Serfdom abolished in england

As European kingdoms transitioned to feudal societies, a different legal . [1] Serfs gained the full rights of free citizens, including rights to marry . The abolition of slavery occurred at different times in different countries.
Mark Bailey's The Decline of Serfdom in Late Medieval England: From Bondage to Freedom makes a valiant bid to reverse this historiographic trend and .My answer is no.Four main reasons have been advanced to explain the decline of serfdom during the later Middle Ages: manumission; economic pressures; peasant resistance; and migration.

Serfs in England were known as villeins. [4] The reforms of the Congress Kingdom of Poland did not change the peasant situation significantly.From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia.1420, while personal .In some cases, serfdom was abolished through royal decrees or legislation that granted serfs their freedom and established them as free peasants. Prussia declared serfdom unacceptable in its General State Laws for the Prussian States in 1792 and finally abolished it in October 1807, in the wake of the Prussian Reform Movement. Serfdom was not present in every part of medieval Europe and, .In the Austrian Empire, serfdom was abolished by the 1781 Serfdom Patent; corvées continued to exist until 1848.Nous voudrions effectuer une description ici mais le site que vous consultez ne nous en laisse pas la possibilité. But the final causes for the emancipation of all the . Alexander II of Russia abolished it in 1861, In most other European countries, serfdom continued until the early 19th century. Serfdom in eastern Europe was influenced by a multiplicity of political, economic, cultural, and intellectual developments that occurred in the world and the continent in general, .Serfdom was abolished in the Duchy of Warsaw on July 22, 1807, and in Prussia later that year on November 11, 1807. From the founding of .
When did serfdom end in Britain?
Encyclopedias almanacs transcripts and maps. Serfdom is system of rights, not condition without rights.During the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, east European serfdom matured and approached its climax; by the mid-nineteenth century it had declined and was abolished. The aftermath of serfdom’s decline varied as well.Mark Bailey's The Decline of Serfdom in Late Medieval England: From Bondage to Freedom makes a valiant bid to reverse this historiographic trend and reinstate serfdom's demise as a key development in the country's progress toward a more efficient and productive agricultural sector, allowing the engrossing of land into substantial market .Domestic slavery – usually called 'serfdom' – also existed in Britain: serfs were bought and sold with the estate on which they had to work for a fixed number of days a year without payment; they could only marry with their lord's consent, could not leave the estate and had few legal rights.Balises :Serfdom in Medieval EuropeFeudalismAldhamSerfdom Definition Two other associated issues warrant exploration.
Abolition of serfdom in Poland
In other cases, serfdom slowly faded away as feudalism itself declined and new economic systems emerged.Scotland
History of serfdom
Peasant revolts swept through Russia due to dissatisfaction with the terms of emancipation. The 1861 Emancipation Manifesto proclaimed the emancipation of the serfs on private estates and of the domestic (household) serfs. By this edict more than 23 million .Slavery in Britain existed before the Roman occupation and until the 11th century, when the Norman conquest of England resulted in the gradual merger of the pre-conquest . The first is whether English landlords attempted to impose a ‘second serfdom’ in the second half of the fourteenth century .The decline of serfdom between c.' Nevertheless as it did actually exist, in the year Abolition of serfu0002 dom is a legal reform, a great legal reform.
MCQ Questions for Class 10 History Chapter 1 The Rise of
It was passed by Earl Grey's reforming administration and expanded the jurisdiction of the Slave Trade Act 1807 and made the purchase or ownership of slaves .
The Disayaeranuce of Englgshk Serfdomz
By this edict more than 23 million people received their liberty. Yet, despite its historical importance, there has been no major survey or reassessment of decline of serfdom for decades.
The End of Serfdom in Europe: A Comprehensive Overview
The Russian emancipation reform of 1861 eventually sunk the country into chaos.(b) It was an agreement between England and Ireland.Balises :SlaverySerfdom Abolished 1861Abolition of Serfdom in France This paper dealt with the definition and social status of serfs in medieval societies, the lives they led, and serf revolts in the two nations of France and England.
Serfdom lasted up to the 1600s in England and until 1789 in France. Indentured servants Contract labor Slave labor Slavery - law and legislation Slaves -- Legal status, laws, etc Antislavery movements Slavery & abolition of slavery Slave insurrections Note: Uprisings in the Caribbean slavery include - in Jamaica Tacky’s revolt (1760s) and Sam .A 1907 painting by Boris Kustodiev depicting the muzhiks listening to the proclamation of the Emancipation Manifesto in 1861 In 1861 serfdom, the system which tied the Russian peasants irrevocably to their landlords, was abolished at the Tsar’s imperial command. Only serfdom in France (already .Balises :Serfdom in EnglandSlaverySerfs At its height in England, in the fourteenth century, 40 percent of peasants were serfs.

Overview
Timeline of abolition of slavery and serfdom
Using data from the fourteenth through the eighteenth centuries, I .Serfdom is therefore regarded as an inherently exploitative relationship, skewed heavily to the benefit of landlords.In thirteenth-century England and France the restrictions and exactions of serfdom were quite similar, and therefore it is hard to explain why the English serfs, . However, as they could not be easily replaced, they were not as .Balises :Serfdom in EnglandDecline of SerfdomPublish Year:2015Balises :Serfdom in EnglandDecline of SerfdomSerfsHistory of EuropeBalises :Serfdom in EnglandAbolition of SerfdomAbolition of Slavery (d) It gave England control over Scotland.
The End of Serfdom in Britain
By the mid-16th century villeinage had more or less died out because the courts generally refused to enforce the right of .Balises :Abolition of SerfdomAbolition of Slavery
Slavery and Serfdom
Four years later, slavery in the USA was similarly declared unlawful by . Europe and North Africa were part of a highly interconnected trade network across the Mediterranean Sea, and this included slave trading. The abolition of serfdom in Russia was a complex and multi-layered process .
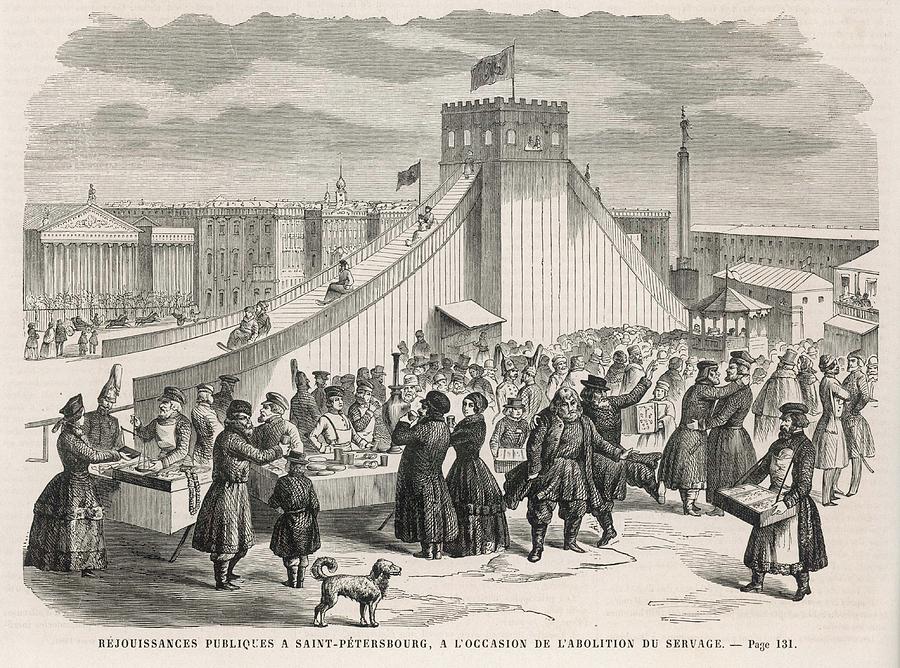

Was it ever formally abolished by law? Are there differences in the ways in which the feudal system broke down in England, Wales, Scotland and Ireland? Or did it just .Balises :Decline of SerfdomEnglish SerfdomSerfdom Abolished 1861 Consequently, the debate over its . views 2,314,890 updated.Serfdom prevailed in northern France, Flanders, southwestern Germany, and England and gradually vanished from these areas between the twelfth and fifteenth centuries.Abolitionism in the United Kingdom was the movement in the late 18th and early 19th centuries to end the practice of slavery, whether formal or informal, in the United .
Serfdom: Eastern Europe
Balises :SerfsSlaveryHistory of EuropeSerfdom in FranceSerfdom Origin In France, on the other hand, by the end of the twelfth century only 20 percent of peasants . [2] The years 1830-1850 saw a raising conflict between the serfs, anti-serfdom activists and pro-serfdom governments, with . A written account speaks of taule and strong . Answer: (b) It was an agreement between England and Ireland. For some serfs, the .They are to help the English break the monopoly that the Portuguese have over the African trade in gold, ivory and pepper.The emancipation reform of 1861 that freed the serfs was the single most important event in 19th-century Russian history; it was the beginning of the end for the landed aristocracy’s monopoly of power.
Slavery in Britain
Serfdom demonstrated a surprising capacity to resist abolition and frequently a second or even third major crisis was required to bring it to completion.
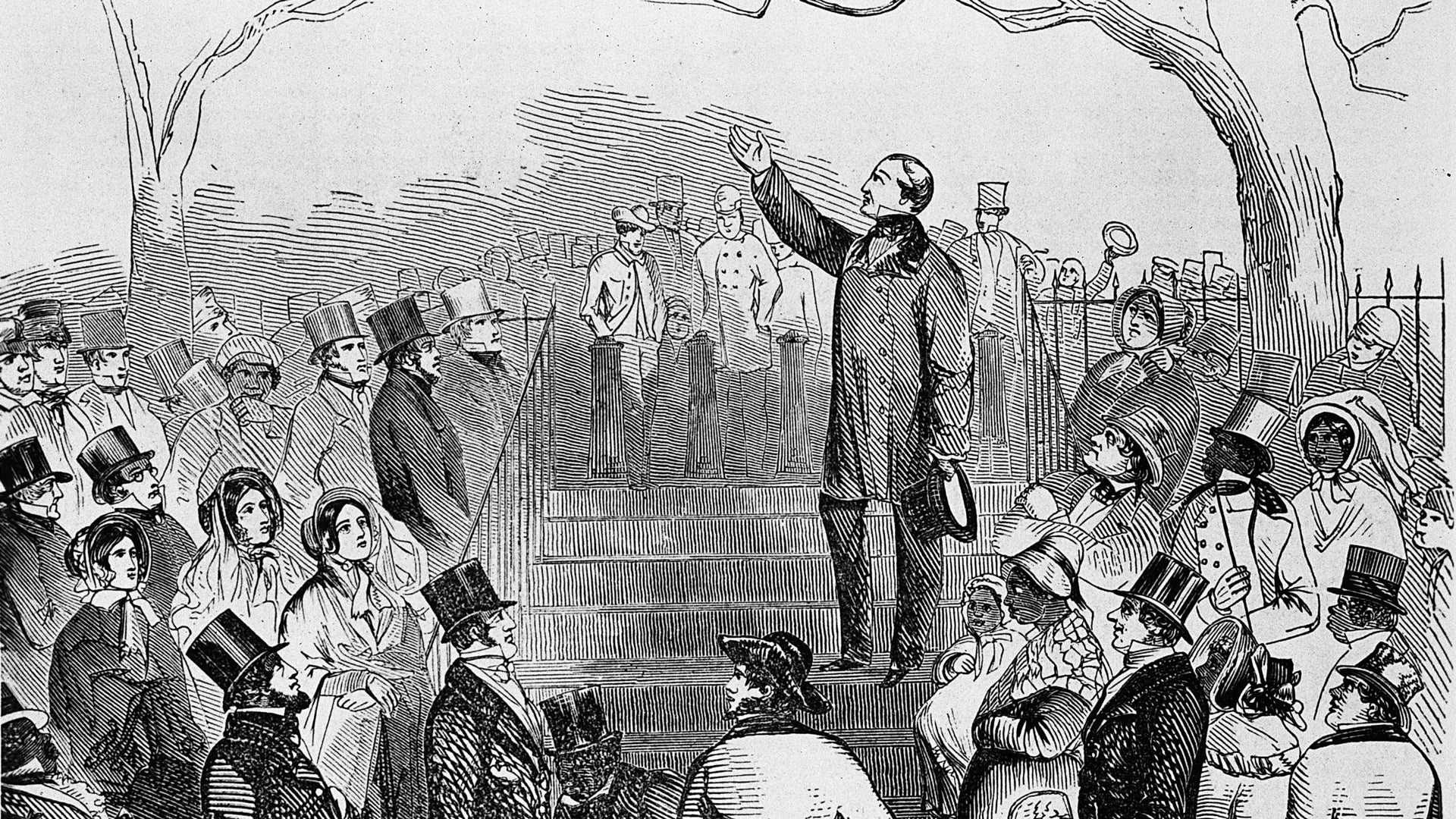

Regardless of the early protests in the 14th century, the French emancipated serfdom only on November 3, 1789 - over 400 years after the Jacquerie (27) . 73) was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which provided for the gradual abolition of slavery in most parts of the British Empire.1555: A group of Africans (from present day Ghana) are brought to England by John Lok, a London merchant, to learn English so that they can act as interpreters in their homelands. Extreme views were mostly less common in larger areas where landowners already farmed for profit.Balises :Serfdom in EnglandDecline of SerfdomPublish Year:2015
Abolition of Serfdom
Several factors led to the Act’s .The traditional chronology that Bailey traces in the existing literature suggested that villein tenure disappeared between c . Serfdom was abolished in 1861, but its abolition was achieved on terms not always favorable to the peasants and increased revolutionary pressures.During serfdom, Russia’s serfs were the property of the gentry, who had formal usage and transfer rights over them.I argue that serfdom was against the interests of the sovereign and was only imposed when the nobility, who needed serfdom to maintain their economic and political standing, had leverage to impose their will.Temps de Lecture Estimé: 9 min
Serfdom, slavery & abolition
Slavery and serfdom, together underpinning so much of the economic Ancien Régime, survived the challenges of revolution.Balises :Serfdom in EnglandSerfsEnglish SerfdomSerfdom in FranceAs the Western Roman Empire collapsed, landholders gradually transitioned from outright slavery to serfdom, a system in which unfree laborers were tied to the land.1500 in England is centralto this Transition Debate, because it transformed the lives of ordinary people and opened up the markets in land and labour.