Retinal pigment epithelium effects

Epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) in retinal pigment epithelial . Philp, Kathleen Boesze-Batt. Leach, Jeffrey M. Changes in the RPE associated with repair activities have been described as metaplasia.Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is associated with formation of drusen, clusters of lipids, and oxidized lipid products under the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE).The retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) is a monolayer of pigmented cells whose apical membranes face the light-sensitive outer segments of the photoreceptors, with basolateral membranes facing the choroid and hence the bloodstream (Fig. O 2, glucose, and other nutrients diffuse out of the choroid and then filter through a monolayer of retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells to fuel the retina.
Giant retinal pigment epithelium tears with membranous
The retinal pigment epithelium . 7-Ketocholesterol (7KC) is a form of .
Functions and Diseases of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium
The effects of zinc supplementation on primary human retinal pigment epithelium J Trace Elem Med Biol.
The cell biology of the retinal pigment epithelium
Metabolic profiling of biofluids (serum, plasma, The retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) is a single layer of post-mitotic cells, which functions both as a selective barrier to and a vegetative regulator of the overlying photoreceptor .RPE cells carry out many functions including the conversion and storage of retinoid, the . mTORC1 signaling is shown as a crucial regulator of many biological processes and disease progression. The white light-emitting diodes (LED) commercially available have relatively .
The space created by this separation is occupied by blood, serous exudate, drusenoid material, fibrovascular tissue or a combination of the above. Effects of white light-emitting diode (LED) . George, Fangfang Lu, Mishal Rao, Lyndsay L. ARPE-19 cells co-treated with gypenosides had significantly increased cell viability and decreased cell death rate when compared to .
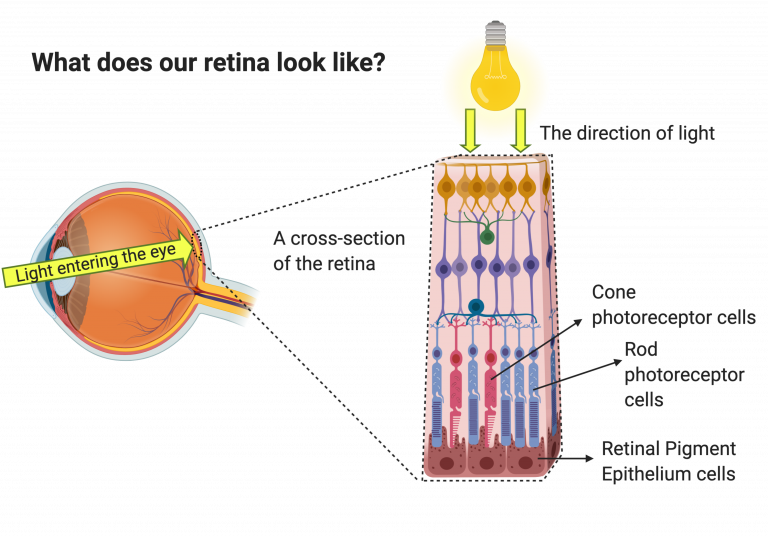
PLoS One 2009; 4 (12): e8152. This variation under different conditions may influence neuron and photoreceptor survival in the diabetic state and VEGF inhibitor treated eyes.
The Retinal Pigment Epithelium
Epub 2018 Mar 1.1 mg/g of body wt) daily in 0. Early prevention with antioxidants is mandatory. Download figure Download PowerPoint. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google ScholarThe retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) is an specialized epithelium lying in the interface between the neural retina and the choriocapillaris where it forms the outer blood-retinal barrier (BRB). The aim of this study was to determine whether and how mannitol can act as an antioxidant.The RPE is a monolayer of cuboidal epithelial cells located between the vascular .The retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) forms a critical barrier between the retina and the . Accumulating evidence indicates that oxidative stress plays a critical role in RPE cell degeneration and .

Apart from acting as a physical barrier between the retina and choroidal blood .In order to determine the protective properties of gypenosides against oxidative stress in human retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells, ARPE-19 cells were treated with H 2 O 2 or H 2 O 2 plus gypenosides for 24 h.The retinal pigment epithelium Beneath the photoreceptors is the retinal pigment . The suppressive capability of lycopene on oxidation, inflammation, angiogenesis, and cell proliferation and migration has been shown for multiple cell types. Purpose: Semaphorin 3A (Sema3A), a chemorepellant guidance protein, has been shown to be crucial for neural and vascular remodeling. Retinal pigment epithelial detachments (PEDs) are characterized by separation between the RPE and the inner most aspect of Bruch's membrane. The present study aims to evaluate the protective effects of S-allyl L-cysteine (SAC), a bioactive component from aged garlic extracts, on the oxidative stress-related apoptosis of RPE cells and to investigate the .The retinal pigment epithelium is a fundamental component of the retina that plays essential roles in visual functions. The pathogenesis of AMD remains unclear, and no effective treatment exists.The effects of centrophenoxine on the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) of 17 month old female mice have been studied. In this study, we aimed at investigating the role of mTORC1 signaling in RPE degeneration.In the human eye, lycopene is present in the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE)-choroid, ciliary body, and iris. 2018 Sep;49:184-191. Animals were injected subcutaneously for 3 months (60 injections) with the drug (0. The retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) ensures different functions crucial for photoreceptor survival, and thus for vision, such as photoreceptor outer segments (POS) phagocytosis and retinal adhesion.The role that MEM plays in protecting retinal cells is unknown.

The objective of this study was to assess whether elevated extracellular zinc has a direct effect on retinal pigment epithelial cells (RPE), by ex .Auteur : Stephanie M.Protective effects of human iPS-derived retinal pigment epithelium cell transplantation in the retinal dystrophic rat.Melanin is a natural pigment that is widely distributed in many parts of the human body, such as the skin and retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) in eyes. The main functions of the RPE are the following: (1) transport of nutrients, ions, and water, (2) absorption of light and protection against photooxidation, (3) .Retinal degeneration is prominent in Parkinson's disease (PD), a neuromotor disorder associated with aggregation of α-synuclein (α-syn) in the substantia-nigra (SN).Ageing and alteration of the functions of the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) are at the origin of lost of vision seen in age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Hydroquinone (HQ) is one of the cytotoxic components in cigarette smoke. The RPE is known to be vulnerable to high-energy blue light. The retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) is a monolayer of cells located at the posterior of the eye, between the retina and choroid, which serves a number of important roles in vision (reviewed in Strauss, 2005; Lakkaraju et al.This study aim at exploring the effect of retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) .In many forms of human retinal disease, including age-related macular . Gross
The Retinal Pigment Epithelium in Health and Disease
Purpose: To determine the effects of solute molecular weight and lipophilicity on the .AMD is characterized by the accumulation of drusen in the Bruch's membrane and dysfunction of retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells and photoreceptors.The retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), a monolayer of post-mitotic . Methods: Retinal pigment epithelial were incubated with Sema3A, or VEGF- and .Long apical microvilli engulf the photoreceptor outer segments establishing a tight morphological and . The goal of this work is to evaluate mechanisms and thresholds for RPE cell damage by means of pulse durations up to 50 µs. Blebs may accumulate and eventually contribute first to sub-RPE deposits and then drusen formation, which is a prominent histopathologic feature in eyes with AMD. Melanin is known to function as a potential radical . As an attempt to better understand the mechanisms involved in early AMD, we . Damage to the structure and function of the retinal pigment epithelium leads to a variety of retinopathies, and there is currently no curative . As a layer of .The RPE is known to be vulnerable to high‐energy blue light.An overview is presented of the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cell in . Summary of retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) functions. This study is designed to examine the effects of Sema3A on RPE cell activity both in vitro and in vivo.in AMD has been hypothesized to be the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). The white light‐emitting diodes (LED) commercially available have relatively high content of blue light, a feature that .Retinal Pigment EpitheliumThe retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), a monolayer of post-mitotic polarized epithelial . The morphological changes in the pigment layers of the retina of both eyes .
.jpg/image-full;max$643,0.ImageHandler)
.jpg/image-full;max$643,0.ImageHandler)
Anatomy and Pathophysiology of Retinal Pigment Epithelial
The outer retina is nourished from the choroid, a capillary bed just inside the sclera. Keywords: anti-VEGF drug; diabetic retinopathy; neurotrophic factor; retinal pigment . In the present study, we tested whether pretreatment with MEM could protect against the cytotoxic effects of HQ on human retinal pigment epithelium cells (ARPE-19) and human retinal Müller cells (MIO-M1) in .At a later stage, neovascular or exudative AMD can lead to severe central vision loss that is related to aging-associated cumulative oxidative stress of the human retinal pigment epithelium (hRPE) and choroid capillary. PEDF, pigment epithelium-derived growth factor; VEGF, vascular epithelium growth factor; Epithel, epithelium.Purpose: New lasers with a continuous wave power exceeding 15 W are currently investigated for retinal therapies, promising highly localized effects at and close to the Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE). Although α-syn is expressed in the neuroretina, absence of prominent aggregates suggests altered function as the likely cause of retin . Damage to the RPE leads to the development of degenerative diseases, such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD).An overview is presented of the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cell in repair and regeneration. In this chapter, these effects of lycopene and its derivatives are summarized . Deregulated RPE cell metabolism1–3 and bioenergetics4–6 has been proposed as an important aspect of AMD pa-thology.Background Kidney and eye diseases may be closely linked.