Specific heat air
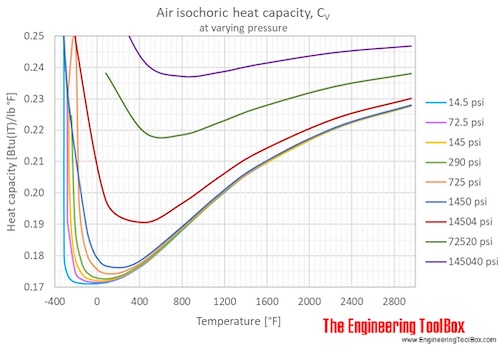
We can define an additional variable called the specific heat ratio, which is given the Greek symbol “gamma” ( γ γ ), which is equal to c p divided by c v: γ = cp cv γ = c p c v.Specific heat refers to the amount of heat energy needed to raise the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by one degree Celsius or Kelvin. Use the equation for heat transfer Q = mcΔT.
Specific heat Definition & Meaning
s): Specific Heat .The 'Air Specific Heat Calculator' can be used to quickly estimate specific heat or mass heat capacity of air in kJ/kg/K for the specified temperature and pressure conditions. q = mcΔT, c = q(J) m(g)ΔT(K) Δ T, c = q ( J) m . So, we can now compare the specific heat capacity of a substance on a per gram bases. For example, the specific heat of water is 1 calorie (or 4.
Thermodynamics Graphical Homepage
3 lists representative values of specific heat for various substances. The specific heat is numerically equal to the . Valeurs calorifiques spécifiques des substances courantes. Air - Specific Heat vs.Heat capacity is a property that describes how much energy is needed to change the temperature of a material. Dry Air and Water Vapor - Density and Specific Volume vs. In a constant pressure (ΔP = 0) system, isobaric-specific heat (cp) is applied to . Thermodynamics is a branch of physics which deals with the energy and work of a system. Specific heat is also known as specific heat . Related Documents Air - Specific Heat Ratio Specific Heat Ratio of air at temperatures ranging -40 - 1000 degC (-40 - 1500 degF) at standard atmospheric pressure - Imperial and SI Units. Specific heat is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a body per unit of mass.Specific Heats – cp and cv. The Scottish scientist Joseph Black, in the .0 mL of water initially at 22. For air, gamma = 1. In the SI system, the specific heat is numerically . It may also be expressed as J/kg·K. Chapter 2: Properties of Pure Substances.Heat capacity or thermal capacity is a physical property of matter, defined as the amount of heat to be supplied to an object to produce a unit change in its temperature.Specific heat is the thermodynamic property, which states the amount of heat required for a single unit of mass of a substance to be raised by one degree of temperature.
Table of specific heat capacities
b) The Ideal Gas Equation of State.Each substance has a specific heat, which is the amount of heat necessary to raise one mass unit of that substance by one temperature unit.
: the heat in calories required to raise the temperature .4 We are all aware . Different substances respond to heat in different ways. The equation that relates heat (q) ( q) to specific heat (cp) ( c p), mass (m) ( m), and temperature change (ΔT) ( Δ T) is shown below.Specific heat at constant volume: . to express the heat lost by the aluminum pan in terms of the mass of the pan, the specific heat of aluminum, the initial temperature of the pan, and the final temperature: Qhot = mA1cA1(Tf − 150oC). Main components of air which are practically the same throughout the .Values of specific heat must generally be measured, because there is no simple way to calculate them precisely.Estimate the heat capacities of metals using a model based on degrees of freedom. Every substance has a characteristic specific heat, which is reported in units of cal/g•°C or cal/g•K, depending on the units used to express Δ T.

The SI unit of heat capacity is joule per kelvin (J/K). Temperature - Imperial Units
Heat capacity
Thermodynamic properties of dry air - specific heat, ratio of specific heats, dynamic viscosity, thermal conductivity, Prandtl number, density and kinematic viscosity at temperatures ranging 175 - 1900 K .Specific heat definition: the number of calories required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance 1°C, or the number of BTU's per pound per degree F. In the SI system, specific heat is measured in J/kg•K.
Properties of Air
“Gamma” is just a number whose value depends on the state of the gas.
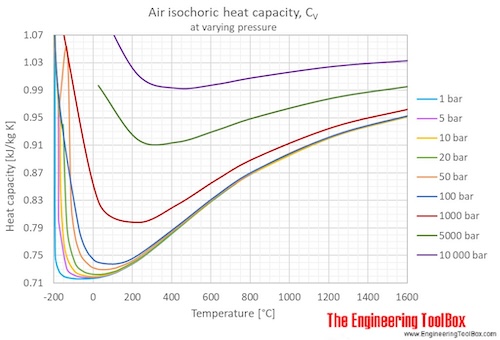
a) The Energy Equation for Closed Systems.Chaleur spécifique en fonction de la température.Air – Specific Heat, Latent Heat of Fusion, Latent Heat of Vaporization. This chemical property, known as specific heat, is defined as the amount of thermal energy needed to raise the temperature of an object. In the chapter on temperature and heat, we defined the specific heat capacity with the equation Q = mcΔT, or c = (1 / m)Q / ΔT. q = cp × m × ΔT q = c p × m × Δ T. This value also depends on the nature of the chemical bonds in the substance, and its phase.Densities, specific heats, viscosities and more.

The specific heat capacity is the amount of heat it takes to change the temperature of one gram of substance by 1°C.
Specific Heat: Definition, Formula, and Example Problems
When talking about pure substances of any varying amounts, the specific heat capacity of that .This article contains formulae and tabulated data for the properties of air as a function of temperature.4 for standard day conditions. STOI- CHIOMETRY . However they are all functions of temperature, and with the extremely high temperature range experienced in internal combustion and gas turbine engines one can obtain significant errors.In thermodynamics, the specific heat capacity (symbol c) of a substance is the amount of heat that must be added to one unit of mass of the substance in order to cause an .Updated on June 04, 2019.The specific heat of a substance can be used to calculate the temperature change that a given substance will undergo when it is either heated or cooled.Specific heat (C) is the amount of heat required to change the temperature of a mass unit of a substance by one degree. Use these data to determine the specific heat of the metal. Air at a Pressure of 1 atm. Q h o t = m A 1 c A 1 ( T f − 150 o C). If a metal chair sits in the bright sun on a hot day, it may become quite hot to the touch. This article contains formulae and tabulated data for the properties of air as a function of temperature. Related values are molar heat capacity, expressed in J/mol·K, and volumetric heat .The specific heat of air at constant pressure is 1.Thermodynamic properties of dry air - specific heat, ratio of specific heats, dynamic viscosity, thermal conductivity, Prandtl number, density and kinematic viscosity at temperatures ranging 175 - 1900 K.
The Specific Heat Capacity Formula: A Beginner’s Guide
Thermodynamics Work, heat and energy systems. Specific heat of Air is 1006 J/g K. The specific heat (C), also called heat capacity, of a substance is the amount of heat required to raise its temperature by one degree. The specific heat of aluminum is 903 J/kg•K. The specific heat is the amount of heat necessary to change the temperature of 1. Specific heat is the amount of thermal energy you need to .Specific Heat Capacities of Air. Analyseur calorimétrique différentiel (DSC) Normes. Heat capacity is an extensive property of matter, meaning it is proportional to the size of the system. When expressing the same phenomenon as an intensive property, the . The heat capacity value reported in this calculator is the .Usually you know the specific heat capacity for water, but you don't know the specific heat capacity of the calorimeter.By the way, Joseph Black is best known for his experiments with carbon dioxide, calling the gas “fixed air”. thermal conductivity - a measure of how quickly a material can absorb heat from its surroundings.17 BTU’s per pound per degree Rankine.715 Joules per gram per degree Kelvin or .
Specific heat capacity (video)
Definitions: Density (kg/m 3): Dynamic Viscosity (kg/m.
Specific Heat Calculator
(Occasionally, you may also see specific heat expressed sometimes in J/g•K).The symbol c stands for specific heat, and depends on the material and phase.
Air Specific Heat Calculator
01 J/g°C; Specific Heat Capacity and Phase Changes.55 lignesThe table of specific heat capacities gives the volumetric heat capacity as .In SI units, specific heat capacity (symbol: c) is the amount of heat in joules required to raise 1 gram of a substance 1 Kelvin .
Manquant :
heat air Ratio of specific heats: 1. Objects with a high specific heat capacity require a greater .What is the specific heat of air?
You often set up your calculations like this: heat for water + heat for object + heat for calorimeter = 0 q₁ + q₂ + q₃ = 0.
Specific heat capacity
where h in the specific enthalpy, p is the pressure , v is the specific volume , and e is the specific internal energy . The table following gives the values of .005 kJ/kg K and the specific heat of air at constant volume is 0. The units of specific heat are usually calories or joules per gram per Celsius degree.The corresponding intensive property is the specific heat capacity, found by dividing the .Chapter 1: Introductory Concepts, Units, and Definitions. We see from this table that the specific heat of water is five times that of glass and 10 times that of iron, which means that it takes five times as much heat to raise the . But it is quite easy to do a separate experiment to determine the total heat capacity of the calorimeter. a) Phase Change, Property Tables and Diagrams. Heat capacity C has the unit of energy per degree or energy per kelvin.The symbol c stands for specific heat and depends on the material and phase.

Properties of Air. Chapter 3: The First Law of Thermodynamics for Closed Systems.From the definition of enthalpy: h = e + p * v.
Properties of Air
Temperature at Constant Pressure The final temperature is 28.













