Succinylcholine mechanism of action
Last updated on Aug 29, 2023. Sustained release: 180 to 540 mg once or twice daily (doses separated by at least 6 hours); Note: It may be necessary to use immediate-release therapy in conjunction with sustained-release therapy.
Acetylcholine and succinylcholine
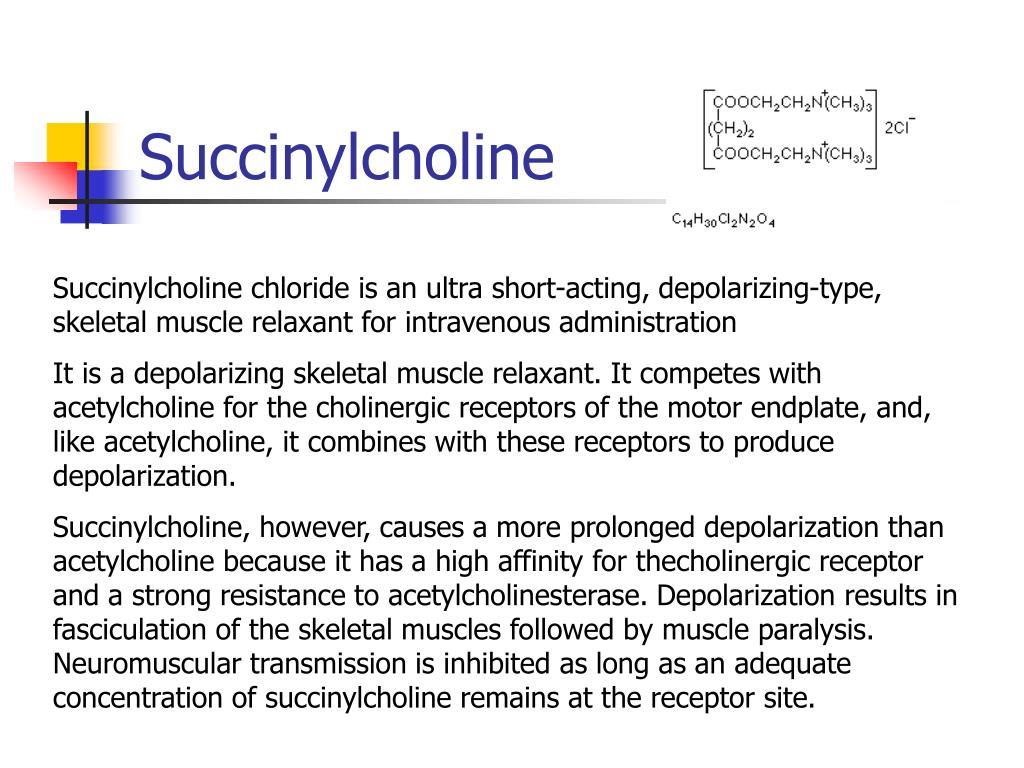
Rocuronium is a non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocker widely used to produce muscle relaxation to help facilitate surgery and ventilation of the lungs in elective and emergent situations.Structure of two acetylcholine molecules linked through acetate methyl groups. La dose active produisant 95 % de bloc à l'adducteur du pouce (DA95) est de 0,3 mg·kg-1. See also: Succinylcholine Chloride (has .8 Mechanism of Action Succinylcholine is a depolarizing neuromuscular blocker, meaning it causes a prolonged period of membrane depolarization in order to exert its therapeutic effects.
PHARMACOKINETICS AND PHARMACODYNAMICS OF SUCCINYLCHOLINE
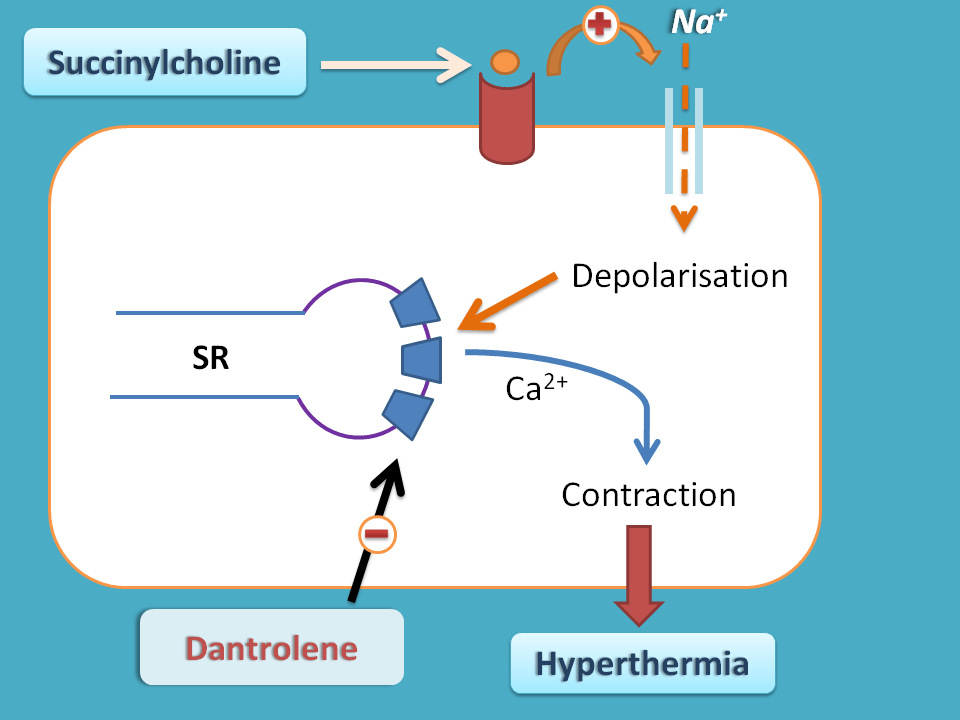
Schematic representation of succinylcholine metabolism and mechanism of action.Overview
Pharmacology of neuromuscular blocking drugs
The mechanism of action is apparent within 60 seconds of intravenous administration and continues up to 360 seconds or 6 minutes.
Depolarizing Neuromuscular Blocking Agents
The drug inhibits acetylcholinesterase which is responsible for the degredation of acetylcholine. So, with acetylcholinesterase inhibited, more acetylcholine is present By interfering with the breakdown of acetylcholine, neostigmine indirectly .PHARMACOKINETICS AND PHARMACODYNAMICS Succinylcholine is hydrolyzed by plasma cholinesterase to succinylmono- choline and choline.Succinylcholine is a depolarizing muscle relaxant that has been used for rapid sequence induction and for procedures requiring only a brief duration of muscle relaxation since the . FDA Pharm Classes.
Succinylcholine: Indications, Side Effects, Warnings
Medically reviewed by Drugs. Diagram Legend.What is the mechanism of action of succinylcholine?Succinylcholine: new insights into mechanisms of action of an old drug.Mechanism of Action.
Pyridostigmine: Dosage, Mechanism/Onset of Action, Half-Life
It acts like acetylcholine and is . Succinylcholine is one of the most widely used muscle relaxants in clinical anesthesia and emergency medicine.Unfortunately, succinylcholine also has a number of well-described complications related to its mechanism of action or pharmacokinetics or that occur as an idiosyncratic effect (Table 23-1).This activity outlines the indications, mechanism of action, methods of administration, important adverse effects, contraindications, monitoring, and toxicity of . Pathway images and data are available under a Creative . A depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent, succinylcholine adheres to post-synaptic cholinergic . Thus succinylcholine is ineffective on the smooth and cardiac muscles of the body.To address questions of specificity and mechanism of action of this important anesthetic adjunct, we obtained a cryo-EM structure of the Torpedo nicotinic receptor in complex with succinylcholine . Classification.

Note: Inhaled anesthetic agents prolong the duration of action of rocuronium.6: Depolarizing Blockers: Mechanism of Action. Depolarizing blockers act on skeletal muscle fibers' membranes and induce their depolarization. MECHANISM OF ACETYLCHOLINE When a nerve action potential reaches and invades the nerve terminal, a shower of acetylcholine vesicles is released into the junction (synapse) between . The aim of this study was to investigate the . Long-acting inhibition of cholinesterase enhances activity of endogenous acetylcholine. “ Suc k it! You can’t get to the ACh receptors. Neuromuscular blockade is achieved by disrupting this pathway.
Neuromuscular blocking agents like succinylcholine and pancuronium work by blocking acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction which results in skeletal muscle paralysis.Mechanism of Action 1.Mécanisme d'action.
Succinylcholine Chloride
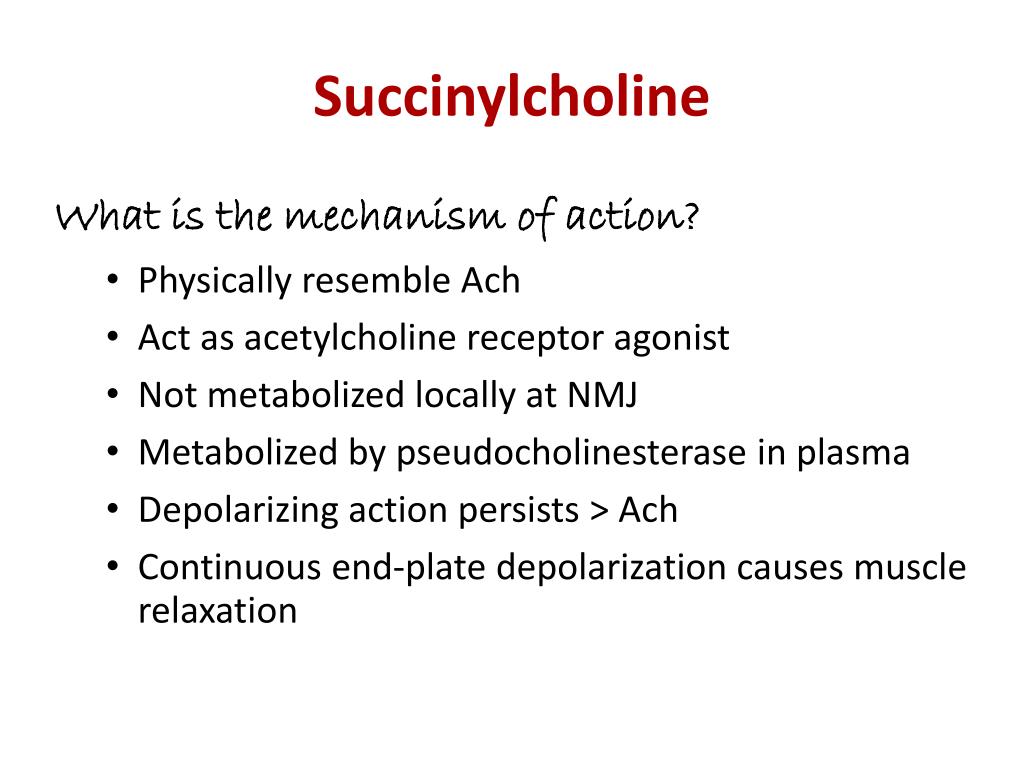
+ + + Action + + Prevents neuromuscular . Metabolism: Plasma pseudocholinesterase hydrolysis. Onset: IV: 30-60 seconds; IM: 2-3 minutes.Here are the main steps in succinylcholine's mechanism of action: Binding to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: Succinylcholine acts as an agonist at the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors located at the neuromuscular junction.Succinylcholine: New Insights into Mechanisms of Action of an Old Drug. Excretion: Urine.The physiologic effect of succinylcholine is by means of Neuromuscular Depolarizing Blockade. Voltage-gated sodium channels then close and are inactivated, while the membrane remains . Succinylcholine is the only depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent that is currently in use.

Duration of Action: IV: 4-6 minutes; IM 10-30 minutes. Anesthesiology. It binds to the post .06 mg/kg given 1.La succinylcholine agit rapidement (1-1,5 min après l'injection) et sa durée d'action est courte (8-12 min) [1]. Although the clinical advantages and cardiovascular side effects are well known, its mechanism of action within the human nicotinic cholinergic receptor system remains to be understood.Succinylcholine is the only depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent that is currently in use. Therapeutic: neuromuscular blocking agents—depolarizing + + + Indications + + Used during surgical procedures to produce skeletal muscle paralysis after induction of anesthesia and provision of opioid analgesics. Observations show that hyperkalemia and cardiac arrest develop soon after succinylcholine administration to patients with thermal injury, trauma, upper and lower .1097/00000542-200604000-00004. Note: the star symbol on the DHPR indicates that it has been activated by depolarization .The duration of action of succinylcholine is dose related with wide interindividual variations.Succinylcholine is a depolarizing NMBD that acts as an agonist at postjunctional nicotinic receptors.
Publiée : 2023/02/20La succinylcholine est un curare dépolarisant qui produit une action curarisante probablement par désensibilisation des récepteurs nicotiniques à la plaque motrice. It causes muscle fasciculation, depolarization block . Succinylcholine is the only depolarizing NMBD in clinical use. McLeod, Russ B. Use lower end of the dosing range; redosing interval guided by monitoring with a peripheral nerve stimulator.
Suxamethonium chloride
Bloqueur neuromusculaire dépolarisant; comme l’acétylcholine, la succinylcholine se lie aux récepteurs nicotiniques postsynaptiques de la jonction . Ces caractéristiques n'ont rien à voir avec son mécanisme . Reduced degradation of acetylcholine leads to continuous stimulation of the ciliary muscle producing miosis; other effects include potentiation of accommodation and facilitation of aqueous humor outflow, with attendant .
Dantrolene
While there are many indications for the use of dantrolene, its primary indication, and FDA-approved usage in both children and adults, is for the treatment of malignant hyperthermia: the very rare but life-threatening disorder . Preinduction defasciculation (off-label use): IV: 0. It mimics the action of .: 126 In patients with genotypically normal plasma cholinesterase, a dose of 1 mg/kg has been found to produce a mean duration of apnea of 5.Background: Succinylcholine is one of the most widely used muscle relaxants in clinical anesthesia and emergency medicine. Depolarizing NMBAs bind to cholinergic receptors on the motor endplate, causing initial depolarization on the endplate membrane followed by blockade of neuromuscular transmission. Bind to nicotinic receptors, resulting in depolarization with opening of voltage-gated channels and muscle contraction.Auteur : Jonas Appiah-Ankam, Jennifer M Hunter
Succinylcholine
Mechanism of Action: Depolarization of the myoneural junction motor endplate. 2006 Apr;104 (4):633-4.Succinylcholine, a depolarizing muscle relaxant, has a rapid onset of action and works by inducing fasciculations of muscle followed by flaccid muscle paralysis .5 to 3 minutes before administration of succinylcholine (Harvey .
Pharmacology: Neuromuscular Blocking Agents & Muscle Relaxants
Suxamethonium / Succinylcholine.Dantrolene sodium is a postsynaptic muscle relaxant with multiple indications in the fields of anesthesiology and neurology.Mode of action.These agents are classified according to their mechanism of action.Succinylcholine works as an acetylcholine agonist, mimicking the action of acetylcholine by depolarization of the post-junctional membrane .
Suxamethonium Chloride
succinylcholine (sux-sin-il-koe-leen) Anectine, Quelicin.

It is one of the many non-depolarizing neuromuscular blockers that is used but has the distinct advantage of being fast-acting and reversible. Jeevendra Martyn, M.Drug class: Neuromuscular blocking agents.
Succinylcholine : Anectine(md), Quelicin(md), suxaméthonium
Succinylcholine's pharmacological and chemical composition makes it neuromuscular receptor site-specific.
Succinylcholine Chloride
La succinylcholine, curare dépolarisant, est un agoniste de l’acétylcholine. Depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agents, such as succinylcholine, open the AChR ion channels, . It is effectively two ACh molecules joined through the acetate methyl groups. Altman, Teri E. Succinylcholine’s mechanism works by the persistent depolarization and subsequent blockage of the nicotinic postsynaptic acetylcholine receptors in the neuromuscular junctions. Mechanism of Action Composed of two acetylcholine molecules joined at the acetate methyl group. 1 It exerts a sort of reversible competitive antagonistic effect at post-synaptic nicotinic receptors, reducing the probability of activation via ACh by repeatedly associating and dissociating from these receptors - in doing so, . Elle induit un bloc dépolarisant, mais peut produire un bloc non .

Propofol
Propofol acts by enhancing the inhibitory effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) through its interactions with GABAA receptors, which are ligand-gated chloride channels, in the central nervous system (CNS).Stylized cells depicting the metabolism and mechanism of action of succinylcholine. Propofol binds to specific sites on GABA A receptors, located at the interface between the α and β . Depolarizing drugs are agonists at ACh receptors.