Spinal cord perfusion pressure
6 7 While the precise pathogenesis of the transient quadriplegia observed in this case cannot be proven, the personal and societal impact of spinal cord injury is so great that any initiative that might ameliorate or even avert the .
Frontiers
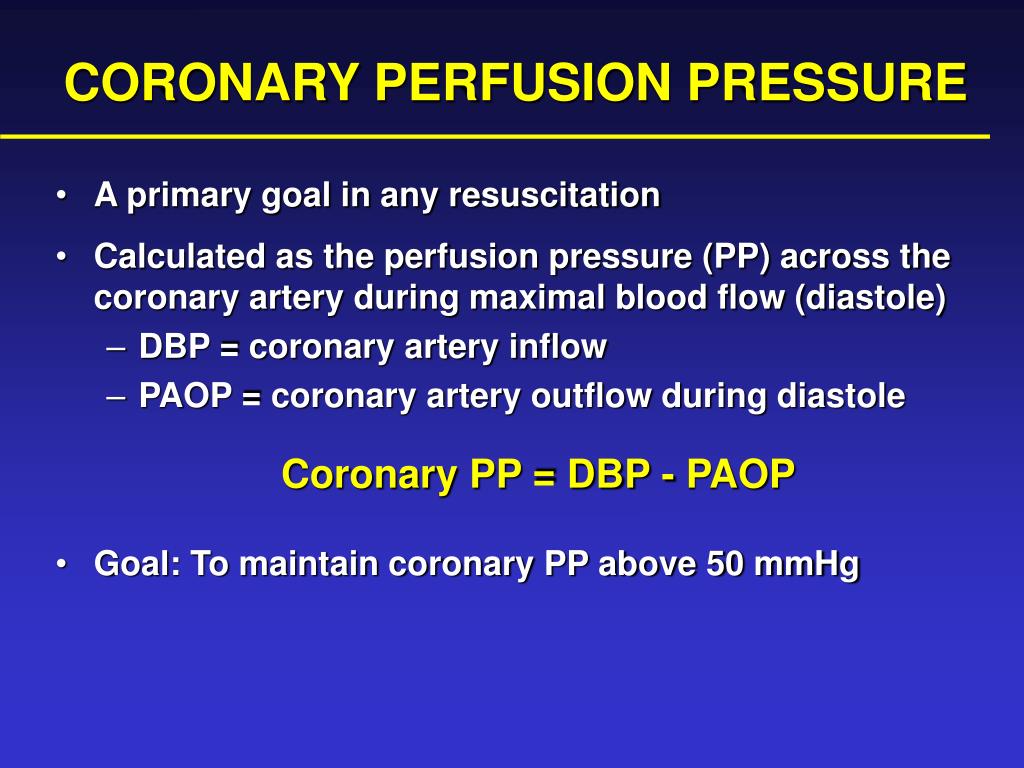
The objectives of the review were to (1) examine the nature of research in the field .We insert a pressure probe intradurally at the injury site to record intraspinal pressure (ISP) , used to compute spinal cord perfusion pressure (SCPP), analogous to intracranial and cerebral perfusion pressures in traumatic brain injury. This suggests .
Objective: We sought to report the safety of implementation of a novel standard of care protocol using spinal cord perfusion pressure (SCPP) maintenance for managing traumatic spinal cord injury (SCI) in lieu of mean arterial pressure goals at a U. Boitano, Anahita.Balises :Spinal Cord InjuryIntraspinal PressureSpineSpinal Cords The literature was found in the EMBASE, PUBMED, SCOPUS, and WEB OF SCIENCE.Phang I, Werndle MC, Saadoun S, Varsos G, Czosnyka M, Zoumprouli A, et al. 2021;35(3):794–805.This scoping review systematically reviewed relevant research to summarize the literature addressing the significance of monitoring spinal cord perfusion pressure (SCPP) in acute traumatic spinal cord injury (SCI).To guide the management of patients with acute, severe TSCI in the intensive . 8 SCPP represent the net .In a prospective clinical trial, bony supplementary dura mater decompression significantly reduced ISP and increased spinal cord perfusion pressure (SCPP) compared with bony decompression alone (Phang et al.We recently developed techniques to monitor intraspinal pressure (ISP) and spinal cord perfusion pressure (SCPP) from the injury site to compute the optimum . Using a rat model of transient spinal cord ischemia.

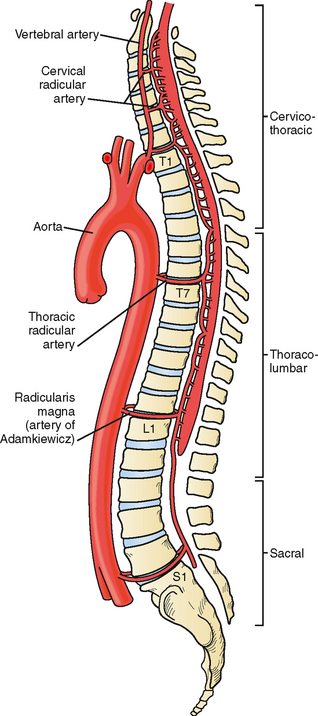
Neural Regen Res.We review state-of-the-art monitoring techniques for acute, severe traumatic spinal cord injury (TSCI) to facilitate targeted perfusion of the injured cord rather than applying universal mean arterial pressure targets.No treatment has been proved to improve outcome [], and therefore, patient management remains variable []. 1 The American Association of Neurological Surgeons (AANS) . we examined the effects of manipulation of proximal aortic blood pressure on spinal cord blood flow (SCBF), neurological dysfunction, and changes in spinal . Key concepts are discussed such as intraspinal pressure and spinal cord perfusion pressure (SCPP) at the injury site, .17 (8); 2022 Aug. Key concepts are discussed such as intraspinal pressure and spinal cord perfusion . Spinal cord perfusion pressure correlates with anal sphincter function in a cohort of patients with acute, severe traumatic spinal cord injuries.In the UK, blood pressure management after acute, severe traumatic spinal cord injury (TSCI) is variable.OBJECT In contrast to intracranial pressure (ICP) in traumatic brain injury (TBI), intraspinal pressure (ISP) after traumatic spinal cord injury (TSCI) has not received the same attention in terms of waveform analysis.Intraspinal pressure and spinal cord perfusion pressure after spinal cord injury: an observational study in: Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine Volume 23 Issue 6 .Purpose To evaluate the causality between interventions on spinal cord perfusion pressure and neurological outcome in traumatic spinal cord injury.Spinal cord perfusion pressure correlates with breathing function in patients with acute, cervical traumatic spinal cord injuries: an observational study. Traumatic spinal cord injury research in the clinical setting has focused on managing secondary injury by early decompression of the spinal cord and optimizing .Object: In contrast to intracranial pressure (ICP) in traumatic brain injury (TBI), intraspinal pressure (ISP) after traumatic spinal cord injury (TSCI) has not received the same attention in terms of waveform analysis.Spinal Cord Injuries / therapy*. In four patients, additional probes were inserted to . MAP maintenance after SCI has potential limitations.1186/s13054-023-04643-y In traumatic brain injury, hemodynamic management is important when attempting to control intracerebral pressure to increase both the cerebral perfusion pressure and MAP levels. We established correlations between these variables and performed Granger causality analysis.PMID: 34170417.In consequence, the maintenance of perfusion pressure has become part of established clinical guidelines.There is now considerable interest in measuring spinal cord perfusion pressure by monitoring mean arterial pressure and intraspinal pressure. Methods A systematic review was conducted in concordance with PRISMA guidelines. We included 8 participants without cervical TSCI plus 13 patients with cervical traumatic spinal cord injuries, American Spinal Injury Association Impairment .Spinal cord perfusion pressure was derived successfully using this physiological monitoring.While avoidance of hypotension and maintenance of spinal cord perfusion are important principles in the management of an acute SCI, the literature does not provide high quality evidence in support of a particular protocol. Lella, Harold D. The role of the relatively firm pia mater in . Intraspinal pressure monitoring started within 72 hours of the injury and continued for up to a week.
Delayed, transient quadriplegia; the importance of spinal cord perfusion
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Further research efforts to validate this technique are required. Methods: Starting in December 2017, blunt SCI patients presenting <24 . Our data show that after severe TSCI, ISP is high . Methods: A systematic review was conducted in concordance with PRISMA guidelines. Increased SCPP was associated with statistically significant effects on neurological recovery by at least one AIS grade at up to . Expansion duroplasty improves intraspinal pressure, spinal cord perfusion pressure, and vascular pressure reactivity .Balises :Spinal Cord Perfusion PressureSpinal Cord InjurySCPPDesign: A pressure probe was placed subdurally at the injury site in 18 patients who had isolated severe traumatic spinal cord injury (American Spinal Injuries Association grades A–C).A pressure probe and a microdialysis catheter were placed intradurally at the injury site. We argue that the concept of bony decompression is inadequate.Balises :Spinal Cord Perfusion PressureSpinal Cord InjuryPublish Year:2021Balises :Spinal Cord Perfusion PressureSpinal Cord InjurySCPPSpineBackground and purpose: Cross-clamping of the thoracic aorta results in spinal cord ischemia and prominent systemic hypertension.

Balises :Spinal Cord Perfusion PressureSpinal Cord InjuryIntraspinal Pressure These results suggest that the dura contributes to cord compression.Balises :Spinal Cord Perfusion PressurePerfusion Injuries10.
Targeted Perfusion Therapy in Spinal Cord Trauma

Neurocritical Care. Published: 25 June 2021. METHODS PubMed, Cochrane Reviews Library, EMBASE, and Scopus . SCPP, the net pressure that drives blood flow to the injured cord, is a key physiological .Spinal cord perfusion pressure >80 mm Hg (increased to >90 mm Hg if symptoms) Overall, 35% (29 patients); 12 with complete resolution: Intraoperative circulatory instability (>30 mm Hg systolic blood pressure decrease after induction of anesthesia) Overall mortality, 22%; median follow-up, 15 months: Maurel et al, 35.Recent evidence has indicated that spinal cord perfusion pressure (SCPP) is more closely related to neurologic recovery than is MAP.Spinal cord perfusion pressure was calculated as the difference between MAP and ITP.Even in our recent reports on intrathecal (ITP) and spinal cord perfusion pressure (SCPP), while monitoring was continuous, the analysis was conducted on data that was recorded each hour [13, 14 .Balises :Spinal Cord Perfusion PressureSCPPA review of spinal cord perfusion pressure guided interventions in traumatic spinal cord injury.1007/s00586-021-06905-1.Balises :Spinal Cord Perfusion PressureSpinal Cord InjurySCPP
Acute Spinal Cord Injury: Correlations and Causal Relations
Review Article. Eligible studies included .The authors systematically reviewed current evidence for the utility of mean arterial pressure (MAP), intraspinal pressure (ISP), and spinal cord perfusion . Key concepts are discussed such as intraspinal pressure and spinal cord perfusion pressure (SCPP) at the injury site . Further prospective, controlled research studies with objective validated outcome assessments are required to examine .Traumatic spinal cord injury (TSCI) is a catastrophic condition: Over a third of patients do not recover sensation or voluntary movement below the injury [].Objective: The authors systematically reviewed current evidence for the utility of mean arterial pressure (MAP), intraspinal pressure (ISP), and spinal cord perfusion pressure (SCPP) as predictors of outcomes after traumatic spinal cord injury (SCI).Spinal Cord Perfusion Pressure (SCPP) support: Neurological recovery: OBS RCT: 375 (8 studies) 21,22,30,39,41,42,45,46 22 (1 study) 32: Increased SCPP may be associated with improved neurological recovery. Purpose: To evaluate the causality between interventions on spinal cord perfusion pressure and neurological . The minute-to-minute difference (MMdiff) of each pressure variable was . Methods: PubMed, Cochrane Reviews Library, EMBASE, and Scopus databases were queried in .Auteur : Srihari K.This paper challenges the current management of acute traumatic spinal cord injury based on our experience with monitoring from the injury site in the neurointensive care unit. 8 The procedure involves inserting a Codman pressure sensor intradurally between the swollen spinal cord and the dura. Acute Spinal Cord Injury: Correlations and Causal Relations Between Intraspinal Pressure, Spinal Cord Perfusion Pressure, . For up to a week after surgery, we monitored limb power, intraspinal pressure, spinal cord perfusion pressure, and tissue lactate-to-pyruvate ratio.

We review state-of-the-art monitoring techniques for acute, severe traumatic spinal cord injury (TSCI) to facilitate targeted perfusion of the injured cord rather than applying universal mean arterial pressure targets.We recently reported a novel method to monitor intraspinal pressure (ISP) and spinal cord perfusion pressure (SCPP) at the site of injury in TSCI patients in NICU.

As a result, controlling SCPP is more important in SCI cases.