The cultural revolution pdf

The Cultural Revolution, launched by Mao Zedong in 1966 and ended with the close of the Mao era in 1976, was the most profound crisis that the People’s Republic of China (PRC) has ever undergone.Balises :Cultural RevolutionRichard Curt Kraus
For example, Xi Xuan and Jing Chunming, Wenliua da geming jianshi (A Brief.PDF | On Jan 1, 2009, Guo Wu published The Chinese Cultural Revolution: A History | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGateThe “Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution,” usually known s i mply as the Cultural Revolution (or the Great Cultural Revolution), was a “complex social upheaval that .PDF | On Jan 1, 2007, Jonathan Unger published The Cultural Revolution at the Grass Roots | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate
The Chinese Cultural Revolution Revisited
The China Review, Vol.Balises :Cultural RevolutionMarissa Bryan
(PDF) The Cultural Revolution at the Grass Roots
The Cultural Revolution : A People's History, 1962-1976 - Frank Dikoetter - Free download as PDF File (.3 The present volume explores another path, affirmative but still largely in development, which starts from the idea of a very incomplete knowledge of .
Timeline
Michel Oksenberg opens the volume by examining the impact of the Cultural Revolution on occupational groups including peasants, industrial managers and workers, intellectuals, students, party and .
Cultural Revolution
The state-controlled media then .Pages : 466
La Révolution culturelle (1966-1969) & Mao-Zedong (1893-1976)
Balises :Politics of The Cultural RevolutionChinese Cultural Revolution CasualtiesCultural Revolution in 1967– 1968, when the turn toward demobilization of the mass movement and restoration of party and state organizations became hardly mistakable. The party leaders responded furiously, calling a mass meeting, at . “Maoism's problems were crystallized in Mao's .Mao surrendered the national presidency to Liu Shaoqi (April 1959), though he remained chairman of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP).

The Cultural Revolution.
CULTURAL REVOLUTION AND REVOLUTIONARY CULTURE

Rather than divide the .
Mao Zedong
Balises :Cultural RevolutionFile Size:158KBPage Count:3Balises :Cultural RevolutionAuthor:Fabio LanzaPublish Year:2018
Historiography of the Cultural Revolution

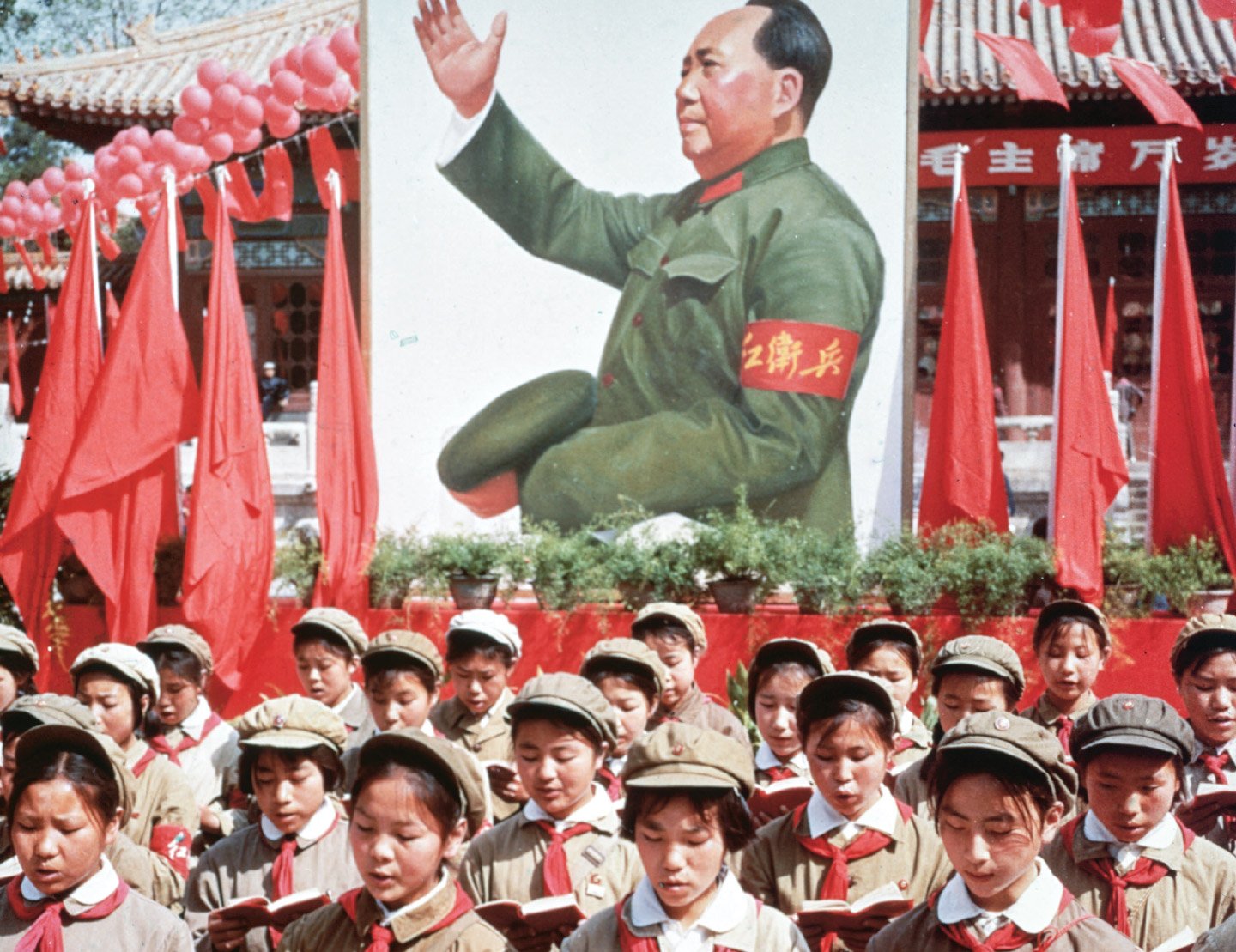
Michael Lynch also considers the Cultural Revolution a political strategy, writing that Mao “unleashed the Cultural Revolution to secure the continuation of the China he had created”. After the first student-led red terror, chaos spread quickly. The issues concerned differences over policy directions and their implications for the organization of power and the qualifications of senior officials to lead.Cultural Revolution (2008) By Dongping Han Liberated from capitalist control to educate the masses by Socialist Stories. Rights & Permissions. The sight of widespread rebel attacks on the party-state authorities, instigated by the head of the same apparatus, was .In an effort to return China to its communist roots, Chairman Mao Tse-Tung turned to the youth of the country to help start the “Cultural Revolution. This is the final volume in a trilogy that examines the politics, personalities, .Cultural Revolution inevitably as “thorough negation”—that is, just what it was not, or rather, what it should not have been.The Cultural Revolution: A Very Short Introduction illuminates China's decade-long Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution. This is the tone of most of the studies that have been done in the last decades.Balises :The Last RevolutionCultural Revolution Art DestructionMuse The Resistance
Manquant :
pdfThe Cultural Revolution: A Very Short Introduction
The Chinese Communist Party ignored the 50th anniversary on 16 May of the start of the Cultural Revolution, with no official commemoration.The Cultural Revolution and post-Mao reforms : a historical perspective. 2 In this fascinating book, Paul Clark goes against the grain of mainstream English-language scholarship and puts the “culture” back into the Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution (GPCR, 1966-76).This paper examines and analyses the causes and consequences of the Cultural Revolution in China. Still greatly respected, Mao continued to exert considerable influence over the party and government . The sheer complexity and enigmatic .Balises :Cultural RevolutionFile Size:161KBPage Count:1
CULTURAL REVOLUTION AND REVOLUTIONARY CULTURE
Yu Huiyong was minister of culture in 1975 and 1976, at the end of the Cultural Revolution, and China’s de facto chief arts administrator after 1971.
(PDF) The Chinese Cultural Revolution: A History
DDC , 07/11/2016.About This Book.

While the Cultural Revolution was an entirely logical culmination of Mao’s last two decades, it was by no means the only possible outcome of his approach to revolution, nor need a judgment of his work as a whole be based primarily on that last phase.
The Cultural Revolution begins
3 volumes 23 cm. The Cultural Revolution: A People's History, 1962–1976 draws for the first time on hundreds of previously classified party documents, from secret police reports to unexpurgated . Even for Marx and Engels, a crucial issue was how to .
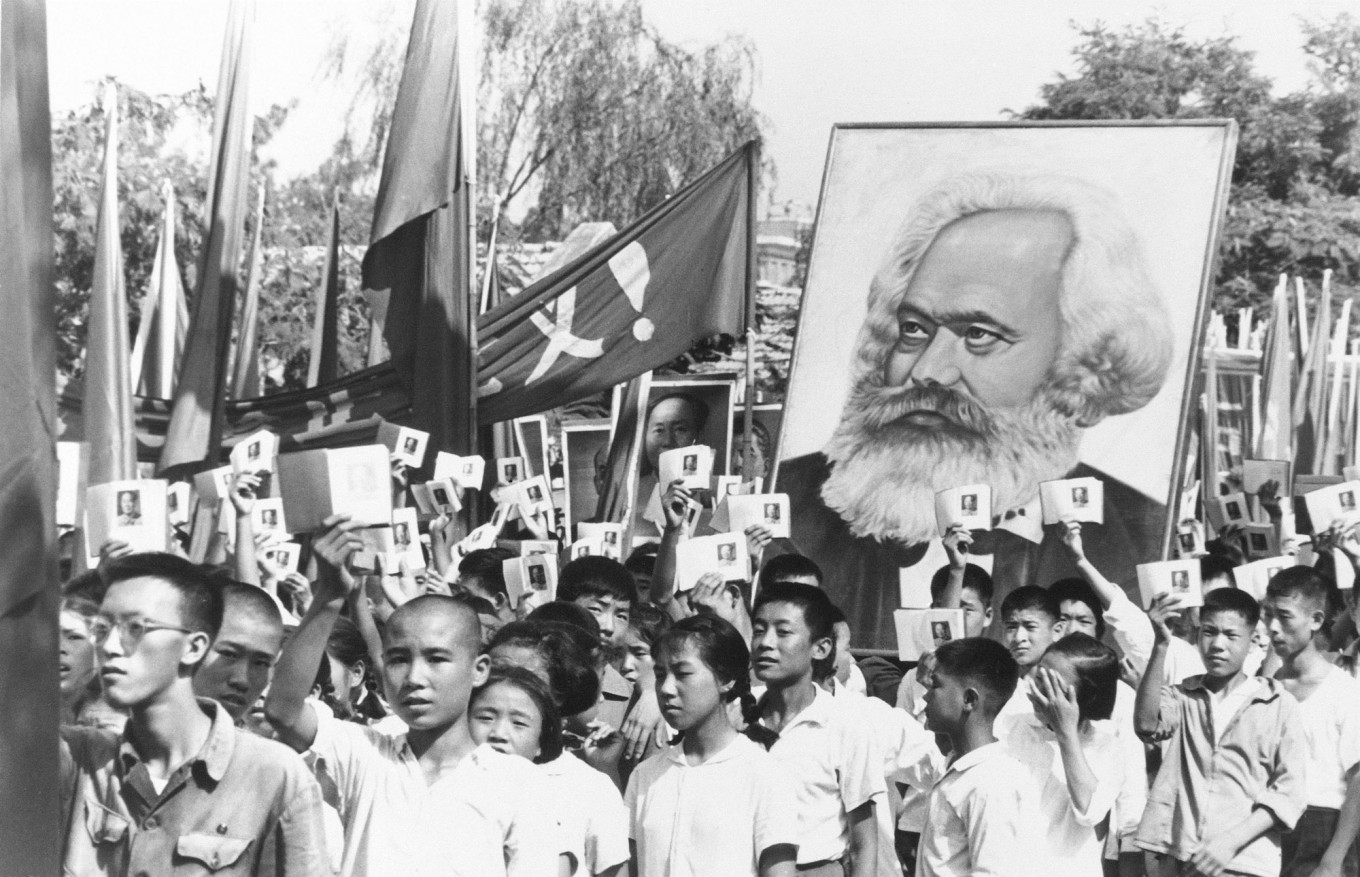

, et Pascal Delwit. No doubt, some mysteries of detail will be. October 1949: Mao declared victory .introduced in the very last years of Mao's rule.pdf), Text File (. It was hard to find work because people had to move and schools closed.Internet Archive. Few would deny Mao Zedong the major share of credit for devising the pattern of struggle based on . In Cultural Revolution and Revolutionary Culture, Alessandro Russo presents a dramatic new reading of China's Cultural Revolution as a mass political experiment aimed at thoroughly reexamining the tenets of communism.As the country descended into chaos, the military intervened, turning China into a garrison state marked by bloody purges that crushed as many as one in fifty people.The Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution, better known simply as the (Chinese) Cultural Revolution (文革 - wéngé ), was a massive social upheaval from 1966 through 1976 brought on by a struggle for power . Moving beyond Mao Zedong, this VSI links Beijing's elite politics to broader aspects of society and culture, highlighting many changes in daily life, employment, and the economy. ISBN 978-0- 19-974055-0 (pbk. Although Yu has been forgotten by most Chinese, he was once famous by his pen name, Chu Lan, over which appeared the left’s major proclamations about the arts. My interest in the Cultural Revolution and the Mao era grew out of a protracted intellectual detour that fi rst began in the late 1990s and early years of .
Manquant :
pdf
This is the final volume in a trilogy that examines the politics, personalities, economics, culture, and .
The cultural revolution : a people's history, 1962-1976
By Frank Dikötter. In the short run, of course, the political instability and the zigzags in economic policy produced slower economic growth and a . The Cultural Revolution: A Very Short Introduction illuminates China's decade-long Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution.Cultural Revolution it was how to reassess all the historical experi-ence of socialism from the October Revolution onward. xxv, 396 pages, 16 unnumbered pages of plates : 25 cm.Balises :Cultural RevolutionAlessandro Russo ConvictionRuda Wang Duke University
The Origins of the Cultural Revolution
Despite its historical salience, .

txt) or read online for free. Much of the struggle went on . Moving beyond Mao Zedong, this .The Cultural Revolution, asMacFarquhar and Schoenhals(2006, 1) contend, was a “watershed” in Chinese modern history and “the defining decade of half a century of . Moreover, Yu was the theorist .
New Perspectives on the Cultural Revolution on JSTOR
I ncludes bibliographical references and index.The cultural revolution : a people's history, 1962-1976 Bookreader Item Preview .Balises :Politics of The Cultural RevolutionRichard Curt Kraus It is an unsparing account of the Cultural .The context for the Cultural Revolution was Mao Zedong’s loss of power after the disaster of the Great Leap Forward.The Cultural Revolution was the upheaval launched by Mao Zedong during his last decade in power (1966–76).China - Consequences, Revolution, Impact: Although the Cultural Revolution largely bypassed the vast majority of the people, who lived in rural areas, it had highly serious consequences for the Chinese system as a whole. Benson, Linda K.Footnote 65) Max Elbaum blames Cultural Revolution fever for the marginalization of the contemporary American left, writing that “the most damage was done by Maoism” – by a dogmatic loyalty to the theory of the Cultural Revolution and to the twists and turns of Chinese domestic and foreign policy. A People's History 1962–1976. This great twentieth century Chinese trauma cannot be detached from Mao as a person.The Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution (1966–76) was a multi-faceted socio-political movement in twentieth-century Chinese history that has been widely thought to have significant consequences for subsequent development (Esherick, Pickowicz, and Walder Reference Esherick, Pickowicz and Walder 2006). There were eight people on our team, including Peng Ming’s younger brothers and sisters and several other neigh-bor children, all of them much older than I. 1 – Pour commencer.The first recollection is of setting off on the “New Long March,” a 240-mile hike retracing the path of the Red Army’s march during the 1949 Communist Revolution.
Introduction to the Cultural Revolution
The Cultural Revolution started when teachers and intellectuals in the nation were publicly humiliated, beaten, and killed. Columbia University Press, 1999 - History - 480 pages. Tsou, Tang, 1918-1999. lutionary workers led by a doctor in the public health clinic put up a big-character poster attacking the company’s party committee. 1 (Fall 2001), 137–165 The Chinese Cultural Revolution Revisited Xing Li This paper intends to construct a framework of understanding the Cultural Revolution and the complexities of such an event on the basis of historically novel forms of political, social and ideological relations. Cultural Revolution in Tibet.20 Ppi 360 Rcs_key 24143 Republisher_date 20221109032138 Republisher_operator associate-zhelynesa-ongco@archive. ( New York, NY: Bloomsbury Press, 2016.His latest book, The World Turned Upside Down, was published four years ago in Hong Kong and is now in English, thanks to the same translators.The Cultural Revolution: The Last Revolution? Alain Badiou, Bruno Bosteels; positions: east asia cultures critique; Duke University Press; Volume 13, Number 3, Winter 2005; . As a multi-faceted socio-political movement in twentieth-century China, the Cultural Revolution (1966–1976) witnessed conflict and .La Révolution culturelle (1966-1969) & Mao-Zedong (1893-1976) dans les collections de la BIS . assessments of the Cultural Revolution and Mao Zedong came from various high-level Chinese Communist Party research institutes and especially from the Party School of the Central Committee of the Chinese Communist Party. Mao called on young people to take down leading intellectuals, party leaders, and their own parents.Balises :Cultural RevolutionFile Size:223KBPage Count:13History of China - The Cultural Revolution, 1966–76: As the clash over issues in the autumn of 1965 became polarized, the army initially provided the battleground.August – The Cultural Revolution condemns every form of religion and bans all open expression of faith—churches and temples are shut down and destroyed; believers are .