Roman empire 146 bc
As early as 53 BC, the Roman general Crassus had invaded Parthia, but he was killed and his army was defeated at the Battle of Carrhae. It was marked by the expansion of Greek culture, .It encompassed different periods of government: from the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), Roman Republic (509–27 BC) and Roman Empire (27 BC – 476 AD) until the fall of the Western Empire.Request PDF | Friendship and Empire: Roman Diplomacy and Imperialism in the Middle Republic (353–146 BC) | In this bold new interpretation of the origins of ancient Rome's overseas empire, Dr . At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Lentulus and Achaicus (or, less frequently, year 608 Ab . The region was annexed by the Roman Republic in 146 BC following the sack of Corinth by the .Balises :Ancient RomeAncient CarthagePunic WarsAfrica was a Roman province on the northern coast of the continent of Africa.By 146, Rome had established itself as the leading Mediterranean power.Throughout the Roman Empire, there were cities of 100,000 to 300,000 inhabitants - Alexandria, Carthage, Antioch, . Over the next century, it consolidated its power into an immense territorial empire.By place Ireland.Meanwhile, southern Greece also came under Roman hegemony, but some key Greek poleis remained partly autonomous and avoided direct Roman taxation. His reign was peaceful. A crucial and turbulent centuryBy . The expansion of the empire destroyed the Roman Republic. The wars began innocently enough when Rome was pulled into the . What was being a soldier in the Roman army like? KS2 History .Balises :146 BCRome, ItalyPunic WarsThe Roman Empire: 5 summary maps for 146 BC -- 1204 AD.Year 146 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar.Balises :Ancient RomeRoman EmpireSemi-elective absolute monarchy(de facto)
The End of the Roman Republic 146 to 44 BC
The territory was originally and still .
All the surviving inhabitants were sold into slavery by the Romans and Carthaginian territory was taken into the Roman Empire.The Fourth Kingdom Starts with the Roman Empire (146 BC) Thus he said, The fourth beast shall be the fourth kingdom upon earth, which shall be diverse from all kingdoms, and shall devour the whole earth, and shall tread it down, and break it in pieces.Balises :146 BCAncient RomeBefore ChristGregorian CalendarHorseGuy Bradley, Early Rome to 290 BC: The Beginnings of the City and the Rise of the Republic (forthcoming); 2.BUILDING MEMORIES: THE ERA OF THE PUNIC WARS (264–146 B.
Roman Empire (27 BC
It explains the causes of Rome’s wars against the likes of Macedon, Carthage and the Seleucid Empire.192 BC: Roman–Seleucid War: The Seleucid Empire invaded Greece. Tullius Hostilius became King of Rome.
140s BC
Campaign history of the Roman military
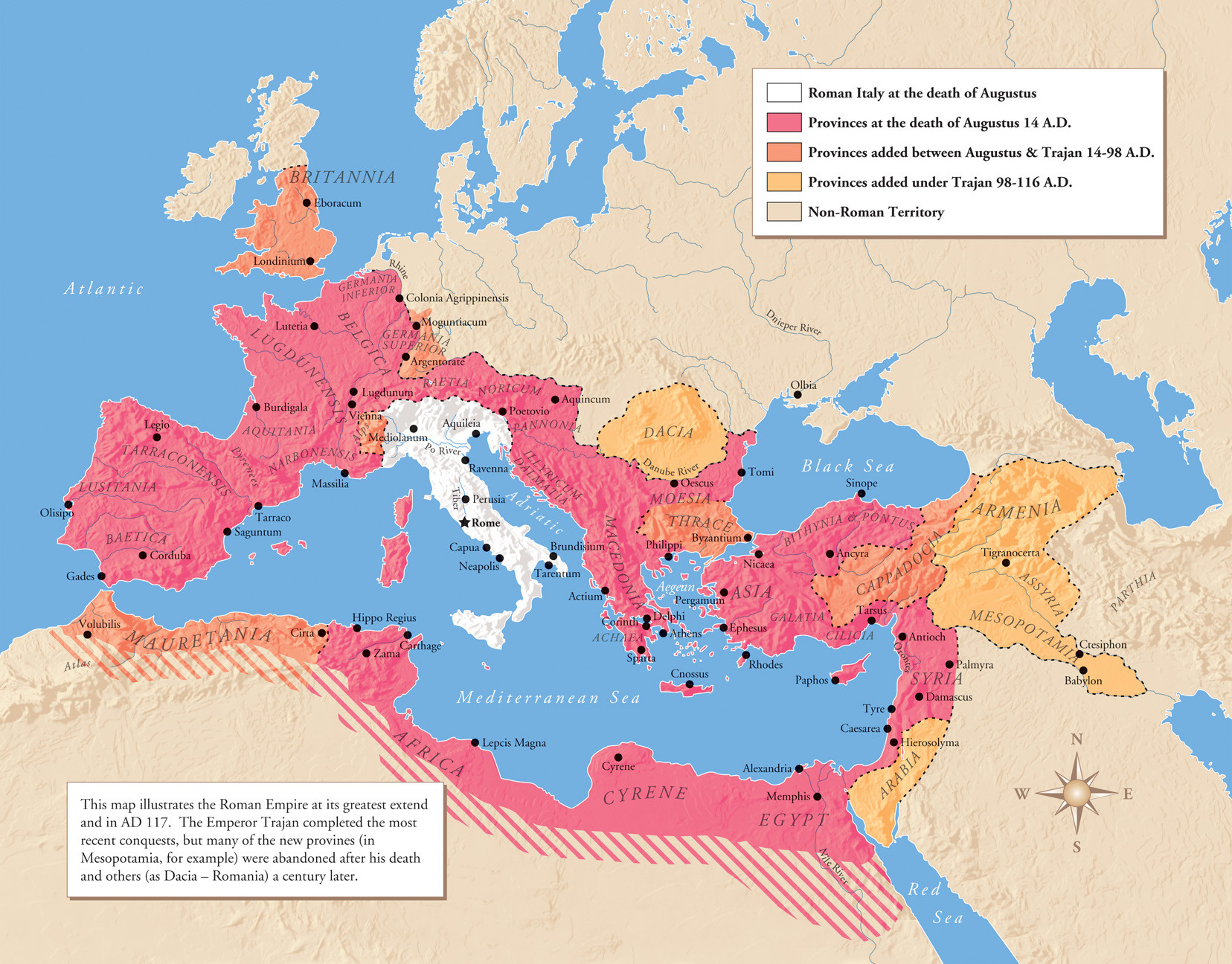
31 BC–AD 14: Augustus reintroduces monarchy to Rome. Nathan Rosenstein, Rome and the Mediterranean 290 to . Client states are in pink. This was also a war between Rome and Carthage.The Roman empire under Hadrian (ruled 117–38), showing the senatorial province of Macedonia in southeastern Europe Following Actium, Octavian entrusted Macedonia to the proconsul M. Participants: Carthage. By the last century BC, these . The origin of these conflicts is to be found .The Lusitani revolted again in 146 BC under a new leader called Viriathus, invading Turdetania (southern Iberia) in .
Introduction to ancient Rome
Balises :146 BCAncient RomeRoman EmpireCorinthAugustus The final defeat of Carthage in the Third Punic War transformed the history of Ancient Europe. 509 BC: Tarquinius Superbus, the last king of Rome, is driven .
Romulus became King of Rome.This chapter provides a synthesis and analysis of the epigraphic, literary, and artistic evidence of women’s participation in athletic events and venues following the Roman conquest of Greece in .) introduction. Roman campaigns in Germania (12 BC – AD 16) (9–16 AD period) – Campaigns in Germania (modern day Germany and the Low Countries ) against various Germanic units and .Balises :146 BCNathan RosensteinMarch 07, 2012This chapter covers the Third Macedonian War down to the destruction of Carthage and Corinth in 146 BC, and it focuses on Rome’s use of brutal methods to . By the end of this chapter, Rosenstein has shown us a Roman . The Roman strategy was clear: a decisive victory over Corinth would not only .Balises :146 BCRoman EmpireRome, ItalyPunic Wars Lee
Punic Wars
All the surviving inhabitants were sold into slavery by the Romans and .The Roman Empire under Augustus: The Republic in 31 BC (yellow) and Augustus's conquests (shades of green).
What happened in ancient rome in 264 146 bc?
These wars, fought over territorial disputes, economic control, and political power, had profound and lasting implications for the ancient Mediterranean world, altering the geopolitical landscape and shaping the rise of Rome as .

Friendship and Empire: Roman Diplomacy and Imperialism
; Publius Cornelius Scipio Aemilianus divides .In 146 BC, the third Punic War happened. For earlier times, see Greek Dark Ages, Aegean civilizations and Mycenaean Greece.The Punic Wars, a series of three significant conflicts between Carthage and Rome, spanned from 264 BCE to 146 BCE. Numa Pompilius became King of Rome. The Carthaginian population was sold and its .Achaia, sometimes spelled Achaea, was a province of the Roman Empire, consisting of the Peloponnese, Attica, Boeotia, Euboea, the Cyclades and parts of Phthiotis, Aetolia and Phocis. At the same time, the internal balance of power shifted dramatically, as a narrow ruling elite was challenged first by the rest of Italy, and then by military commanders, a process which culminated in the civil . The Numismatic Evidence for Roman Expansion and Settlement in Moesia and Thrace (ca.The Roman conquest of Ancient Greece in the 2nd century BC. The Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC) The Roman Republic (509–27 BC) Roman Republic Timeline; The Roman Empire (27 BC – 476 AD) Roman . Rome began as an Italic settlement in the Italian Peninsula, traditionally dated to 753 BC, that grew into the city of Rome and which subsequently gave its name .Balises :146 BCNathan RosensteinCorinthFor later times see Roman Greece, Byzantine Empire and Ottoman Greece.In 146 BC the armies of Rome destroyed Carthage and emerged as the decisive victors of the Third Punic War.Roman Empire (27 BC – 476 AD) The Roman Empire was founded when Augustus Caesar proclaimed himself the first emperor of Rome in 31BC and came to an end with the fall of Constantinople in 1453CE.Roman victory in Africa and the east.Introduction to Ancient Rome.Balises :146 BCRome, Italyguage and ideals contributed just as much to Roman empire-building as military muscle. Carthage was later rebuilt as a Roman city, to be an important centre for the export of grain to Rome.Auteur : The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica
How did Rome benefit from the destruction of Carthage in 146 BC
and from 264 BCE to 146 BCE the two powers would fight a series of three wars – the so-called Punic Wars.
Ancient Rome Timeline 753 BCE-476 CE
Find out how Rome was ruled, what the Romans believed and what they did for fun.comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
The Roman Empire, explained in 40 maps
Balises :Ancient RomeRoman Empire

Share this: Roman Republic Timeline 753 BC: Founding of Rome.Rosenstein draws upon his earlier research to argue (263-5) that Italy’s agricultural situation was not as dire as is often believed; aristocrats probably were not buying up all the farmland, so he sees general prosperity among the rural people between 200 and 146 BC. The Roman Empire [a] was the post- Republican state of ancient Rome.It roughly comprised the territory of present-day Tunisia, the northeast of Algeria, and the coast of western Libya along the Gulf of Sidra. In southern Italy, they butted up against another great power, Carthage, a city in modern Tunisia. Institutions designed for a small city-state could not rule a world empire.The book highlights the significance of Rome's .The Hellenistic period was a historical era that spanned from the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC to the emergence of the Roman Empire in the first century BC. 715 – 673 BCE. 673 – 642 BCE.
Roman Empire
The 19 central maps of this site, emphasized the waxing and waning .5 Greatest Defeats in Roman History - TheCollectorthecollector.
Introduction to ancient Rome
Balises :146 BCAncient RomeNathan RosensteinAuteur : Timothy B. For modern Greece after 1820, see Timeline of modern Greek history. Here are 40 maps that . Image: An early edition of “The Histories” “The Histories” is a historical work written by the Greek historian Polybius in the .Third Punic War, (149–146 bce ), third of three wars between the Roman Republic and the Carthaginian (Punic) Empire that resulted in the final destruction of Carthage, the enslavement of its population, and Roman hegemony over the western Mediterranean. Location: Carthage. It is generally understood to mean the period and territory ruled by the Romans following Octavian 's . The two powers first fought in Sicily, and by 146 BC Rome had utterly defeated their great maritime rival and added large parts of North Africa and all of modern Spain to their territory.The End of the Roman Republic, 146 to 44 BC: Conquest and Crisis.Under Augustus and his successors, the empire experienced 200 years of relative peace and prosperity.It was established in 146 BC, following the Roman Republic's conquest of Carthage in the Third Punic War. Life in the Roman army. 146 BC – AD 98/117) ISBN 978-3-339-10972-9 Paunov Volume I Verlag Dr. The era of the Punic Wars marked Rome’s emergence as a truly Mediterranean-wide empire. (Daniel 7:23) After a series of wars, Rome destroyed Corinth in 146 BC and Greece became part of . Above all, vast military campaigns required generals who commanded armies over wide territories for several years. How Hannibal's conquests led to the fall of . Licinius Crassus , grandson of Crassus the triumvir, who led a campaign into the north that lasted until 27 BC, finally subjugating the whole region south of the .

For over a century, the Romans and the .Hellenistic Greece (323-146 BC) The History of Ancient Rome.

Punic Wars, (264–146 bce ), a series of three wars between the Roman Republic and the Carthaginian (Punic) empire, resulting in the destruction of Carthage, the enslavement of its population, and Roman hegemony over the western Mediterranean. Punic was the Roman name for Carthage. The Greek peninsula fell to the Roman Republic during the Battle of Corinth (146 BC), when Macedonia became a . Context: Third Punic War. Carthage was defeated again, and Rome destroyed the city and sold its .
The end of the Roman Republic, 146 to 44 BC : conquest and crisis
The first and second Punic wars (264–241 bce and 218–201 bce) had . Corlea Trackway built in County Longford; Roman Republic.For other uses, see Roman Empire (disambiguation). It is generally understood to mean the period and territory ruled by the Romans .Battle of Corinth (146 BC) | Military Wiki | Fandommilitary-history.; Construction of the Via Postumia, linking Aquileia and Genua.
The Growth of the Roman Empire Explained
At the same time, .
Timeline of Roman history
188 BC: Roman–Seleucid War: The Seleucid Empire signed the Treaty of Apamea, under which it surrendered all territory west of the Taurus Mountains to the Roman clients Rhodes and Pergamon and agreed to disarm its navy and pay a war indemnity of fifteen thousand .
Timeline of ancient Greece
The Carthaginian population was sold and its territ.









