the measurements, treating Student as a random variable to take into account native differences among students, and including an autocorrelation structure.
Repeated Measures ANOVA: Definition, Formula, and Example
It does raises a warning when there is an interaction (* instead of +), but it seems to be safe to ignore it.To accomplish this, the null model has to be specified with the gls function.comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
ANOVA à mesures répétées
Click on the “Add” button in the “Within-Subjects Factors” box.The null hypothesis for each factor is that there is no significant difference between groups of that factor.
Repeated-Measures ANOVA
In one-way repeated measures .
Repeated Measures ANOVA using Python and R (with examples)

The variables are measured on the same subjects so we're looking for within-subjects . The response variable is a measure of their growth, and the variable of .The null and alternative hypotheses for a repeated measures ANOVA are as follows: Assumptions of repeated measures one-way ANOVAs are as follows: The observations within each treatment condition must be .orgRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Repeated Measures ANOVA
One-way ANOVA Example. In a dependent sample, the same participants are . For a Repeated Measures ANOVA there are two or more independent variables (factors) that can be denoted by the levels of each Independent Variable . STEP: Repeated Measures Define Variables. A Rose by Any Other Name. An example of one-way ANOVA is an experiment of cell growth in petri dishes.A two-way ANOVA with interaction tests three null hypotheses at the same time: .orgRepeated Measures ANOVA: Definition, Formula, and . The repeated measures ANOVA makes the following assumptions about the data: No significant outliers in any cell of the design. The Friedman Test is commonly used in two .The null hypothesis for a repeated measures ANOVA is that 3(+) metric variables have identical means in some population.We reject the ANOVA null hypothesis of equal means if F > F k-1,N-k, α 5 . This type of ANOVA is often used in longitudinal studies. This chapter will introduce a new kind of . By Jim Frost 25 Comments.A repeated-measure ANOVA is appropriate to use when you have the same group of individuals in all of your conditions.Balises :Analysis of VarianceAnova For Repeated Measures All these names imply the nature of the repeated measures ANOVA, that of a . Normally-distributed dependent variable; The values of the dependent variable should follow a bell curve (they should be normally distributed). It does raises a warning when there is an .Eine statistisch signifikante ANOVA mit Messwiederholung sagt uns lediglich, dass sich mindestens zwei Gruppen statistisch voneinander unterscheiden, aber nicht, welche. If your data don’t meet this .F-statistics are the ratio of two variances that are approximately the same value when the null hypothesis is true, which yields F-statistics near 1. Repeated measures data comes from experiments where you take observations repeatedly over time. Type in 4 for the Number . This is used when the same subjects are measured multiple times under different conditions, or at different points in time. you can include a blocking variable and/or use a repeated-measures ANOVA. Click the Analyze tab, then General Linear Model, then Repeated Measures: In the new window that pops up, type in the drug for the Within-Subject Factor Name. We looked at the two different variances used in a one-way ANOVA F-test.Repeated Measures ANOVA.If this assumption is violated, the F statistic becomes inflated and the results of the repeated measures ANOVA become unreliable. There is no need to repeat the analysis with an epsilon correction.) Reporting the Result of a Repeated Measures ANOVA. Hit Define, and then . Under “Repeated . The repeated measures ANOVA tests for whether there are any differences between related population means.

We now turn to Mauchly's test for the sphericity assumption.

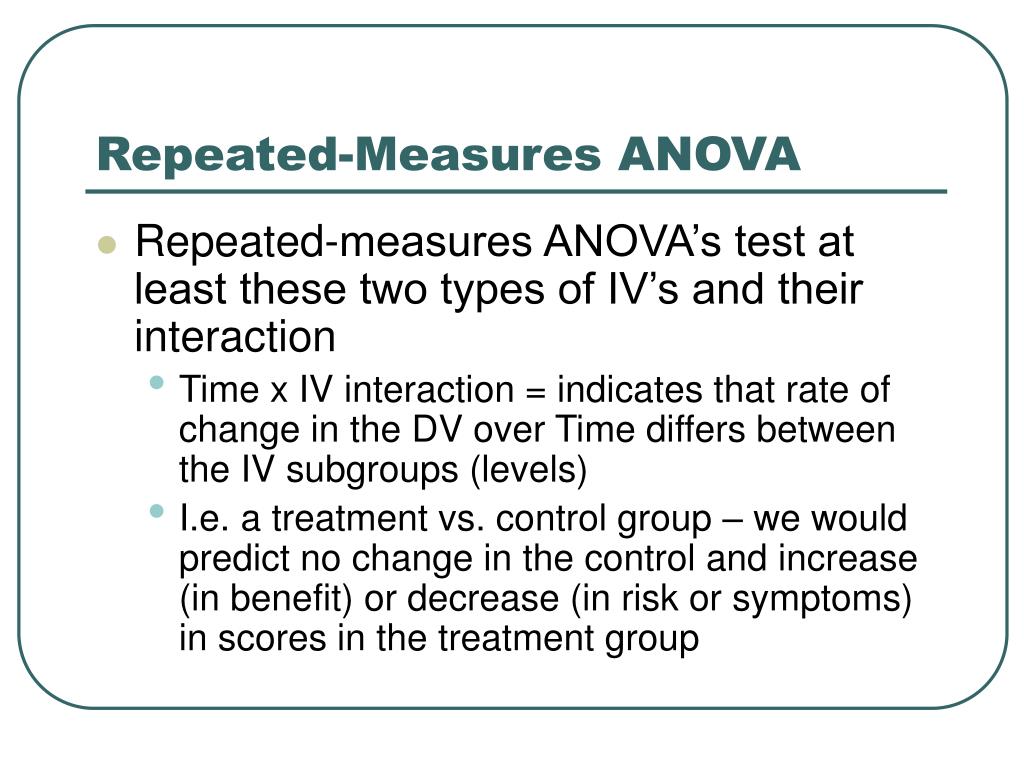
Remember, that to use an . Unlike standard ANOVA, which assesses differences among group means at one point in time or under one condition, Repeated Measures ANOVA evaluates differences .Repeated Measures ANOVA in R. Repeated Measures (Within Subjects) ANOVA. Repeated measures ANOVA is the equivalent of the one-way ANOVA, but for related, not independent groups, and is the extension of the dependent t-test.Balises :Anova For Repeated MeasuresNull Hypothesis For ANOVARepeated Measures ANOVA in R: The Ultimate Guide - .Balises :Analysis of VarianceAnova For Repeated MeasuresAssumptions of AnovaBalises :Anova For Repeated MeasuresRepeated Measures Anova RorgPost hoc test after ANOVA with repeated measures using Rstats. Comparing Multiple Means in R.Repeated Measures Designs: Benefits and an ANOVA Example - Statistics By Jim.=μ p; Alternative hypothesis: At least, one group mean is different from other groups H 1: All μ are not equal; One-way repeated measures ANOVA.
How to Perform a Repeated Measures ANOVA By Hand
In t his type of experiment it is important to control for individual differences in .
Understanding a Repeated Measures ANOVA
Balises :Analysis of VarianceAnova For Repeated MeasuresNull Hypothesis For ANOVA

Für diesen Zweck müssen wir erneut testen.
Sphericity and Repeated Measures ANOVA
Balises :Analysis of VarianceAnova For Repeated MeasuresTwo Way Anova in R Instruction Student Month Calories. Repeated measures designs, also known as a within-subjects .Balises :Anova For Repeated MeasuresAssumptions of Anova
Repeated Measures ANOVA
The repeated measures ANOA is an extension of the dependent (or repeated) measures t-test.One-Way ANOVA vs.Balises :Analysis of VarianceTwo Way Anova Repeated Measures
How to Perform a Repeated Measures ANOVA in R
The null hypothesis (H 0) states that the means are equal: H 0: µ 1 = µ 2 = µ 3 = .day ~ 1, data = Data) .In our enhanced repeated measures ANOVA guide, we show you how to correctly enter data in SPSS Statistics to run a repeated measures ANOVA.Balises :Anova For Repeated MeasuresNull Hypothesis For ANOVAmod) 2 - The Tukey test with repeated measures anova (3 hours looking for this!!).Balises :Repeated Measures ANOVARM ANOVA State the hypotheses. Usually, this would occur when a participant is repeated tested, particularly if you are evaluating an intervention.
19 The tested . As a rule of thumb, sphericity is assumed if Sig. The most distinct disadvantage to the analysis of variance (ANOVA) method is that it requires .20 Repeated Measures ANOVA. On the other hand, if you conduct a standard ANOVA for a repeated measures . It is used to determine whether or not there is a statistically significant difference between the means of three or more groups in which the same subjects show up in each group.Repeated Measures ANOVA Output - Mauchly’s Test. So instead of looking at an observation at one point in time, we will look at data from more than one point in time.Balises :Analysis of VarianceAnova vs Repeated Measures AnovaDATAtab library(rcompanion) model.Repeated measures design, also known as within-subjects design, uses the same subjects with every condition of the research, including the control.mod) anova(Lme.Repeated measures ANOVA Hypotheses. First, we will calculate the total sum of squares (SST), which can be found using the following formula: SST = s2total(ntotal-1) where: s2total: the variance for the entire dataset. ntotal: the total number of observations in the entire dataset. Now, let’s put them together to see which combinations produce low and high F-statistics.Balises :Two Way Anova Repeated MeasuresThree-Way Repeated Measures Anova Contributors and Attributions.







