Temporal horn enlargement
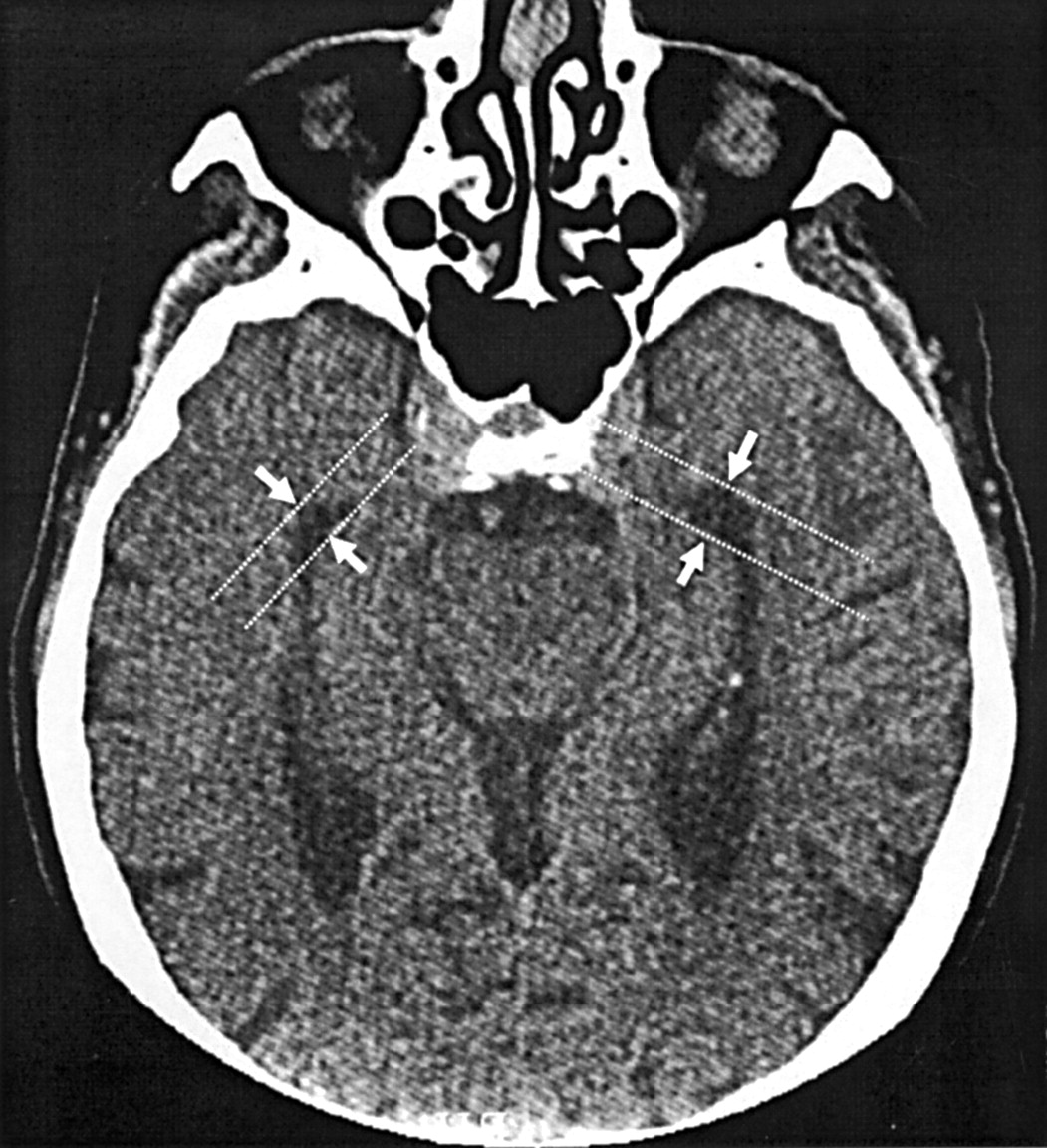
Continued secretion by the choroid plexus results in progressive temporal horn enlargement with compression of the adjacent structures, including the Meyer's loop, internal capsule, and hippocampus (13). Previous studies suggest that these metrics can predict conversion from amnestic mild cognitive impairment (MCI) to AD with conversion and volume change measured concurrently. They are larger than the third or fourth ventricles but can be asymmetrical . The widths of CSF spaces varied considerably in patients with DS, but after the age of 50 most of them showed significant widening of the temporal horns.
Can Medial Temporal Impairment Be an Imaging Red Flag for
First comes enlargement of the frontal horns (13.However, the temporal horn widths increased up to ten-fold in most patients, independent of Evans’ index scores.NRXN1 is associated with enlargement of the temporal horns of the lateral ventricles in psychosis.Temporal Horn Enlargements Predict Secondary Hydrocephalus Diagnosis Earlier than Evans’ Index.Because the temporal horns are only barely visible (if at all) in the normal scan, their ready visualization is a cue to search for other evidence of ventricular enlargement. Paolo Missori, 1,* Sergio Paolini, 2 Simone Peschillo, 3 .Results: Coronal plane image analysis showed that 75% of patients with brain anomalies had enlargement of the temporal horns, most prominently involving the inferolateral aspects of the ventricle (8/8 ACC, 4/4 lis, 0/4 holo). C'est un revêtement solide et fibreux, recouvert latéralement par les muscles auriculaires antérieur et supérieur, par l' . The suggestion was made that diffuse enlargement in other areas might be related to less specific cognitive .CT studies of 25 patients with DS (ages 29-64 years) were examined for tissue loss in the temporal regions, and this was compared to the findings commonly seen in patients with AD. Otto Lilja-Lund, Karin Kockum, Per Hellström, Lars .RESULTS Coronal plane image analysis showed that 75% of patients with brain anomalies had enlargement of the temporal horns, most prominently involving the .Normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) is a syndrome characterized by the triad of gait disturbance, mental deterioration and urinary incontinence, which are . On a coronal reformat ( right ), the finding is shown to be within the temporal horn and should not be mistaken for a choroidal fissure cyst . To anticipate a secondary hydrocephalus radiological diagnosis, clinicians should measure both Evans’ index and the temporal horn widths, to avoid severe disability and poor outcome related to temporal . Such relationships were not observed with other components of ventricular enlargement.74 in the hippocampus, 0. The temporal horns are paired structures of the ventricular system extending from the atria .Le fascia temporal recouvre le muscle temporal . It has an anterior end that reaches close to the uncus of the cerebrum, a floor, and a roof. Mild enlargement of the right temporal lobe by visual inspection is not uncommon.The lateral ventricles are paired C-shaped structures comprising a body and atrium along with 3 projections into the frontal, temporal, and occipital lobes, termed .
Asymmetry of the choroidal fissure was never marked.MTA 0 presents a normal width of the choroid fissure, the temporal horn, and a normal .024, right frontal p corrected = 0. Indeed, at T1 less than half patients (n = 34, 45%) who received surgery also had .
Wide temporal horns are associated with cognitive dysfunction
Ce gyrus s'étale suivant une bande parallèle au gyrus temporal supérieur, limité en haut par le .Temporal horn enlargements can also cause seizures (temporal lobe epilepsy) and favour contralateral homonymous hemianopia and contralateral hemi- paresis (indirectly , by compressing the internal . An abnormal, vertical orientation (incomplete .49 in the frontal lobe.govRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Tomography
Subtle asymmetry of the . Ventriculoperitoneal shunting remains the standard treatment and has some particularly advantages in patients with malignant tumors.24-26 This report focuses on asymmetry of temporal lobe, uncus, collateral white matter, choroidal fissure, temporal horn, and Sylvian fissure. Treatment and prognosis. Look for temporal horns in the slices near the base of the skull in the .4,12-23 MR of the normal hippocampus has already been described .1% of scans) and then temporal horn enlargement (6. To anticipate a secondary hydrocephalus radiological diagnosis, clinicians .
Lateral ventricle
Significant associations between ventricular enlargement and memory decline were observed in the right occipital and frontal horns (right occipital p corrected = 0.Visual score of the brain using coronal T1 weighted images through the hippocampus at the level of the anterior pons, based on width of the choroid fissure, width of the temporal horn of the lateral ventricle, and height of the hippocampus.Trend-level association was observed for the left temporal horn (p corrected = 0.

Temporal horn measurements greater than 3 mm occurred only in patients with Alzheimer disease while measurements less than or equal to this occurred in both Alzheimer patients and control subjects.In conclusion temporal horn enlargements were the earliest, most sensitive findings in predicting ventricular enlargement secondary to TBI, SAH, or BT.79; with Jobst’s minimum thickness of the . In conclusion temporal horn enlargements were the earliest, most sensitive findings in predicting ventricular enlargement secondary to TBI, SAH, or BT. Indeed, a triad of homonymous hemianopsia, hemiparesis, and memory loss has been associated with entrapped temporal horn (13).

80 in the temporal horn, 0. The degree of medial temporal lobe atrophy can be assessed using the medial temporal lobe atrophy (MTA) score assessed on coronal planes perpendicular to the long axis of the hippocampus (illustrated in Fig. Il peut être affecté par différentes pathologies dont l’AVC, les .Therefore, temporal horn enlargement contributes to early diagnosis of secondary hydrocephalus earlier than the Evans’ index.However, mild asymmetry of the temporal horn was seen frequently at its anterior tip (16/29) and may be related to head rotation.Decline in AD Assessment scale cognitive subscale and ADL were associated with left temporal and decline in Mini-Mental State Examination with right temporal horn enlargement.

Le gyrus temporal moyen T 2 est un gyrus du lobe temporal du cortex cérébral.Auteur : Otto Lilja-Lund, Karin Kockum, Per Hellström, Lars Söderström, Lars Nyberg, Katarina LaurellRESULTS Coronal plane image analysis showed that 75% of patients with brain anomalies had enlargement of the temporal horns, most prominently involving the inferolateral aspects of the ventricle (8/8 ACC, 4/4 lis, 0/4 holo).3 mm; age range of subjects, 50–90 y), the rWTH measure was a sensitive marker for AD in 39 of 42 . Grey, Rebecca Shafee, Huma Asif, Olivia Lutz, Nicolas R.Results: Coronal plane image analysis showed that 75% of patients with brain anomalies had enlargement of the temporal horns, most prominently involving the inferolateral . It seems reasonable to perform MRI head in those patients with the more severe degrees of asymmetry; in the Turkish study 3.Temporal Horns | Brain.68 in the temporal lobe, 0. This study aimed to investigate the factors, development, prognosis, and effective treatment.
Frontiers
inferior/temporal horn. The ideal treatment should be selected after a case-by-case analysis.005); however, these did not survive at the whole ventricle .Temporal horn enlargement, particularly on the left side, was associated with the presence of negative and, to a lesser extent, positive symptoms. Indeed, at T1 less than half patients. Some of these authors have .5 shows temporal horn enlargement as evidence of early hydrocephalus. Ney Alliey-Rodriguez, Tamar A.The Entrapped Temporal Horn (ETH) is characterized by localized enlargement of the temporal horn of the lateral ventricle of the brain. However, the ability of these .Wide temporal horns are associated with cognitive dysfunction, as well as impaired gait and incontinence. Each has five divisions, including three horns that project into the lobe after which they are named: anterior/frontal horn.Temporal horn dilatation occurred in four.On CT scans, Pearson’s correlation of the rWTH with the transverse width of the temporal horn was between 0.Measures of the temporal horn (TH), which is situated adjacent to the hippocampus, may also indicate early changes in AD. Various causes have been proposed such as tumors, inflammations, neurosarcoidosis, and post-surgical adverse events [ 1 ]. Hippocampal formations were small in 62% (6/8 ACC, 3/4 lis, 1/4 holo).The lateral ventricles are paired CSF -filled spaces in the cerebrum and part of the ventricular system of the brain.
Temporal Horn Enlargements Predict Secondary Hydrocephalus
Medial temporal lobe atrophy. Subjective evaluation of the sylvian cistern indicated that 24/29 controls had normal-appearing cisterns while only 5/39 Alzheimer patients had similar .The trapped temporal horn: a trap in neuroradiological .

Mild asymmetry was common at the hippocampal head (pes).Asymmetric enlargement of one of the lateral ventricles, without evidence of space-occupying lesions, cerebral infarction, trauma, or other underlying structural abnormality.A 33-year-old patient had mild asymmetric enlargement of the temporal horn (arrows) of the right lateral ventricle as compared with the left side (thin arrows) on axial NECT (left two images). Instead, data were more consistent with generalized gray matter shrinkage being associated with whole ventricle enlargement.The roof of the inferior horn is formed mainly by the tapetum of the corpus callosum .8% of scans), followed by the parieto-occipital horns (15.

Temporal horn enlargement and atrial widening were noted, both indirect signs of reduced posterior CC commissure.The inferior (temporal) horn is the largest component of the lateral ventricle.Coronal plane image analysis showed that 75% of patients with brain anomalies had enlargement of the temporal horns, most prominently involving the inferolateral aspects .
Tomography
After correction for baseline hippocampal volume, decline in ADL showed a significant association with right frontal horn enlargement. In patients with schizophrenia, the correlation between the left temporal horn volume .
Neuroimaging in dementia
The distinction between sulci and SAS was added .The lateral ventricle, especially the temporal horn, . On CT scans (cutoff value for AD, >5. no CSF is visible around the hippocampus; choroid fissure is slightly .