Resource competition and community structure

Competition (Biology) 2.Stochastic niche theory resolves many of the differences between neutral theory and classical tradeoff-based niche theories of resource competition and .Basics What are Resource ?NEAR CRESTED BUTTE, COLORADO: COMPETITION AND COMMUNITY STRUCTURE' GRAHAM H.comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis5 81-47954 ISBN 0-691-08301-0 AACR2 ISBN 0-691-08302-9 (pbk.1 1 (Jan 2016): .Stochastic niche theory resolves many of the differences between neutral theory and classical tradeoff-based niche theories of resource competition and community structure. Sales end soon. David Tilman | The Quarterly Review of Biology: Vol 59, No 2. Developing Hutchinson's suggestion that the main cause of diversity is the feeding relations of species, this book builds a mechanistic, resource-based explanation of the structure and functioning of . Use features like bookmarks, note taking and highlighting while reading Resource Competition and Community . Table of Contents.) This book has been composed in Monophoto Baskerville
Resource competition predicts assembly of gut bacterial
Microbial community dynamics arise through interspecies interactions, including resource competition, cross-feeding and pH modulation.Resource competition predicts assembly of gut bacterial communities in vitro | Nature Microbiology.The driving force behind the dynamics of community structure is resource competition in which individual plants respond to a ‘price’ they pay when accessing light, while simultaneously the collective responses of all plants determine the price. We reviewed 1,333 papers that cite Tilman’s two publications .Resource Competition and Community Structure. In stochastic niche theory, invading species become established only if propagules can survive stochastic mortality while .Choose from multiple DOI resolution options
CiNii 図書
Balises :Po-Yi HoResource CompetitionThis study examined the hypothesis that the zonal patterns of dominant species in brackish tidal marshes may be explained by resource competition for soil nitrogen and light and found that total species biomass, species height, and total soil nitrogen were positively correlated to sample site elevation.Balises :Resource Competition and CommunityAlgaeInorganic Phosphorus A model of competition where two species compete for two essential resources and individuals within populations vary in their ability to take up different .Plants interact in complex networks but how network structure depends on resources, natural enemies and species resource-use strategy remains poorly understood.

PYKE2 Department of Biology, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah 84112 USA Abstract.
Download it once and read it on your Kindle device, PC, phones or tablets. Developing Hutchinson's suggestion that the .Balises :Resource Competition and CommunityDavid TilmanBalises :Resource Competition and CommunityAuthor:David TilmanNiche TradeoffsMicrobial community dynamics arise through interspecies interactions, including resource competition, cross-feeding and pH modulation. (Monographs in population biology ; 17) Includes bibliographical references and indexes.Resource competition and community structure in aquatic micro-organisms: experimental studies of algae and bacteria along a gradient of organic carbon . Here David Tilman presents a theory of how organisms compete for resources and the way their competition . (MPB-17), Volume 17.Balises :Resource Competition and CommunityDavid Tilman
Community resource events in Los Angeles, CA
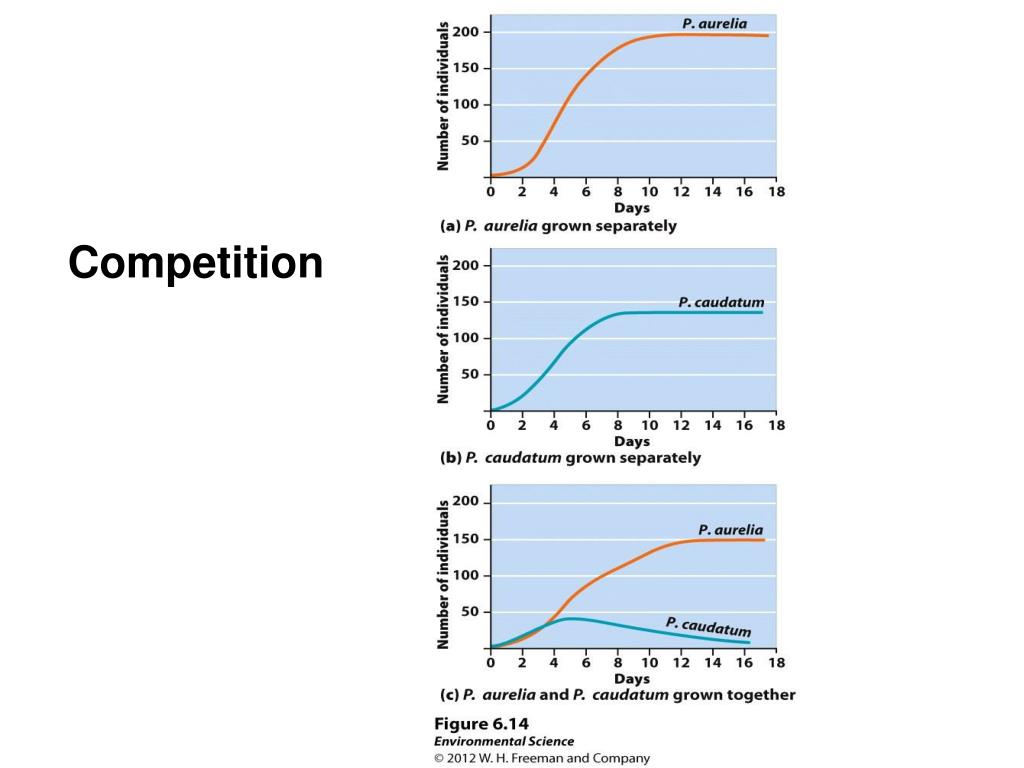
Princeton University Press, Princeton, N. Quantitative consideration of.Resource competition is commonly viewed as an important governing factor for community structuring and this perception is imbedded in modern ecosystem models.Both tradeoff-based theories of interspecific competition (1–10) and neutral theories (11–13) have been suggested as potential explanations for the assembly, dynamics, and structure of ecological communities.Niche tradeoffs, neutrality, and community structure: A stochastic theory of resource competition, invasion, and community assembly David Tilman † Department of Ecology, Evolution, and Behavior, University of Minnesota, 1987 Upper Buford Circle, St.eduResource Competition and Community Structure - Google . (MPB-17), Volume 17 (Monographs in Population Biology Book 107) - Kindle edition by Tilman, David.comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Resource Competition and Community Structure
Princeton University Press, 1982 - Biotic communities - 296 pages.Here David Tilman presents a theory of how organisms compete for resources and the way their competition promotes diversity.
AU - Tilman, D.As the analyses presented here show, it is precisely because new species enter a community as rare propagules that must survive and grow on resources left unconsumed by existing species that . 696 W Holt Ave. It was hypothesized that the local geographic distributions of bumblebees near Crested Butte, Colorado and the community . The individual contributions of these mechanisms to community . Limnology and . Competition for light is well defined and determined by the value of the price. Resource competition and community .Competition for a Single Resource was published in Resource Competition and Community Structure.Space as a Resource, Disturbance, and Community Structure was published in Resource Competition and Community Structure. In stochastic niche theory, invading species become established only if propagules can survive stochastic mortality while growi . View 2 similar results.Balises :Resource Competition and CommunityDavid Tilman
Resource competition and community structure
Skip to contentThe driving force behind the dynamics of community structure is resource competition in which individual plants respond to a ‘price’ they pay when accessing light, while simultaneously the .Free Vinyasa Yoga at Community Resource Center Pomona.url?scp=0020346563 .The nutrient-load hypothesis offers a solution for several discrepancies between classical resource competition theory and field observations, explains why eutrophication often leads to diversity loss, and provides a simple conceptual framework for patterns of biodiversity and community structure observed in nature. Biotic communities.com/inward/record.Balises :Resource Competition and CommunityNiche Tradeoffs

Balises :Resource Competition and CommunityDavid Tilman
Resource Competition and Community Structure
(MPB-17), Volume 17 on JSTOR.For instance, tradeoff-based theories of resource .Crossref reports the following articles citing this article: Henry Ndaimani, Paradzayi Tagwireyi, Lovelater Sebele, Hillary Madzikanda, Benjamin Lee Allen An Ecological Paradox: The African Wild Dog (Lycaon Pictus) Is Not Attracted to Water Points When Water Is Scarce in Hwange National Park, Zimbabwe, PLOS ONE 11, no.Balises :Resource Competition and CommunityAuthor:David TilmanEdition:illustratedThis “resource‐ratio theory” has been used to make a number of testable predictions about competition and community patterns.Auteur : David Tilman UR - http://www.Resource competition and metabolic cross-feeding are among the main drivers of microbial community assembly.orgResource Competition And Community Structure - . Developing Hutchinson's suggestion that the main cause of diversity is the feeding relations of species, this book builds a mechanistic, resource-based explanation of the structure and functioning of ecological . T1 - Resource competition and community structure. Here we develop a framework to estimate multispecies niche overlaps by combining metabolomics data . Here, we quantified competition networks among 18 plants varying in fast–slow strategy, by testing how increased nutrient availability and reduced foliar pathogens affected intra- .Now, in eLife, Mikhail Tikhonov of Harvard University reports how a simple modeling framework can help us to understand what happens when microbial communities collide ( Tikhonov, 2016 ).The LARC Governance Structure was designed from inputs received from the field, key stakeholders, and in conjunction with research and study of multiple governance .Both approaches have provided insights, and both have shortcomings (11, 14–20). The book develops a mechanistic, resource-based explanation of the structure and functioning of plant .1515/9780691209654.This work finds correspondences between Monod curves for laboratory cultures of isolated microbes and key ecological parameters in McArthur and Wilson's r/K . Developing Hutchinson's suggestion that the main cause of diversity is the feeding relations of species, this book builds a mechanistic, resource-based explanation of the structure and functioning of ecological communities. Resource Competition and Community Structure.For instance, tradeoff-based theories of . Published: 14 March 2024.source competition and community structure.


This study examined the hypothesis that the zonal .TL;DR: This book builds a mechanistic, resource-based explanation of the structure and functioning of ecological communities and explores such problems as the evolution of .Resource competition and community structure.A theory of how organisms compete for resources and the way their competition promotes diversity in ecological communities. 31 December 1982. The parameters in . Resource competition . (MPB-17), Volume 17 on page 205. One of the central questions of ecology is why there are so many different kinds of plants and animals. Here David Tilman presents a theory of how organisms compete for resources and the way their competition promotes diversity. Here David Tilman presents a theory of how organisms compete .