Tang dynasty and buddhism
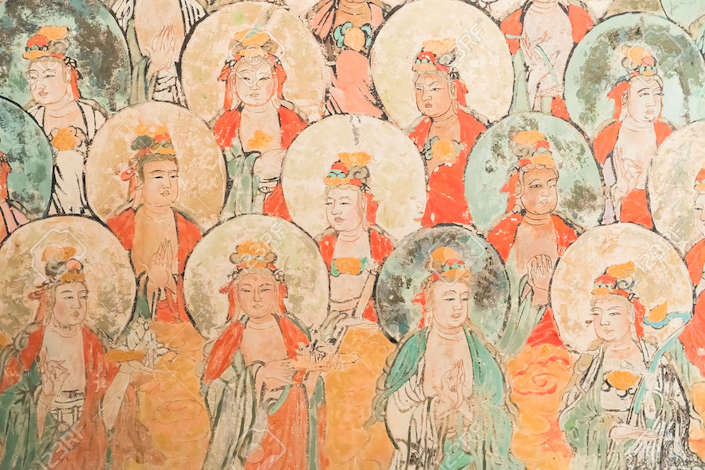

The relationship between Chan Buddhism and poetry in Wang Wei’s work illustrates the powerful interplay of philosophy, religion, and literature during the Tang .Buddhism in China flourished during the Tang dynasty (618-907), with many large monasteries that were active in their communities, including performing services such as caring for orphans and the old and sick.
Buddhism
Taoism
Tang dynasty summary
Tang dynasty (618–907 CE), Chinese dynasty that succeeded the short-lived Sui dynasty (581–618), developed a successful form of . In power from .In 650, the Western Turk Empire shrank further with the loss of Kashgar to the Han Chinese, who had been expanding their empire since the founding of the Tang Dynasty in 618.A silk painting of sacred Buddhist images from Dunhuang. Its doctrine and . Dunhuang, in the Gansu province of China, was an important Buddhist center between . The fortunes of all Chinese Buddhist schools grew in this period thanks to the explosion of intellectual productivity that came from its monks, thinkers, and .In the late Tang Dynasty , Zhang Yanyuan said in his Record on Stele of the Third Patriarch: “In practicing Confucianism, one’s sentiment will be refined; in exercising Buddhism, one’s character will be nurtured, which are the best standards to be set up”.
Smarthistory
390) Footnote 2.
Chapter 1
563 BCE), Buddhism first entered China in the first century CE .
By the eighth century Buddhism was widely accepted and recognized as the dominant faith throughout the Tang empire. Emperor Wuzong is mainly known in modern times for the religious persecution that occurred during his reign.According to Tang Huiyao, an institutional history of Tang dynasty: On the 17th day in the sixth month in the first year of the era of Longshuo (661 AD), the emissary to Tokharistan (Tarim Basin), Wang Mingyuan, presented An Illustrated Account of the Western Regions , and requested to set up administrative bodies in the 16 nations .Unlike the Northern Zhou, they actively supported Buddhism and favored its spread. Initially, China was split into the Three Kingdoms (220–280 CE).This paper investigates the formation of monastic networks in Tang Dynasty (618–907) China, focusing primarily on the Buddhist traditions of Tiantai, Chan and .
Chinese Buddhism

Buddhism in the Tang (618
Tang Dynasty’s Administrative Excellence. Emptiness arises from the “Buddha’s observation that there is no inherent, unchanging, independent self.The history of Chinese Buddhism begins in the Han dynasty, when Buddhism first began to arrive via the Silk Road networks (via overland and maritime routes). The defeat of the Song dynasty was a serious blow to Tiantai which suffered another setback during the Yuan dynasty which supported Tibetan Buddhism, while Chan Buddhism continued to grow in . Think of it as the ancient version of going from dial-up to high-speed internet.Wuzong of Tang (also Wu-Tsung, formerly Li Yan) reigned as emperor of China from 840 to 846 CE.For a long time, scholarly research on Buddhism in Luoyang during the Tang Dynasty has mainly focused on eminent monks and Buddhist temples. Before gaining control of Kashgar, the Tang forces had taken Mongolia from the Eastern Turks and then the city-states along the northern rim of the Tarim Basin.Buddhism trickled into China as early as the Han Dynasty (206 BCE – 220 CE) and was initially used by the Emperor and other nobles as one of their many .As his legend grew, an embellished story cycle began referring to him as the Tang monk Tripitaka (Tang Sanzang, 唐三藏; lit: . It was probably introduced to China by Silk Road traders from the west in about the 1st century CE.The Tang dynasty saw the growth to prominence of Chinese Tantric Buddhism.Temps de Lecture Estimé: 7 min
Tang Dynasty
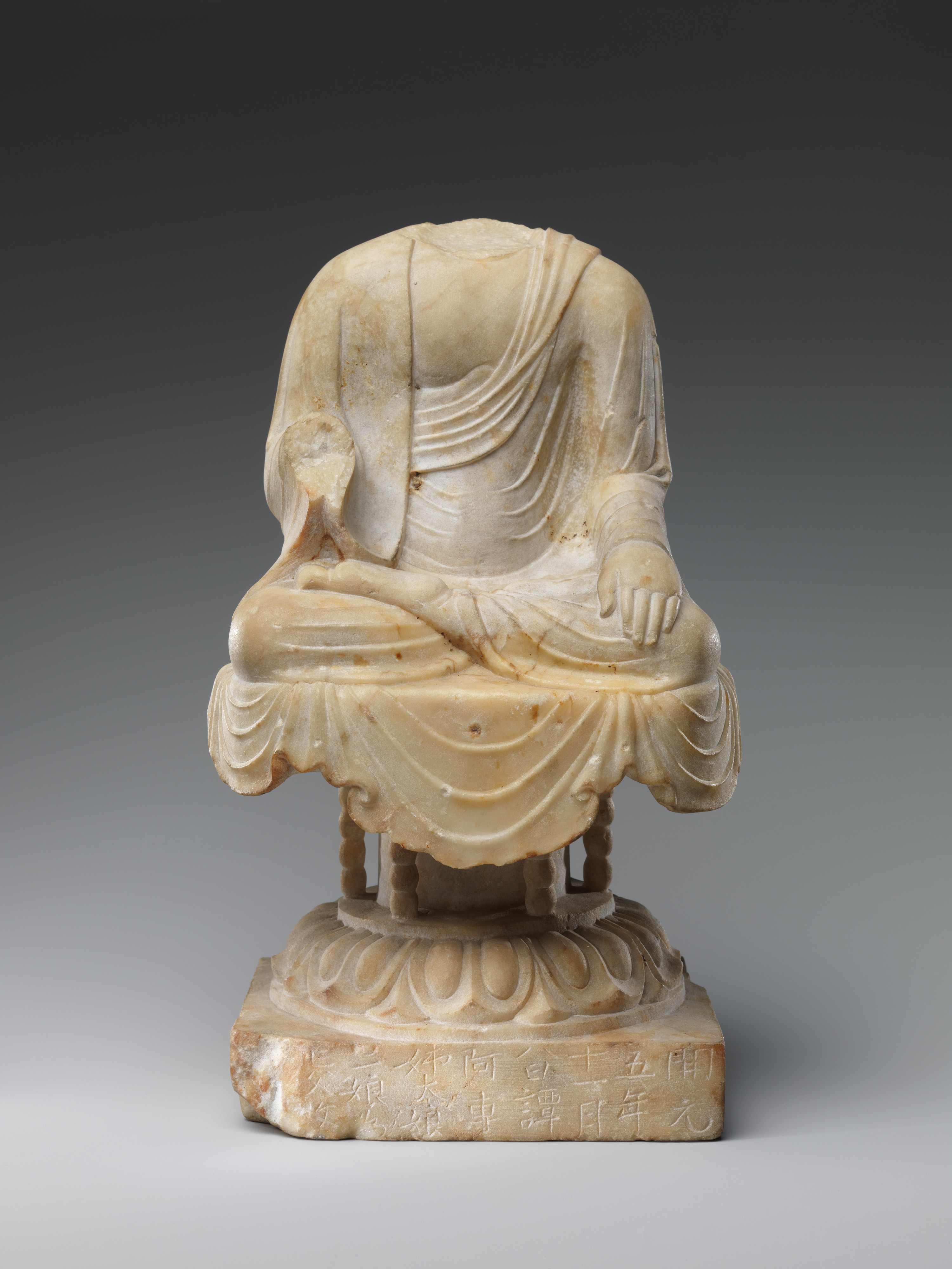
Among its purposes was to appropriate war funds and to cleanse Tang China of foreign influences. Chinese, Tibetan, and Mongolian Buddhism . The donative dedication of the sculpture can be seen in inscribed characters in the lower register on . Early Tang translators such as Atikūta, Bodhiruci, Yijing, and Manicintana worked on esoteric texts promoting mantras and dharanis such as the Tuoluoni ji jing 陀羅尼集經 or Collection of Coded Instructions (Dhāraṇīsaṃgraha sūtra, T.The Tang dynasty (618–907) is considered a golden age in Chinese history. Accordingly, 52 caves of Dunhuang Grottoes were excavated during the Tang dynasty (Hu & Mei, Citation 1997) Footnote 1, which involved creating 56 frescoes of Mañjuśrī Jingtu Bian (Buswell & Lopez, Citation 2013, p.Perspectives on Buddhism in Dunhuang during the Tang and Five Dynasties Period.forms of Buddhism especially during the Tang dynasty (618-907) that transformed Daoist liturgy, art, and practices under the Song (960-1279).

Li Yuan, the founder of the Tang dynasty, had attracted .Late medieval China (Tang 唐 dynasty, 618–907) witnessed a relatively rapid change in drinking habits as alcohol increasingly made way to tea as the drink of choice at all levels of society.The Tang Dynasty (618–907) is considered the zenith of Chinese history and culture, often referred to as a Golden Age.
Tang Dynasty
712–56), called minghuang —the Brilliant Monarch. rphe roots of Buddhism in Tibet go back to a dynasty of kings beginning with Tr'i-srong-tzän ( Khri .This “philosophical decoupling” of Buddhism and Daoism culminated in the travels of Chinese pilgrims to India during the Tang dynasty (618–907). Stepping back from the Chinese perspective, the same Sino-Indian interaction can be viewed from the vantage point of the spread of Buddhism across Asia. The Worlds of the Indian Ocean. McRae argues that these Chinese pilgrims .

As is clearly illustrated in The Circle of the Way, while the Partiarchs occupy center stage, there was an enormous amount of development in Chan thought, practice, the .Marked by strong and benevolent rule, successful diplomatic relationships, economic expansion, and a cultural efflorescence of cosmopolitan style, Tang China emerged as one of the greatest empires in the medieval world.Taoism exerted a great influence during the Tang Dynasty (618-907 CE) and the emperor Xuanzong (reigned 712-756 CE) decreed it a state religion, mandating that people keep Taoist writings in their home.
Tang Dynasty Influences on the Early Spread of Buddhism
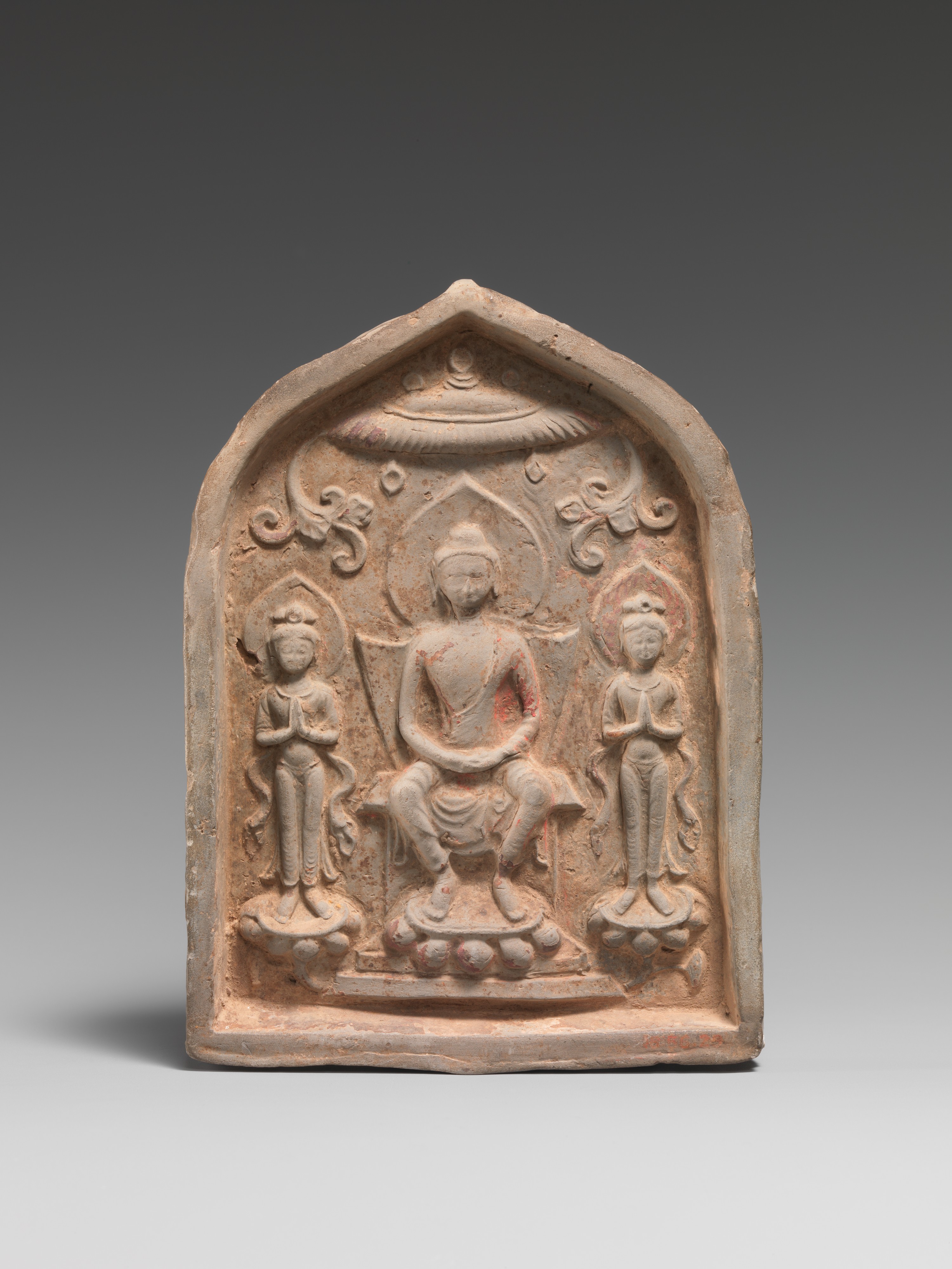
The effort was led by non-Chinese missionaries . The Tang Dynasty is considered a golden age of Chinese arts and culture.This artwork is dated 687, during the Tang dynasty (618–906), and depicts the future Buddha Maitreya in a niche flanked by two monks and two bodhisattvas. The early period of Chinese Buddhist history saw efforts to propagate Buddhism, establish institutions and translate Buddhist texts into Chinese.The eighth century heralded the second important epoch in Tang history, achieved largely during the reign of Emperor Xuanzong (r.For centuries after the fall of the Han, China was ruled by many different factions, largely land-owning warlords, but there wasn't much of a centralized government.Taoism was the official religion of the Tang; it is a native Chinese religious and philosophical tradition, based on the writings of Laozi.
Tang dynasty
The historical Buddhist monk Xuanzang (玄奘, 602-664) is famous for traveling to India between 629 and 645 in order to supplement the Chinese Buddhist canon with fresh scriptures (). During the Tang and Yuan dynasties, Chinese Buddhism was also in proximity to Chinese branches of the Church of the East and Christianity in general, and competed with these traditions, especially in the Tang dynasty. During the eighth century, three . These pilgrims, including Xuanzang and Yijing, traveled to India to study Buddhism and bring the Buddhist teachings and texts back to China. The Huichang Persecution of Buddhism (Chinese: 会昌毁佛) was initiated by Emperor Wuzong (Li Chan) of the Tang dynasty during the Huichang era (841–845). It is rightfully ranked as the classical period of Chinese art and literature, as it set the high standard to which later poets, painters, and sculptors aspired.The Tang Dynasty (618-907 CE) was one of the greatest in Imperial Chinese history. Seven Buddhas of the past frame the central niche. This lasted for several decades before it fell apart.In the Chinese context, Buddhism dealt mainly with the afterlife, the effects of good and bad deeds; addressing life’s misfortunes; it also promised . The Tang dynasty (唐|朝) or the Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty that ruled China from 618 to 907 AD, with an interregnum .
Buddhism in Central Asia before the Advent of the Arabs
Emperor Wuzong of Tang (July 2, 814 – April 22, 846), né Li Chan, later changed to Li Yan just before his death, was an emperor of the Tang dynasty of China, reigning from 840 to 846.Buddhism first reached China from India roughly 2,000 years ago during the Han Dynasty.The formation of Buddhist schools during the Sui and Tang Dynasties is the most significant achievement in the Sinification of Buddhism and holds profound .
Huichang persecution of Buddhism
A Global History.
Tang dynasty
Buddhism in Early Tang
The Works of Zen in the Tang Dynasty
However, in 842, as a result of a civil war, the emperor turned against the monasteries in order to obtain their wealth.

As such, the persecution was directed not .Last updated: 04-09-2024.

This shift cannot be understood without appreciating the fact that Buddhists were active not only in changing people’s attitudes toward intoxicating substances, but also in .
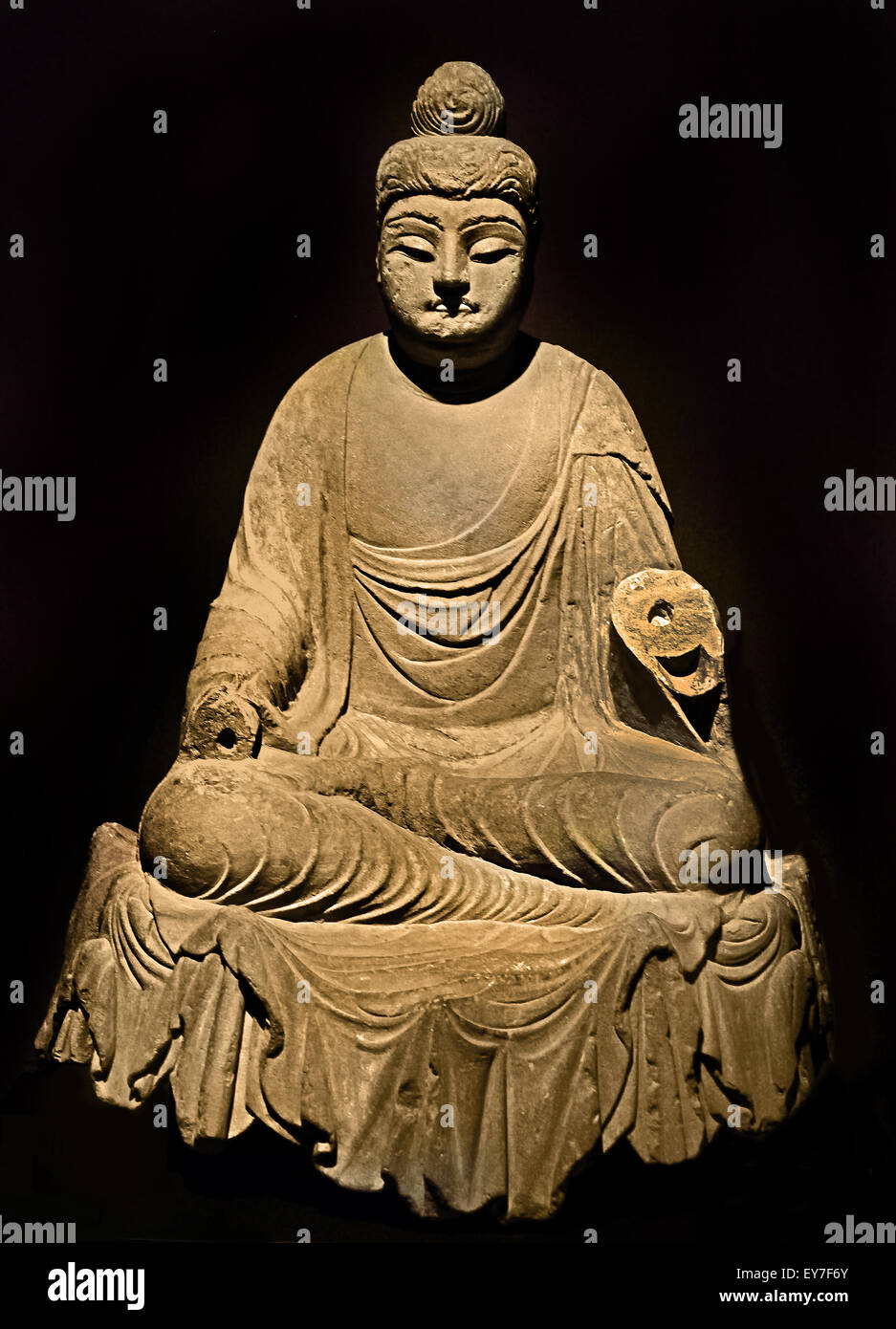

During the Tang Dynasty, China witnessed not merely the construction of magnificent palaces and the creation of monumental poetry but also experienced a significant enhancement in governmental operations.Buddhism played a dominant role in Tang dynasty China (618-906 CE), A universalistic religious philosophy that originated in India (the historical Buddha was born in c. Confucianism is focused on ethics and maintaining harmony and social order in society. Two extensive .Works like Gregory and Getz 1999, a series of articles devoted to various aspects of Buddhism in the Song dynasty (960–1279), have successfully challenged the suppositions assumed in Ch’en’s work regarding the alleged “decline” of Buddhism in China, even postulating that if any period deserved the sobriquet of “golden age,” it might . He is best remembered today for his persecution of Buddhists, the worst such attack in all of China's history, .The Buddhist monasteries of China had gradually and relentlessly been gathering wealth largely thanks to their land ownership and exemption from taxes and, . Monk Zhi Yuan in the Northern Song Dynasty also said, “For a person, Confucianism is .
Ming Buddhism (Chapter 14)
The Silk Road Between China and South Asia as Illustrated by
The Tang dynasty (/ t ɑː ŋ /,; Chinese: 唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an interregnum between 690 and 705.Emperor Wuzong of Tang, reigned 840–846.The school's influence waned and was revived again through the Tang dynasty and also rose again during the Song dynasty.