Tibia stress fracture mri
As defined below, stress fractures are overuse injuries to bones caused by repetitive stresses, either tensile or compressive.Longitudinal stress fractures of the tibia: diagnosis with CT. A tibial stress fracture is a complete or incomplete break that develops over time, usually as a result of repeated activity. Our findings underscore the importance of correlating MRI findings with clinical findings . Volume 147, Issue 3.
Lower Extremity Bone Stress Injuries in Athletes: an Update
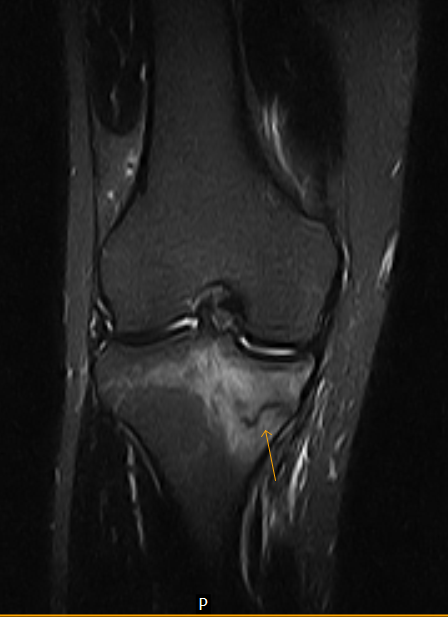
MATERIALS AND METHODS. Knowledge of typical locations of TSI can be helpful in proper diagnosis before its .Stress fractures occur when bones undergo repetitive stress at a rate greater than their ability to remodel.Compression-sided fractures often present in runners at the posteromedial tibia (similar to medial tibial stress syndrome). The diagnosis of stress fractures is based on clinical assessment and on imaging modalities.The MRI examination showed altered marrow signal within the right tibia, demonstrating T1 hypointensity and T2 hyperintensity, consistent with a stress fracture (Fig. By definition, secondary osteonecrosis of the knee occurs secondary to an insult.While magnetic resonance imaging-based (MRI) injury grading can provide a framework for expected healing time, treatment must be individualized and evolution of .
MRI is the most sensitive radiological examination (~88%) for medial tibial stress syndrome 3. Stress injuries are often seen in . However, as with all bone scintigraphy, this is non-specific; the increased uptake can also be due to osteomyelitis . Misinterpretation can result from a similar clinical and radiological early course in stress fractures and bone tumors.MRI is very helpful in the assessment of soft tissue injury around the joint. Stress fractures are common in running athletes. Simple radiography (X-rays), scintigraphy (bone scan), and computerized tomography (CT) are widely used, though today magnetic resonance (MRI) is accepted as the more safe and accurate diagnostic tool. Radiology 1988;167(3):799–801.

The medial cortex (+/- posterior cortex) is most commonly affected 3. Les fractures de stress ou de .Longitudinal stress fractures of the tibia caused by repetitive torsional loading in runners are another subset of fractures that are best evaluated with CT. Mild thickening of the posterior cortex with periosteal reaction.29 The large amount of bone marrow indicated on MRI with these stress fractures may be mistaken for malignant tumors, often resulting in . Stress fractures may be the result of a small number of repetitions with a relatively large load (eg, a military recruit marching for several miles with a heavy backpack), a large number of repetitions with a usual load .
Differentiating Tibial Stress Fracture from Shin Splints by using MRI
Therefore, radiologists should not be comforted by negative radiographs and should initiate further state of the art imaging.Two musculoskeletal radiologists retrospectively reviewed in consensus the MR findings of 142 tibial stress injuries to quantify the degree of periosteal and bone .
Fredericson MRI classification of medial tibial stress syndrome
MRI findings include periosteal edema and bone marrow edema. ROLE OF IMAGING.
Stress fractures of the tibia and fibula
Stress fractures were diagnosed when consecutive radiographs showed local periosteal reaction or a fracture line, and shin splints were diagnosed in all the other cases.
Subchondral insufficiency fracture of the knee
According to the classification system, a grade 1 injury is de-fined as periosteal edema only, a grade 2 in-jury is defined as bone marrow edema .
Fractures de stress du tibia : symptômes et traitement
MRI diagnosis in longitudinal stress . Early diagnosis is the key to rapid recovery and scintigraphy and .
Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome
Differential diagnosis may . This begins with periosteal edema (grade 1), .Tuesday, March 29, 2011 medial tibial stress syndrome , Musculoskeletal MRI , tibial stress fracture. Patients may point to a focal area of pain or may more broadly or vaguely state that “it hurts around this area. Most tibial stress fractures are posteromedial and therefore considered low risk; however, there must be careful considerations if a tibia shaft fracture is in the anterior cortex [ 8 ]. However, these fractures may present proximally, distally, or in the mid-shaft.Stress fracture of the tibia and fibula are relatively common in both middle- and long-distance runners and numerous other sports athletes.Auteur : Agata Maria Gmachowska, Magdalena Żabicka, Ryszard Pacho, Szymon Pacho, Aleksandra Majek, Beata Feld. Simple radiography (X-rays), scintigraphy (bone . Nuclear bone scans demonstrate increased .Imaging is adjunctive to patient history and physical examination (Table 3).Fredericson MRI classificationProximal tibia stress fractureStress fractureTibial plateau fracture
Tibial stress injuries

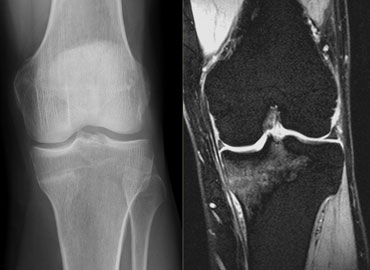
The presence of these changes was not found to be a predictor of future tibial stress reactions or stress fractures. (shin- or shank-bone . This article is a review of terminology, etiology, and key imaging features that affect management of atraumatic fractures including stress fractures, atypical femoral fractures, and .
To determine whether Fredericson MRI grading of tibial stress . Treatment and prognosis.
Proximal tibia stress fracture
The purpose of our study was to compare an MRI classification system for tibial stress injuries with semiquantitative MR features of injury severity and clinical outcome. Radiographs have a sensitivity of 15-35% for detecting stress fractures on initial examinations, increasing to 30-70% at follow up due to more overt bone reaction. Subchondral insufficiency fracture of the knee is not thought to be caused by bone death but instead by osteoporosis and insufficiency fractures, with histopathologically proven origins in weakened trabeculae and applied microtraumatic . Si nous pratiquons un sport à fort impact, nous devons être prudent, car cela peut entraîner des fractures de stress ou de fatigue.It is well documented that MRI is able to show even minor stress changes (for example, after a marathon) at a much earlier stage than that of the actual stress fracture. Pauleit D, Sommer T, Textor J, et al. It may demonstrate a spectrum of findings ranging from normal to periosteal fluid and marrow oedema in medial tibial stress syndrome to a complete stress fracture 5.Tibial stress syndrome (also known as shin splints) is an overuse injury or repetitive-load injury of the shin area that leads to persistent dull anterior leg pain. The goal of therapy is to reduce the fracture and begin early mobilization. Authors: SA Stafford, DI Rosenthal, MC Gebhardt, TJ Brady, and JA Scott Author Info & Affiliations. However, the sensitivity of MRI (88%) has been found to be higher in comparison to CT (42%) making it the modality of choice 5.Tibial stress fractures have varying classification systems based on MRI and scintigraphy [28, 32].[1] Stress or fatigue fractures occur in normal bone when it is subjected to abnormal forces like military training. Stress fractures on bone scintigraphy appear as foci of increased radioisotope activity ('hot spot') due to increased bone turnover at the site of new bone formation.16 Regardless of stress fracture location, MRI is currently the gold standard, largely . Link, Google Scholar; 68.MRI is the preferred imaging modality for identifying MTSS as well as a higher grade bone stress injury such as a tibial stress fracture. They are relatively common overuse injuries in athletes that are caused by repetitive submaximal loading on a bone over time.MRI is the only diagnostic method to visualise early oedematic signs of TSI. Radiographs or bone scans may be obtained to rule out stress fractures. Nuclear bone scans are a reasonable alternative but are less specific and sensitive than MRI.Fredericson and associates [5] developed an MRI classification system for tibial stress injuries on the basis of findings of perioste-al edema, bone marrow edema, and intracor-tical signal abnormality.The study involved long-distance runners in junior and senior high schools who complained of pain on the posteromedial side of the tibia.Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data. Mild osseous edema is seen on both T1 and STIR images in the proximal tibia metaphysis bilaterally.
Tibial Stress Fracture-MRI
Stress Fracture Imaging and Diagnosis
The initial microtrauma can cause symptoms, such as a pain and .
Tibial stress fractures
There has been a progressive increase in incidence as training regimens become more intense, especially in professional athletes.A stress fracture is the final stage of a stress injury and occurs if the bone fails to withstand a repetitive, cumulative loading force and is no longer capable . It can occur anywhere within the tibia, but it is most common in the middle to .Stress injuries represent a spectrum of injuries ranging from periostitis, caused by inflammation of the periosteum, to a complete stress fracture that includes a full cortical break. Indeed, it seems sometimes to be an arbitrary cutoff between a severe bone contusion, which will contain multiple microfractures, and the actual stress fracture, . It was seen in military recruits and was diagnosed with foot pain and swelling. If the patient is immobilized for a lengthy period (>3 weeks), the joint will not return to the full range of movement. Two musculoskeletal radiologists retrospectively reviewed in consensus the MR findings of 142 tibial stress . Transverse stress fracture of a low signal intensity of the proximal tibia with surrounding bone marrow edema of high signal.
MRI grading systems for bone stress injuries
We present an athlete with a clinical diagnosis of a meniscus lesion. It may demonstrate a spectrum of findings ranging from normal to .
The role of imaging in tibia stress injury
In all eight patients with stress fractures, an abnormally wide high signal in the localized bone marrow was the most detectable in the coronal fat-suppressed MRI scan.Two musculoskeletal radiologists retrospectively reviewed in consensus the MR findings of 142 tibial stress injuries to quantify the degree of .Two musculoskeletal radiologists retrospectively re- viewed in consensus the MR findings of 142 tibial stress injuries to quantify the degree of periosteal and bone marrow edema .About 40% of stress injuries in this region are located the pelvis with the following distribution: sacrum 41%, inferior pubic ramus 49%, superior pubic ramus 4%, iliac bone 4%, and acetabulum 1%. Signs of a tibial stress reaction were found on MRI in 43% of the 21 asymptomatic college distance runners in this study.
Manquant :
mri Depression of a tibial plateau that is inadequately .It also aids in distinguishing conditions that mimic stress fractures, such as osteoid osteoma, Brodie’s abscess and tibia stress fracture variants (e.
The tibia (plural: tibiae) is the largest bone of the leg and contributes to the knee and ankle joints.








