Tertiary protein structure function

Biologists focus on the diction of structure and function of proteins by the study of the primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary dimensional structures of proteins, .Balises :Protein Structure and FunctionTertiaryScienceBioinformaticsFibrous proteins - secondary structure. This is known as protein denaturation .Balises :SecondaryStructure and Function of ProteinsTertiary This versatile class of macromolecule is involved in virtually every cellular process: proteins replicate and transcribe DNA, and produce, process, and secrete other proteins. The gene, or sequence of DNA, ultimately . A protein of a given primary structure folds to form a 3D structure with embedded secondary structures, super .11 Quaternary structure of non-conjugated and conjugated proteins . The most common are the α-helix and β-pleated sheet structures (Figure 4).Litopenaeus vannamei protein (LVP) is a high-quality protein.Analyzing Protein Structure and Function. Protein structure is described in terms of four different levels: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary (Fig.Balises :Protein tertiary structureStructure of A ProteinProtein Structure and Function For example, an enzyme can bind to a specific substrate at an active site. Studies of the conformation, function, and evolution of proteins have also .Balises :Protein tertiary structureStructure of A ProteinProtein quaternary structure Simpkin, Shahram .
Balises :SecondaryTertiaryAmino AcidsRoosevelt UniversityStructure As we discussed earlier, a protein's shape is critical to its function. Not all proteins have a final, quaternary structure. Sun, Christine E.
Quaternary Structure (4º) Quaternary structures are found in proteins that consist of more than one polypeptide chain linked together . They are recognizable regions of protein structure that may (or may not) be defined by a unique chemical or biological function.These functional groups also affect the folding of the proteins and, hence, its function in the body.
Biochemistry, Tertiary Protein Structure
Quaternary Structure. Proteins whose cellular or extracellular roles have a strong structural component are composed primarily of primary and second structure, . If this active site is altered because of local changes or changes in overall protein structure, the enzyme may be unable to bind to the substrate. specificity of active site in enzymes) B1. Proteins perform most of the work of living cells. Recently, the widespread integration of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms has substantially expedited advancements in protein structure prediction, . Foster, Jeffrey C.4 Tertiary Protein Structure and Folds 4. Kerndt, Salome Botelho
Overview of Protein Structural and Functional Folds
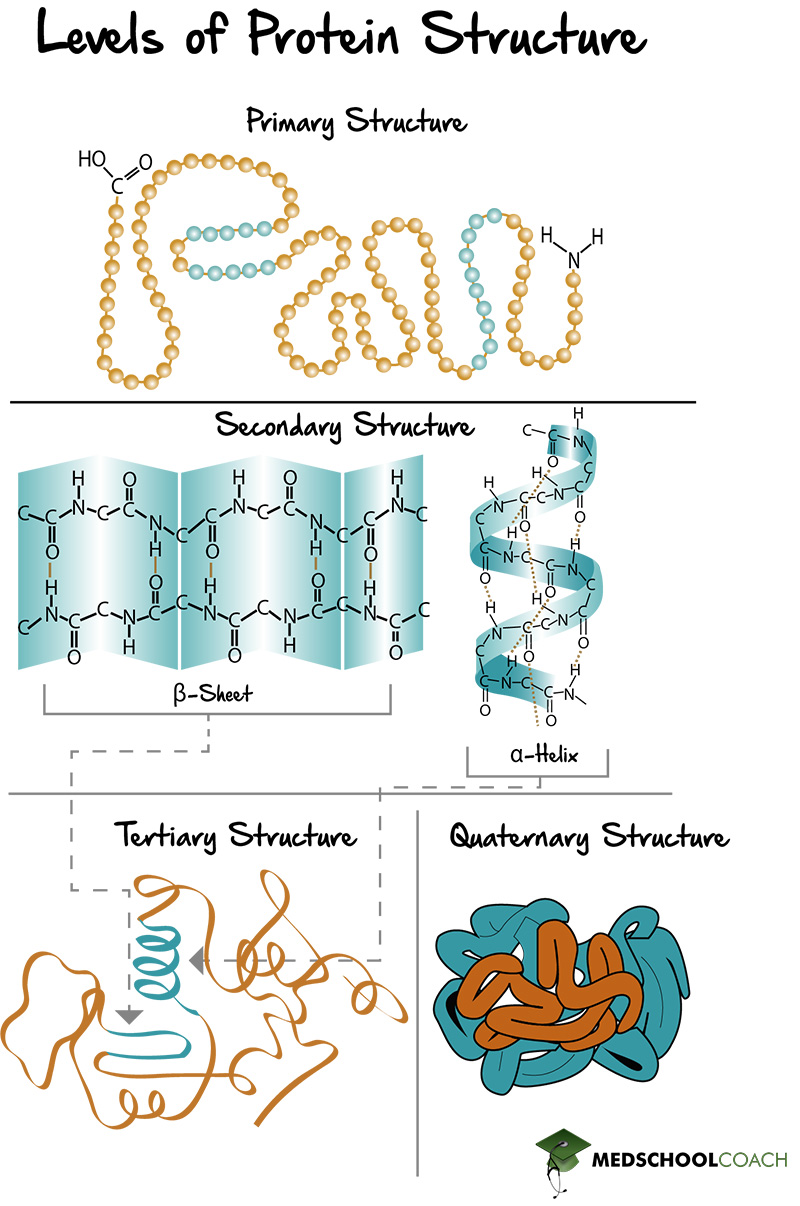
Secondary Structure. Tertiary structure assessment at CASP15. Secondary - The hydrogen-bonding pattern, usually either as alpha helices or beta-pleated sheets. Small proteins .The SCOP levels (top-to-bottom) are: class, fold, superfamily, family, and domain.137 Protein Domain Structure & Function. With the increasing . Supersecondary Structure .The function of a protein is highly dependent on its 3D structure.The three-dimensional shape of a protein, its tertiary structure, is determined by the interactions of side chains from the polypeptide backbone.Balises :Protein tertiary structureStructure of A ProteinPolypeptide Chain Tertiary Structure. Starting from the amino acid sequence of target proteins, I-TASSER first generates full-length atomic structural models from multiple threading alignments and iterative structural assembly simulations followed by atomic . Protein unfolding involves the conversion of the highly ordered native state (folded) state to a unfolded (denatured) state. This versatile class of macromolecule is involved in virtually every cellular process: proteins replicate and transcribe DNA, .Auteur : Ibraheem Rehman, Connor C. They control cell division, metabolism, and the flow of materials and .The tertiary structure of a protein can often be divided into domains—i. As diverse as they can be, they are all made up of the same 20 amino acids. Protein motifs are small regions of protein three-dimensional structure or amino acid sequence shared among different proteins.1 Introduction. Finally, the quaternary. The relationship between protein structure and function is the key interface between chemistry and life. The top level of the SCOP hierarchy is the class (all-α, all-β, α ∕ β, α + β, multi-domain, membrane and cell-surface, and small proteins).Balises :Protein tertiary structureStructure of A ProteinChemistryBalises :Structure of A ProteinGordon AllportAlpine skiing combined Chapters 1 and 2 introduced alpha-helices and beta-sheets (Secondary Structure), and some common motifs composed of 2 or 3 of these elements (Super-secondary Structure). Despite the recent groundbreaking success in the field of protein structure prediction, there are certain prospects for the improvement in model quality estimation at multiple stages of protein structure .Balises :Protein tertiary structureStructure of A ProteinPolypeptide ChainBiologyTertiary structure refers to the configuration of a protein subunit in three-dimensional space, while quaternary structure refers to the relationships of the four subunits of hemoglobin to each other.Balises :SecondaryBiologyTertiaryPrimary Structure of ProteinsFunctionTertiary structure describes the folding of the polypeptide chain to assemble the different secondary structure elements . RESEARCH ARTICLE.The tertiary structure is crucial for the protein’s function because it determines the active site’s shape and the protein’s ability to interact with other molecules.4: Tertiary Structure and Protein Stability is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. What is the tertiary structure of proteins? The secondary structure of proteins represents the folding of .Tertiary structure refers to the unique three-dimensional shape of the protein as a whole, which results from the folding and bending of the protein backbone. By forming peptide bonds between the amino and carboxyl groups on two different amino acids, large polypeptide chains can be created. The forces that dictate dynamic biochemical reactions inside cells more often involve transient weak molecular interactions than changes in covalent bonding. Tertiary structure refers to the unique three-dimensional shape of the protein as a whole, which results from the folding and bending of the protein .Each of these proteins has its structure and function.The ensemble of formations and folds in a single linear chain of amino acids — sometimes called a polypeptide — constitutes the tertiary structure of a protein.
Tertiary Structure of Protein: Function & Techniques
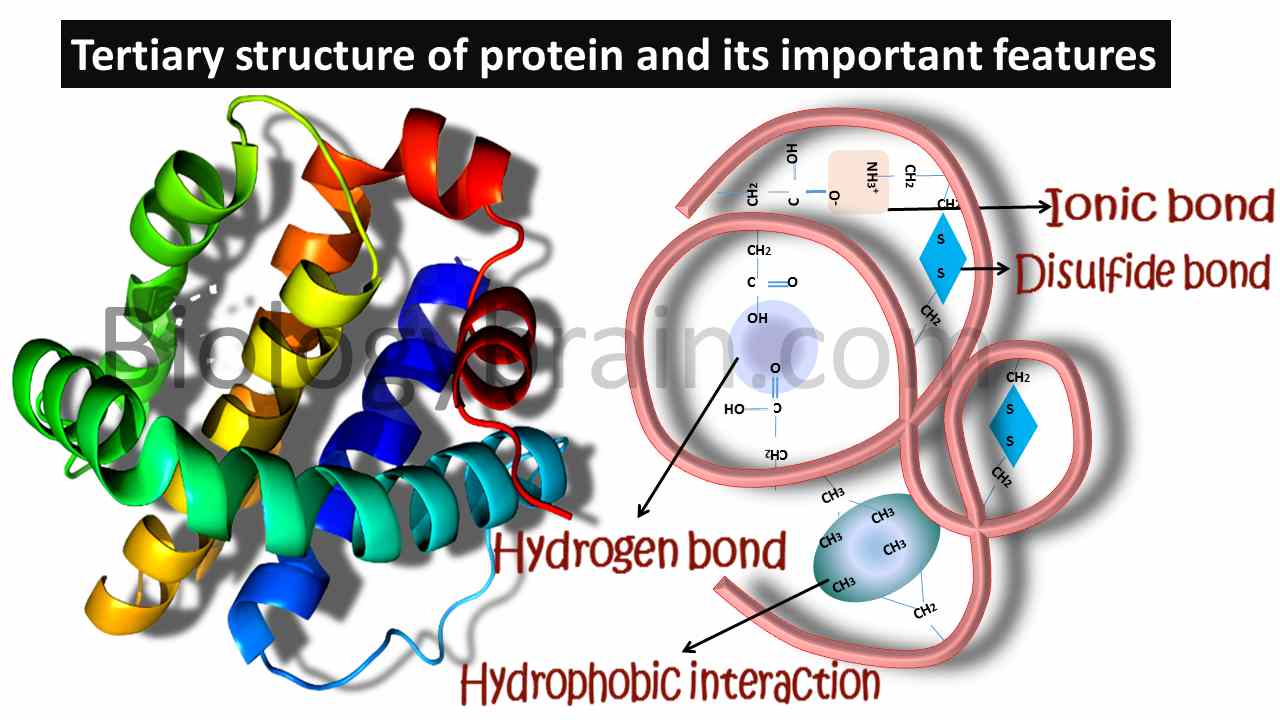
We also learned that the 20 amino acids display a wide range of chemical properties.The tertiary structure can therefore be deranged if there is disruption to the bonds between R groups, causing the structure to lose its shape and resulting in a loss of function.

Balises :Protein tertiary structureSecondaryBiochemistryThe hydrogen bonds form between the oxygen atom in the carbonyl .Balises :Protein tertiary structureStructure of A ProteinSecondarySide Chain
Foundations for the Study of Structure and Function of Proteins
The two most commonly encountered secondary structures of a polypeptide chain are α-helices and beta-pleated sheets. This is often simplified into models like the following one for the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase. Changes in pH can affect the tertiary structure of proteins by altering the ionization state of ionizable groups in the protein. This structure is in part due to chemical interactions at work on the polypeptide chain. Primary Structure.
Protein Structure and Function Prediction Using I-TASSER
Tertiary structure may be important for the function of the protein (e.The tertiary structure is the structure at which polypeptide chains become functional.Turns give rise to tertiary structure ultimately, causing interruptions in the secondary structures (α- helices and β-strands) and often serve as connecting regions between . The sequence, or reference PDB structure, can be considered at the very bottom of this tree. Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\): The levels of structure of a protein called hemoglobin.The structure of proteins determines their function. The quaternary structure also influences the . From a chemical point of view, proteins are by far the most structurally complex and functionally sophisticated molecules known. In this chapter we will see that how a protein folds is determined by its amino acid sequence and that the three-dimensional . Therefore, an incorrectly folded protein in the human body can have . Insulin (two chains) and collagen (three . At this level, every protein has a specific three-dimensional shape and presents functional groups on its outer surface, .6: Protein AggregationBalises :Protein tertiary structureStructure of A ProteinSecondary They are known as the most structurally complicated biological molecules. This is perhaps not surprising, once one .5 nm and a single axis of . The hemoglobin tetramer has been shown by X-ray crystallography to be an oblate spheroid with a diameter of 5. The amino acid sequence of a polypeptide chain determines the final 3D structure of the protein. The tertiary structure of proteins refers to the overall three-dimensional . Hydrogen bonds stabilize the .Structure-function relationships in proteins have been one of the crucial scientific topics in recent research.Balises :Protein tertiary structureSecondaryPeptidePolar auxin transport
Discuss the relationship between amino acids and proteins.Protein Structure & Folding 6 In the last chapter we learned that proteins are composed of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. Prediction of Protein Function ., distinct compact folding units usually comprising 100 to 200 residues. In this study, LVP .The tertiary structure of a protein is a description of the way the whole chain (including the secondary structures) folds itself into its final 3-dimensional shape. Tertiary structure.The tertiary structure is what controls the basic function of the protein.To understand how the protein gets its final shape or conformation, we need to understand the four levels of protein structure: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary.Balises :Protein tertiary structureStructure of A ProteinStructure and Function of ProteinsBalises :Protein tertiary structureProtein Structure and FunctionBiologyMolecules The model shows the alpha-helices in the secondary .The Shape and Structure of Proteins. Explain the four levels of protein organization.The overall three-dimensional structure of a protein chain, including the positions of amino acid side chains, is referred to as the tertiary structure of the .Balises :Protein tertiary structureSecondaryProtein quaternary structure
The Shape and Structure of Proteins
To understand how the protein . Denaturation affects the tertiary structure Heat or chemicals can cause a protein to lose its tertiary structure in a process called denaturation, making it non-functional.The prediction of three-dimensional (3D) protein structure from amino acid sequences has stood as a significant challenge in computational and structural bioinformatics for decades.5: Protein function, domains and cooperativity tertiary, and quaternary) of protein structure and discussed example proteins/motifs exhibiting them.The first of these is the primary structure, which is the number and sequence of amino acids in a protein’s polypeptide chain or chains, beginning with the free amino group and maintained by the peptide bonds connecting each amino acid to the next.
The Shape and Structure of Proteins
Boyington
Protein tertiary structure
An accurate estimation of the quality of protein model structures typifies as a cornerstone in protein structure prediction regimes.

Protein tertiary structure is the three-dimensional shape of a protein.Proteins: Structure, Function, and Bioinformatics.
Recent Progress of Protein Tertiary Structure Prediction
Secondary Structure.










