Svt ecg criteria
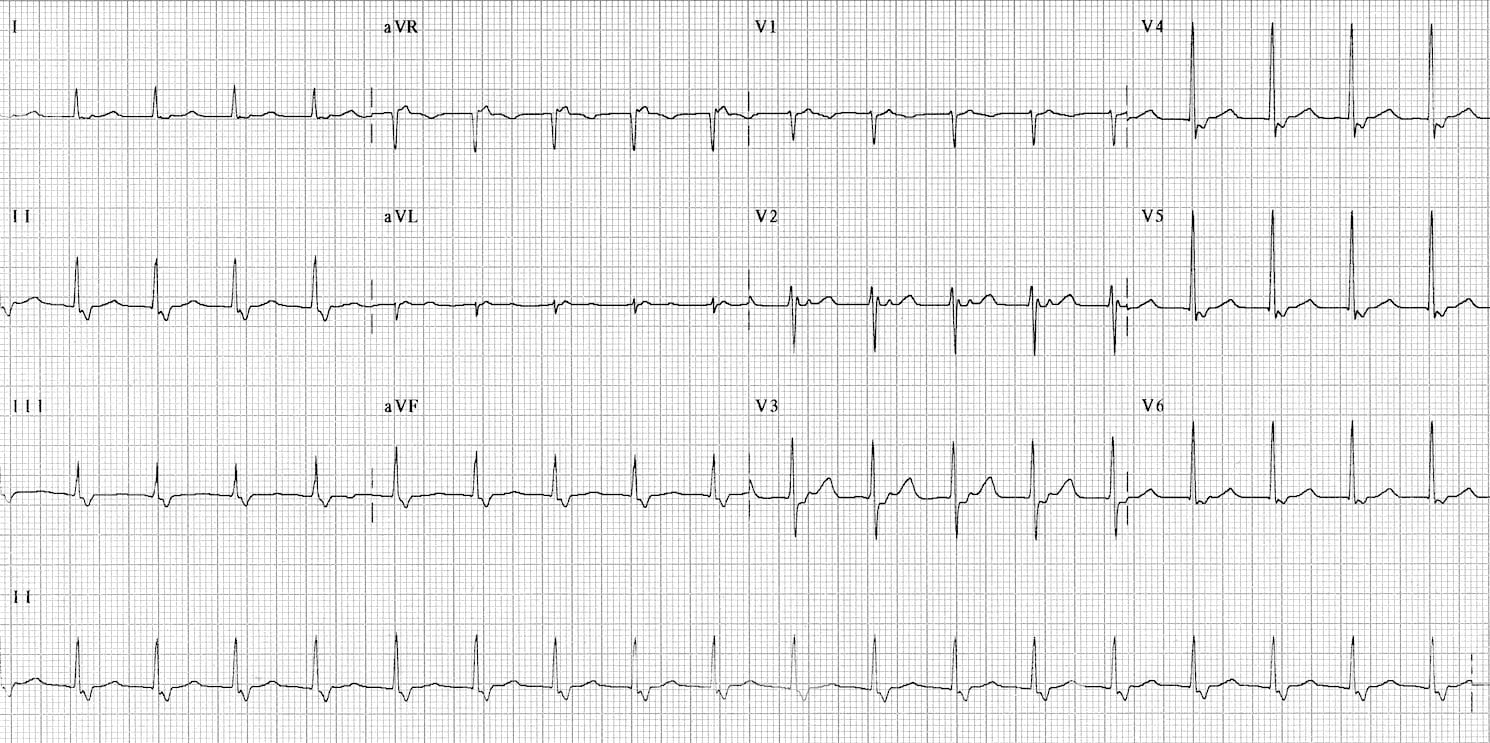
ST elevation in V1-3.Prépa ECG : définition, difficulté et matières.De afkorting SVT staat voor supraventriculaire tachycardie: een tachycardie die BOVEN het ventrikel vandaan komt. Prominent U waves in .This ECG fulfils the Brugada Morphology Criteria for VT.<45 .Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) occurs when the heart experiences a disruption of electrical activity, triggering rapid beating. When considering the heart is a pump and if everything else is functioning properly, we should expect a patient with accelerated junctional rhythm to display signs of normal .
Clinical Practice Guidelines : Supraventricular Tachycardia SVT
ECG changes in acute pericarditis, myocarditis, perimyocarditis.Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is caused by faulty signaling in the heart. Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). It relates to pre-excitation of the ventricles, and therefore often causes an associated shortening of the PR interval. Most SVT in children is due to a re-entrant mechanism and usually occurs in otherwise normally well children.ECG criteria for left bundle branch block (LBBB) It is easy to diagnose left bundle branch block (LBBB). Because of the paroxysmal nature of SVT, ECG findings may be normal . The P-wave is positive in lead II. Have the ESC Pocket Guidelines with you all the time. Sinus tachycardia fulfills all criteria for sinus rhythm but the heart rate is faster than 100 beats per minute.
Supraventricular Tachycardia
The ECG is used to diagnose acute pericarditis.
Ventricular Tachycardia
Supraventriculaire tachycardie (SVT)
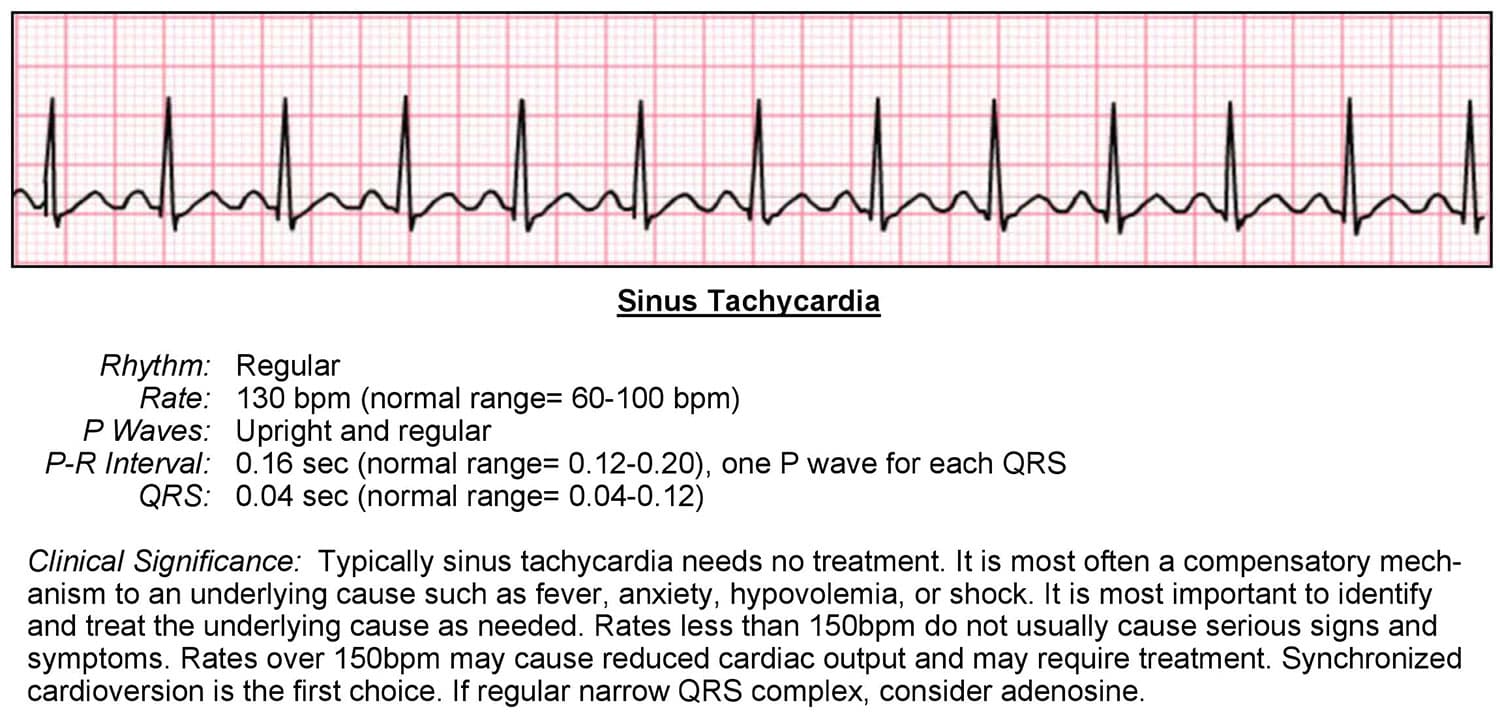
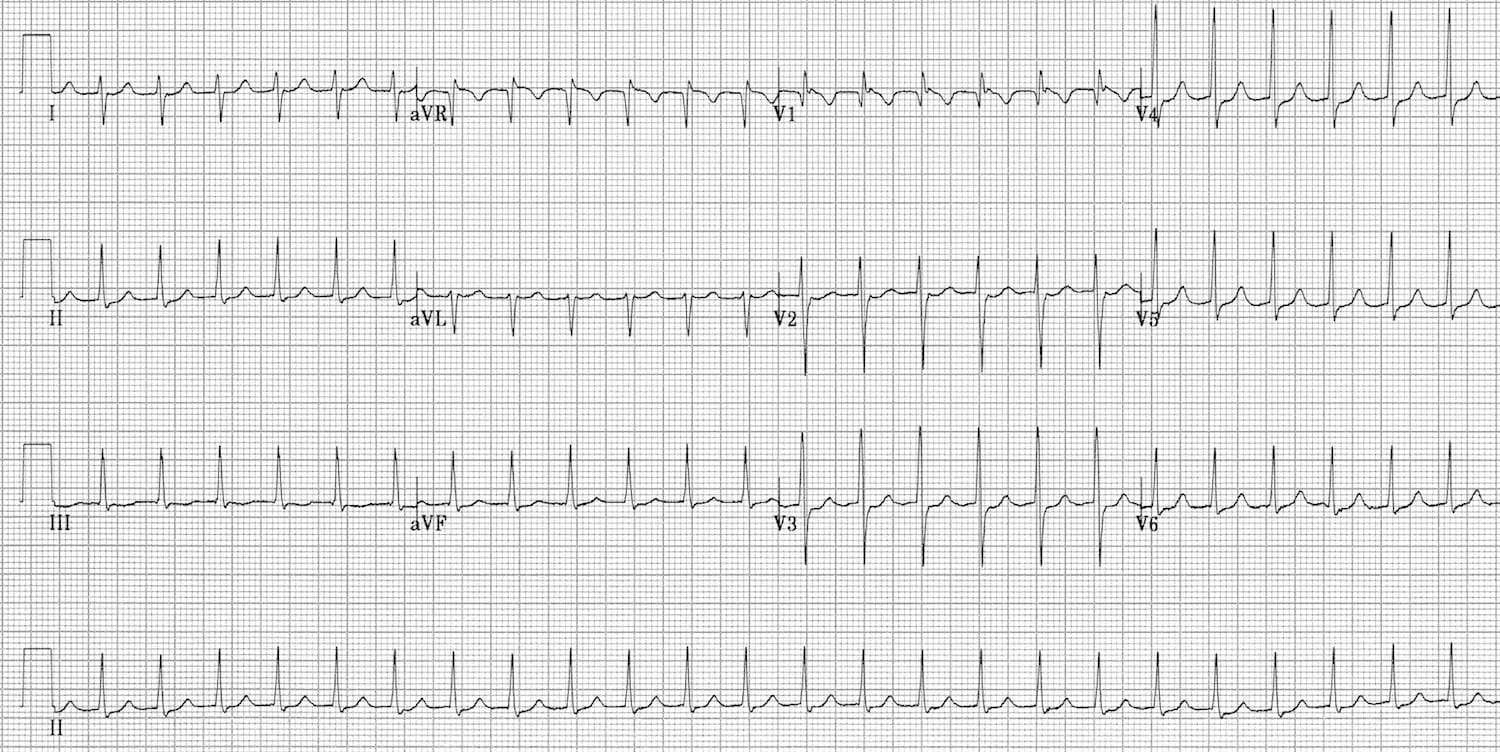
Rate: Fast (150-250 bpm) Rhythm: Regular.
The delay between activation of the RV and LV produces the characteristic “M-shaped” R wave seen in lateral leads.Ed Burns and Mike Cadogan. This cardiac rhythm occurs due to improper electrical conduction within the heart that disrupts the coordination of heartbeats. Hommes: onde S en V3 + onde R en aVL > 28 mm. The QRS complex is generally normal, unless there is concomitant intraventricular conduction disturbance. Thus, the ECG criteria for sinus tachycardia follows. Electrical signals in the heart control the heartbeat. In addition to prolonged QRS duration, LBBB is characterized by deep and broad .12 s) or more is required to diagnose a complete left bundle branch block. Expand Search Menu. Suite à la réforme du lycée initiée par Jean-Michel Blanquer en 2021, la . It is often referred to as Brugada sign.Conventional ECG criteria have reduced sensitivity to distinguish VT from SVT with aberrancy in patients with idiopathic VT. A 24-hour ECG (heart monitor) may be used to record the heart rhythm continuously.Definition (criteria) for sinus rhythm.The Brugada criteria are sensitive and specific for distinguishing between SVT with aberrancy and ventricular tachycardia.
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) patient information
ECG Features: Sinus tachycardia – the most common abnormality (seen in 44% of patients with PE) Complete or incomplete RBBB (18%)This article is a guide for interpreting abnormal Supraventricular Tachycardia EKGs, including qualifying criteria and a sample EKG rhythnm strip. Major Prépa > Intégrer une prépa > La prépa ECG : débouchés, spécialités et contenu. Indice de Cornell. The heart can't fill with blood properly. This quick test checks the .In order to provide the reader with knowledge on this matter, we will now discuss the characteristics of all ECG .Supraventricular tachycardias (SVTs) are a common cause of presentation to primary and secondary care services and can cause significant patient discomfort and . With very fast heart rates the P waves may be hidden in the preceding T wave, producing a ‘camel hump’ appearance.The following are key points to remember from the 2019 European Society of Cardiology (ESC) guidelines for the management of patients with supraventricular .The criteria is the same with the only difference being the heart rate range is 60 – 100 bpm.
If the patient is experiencing SVT during the ECG, a clear diagnosis can be made. Sinus tachycardia: Heart rate 150 bpm.
Sinus rhythm: physiology, ECG criteria & clinical implications
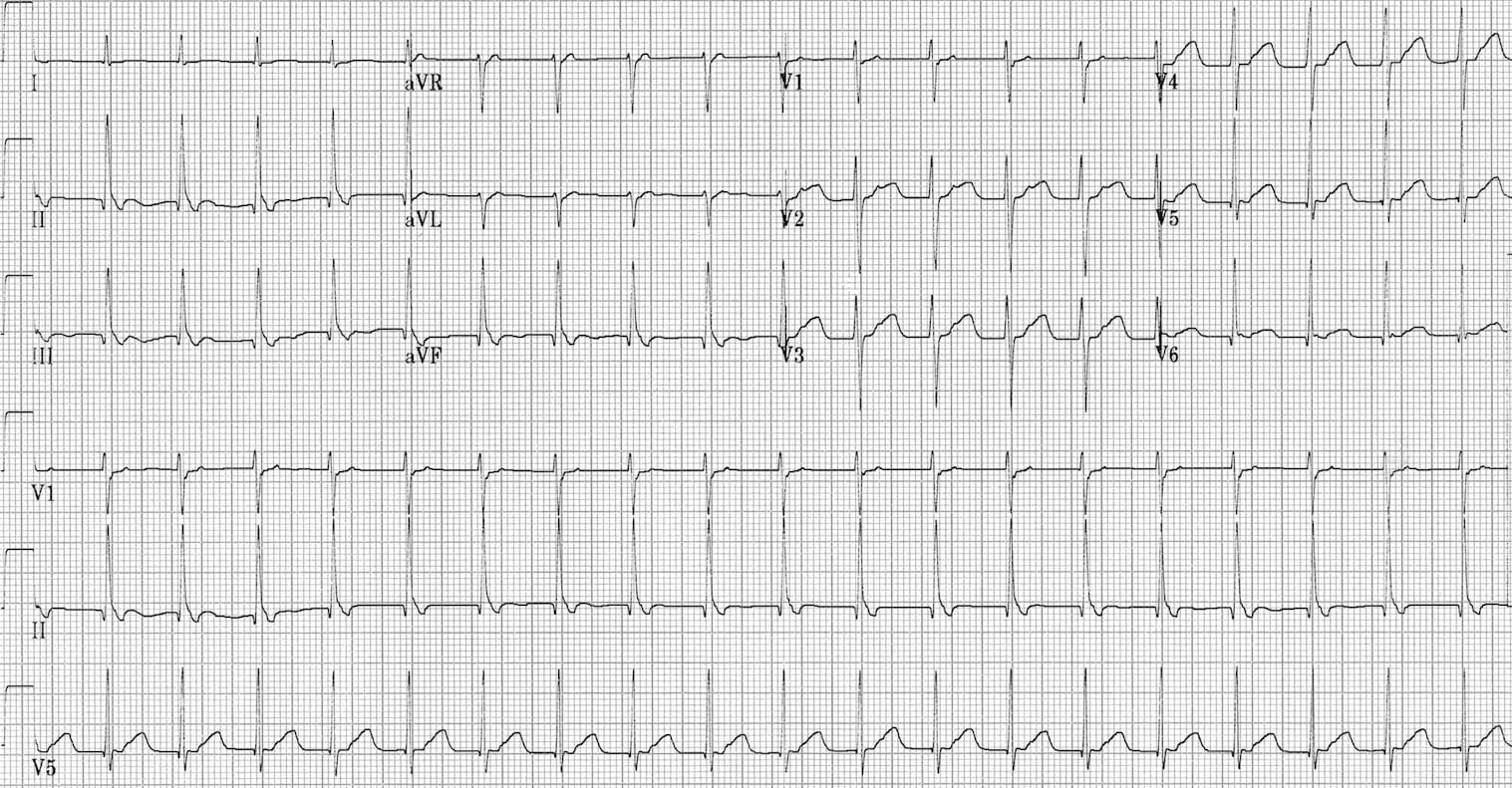
LV strain pattern with ST depression and T-wave inversions in I, aVL and V5-6. Regular broad complex tachycardias can be ventricular (VT) or supraventricular (SVT with aberrancy) in origin, .
#2: B is for Broad complexes. The hallmark of LBBB is the prolonged QRS duration.AVNRT characteristic findings on the electrocardiogram are: Regular narrow QRS complex tachycardia with heart rate between 120 and 250 bpm. This ECG abnormality must be associated with one of the following clinical criteria to make the diagnosis: Documented ventricular fibrillation (VF) or polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (VT).Critères diagnostiques ECG de l'hypertrophie ventriculaire gauche. Voie royale pour intégrer une grande école, découvrez tout ce qu'il faut savoir sur la prépa ECG.< 1) See “VT versus SVT with aberrancy” for more details.Critiques : 5
ESC Guidelines on Supraventricular Arrhythmias
Common symptoms include palpitations, .

SV rhythm rates are above 100 beats per minute and are typically 150-250 bpm. Findings or Leads on ECG Assessed Interpretation; QRS complex in leads V1-V6 (Brugada criteria) 73 • Lack of any R-S . Figure 1 (below) shows normal sinus rhythm at paper speed 25 mm/s. Explore SVT symptoms and causes. Access myPennMedicine 800-789-7366. Clinicians should be aware that application of c .

In the novel Basel algorithm, VT was diagnosed in . Dat kunnen best een aantal aritmieën zijn en om die onder één noemer te scharen is de term ‘supraventriculaire tachycardie’ bedacht. This causes your heart to suddenly beat much faster. If the patient is experiencing SVT . It is most commonly associated with pre-excitation syndromes such as WPW.
Myocardial Ischaemia • LITFL • ECG Library Diagnosis
The Delta wave is a slurred upstroke in the QRS complex. It is the same as the range for normal sinus rhythm. A QRS duration of 120 ms (0.This is the only ECG abnormality that is potentially diagnostic.The ECG changes associated with acute pulmonary embolism may be seen in any condition that causes acute pulmonary hypertension, including hypoxia causing pulmonary hypoxic vasoconstriction. Home ECG Library. Figure 1 (below) displays two ECGs with junctional escape rhythm. Retrograde P-wave before or after the QRS, or no visible P-wave. Note the heart rate range. This page covers the ECG signs of myocardial ischaemia seen with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndromes (NSTEACS). In This Section . See the modified Sgarbossa criteria in action in this excellent . ESC Clinical Practice Guidelines aim to present all the relevant evidence to help . This page covers the pathophysiology and ECG features of pre-excitation syndromes in sinus rhythm. The failure to correctly identify VT can . Regular rhythm with ventricular rate >100 beats per minute. ECG criteria for sinus tachycardia.SVT has a sharp start of the QRS complex. Sequence of conduction in LBBB: 1) Conduction delay means impulses travel first via the right bundle branch (black arrow) 2) Septum is .
The two main forms of tachyarrhythmias .
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
An electrocardiogram (ECG) provides a tracing of the heart rhythm and is recorded by placing stickers and leads on the chest and limbs. Proportionally excessive discordant STE in ≥ 1 lead anywhere with ≥ 1 mm STE, as defined by ≥ 25% of the depth of the preceding S-wave. Dat kan dus uit de atria zijn, maar ook uit het AV-knoop gebied.Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is common in infancy and childhood.Supraventricular Tachycardia EKG Interpretation with Rhythm Strip. Use a cut-off of > 200ms, which has a specificity of 85-90% for VT. Below this, there is too much overlap between VT and SVT . Regular ventricular rhythm with rate 40–60 beats per minute.Auteur : Lior Bibas, Michael Levi, Vidal EssebagOther, more complicated ECG algorithms have been developed to distinguish VT from SVT, such as the Brugada criteria, which rely on an examination of the QRS morphology in the precordial leads, 73 and the Vereckei algorithm, which is based on an examination of the QRS complex in lead aVR 74 .
Qu’est-ce que la prépa ECG et ECT?
Publiée : 2023/08/07
Diagnosis and management of supraventricular tachycardias
The characteristic ECG findings in Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome are: Short PR interval (< .Diagnostic clues on ECG include a warm-up phenomenon in which the atrial rate increases slightly over the first 5 to 10 seconds before stabilizing. P-wave with constant morphology preceding every QRS complex.ECG criteria for junctional rhythm. Skip to main content Skip to navigation Penn Medicine. Duration from start of QRS complex to nadir of S-wave ≥60 ms suggests . In SVT, a change in heart signaling causes the heartbeat to start too early in the heart's upper chambers.
Sinus tachycardia & Inappropriate sinus tachycardia
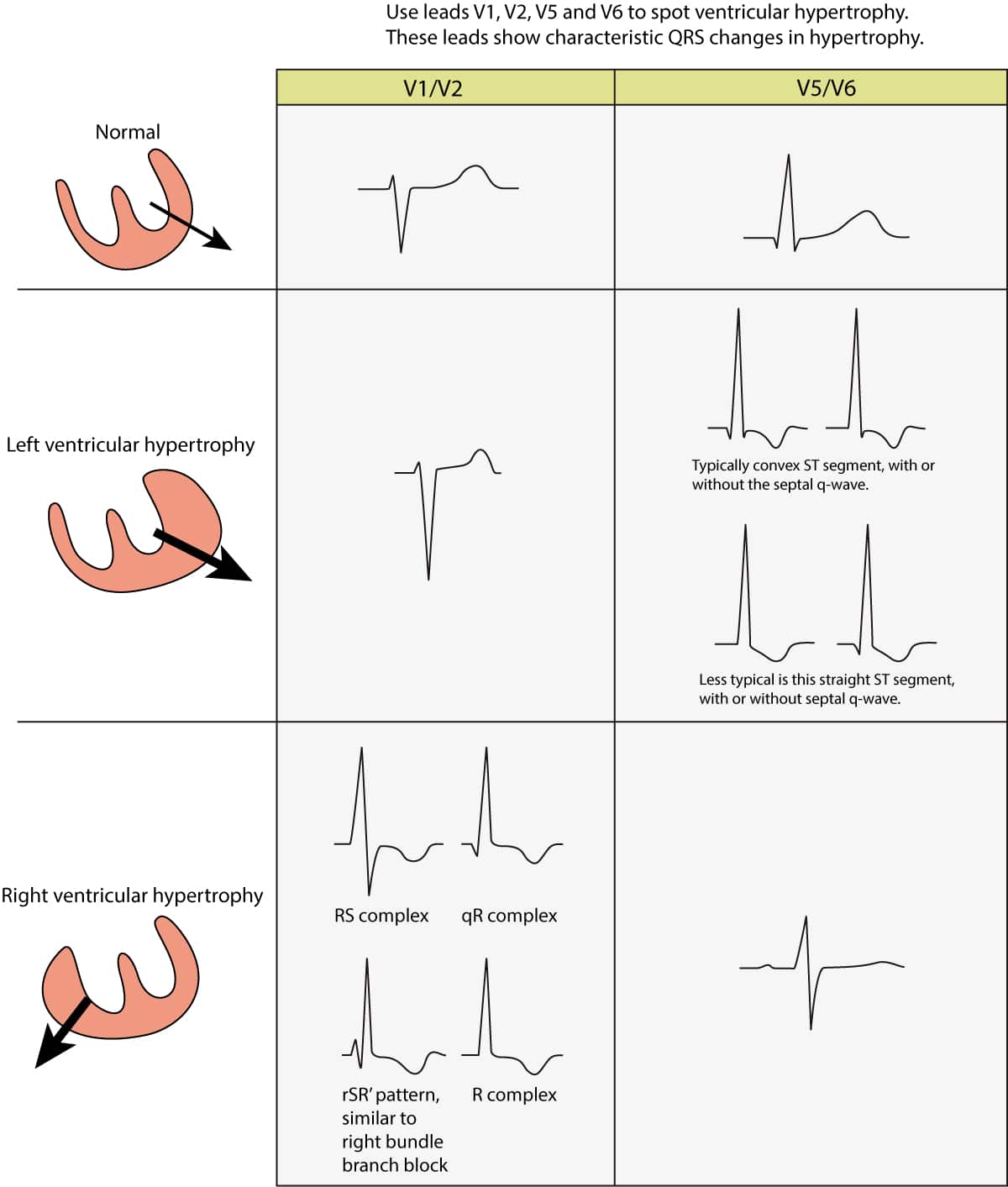
When this happens, the heartbeat speeds up. Regular rhythm with ventricular rate between 50 and 100 beats/min.Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH): Markedly increased LV voltages: huge precordial R and S waves that overlap with the adjacent leads (SV2 + RV6 >> 35 mm).
VT versus SVT • LITFL Medical Blog • ECG Library Basics
ECG in sinus tachycardia.Causes of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) SVT happens when the electrical system that controls your heart rhythm is not working properly. Early beats occur within the atria of the heart due to improperly functioning electrical .The first test to evaluate for SVT is to obtain an ECG.Supraventricular tachycardia comprises a group of conditions in which atrial or atrioventricular nodal tissues are essential for sustaining the arrhythmia.The 12-lead ECGs of 206 monomorphic WCTs (153 VT, 53 SVT) with electrophysiology-confirmed diagnoses were analyzed. This is most pronounced in VT originating from septal sites, particularly Purkinje sites and the septal outflow tract regions.
Pericarditis, myocarditis & perimyocarditis: ECG, criteria

Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is an arrhythmia initiated above the ventricles, at or above the atrioventricular (AV) node. P waves are hidden within each preceding T wave.
VT versus SVT: It's as easy as ABCDE • LITFL • ECG Library
ST-elevation and Q-wave myocardial infarction patterns are covered elsewhere: LMCA occlusion, Anterior STEMI, Lateral STEMI, Inferior STEMI, . In many cases, the underlying mechanism can be deduced from . Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is a rapid heart rhythm originating at or above the AV node. P-wave with constant morphology preceding every QRS . Refer to Figure 2. Symptoms you may experience during SVT.If a previous ECG is not at hand, one could suspect such waves to be P-wave if the waves are smooth (as is the P-wave); ventricular deflections are sharp waves.A sample of blood is taken to check for other causes of a fast heartbeat, such as thyroid disease.
Supraventricular Tachycardia EKG Interpretation with Rhythm Strip
R-wave duration ≥40 ms suggest ventricular tachycardia.Educational material.