Synchronous electric motor
henshawcompressor. The synchronous speed is . The synchronous motor operates both for leading and lagging power factor. Alternating Current (AC) Chapter 13 AC Motors.Synchronous Electric Motors 3318 Lilac Street, Pasadena, Texas 77505, United States Office 281-998-1400 Larry Williams 281-910-2200 Bill Henshaw Jr. The late 1880s – Electric motors started to be used for commercial use Engineers and scientists started to modify and . Both of them share some similarities .com More Info www. By maintaining precise synchronization between the supply .Synchronous motors are a variant of alternating current motors that offer higher efficiency and better performance.ดังนั้นใน EP: 2 ของเราในครั้งนี้ เราจะมารู้จัก “AC Motor” ที่เราจะเริ่มต้นที่ AC Motor แบบแรกที่เราเรียกว่า มอเตอร์ไฟฟ้ากระแสสลับแบบซิงโครนัส (Synchronous motor) กัน .A synchronous motor is an electrical machine that runs at synchronous speed (constant speed) and converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.A synchronous motor is one in which the rotor normally rotates at the same speed as the revolving field in the machine.Parts of electric motors. It consists of a rotor with permanent magnets and a stator with a set of windings. This difference in the speed of the rotor and stator magnetic field is termed a slip. Its small volume, light weight, high efficiency, high power factor, fast response, . The stator is fed by single phase AC supply.
They are generally made up of chrome, cobalt steel or alnico. The synchronous motor is identical in construction to the synchronous generator, although virtually all synchronous motors are of the salient-pole type.Dive into the basics of synchronous motors with Johnson Electric's valuable resources for engineers. Introduction 1 2. Constant Voltage Operation 30 9. The asynchronous motor is also comprised of a stator winding, .Temps de Lecture Estimé: 6 min An electric motor that operates at a constant speed is known as a synchronous motor as the frequency of the AC voltage that is . 918-629-3782 Larry@cmicompressors. What is a Synchronous Motor? A synchronous motor (short for synchronous electric motor) is an AC motor where the . Energy Conversion – Motional E.Most people understand that electric motors use electrical power to generate motion, yet few know just how many different ways this can be accomplished.

ZF has developed an electric motor which does not require magnets.An asynchronous motor is defined as an electric machine whose rotor does not rotate at the same speed as that of the stationary rotatory magnetic field (i.AC motors can be further divided into induction and synchronous motors. The synchronous motor can also be started with the help of the damper windings. These motors can be designed to operate on alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC). Anibal de Almeida, Steve Greenberg, in Encyclopedia of Energy, 2004. Since a synchronous motor is not an induction motor, an electrical supply needs to be attached to the rotor.Precise speed control: Synchronous motors maintain a constant speed, regardless of load changes, which is essential for applications requiring strict speed regulation.Synchronous Machine Working Principle. The fixed connection between the stator and rotor magnetic fields is maintained by it. Let’s now take a closer look at some of the different parts found in an electric vehicle’s motor: from electric motor magnets or Externally Excited Synchronous Motors (EESM) to the powertrain unit in general. General Properties of Electric Motors 36 2.
3-phase Motor Types: Synchronous and Induction Motors
Image used courtesy of ABB .
Synchronous Motor: Construction, Working, and Applications
A synchronous condenser, also known as a synchronous capacitor or synchronous compensator, is a specialized device used in power systems for voltage regulation, power factor correction, and stabilization of the grid. Synchronous Motors. Electrical Controls.

The motor which runs at synchronous speed is known as the synchronous motor. Torque Production 15 5.Johnson Electric provides AC synchronous motors for rotary applications with speed up to 720 rpm and linear applications with speed up to 8.The permanent-magnet synchronous motor (PSM) is the leading technology solution regarding the shown criteria and is therefore chosen as the electric motor for both hybrid and electric drivetrains. The rotors are cylindrical in shape and have high hysteresis loss property. Let’s take a closer look at synchronous motors.A new high efficiency and high-speed Hybrid Synchronous motor (HSM) is developed for pure electric vehicle. High efficiency: Synchronous motors .This paper presents a review on the recent research and technical progress of electric motor systems and electric powertrains for new energy vehicles.
Synchronous Motor: Equivalent Circuit & Phasor Diagram

Non-Salient Pole or Cylindrical Rotor.

com Bill@henshawcompressor. Based on the type of input, they have been classified into single-phase and three-phase motors. The power supplied to the rotor needs to be DC power in order to .The prime mover is used for rotating the motor at its synchronous speed.A synchronous motor is an electric motor that synchronizes with the stator's rotating magnetic field.The rotor of this type of motor is a wound rotor, which receives the excitation (magnetizing) current from its excitation system (a separate direct current .
Synchronous Motors : Basics
The motor always runs at synchronous speed due to magnetic locking between the rotor magnetic field and the stator magnetic field.A synchronous motor is an AC motor in which the rotation of the shaft is the same pace as the frequency of the applied current.A synchronous motor is a type of electric motor that operates at a constant speed determined by the frequency of the alternating current (AC) power supply.
Research on a PMSM control strategy for electric vehicles
Like all electric motors, the synchronous motor converts electrical power into mechanical power. Through the analysis and comparison of direct current motor, induction motor, and synchronous motor, it is found that permanent magnet synchronous motor has better overall .
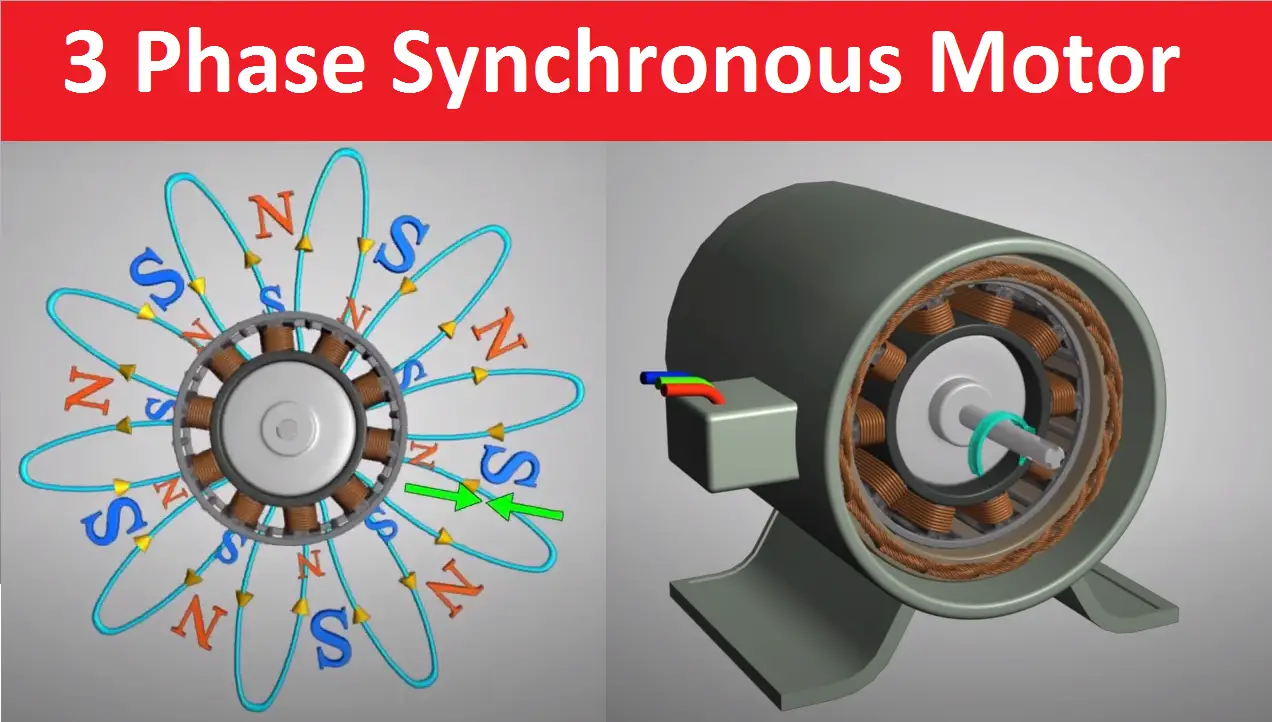
2 Synchronous Motors.Temps de Lecture Estimé: 10 min
Electric motor
The NdFeB-magnets used in PSMs allow for a very high efficiency and low noise. The term “synchronous” refers to the motor’s ability to operate at a speed directly proportional to the supplied .
Types of Synchronous Motors: A Full Description
Imagine a world free of electricity, where every job is carried out by hand.Last Updated : 20 Apr, 2024. Permanent magnets.The electrical motors are machines that convert electrical energy into mechanical energy for performing mechanical operations.
Synchronous Motor Working Principle
Synchronous motors and generators function as synchronous machines based on the two fundamental laws of electromagnetic induction and interaction, which are .Electric Motors. The stator is similar to that of an induction machine . It offers several benefits, such as constant speed operation, high efficiency, and power factor correction capabilities. Offered in various . What are the advantages and disadvantages of synchronous and induction motors? Powered by AI and the LinkedIn community.Synchronous Motors. The most common three-phase motor types are synchronous motors and induction motors.electric motor, any of a class of devices that convert electrical energy to mechanical energy, usually by employing electromagnetic phenomena. Some motors are powered by DC current, others by AC current, .
Synchronous Motors
Torque and Motor Volume 19 6. the stator magnetic field) at synchronous speed. Learn about the principles, construction, and applications of synchronous . The primary difference in operation, however, is . In contrast to the magnet-free concepts of so-called separately excited synchronous motors (SESM) already available today, ZF’s I 2 SM (In-Rotor Inductive-Excited Synchronous Motor) transmits the energy for the magnetic field via an inductive exciter inside the rotor shaft . In a DC motor, the torque is produced due to interactions between . Most electric motors develop their mechanical torque by the interaction of conductors carrying current in a direction at right angles to a magnetic field. When three-phase electrical conductors are placed in certain .
Synchronous motor
ZF makes magnet-free electric motor uniquely compact and competitive. It includes a rotor spinning with coils passing magnets at the same frequency as the AC and produces a magnetic field to drive it.cmicompressors. Inductive current transmission unit inside the rotor enables ultra-compact e-motor .Synchronous reluctance motor is an electromechanical energy conversion device, which converts electrical energy to mechanical energy. The AC motors are classified into two types; Synchronous Motors and Asynchronous Motors. However, the biggest advantage is also the biggest disadvantage.An electric motor is an electromechanical device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.synchronous motor, alternating-current electric motor designed to run at a speed that is directly proportional to the frequency of the electric power source.Synchronous Motor Working Principle.Learn about the synchronous motor equivalent circuit, which represents the electrical characteristics of the motor and helps analyze its performance.The main difference between a permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) and an induction motor is in the rotor.Overview and Comparison of the 3 Types of Synchronous Motors:1) PMSM Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor- IPMSM- SPMSM2) EESM Electrically Excited Synchronous. Based on the input type, they are divided into single-phase and three-phase motors.
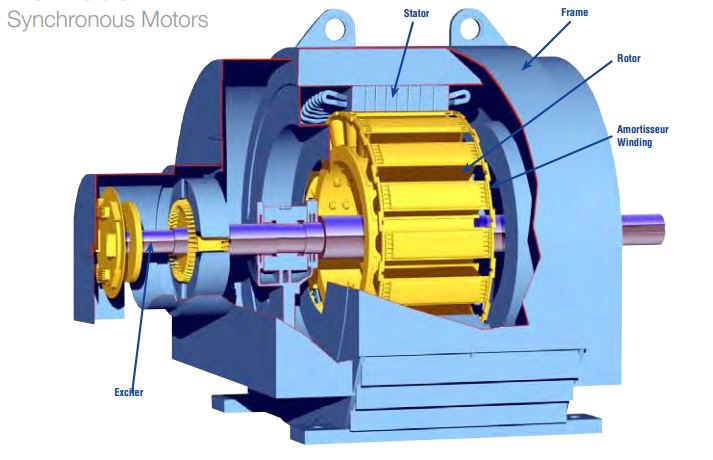
Synchronous Motor Construction and Working Principle
Electric Motors – The Basics 1 1. Construction of Synchronous Motors. Synchronous motors, as the name implies, rotate at a constant (synchronous) speed.
How an electric car’s motor works
The HSM employs multi-layer magnet layout with high salient rate .Studies 1 show that the PMSM has an efficiency of approximately 2% more than a highly efficient (IE3) induction electric motor, provided that the stator has the same design, and the same variable frequency drive is used for . Equivalent Circuit 28 8.What is a Synchronous Motor? Additionally, explore the phasor diagram of the synchronous motor, illustrating the relationship between voltage, current, and power factor at both leading and lagging current conditions. These motors can be designed to operate on . Some synchronous motors use a permanent magnet motor for .









