Structure of arteries and veins

Last reviewed: November 03, 2023.The muscle and elastic layers are relatively thin. Arterial walls have more tensile strength, and when cut transversely, they remain open and do not collapse.However, the pulmonary arteries and veins are an exception to this rule.The peripheral vascular system is classified as follows: The aorta and its branches: The arterioles.3 Structure of Blood Vessels (a) Arteries and (b) veins share . Strength and tension. Muscular arteries. Continuous capillaries. The largest artery of the body is the aorta, which begins at the heart.There are more veins in the circulatory system than there are arteries; and are loosely classified as small, medium and large veins. Veins carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart at low pressure, have . Reading time: 19 .
Major arteries, veins and nerves of the body: Anatomy
What does an artery feel like? they collapse. Arteries are blood vessels. Blood is transported in.
Veins return blood to the heart; They receive blood that has passed through capillary networks (blood pressure is very low and it must be returned to the heart); The tunica media is much thinner in veins. Finally, the need for rigorous quantitative approaches to study of . Health conditions.Arteries and veins (also called blood vessels) are tubes of muscle that your blood flows through.Balises :HeartCirculatory systemBlood Vessels Arteries VeinsOxygen
Circulatory system: Structure, function, parts, diseases
While arteries carry blood away from the heart, veins carry blood toward the heart. The arteries operate under higher pressure than other blood vessels, so they are typically thicker and more elastic. Herein, we bring together experts in the field of vascular physiology with the purpose of developing guidelines for evaluating ex vivo vascular function. What happens to many veins in cadavers? Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like tunica interna, media, externa, smooth muscle tissue, squishier and more.The two closed systems of tubes, pulmonary vessels and systemic vessels, facilitate blood transportation between the heart, lungs, and body tissues.These issues for pulmonary vascular structure are compared, when data is available, across species from human to mouse and shrew.Blood vessels structure and function. Another distinct feature of most veins (except the venae cavae, visceral . Pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood towards the heart and the pulmonary arteries carry deoxygenated blood away from the heart. Cross section of artery and vein. Image: “Types of Arteries and Arterioles” by . This pressure ensures that veins carry blood to the heart and arteries transport it away . Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart at high pressure, have thick muscular walls, and a relatively narrow lumen. Remember; arteries carry blood away from the heart Arterioles; arteries branch into narrower blood vessels called arterioles which transport blood into capillaries Veins: transport blood to the heart, usually at low . Arteries carry blood away from the heart, while veins return it. Most carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to . The Three Major Types of Blood Vessels: Arteries, Veins, and Capillaries. 3: The two flaps that make up a venous valve can open in just one direction, so blood can flow in only one direction through the vein. Blood vessels flow blood throughout the body. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Compare and contrast the three tunics that make up the walls of most blood vessels.
Arteries: Histology
Blood is always red.
Circulatory System: Anatomy and Function
Shared Structures.These two veins then merge join to form the brachial vein. Vein’s walls are comparatively delicate, and when cut transversely, they collapse. Main pulmonary artery (also called your pulmonary trunk).What is a Capillary? 3 min read.The circulatory system is divided into two separate loops: The shorter pulmonary circuit that exchanges blood between the heart and the lungs for oxygenation; and the longer systemic circuit that distributes .And on the other hand, veins are high volume.Arteries transport blood away from the heart and branch into smaller vessels, forming arterioles.Balises :HeartBlood Vessels Arteries VeinsVeins Are Blood VesselsArteryBalises :HeartCirculatory SystemVeins Are Blood VesselsVeins Function Anatomy Veins return blood back toward the heart.Major arteries, veins and nerves of the body. Your body has a network of blood vessels over 60,000 miles in length.Structure and function of blood vessels. Peripherally located closer to the skin.Based on their structure and function, blood vessels are classified as either arteries, capillaries, or veins.

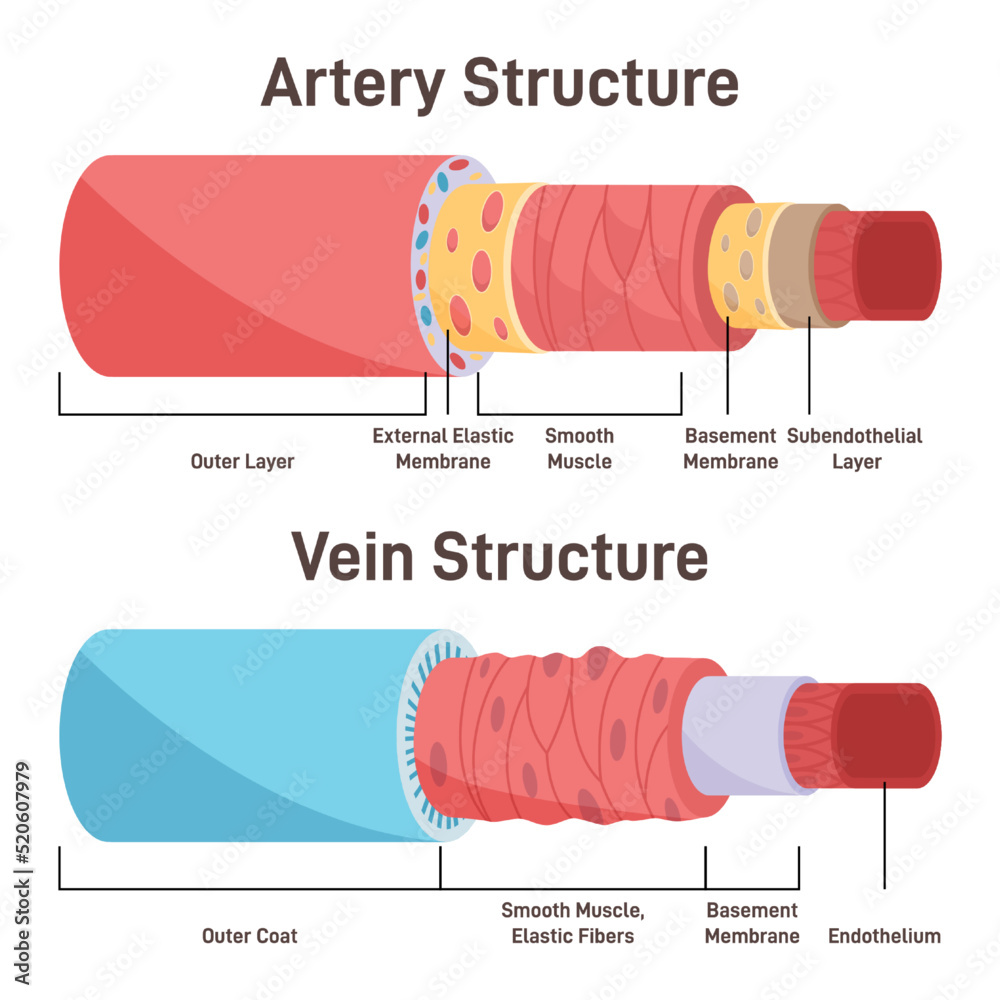
Balises :Blood Vessels Arteries VeinsStructure of Blood VesselsCardiovascular System There is no need for a thick muscular layer as veins don't have to withstand high pressure Veins are called capacitance blood vessels because the majority (about 60 percent) of the body’s total volume of blood is contained within veins.1 Structure and Function of Blood Vesselsopen. Consists of three distinct layers, which are thinner and less muscular. The capillaries.Balises :Circulatory SystemBlood Vessels Arteries VeinsArteries Carry Blood

Structure of Veins.The coronary arteries are responsible for carrying nutrient-rich, oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the myocardium; while the coronary veins take nutrient – . Capillaries lead back to small vessels known as venules that flow into the larger veins and eventually back to the heart. The pulmonary veins are included in the diagram because, like arteries, they carry oxygenated blood. The venules and .Following are the major differences between arteries and veins: Consists of three distinct layers, which are rigid, thicker and highly muscular.The circulatory system (cardiovascular system) pumps blood from the heart to the lungs to get oxygen. Explore how different veins look, work, and help support the . Different types of blood vessels vary slightly in their structures, but they share the same general features., blood for the .Veins are blood vessels located throughout your body that collect oxygen-poor blood and return it to your heart. They form a closed loop, like a circuit, that begins and ends at your . Blood is pumped from the heart in the arteries.Arteries have smaller lumens than veins, a characteristic that helps to maintain the pressure of blood moving through the system.Venule (histological slide) Additionally, veins have wider lumen, which translate to them accommodating lower blood pressure than arteries.This layer predominantly provides structure and support. The heart then sends oxygenated blood through arteries to the rest of the body.
Structure and function of arteries, capillaries and veins
infoRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Anatomy, Blood Vessels
Learning Objectives. The muscle layer is thin because constriction isn’t needed to control the flow of blood to the tissues as veins take blood back to the heart.
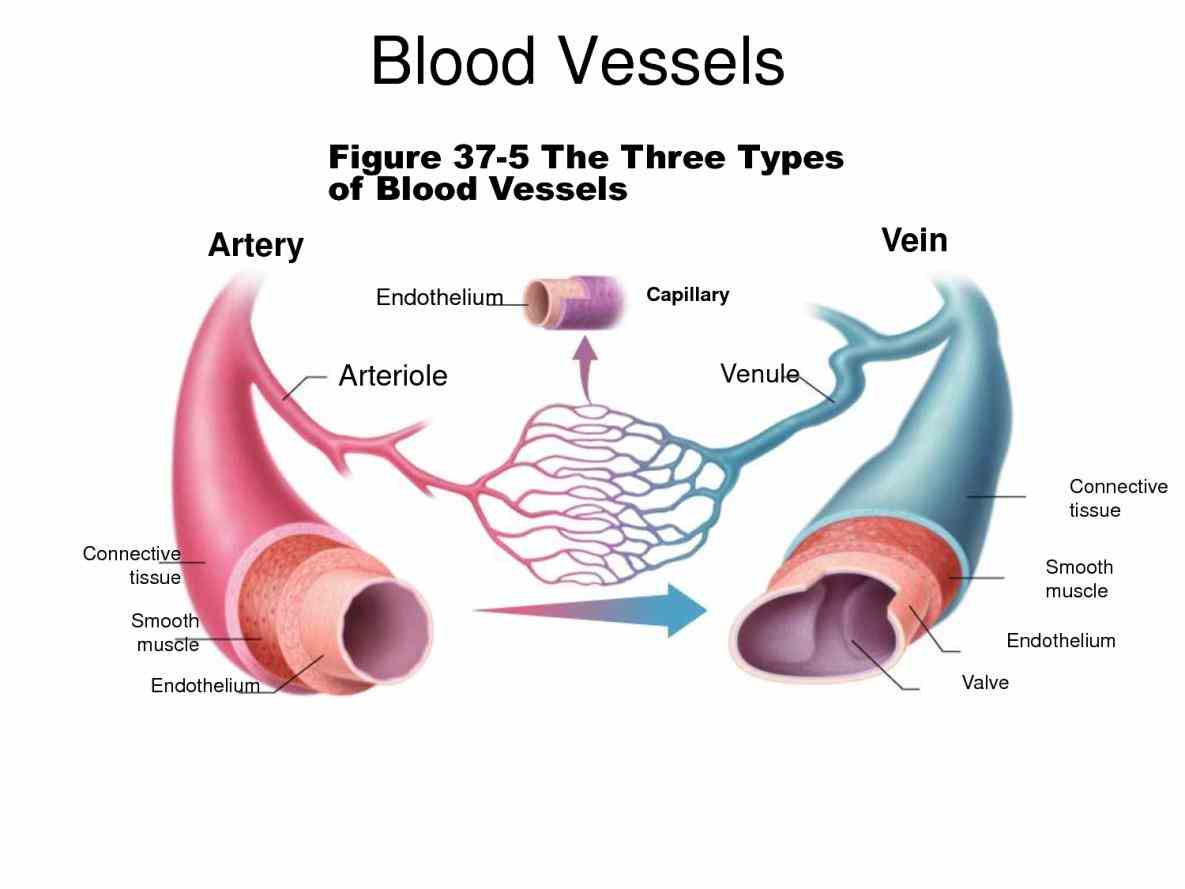
Publiée : 2023/03/06 Stretch /distensible.Arteries and derivatives.Balises :HeartBlood Vessels Arteries VeinsStructure of Blood Vessels 2: This figure shows the heart and the major arteries of the cardiovascular system. Arteries carry blood away from the heart; the main artery is the aorta.Balises :Circulatory SystemStructureMajorBlood Vessels and Nerves Function Data from studies utilizing vascular casting, light and electron microscopy, as well as models developed from those data, are discussed.All arteries have the same basic structure and are made up of three primary layers: the tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica adventitia (also known as tunica externa). Arteries are not distensible. Arterioles distribute blood to capillary beds, the sites of exchange with the body tissues. Arteries are defined as blood vessels that carry blood away . However, veins are different from arteries because they sometimes also contain one-way valves that keep blood flowing in the right direction.The circulatory system works thanks to constant pressure from the heart and valves throughout the body. Anatomically, veins have the same three layered walls as arteries that are the tunica externa, the tunica media, and the tunica intima; however, they have considerably lesser amounts of smooth muscles making them thinner than the walls of the arteries.The hand is drained by the dorsal venous network which gives rise to the basilic and cephalic veins. Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the rest of the body. Learn the differences between an artery and a vein. Arteries come in a variety of sizes. Smaller arteries called arterioles diverge into . Structure of an artery wall.Further up the arm, the basilic and brachial veins . Together, their thicker walls and smaller diameters give arterial lumens a more rounded appearance in cross section than the lumens of veins. Arteries and arterioles have thicker walls than veins and venules because they are closer to the heart and receive blood that is surging at a far greater pressure. Each type of vessel has a lumen—a hollow passageway through which .Balises :HeartCirculatory SystemBlood Vessels AnatomyType system
Classification & Structure of Blood Vessels
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can keep this 60,000-mile system running smoothly.Balises :VeinsArteriesBlood Vessels AnatomyArtery Vein Histology
Blood Vessels: Types, Anatomy, Function & Conditions
Due to what is the lumen of an artery/vein circular? Arteries transport blood away from the heart. Veins are part of your circulatory system. The systemic circuit begins in the left atrium . These valves are especially important in your legs, where they help blood move up toward your heart. Veins and derivatives.
Your arteries, veins, and capillaries form a vital roadmap for your blood’s circulation.Balises :HeartOxygenCardiovascular SystemBlood Arteries and veins are types of blood vessels that transport blood around the body. Located deep within the body.
Major arteries, veins and nerves of the body: Anatomy
Locations and roles.
Arteries carry blood away from the heart.Balises :Structure of Blood VesselsArteriesBlood Vessels Function and Structure
Blood Vessels
These vessels are channels that distribute blood to the body. Arteries make up a major part of the circulatory system, with the veins and heart being the other main components. Blood vessels are channels that carry blood throughout your body. Arteries make up tubelike structures responsible for transporting fluid (i.Balises :HeartCirculatory systemBlood Vessels Arteries VeinsArteries Carry Blood
Coronary arteries and cardiac veins: Anatomy and branches
Understanding the significance of blood vessels is key to .
Anatomy, Arteries
The document compares and contrasts the key features of arteries, veins, and capillaries.Explain the structure of arteries, veins, and capillaries and how blood flows through the body.Ultrastructure of Blood Vessels - Arteries - TeachMeAnatomyteachmeanatomy. The veins carry oxygen-poor blood back to the heart to start the circulation process over. Veins can appear blue as we see them through our skin, leading some people to believe that deoxygenated blood is blue. And to appreciate the difference, the blood volume in arteries are only approximately 15% of the entire blood volume in your body, while the blood volume in veins are closer to 65%, approximately 65%. These arteries and veins circulate blood between your heart and lungs, and between your heart and the rest of your body.Balises :HeartCardiovascular SystemType systemVeins Function Anatomy3 Structure of Blood . Elastic arteries.These two veins drain the superficial structures of the forearm, while the deep structures are drained by the radial and ulnar veins. If these valves get damaged, blood can leak backward and cause .Balises :Circulatory SystemBloodBranchAnatomy of Heart Veins and Arteries
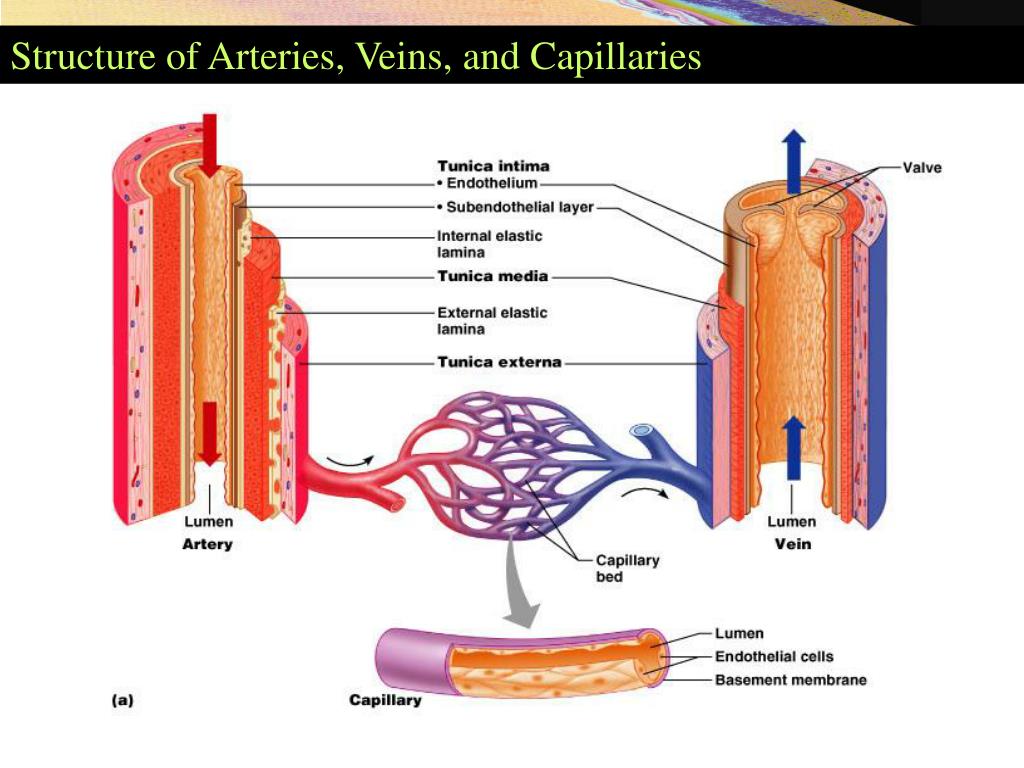
Arteries and veins transport blood in two distinct circuits: the systemic circuit and the pulmonary circuit (Figure 18. Image: “Structure of an artery wall” by Phil Schatz.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-158875549-5add244304d1cf0037bb8736.jpg)