Stretching a graph
Stretch a Graph Vertical or Horizontal Examples - .Graph Basic Exponential Functions.In this video you will learn how to stretch and shrink a graph both vertically and horizontally. Figuring out the Shape of a Graph after several Transformations. Where the graph of the tangent function increases, the graph of the cotangent function decreases.We have an exponential equation of the form f(x) = bx + c + d, with b = 2, c = 1, and d = − 3. In general, a vertical stretch is given by the equation y=bf (x) y = b f ( x ) . Note : Point on the original curve : (x, y) Point on the curve after it is horizontally stretched by the factor of k : (kx, y) How to Do Horizontal Compression in a Function. Sometimes graphs are translated, or moved about the xy xy -plane; sometimes they are stretched, rotated .Would stretching in the x direction by scale factor 2 be the . σe = P A0,ϵe = δ L0 (1.The force exerted back by the spring is known as Hooke's law.Translating (Shifting) A GraphorgTransformations of Trig Graphs - Stretch parallel to the x-axis . Combining Translating and Stretching.comStretches and compressions of graphs - Functions - BBC .comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Compressions and Stretches
The procedure for stretching the graph of a function vertically or horizontally is illustrated by the following examples : Question 1 : Define a function g by g (x) = 2f (x), where f is the function defined by f (x) = x 2, with the domain of f the interval [−1, 1]. At first, working with dilations in the horizontal direction can feel counterintuitive. Forces are responsible for changing the motion of objects. What do I need to know about graph stretches? Transformations This page titled 1. According to Hooke’s Law: F = kx. Let g(x) be a function which represents f(x) after a horizontal compression by a . In general, a horizontal stretch is given by the equation y=f (cx) y = f ( c x ) .Stretching a Graph Vertically or Horizontally - Examples.Analysing the Results.thestudentroom.If f is a function and c is a positive constant, then the graph of y = cf ( x) is the graph of y = f ( x ) compressed (shrunk) vertically by a factor of c if c 1.
and theoretically both are just a reflection . y = f (bx), b > 1, will compress the graph of f (x) horizontally.
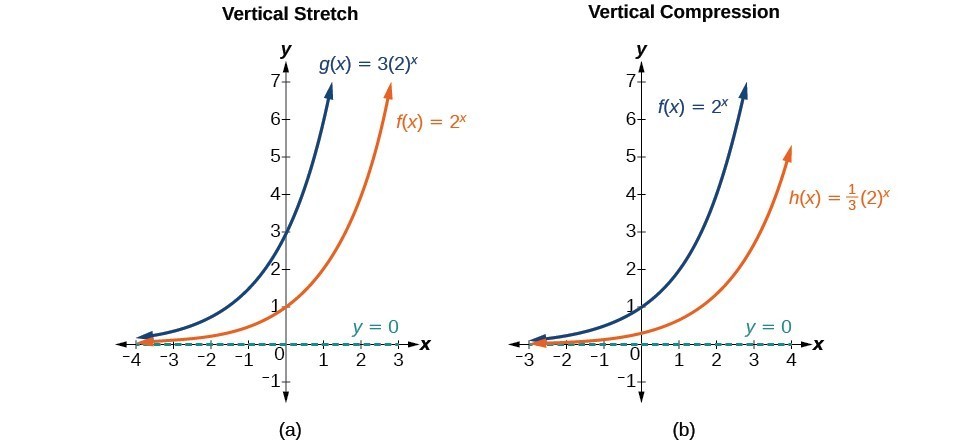
Where the graph of the tangent function decreases, the graph of the cotangent function increases.Notice that the effect on the graph is a vertical stretching of the graph, where every point doubles its distance from the horizontal axis. We can also stretch and shrink the graph of a function.Explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator.com/ExamSolutionsEXAMSOLUTIONS WEBSITE at https://www. So we have two days to get it right and . Let’s start with the midline. If \ (f (x) = x^2\), then \ (af (x) = a (x^2)\). Performing a Sequence of Transformations.
Transformations of Graphs (stretches) : ExamSolutions
By recognizing the family to which a more complex equation belongs, and then identifying what changes have been made to the . Since the cosine function has an extreme point for x = 0, let us write our equation in terms of a cosine function. To stretch or shrink a graph you have to multiply the origi.With a stretch all the points on the graph are moved towards or away from either the x or the y axis by a constant scale factor.
Auteur : Tarcia Hubert
Operations on Functions: Stretches and Shrinks
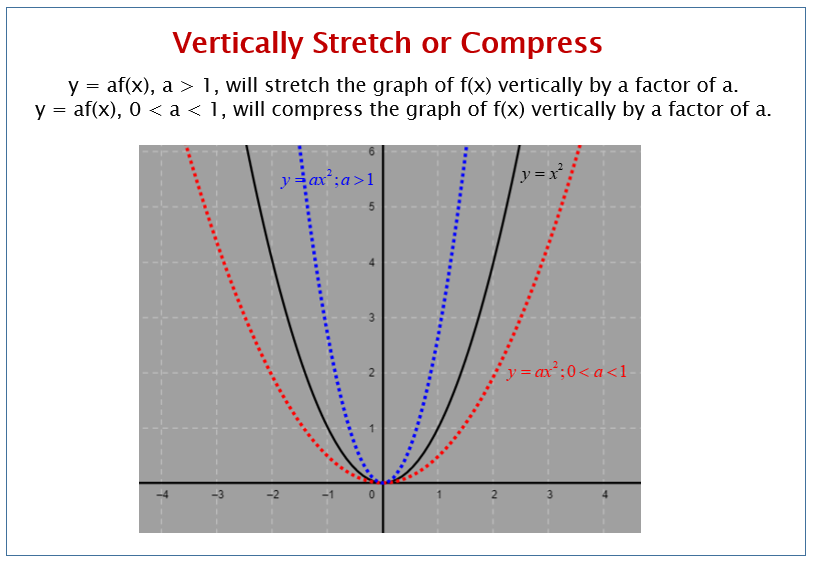
If a < 0 a < 0, the graph is either stretched or .y = Acos(Bx − C) + D.) (Edit: even for lines, the two operations are . A non-rigid transformation 58 changes the size and/or shape of the . In fact, for any exponential function with the form \ (f (x)=ab^x\), \ (b\) is the growth factor of the function. the extension/ compression is no longer proportional to the applied force; The point is identified on the graph where the line starts to curve; The elastic limitWhen the graph of a function is changed in appearance and/or location we call it a transformation.5 Stretching GraphsUnit 4 - Graphs and TransformationsSketching graphs then stretching them in the vertical or . The spring force is called a restoring force because the force exerted by the spring is always in the opposite . y = Load / force, F.GCSE; AQA Trilogy; Forces and elasticity - AQA Hooke's law. Understanding these translations will allow us to quickly recognize and sketch a new function without having to resort to plotting points.Given the graphs of functions f and g, where g is the result of reflecting & compressing f by a factor of 3, Sal finds g(x) in terms of f(x). Plot a graph of the load applied on the horizontal axis and the extension of the spring on the vertical axis and draw a line of best fit.We call the base \ (2\) the growth factor.When we multiply a function by a positive constant, we get a function whose graph is stretched or compressed vertically in relation to the graph of the original function.The key features of the graph are: The limit of proportionality. Stretching a function in the vertical direction by a scale factor of 𝑎 will give the transformation 𝑓 ( 𝑥) → 𝑎 𝑓 ( 𝑥).’ Pick a point, say, (2, -4). Since the given scale factor is 1 2, the new function is 𝑦 = 𝑓 ( 𝑥) 2. The basic function is y = 2x. Learning how we can stretch graphs horizontally can help us . Randy Anderson. And those are the ones that cost us.4K subscribers. Similarly, if f is a function and d is a positive constant, then the graph of y = f ( dx) is the graph of y = f ( x ) stretched .comOperations on Functions: Stretches and Shrinks | SparkNotessparknotes.Stretching Graphs. When x = 0, the graph has an extreme point, (0, 0). (a) Find the domain . To get a sense of the behavior of exponential decay, we can create a table of values for a function of the form f(x) = bx whose base is between zero and one.
Horizontal and Vertical Stretching/Shrinking

Vertical Translation. If more than one force is present, the shape of an object can also be changed. Graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more.For this graph, the number ½ is in front of the ‘x,’ so we DIVIDE the x-values by ½, which is the same as multiplying by the reciprocal, or ‘2. It looks at how a and b affect the graph of f (x).By understanding the basic graphs and the way translations apply to them, we will recognize each new graph as a small variation in an old one, not as a completely different graph that we have never seen before.Vertically Stretching and Shrinking Graphs - YouTube. (Since these two transformations operate perpendicularly to each other, the order they are done does not matter, but it is a good .Graph transformation is the process by which an existing graph, or graphed equation, is modified to produce a variation of the proceeding graph. Gradient = Force constant, k.
Horizontal And Vertical Graph Stretches And Compressions
onlinemath4all.
Squeezing, stretching, and squishing functions
When by either f (x) or x is multiplied by a number, functions can “stretch” or “shrink” vertically or horizontally, respectively, when graphed. This results in the graph being pulled outward but retaining the input values (or .2: Stretching and Reflecting Transformations is shared under a CK-12 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by CK-12 Foundation via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform; a detailed edit .
Manquant :
A translation in which the size and .Vertical and Horizontal Stretches and Shrinks of Graphs
Comparing this to the equation of a straight-line, y = mx.Pearson Edexcel IAL Pure Mathematics 1 Unit 4.Stretching and Compressing Graphs. The key concepts are repeated here.

When the graph gets wider, it is either a vertical shrink or a horizontal stretch: essentially, shrinking TO the x-axis or stretching AWAY from the y-axis.Understanding how changes in the equation of a function result in stretching and/or reflecting and/or the graph of the function is a great way to take some of the mystery out of graphing more complicated equations.If a > 1 a > 1, the graph is stretched by a factor of a a. The graph will shift left 1 unit and down 3 units.net/ where you will have access to all playlists c. A translation in which the size and shape of a graph of a function is not changed, but the location of the graph is. Shifting left 1 unit and down 3 units results in the y-intercept of the basic graph shifting to ( − 1, − 2). Basic Toolkit Functions. The cotangent graph has vertical asymptotes at each value of \(x\) where \(\tan x=0\); we show these in the graph below with dashed lines.Stretches and Shrinks. The input values, \(t\), stay the same while . Now, divide the x-value by ½, which is the same as multiplying the x-value by the reciprocal, 2,graphs will help you analyze the shapes of more complicated graphs. x = Extension, x.ukRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Shifting and Stretching Graphs
YOUTUBE CHANNEL at https://www. Where F s is the force exerted by the spring, x is the displacement relative to the unstretched length of the spring, and k is the spring constant. This means that as the input increases by \ (1\), the output value will be the product of the base and the previous output, regardless of the value of \ (a\). In this text, we will be .Stretches of graphs.< a < 1 0 < a < 1, the graph is compressed by a factor of a a.The engineering measures of stress and strain, denoted in this module as σe and εe respectively, are determined from the measured the load and deflection using the original specimen cross-sectional area A0 A 0 and length L0 L 0 as.
Reflecting & compressing functions (video)
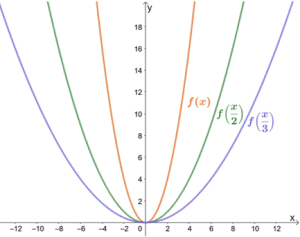
249K views 14 years ago Precalculus. When the stress σe is plotted against the . Let f(x) be a function. In that case, stretching would also stretch the shift, so you should first stretch and only then shift. Given a function f (x), we can formalize .And multiplying by ½ (which is smaller than 1) caused the highs and lows of the original graph to contract, drawing closer to the x-axis.comHorizontal Stretch/Shrink | Desmosdesmos.In order to compress or stretch a function, either from top to bottom or from side to side, we multiply the function, or its argument, by some number. F → s = − k x →. y = f (bx), 0 < b < 1, will stretch the graph of f (x) horizontally. Shifts, stretches, shrinks, and reflections are called transforma-tions. If we multiply a function by a coefficient, the graph of the function will be stretched or compressed. Multiplying the number on the .(The only case I noticed where horizontally shifting and stretching in y-direction aren't interchangeable is for lines, where horizontally shifting is equivalent to vertically shifting. Throughout this section, you will discover how many complicated graphs are derived by shifting, .As you can see, multiplying on the outside of the function by 2 (which is larger than 1) caused the highs and lows of the original graph to go higher and lower. Many graphs of functions can be created from combinations of these transformations. The exercises in this lesson duplicate those in Graphing Tools: Vertical and Horizontal Scaling .The graph of g(x) can be obtained by stretching the graph of f(x) horizontally by the factor k. Exponential decay occurs when the base is between zero and one.Horizontal Stretches and Compressions.Stretching a graph means to make the graph narrower or wider. The graph could represent either a sine or a cosine function that is shifted and/or reflected.
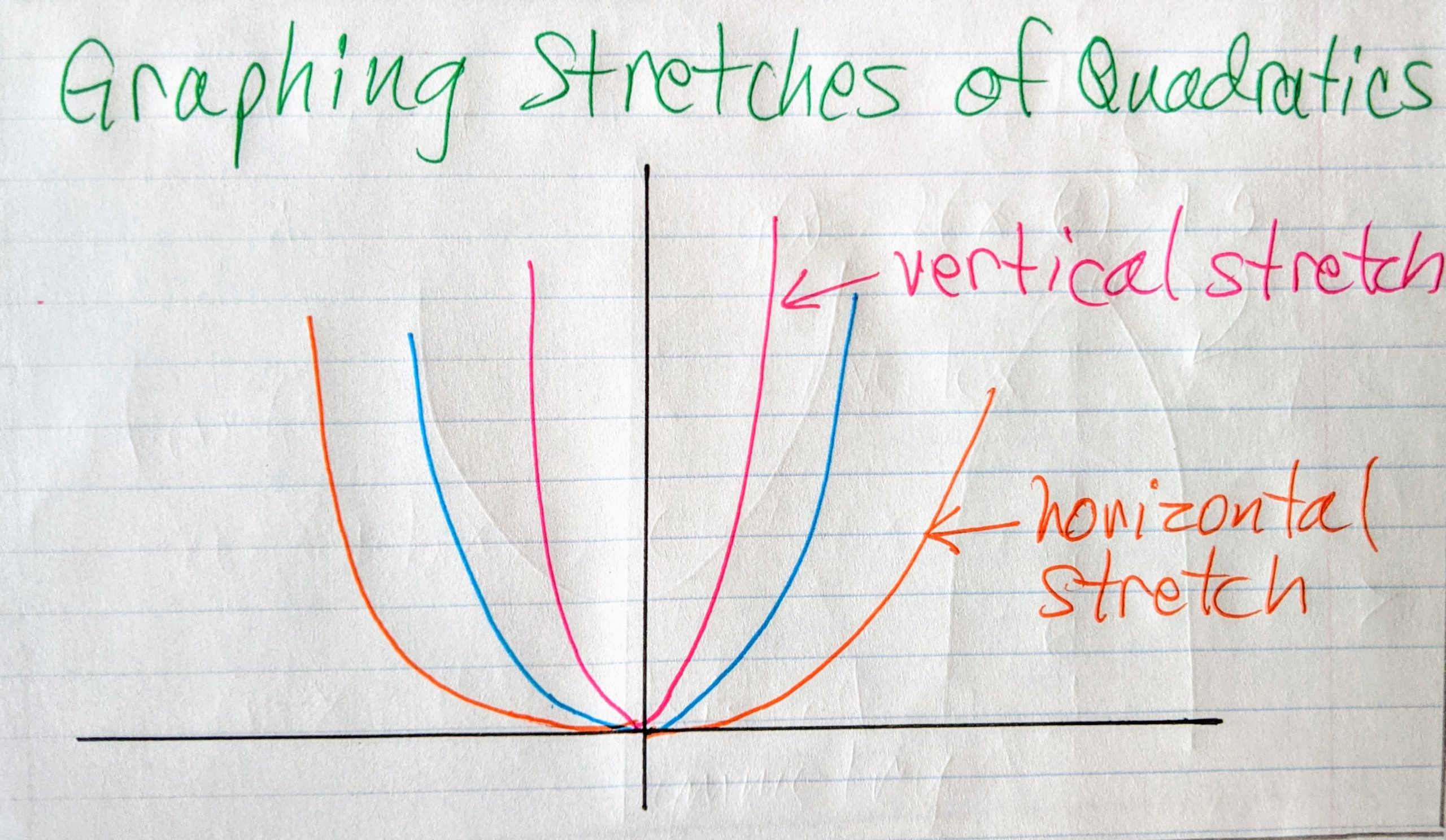
The lesson Graphing Tools: Vertical and Horizontal Scaling in the Algebra II curriculum gives a thorough discussion of horizontal and vertical stretching and shrinking. Translating Graphs.Horizontal stretches happen when a base graph is widened along the x-axis and away from the y-axis.












:quality(70):focal(983x596:993x606)/cloudfront-eu-central-1.images.arcpublishing.com/liberation/CIYJOUQET5CVBGGZXDIMM2AP4Q.jpg)
