Tunneled catheter insertion

Via Separate Venous Access: If replacement involves removing an existing dialysis catheter and inserting a new dialysis catheter via . You will now be able to get medicine, blood, nutrients, or other fluids with more comfort. Venous access is commonly performed in . Fourteen male and 19 female patients with a mean age of 56 years (range 29–78 years) were included in the study.
4 percent developed deep vein thrombosis attributable to the central venous catheter . There are two main types of urinary catheterization: . While these catheters are biocompatible and, thus less thrombogenic, their main disadvantage is the thicker wall, which decreases the internal lumen.In contrast to non-tunneled central venous catheters (CVCs), subcutaneously tunneled CVCs travel under the skin, away from the . Ideally, the catheter . Patients often need central venous access for indications including ongoing hemodynamic monitoring, difficult venous access, or long-term intravenous therapy (eg .Interventional radiology (IR) is an underutilized resource for the placement and management of tunneled peritoneal dialysis (PD) catheters, as only about 5% of PD .
2021 BILLING AND CODING GUIDELINES HEMODIALYSIS CATHETERS
The specific CPT codes for catheter insertion vary based on the patient’s age and the type of catheter being used.1 percent of patients had mechanical complications during insertion, 0.Placement of Tunneled Catheter.Tunneled dialysis catheter insertion is a procedure to place a long, thin, plastic tube (catheter) into a vein in the neck and move it to a larger central vein near the heart. A long, thin, flexible tube called a catheter is tunneled under your skin and then placed into the vein. It is important to select the appropriate CPT code to ensure accurate billing and coding. [] Combined use of ultrasonographically guided vein puncture and fluoroscopy has significantly reduced the . Your doctor will decide which type . Nontunneled catheters; Implanted - Tunneled catheters - Totally implantable (ports) Coated and impregnated . There are double major types of tunneled .Predictors of tunneled CVC-related candidemia are summarized in figure 3 and include the following: isolation of Candida parapsilosis from blood samples; quantitative blood cultures that suggest catheter-related candidemia (5-fold the number of colonies isolated from blood drawn through the CVC, compared with blood drawn from a .Principles of tunneled cuffed catheter placement - PubMedpubmed.The right internal jugular vein is the preferred initial insertion site for tunneled catheters (see “Catheter Site Selection” section in Clark et al 23).The catheter is a soft, flexible tube that runs under your skin, usually from a vein in your chest or neck to a large vein near your heart.Long-term venous access is of critical importance to a wide group of patients.
36558 Insertion of tunneled centrally inserted central venous catheter, without subcutaneous port or pump, age 5 years or older Facility :$891 $ 1,365 .7%) and 3 patients underwent left-sided insertion. The patients with femoral catheter insertion were on hemodialysis for a median duration of 24 months (range 2–144 months). Non -Facility : $264 . Clinicians involved in the placement or maintenance of tunneled catheters require an appreciation of their best clinical application. Interventional radiology (IR) is an underutilized resource for the placement and management of tunneled peritoneal dialysis (PD) catheters, as only . Alternate imaging techniques may be used to ensure correct catheter tip position if fluoroscopy is unavailable.In urinary catheterization, a latex, polyurethane, or silicone tube known as a urinary catheter is inserted into the bladder through the urethra to allow urine to drain from the . The traditional technique is conventional open surgery. 51 Patients (64.
Vascular Tunneled Central Catheter Access
The KDOQI clinical practice guidelines for vascular access recommends image guided placement of tunneled cuffed hemodialysis catheter (tHDC).
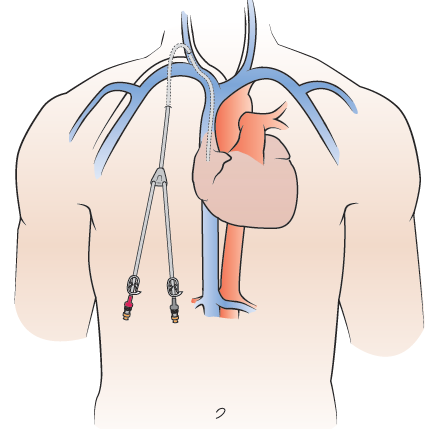
Central venous access (ie, insertion of a vascular catheter such that the tip terminates in a deep vein of the neck, chest, or abdomen) is a key component of this practice.

Artistic representation of three common CVCs, from left to right, PICC, Hickman and port.The incidence of patients with CKD diagnosed at a stage requiring hemodialysis increases the use of tunneled catheters. A small incision is made in the skin, and the catheter is inserted into a large vein in the neck or groin.comVascular Access for Placement of Tunneled Dialysis .TYPES OF CENTRAL VENOUS CATHETERS.What Is It? In urinary catheterization, a catheter (hollow tube) is inserted into the bladder to drain or collect urine. The catheter is then tunneled under the skin and attached to the outside of the body.PD Catheter Insertion Strategies.Tunneled double-lumen catheters are used for short- and intermediate-term venous access among hemodialysis patients who do not have a permanent .
Taille du fichier : 774KB
Inserting your tunnelled haemodialysis catheter (permcath)
Two types of tunneled hemodialysis catheters were used: palindrome (Covidien Medtronic) and .A tunneled catheter is a flexible catheter (thin tube) that goes into a vein in your chest. The mean age was 66. 3 Replacement of Catheter . You will not be poked with a needle every time. Consider changing anticoagulation to warfarin.Permcath: Placement, Cost, Complications Explained By A . Tunneled hemodialysis catheter insertion is a common and important procedure. You may hear this type of line called a Central line, PowerLine, Hickman, or an Apheresis Catheter. The insertion of a permacath involves a minor surgical procedure.7 Silicone catheters are more flexible which decreases vascular damage during insertion, however, makes the catheter insertion theoretically harder. The decision to insert a TCVC is not without risk of infections, thrombotic and other complications. This means that the catheter is inserted under the skin and then moved away from the insertion site.One major challenge when inserting a tunneled, cuffed central venous catheter (CVC) for hemodialysis under fluoroscopy is to accurately place the catheter tip by assessing its position in relation to . Like such, tunneled CVCs can be in place for weeks to months, while an non-tunneled catheterized need be exchanged every few days to a week.
The authors routinely clean this area on both sides, in case occlusion or stenosis of central vessels is encountered and it .
Urinary Catheterization
4 percent experienced bloodstream infections, and 0. Clinicians involved in the placement or maintenance of tunneled catheters require an appreciation of their .A step by step video illustrating the insertion of a tunneled cuffed central venous catheter from start to finish Background/objective: To study the safety and outcome profiles of tunnelled dialysis catheter (TDC) insertions and exchanges with fluoroscopy versus . These can stay for . The prevention requires strict compliance with asepsis rules, during the placement and manipulation of tunneled .Tunneled central venous catheter insertion is a procedure that should be in the armamentarium of all interventional radiologists.Right-sided femoral catheter insertion was performed in 18 patients (85. You may have it for weeks, months, or longer. Although blood flow rates are generally .
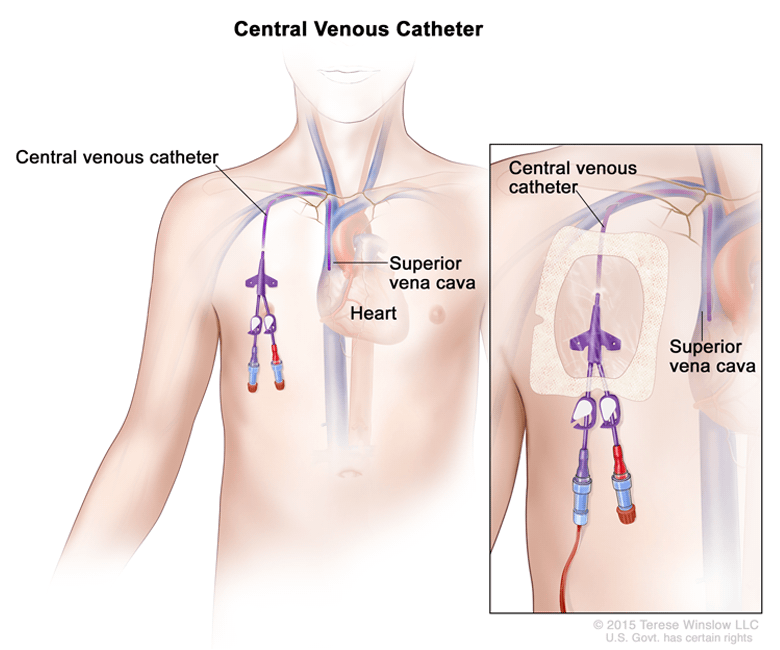
Tunneled Central Venous Catheter (CVC) Placement
5 or a platelet count lower than 50,000/dL. During an outpatient procedure, a physician who specializes in vascular access makes a small incision in the skin over the selected vein located in the neck, upper chest, or groin.Administration of prothrombin complex concentrate followed by temporary dialysis catheter insertion and tunneled dialysis catheter placement the next day.tunneled Central Venous Catheter (CVC) is a special type of intravenous (IV) line that is placed into a large vein in your chest.govTunneled femoral dialysis catheter: Practical pointers - .A tunnelled haemodialysis catheter is a soft plastic tube, which is inserted into one of the large veins in your neck or, occasionally, in your groin.
Tunneled Central Line (Tunneled Central Venous Catheter)

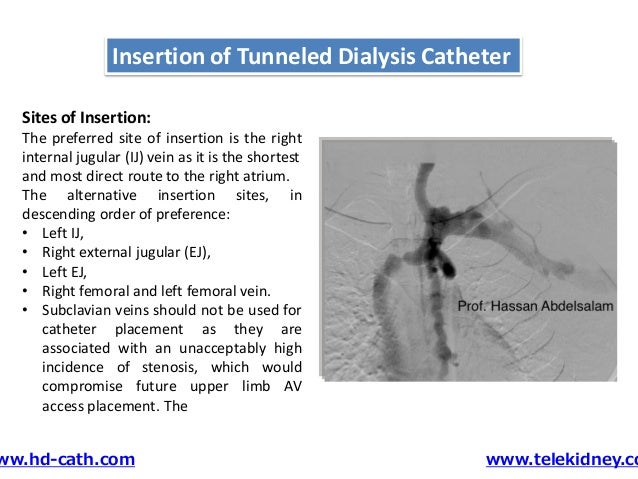
Answer: Choice D.All major guidelines recommend the right internal jugular (IJ) vein as the preferred approach for TDC placement.The first insertion of a central venous catheter (CVC) . The tip of the CVC in SVC is shown at the . Surgeons place a large percentage of PD catheters but have mostly converted to laparoscopic methods, which are less invasive than conventional surgery. This catheter . Clinicians involved in the placement or maintenance of tunneled catheters require an .comDialysis line insertion | National Kidney Federationkidney. They are most common in acute and emergency situations because of their easy insertion .A step by step video illustrating the insertion of a tunneled cuffed central venous catheter from start to finish.clinicalimagingscience. Materials and methods: Our division's criteria for acceptable coagulation parameters in patients undergoing TCVC insertion is INR no . Tunneled double-lumen catheters are used for short- and intermediate-term venous access among hemodialysis patients who do not have a permanent arteriovenous access [].
Practice Guidelines for Central Venous Access 2020
It is most commonly placed in the neck into the internal .7% male) were prospectively enrolled.A later study examining the complications of central venous catheters by insertion site noted that 2.
Tunneled Central Catheter Placement Handout
Although comprehensive guidelines are available, many aspects of the published literature on this subject remain uncertain.
Tunneled catheters in hemodialysis: Indications and complications
The age-old anatomical landmark guided method is unsafe due to its lower . One of the main ways in which tunneled and non-tunneled catheters differ is in terms of the manner in which they are inserted. Subclavian catheters are avoided if possible due to increased risk of central venous stenosis (see “Risk Factors for Central Vein Stenosis” section in Miller et al 24).
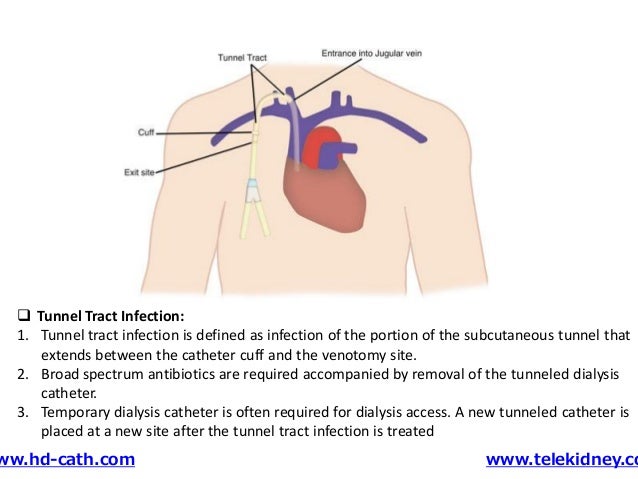
Hemodialysis Tunneled Catheter-Related Infections
Your doctor will decide which type is best for you.These catheters are also used for permanent vascular access in patients with limited alternative options for vascular access []. The entire procedure usually takes about an hour and can be done . The physician will numb the area for the . Tunneled PD catheters can be placed using four different techniques.The number of catheter days, complications, amount of drained ascites and ascites-associated symptoms and hospitalization rate pre- and post-PleurX insertion were analysed.Tunneled hemodialysis catheter insertion is a common and important procedure.











