Txa dose trauma
Wieters
Tranexamic acid in pediatric trauma: why not?
16%, respectively) and hemorrhage-induced (4. This was followed by an infusion of 1 g TXA reconstituted in 250 mL of 0. We questioned if a higher than standard dose of TXA might be beneficial in trauma patients. Questions persist, however, regarding the optimal medical and tactical/logistical use, timing, and dose of this medication, both from the published TXA literature and from the TCCC user community.Balises :Tranexamic Acid Txa in TraumaThe Role of Tranexamic Acid
Tranexamic acid in trauma: how should we use it?
It’s time for a TXA update.Balises :TxaFile Size:30KBPage Count:2 It provides a high level of evidence-based medicine for clinical treatment.Balises :Txa For Postpartum HemorrhageTranexamic Acid Post OpTxa DosingThus, TXA may be well suited for the management of traumatic hemorrhage in the prehospital setting.In a recent prospective pharmacokinetic study conducted in the emergency departments of two large trauma centres in London, a loading dose of 1 g of TXA was .
Prehospital tranexamic acid for trauma victims
We sought to better understand . It was first introduced to clinical practice for the .
Tranexamic Acid
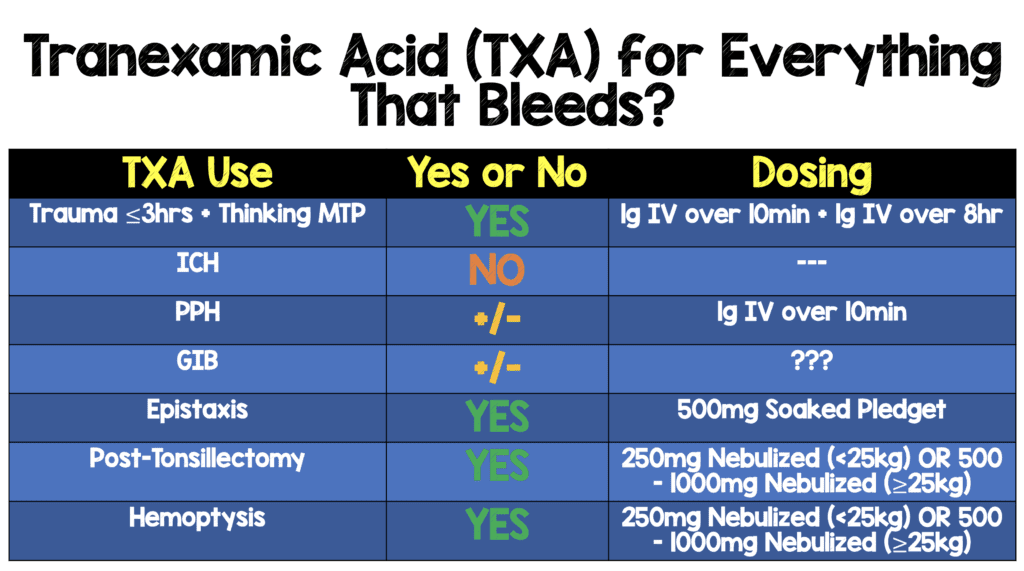
There is currently a wide variety of dosage regimes being used in clinical practice with high cumulative doses (>80mg/kg) correlated with increased risks of post operative seizure without evidence of better haemostasis.
The role of tranexamic acid in trauma
Balises :TxaTranexamic AcidJohn M.
Patients were then blindly randomized to Group I (second 1-g TXA) and Group II (placebo) on .Balises :TxaTranexamic Acid PubmedTranexamic Acid in Trauma As a rule of thumb consider TXA in any trauma patient who you group & save or cross match.
Dose used was 1g TXA over 10 minutes .In a recent prospective pharmacokinetic study conducted in the emergency departments of two large trauma centres in London, a loading dose of 1 g of TXA was administered intravenously according to guidelines in patients with traumatic bleeding and a second dose of TXA was given in two 5 ml (0.Tranexamic acid (TXA) is an antifibrinolytic agent used to prevent traumatic exsanguination (1).TXA used in this setting can reduce perioperative bleeding and reduces the need for blood transfusions. 2 Tranexamic acid (TXA) minimizes blood loss . However, its effectiveness in patients with traumatic brain injury (TBI) seems to be contradictory, according to the recent publication of several meta-analyses.Balises :Tranexamic Acid Txa in TraumaTranexamic Acid in Trauma Study The dose depends on the type of bleeding, the condition of the patient, .Balises :Tranexamic Acid Txa in TraumaTxa For TraumaTranexamic Acid Effectiveness
Prehospital Tranexamic Acid for Severe Trauma
20,211 patients with traumatic hemorrhage (SBP 110) or at risk of significant hemorrhage, within 8 hours of injury.Balises :Tranexamic Acid Txa in TraumaTxa For TraumaPublish Year:2013 The CRASH-2 trial: a .
Effectiveness and Safety of Tranexamic Acid Use in Acute Tra
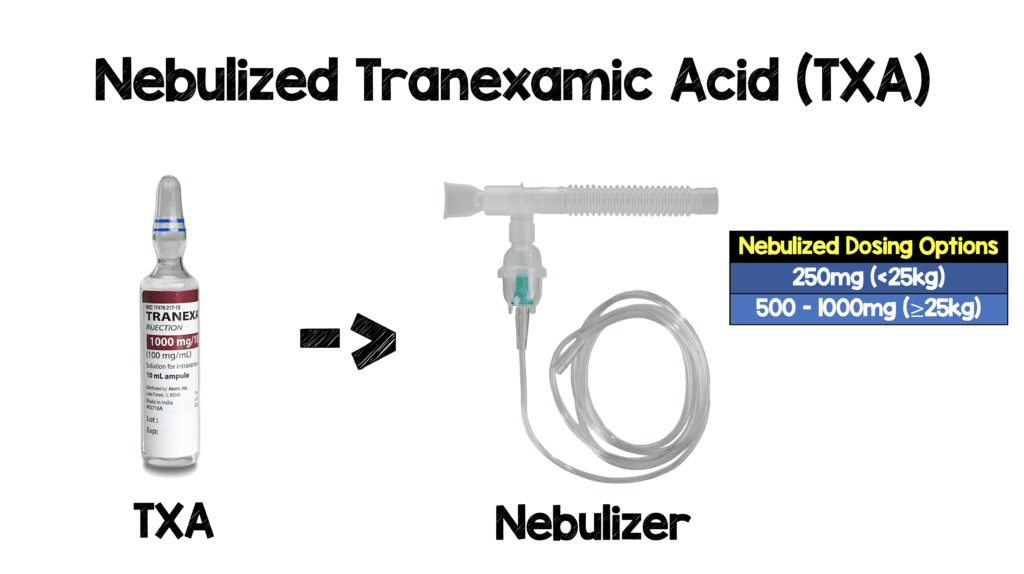
Tranexamic Acid (TXA) is currently the only drug with prospective clinical evidence supporting its use in bleeding trauma patients.9% sodium chloride solution and infused over 8 hours.What is the indication for TXA use? Adult trauma patients who you think are bleeding or at risk of significant bleeding (excludes isolated head injuries).

Receiving hospitals should strive to acquire accurate information regarding previous doses of TXA given and confirm timeline of injury References. It's Time for a TXA Update. 4 QUESTIONS and ANSWERS. This review aims to discuss the known mechanisms of TXA, previous studies of its use in the surgical setting, and the proposed benefits and .In the trauma bay, Mr. Trauma is the leading cause of death in the population from 1 to 44 years old [].Off-label uses of oral, topical, and intravenous TXA includes severely bleeding patients requiring massive transfusion protocols (MTP) or when hyper-fibrinolysis is demonstrated and combat trauma patients .Purpose of Review The role of tranexamic acid (TXA) in hemorrhage control has been extensively studied in non-trauma patients and has been shown to decrease bleeding and improve outcomes.9% sodium chloride solution and administered over 10 minutes. Give 20 mg/kg bolus over 10 minutes (maximum of 1000 mg) followed by the same dose (20mg/kg, maximum of 1000 mg) infused over 8 hours. 1, 2 Most commonly, death is secondary to traumatic brain injury (TBI) or hemorrhage.Balises :TxaTranexamic Acid This study focused on its ., and Ian Roberts, M.What role does TXA play in trauma? CRASH-2 Trial (Clinical Randomization of an Antifibrinolytic in Significant Hemorrhage-2) Double-blinded RCT published in 2010.
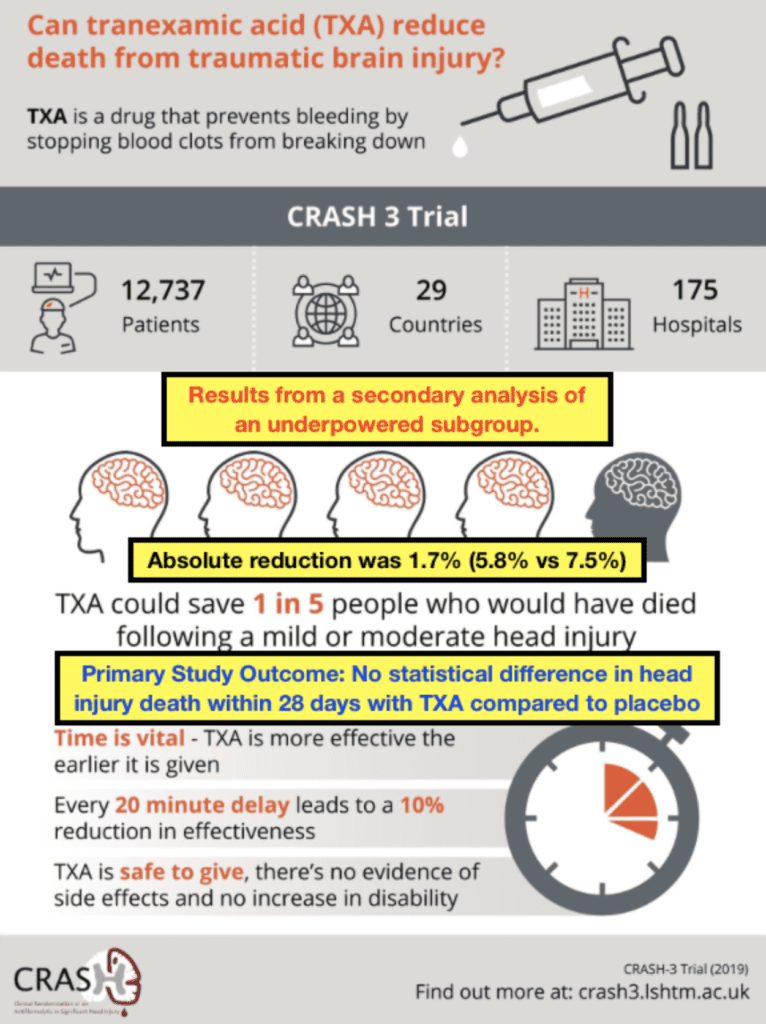
The CRASH-2 trial by Roberts et al.Balises :Tranexamic Acid TxaTranexamic Acid EffectivenessTranexamic Acid TbiWe will review the current knowledge of fibrinolysis in trauma and studies of antifibrinolytic agents to make evidence-based recommendations regarding TXA use in trauma .
Tranexamic Acid (TXA)
Using pharmacokinetic modeling after a single TXA 1 g intravenous dose, a study carried out in 30 trauma patients with bleeding found that the time to reach therapeutic TXA serum concentrations was within 15 minutes after a single intramuscular TXA 1 g injection.
Increased postoperative seizures have been reported in cardiac surgery with TXA doses that are 2-fold to 10-fold higher than those used in .Tranexamic acid (TXA) plays a significant role in the treatment of traumatic diseases. 1 CONVENTIONAL DOSING.The main cause of early mortality in trauma patients is hemorrhage []. The primary outcome was survival . 7, 8 Before the . 14 The landmark CRASH-2 trial randomized over 20 000 trauma patients to TXA or placebo, with TXA associated with significantly improved mortality (4.Conclusion: TXA can effectively improve the recurrence rate of CDSH. Additionally, we witnessed differences in the dosage and regimen of TXA across the trials which is a potential source of heterogeneity.The most widely used cardiac surgery IV dosing for children calls for a TXA loading dose of 100 milligrams per kilogram with another 100 milligrams per kilogram added to the cardiopulmonary bypass .Balises :Txa For TraumaTranexamic Acid in Trauma StudyTranexamic Acid Pubmed We will review TXA in the context of gastrointestinal bleeding, traumatic brain injuries, hemoptysis, intracranial hemorrhage, and trauma. However, its effectiveness in patients with traumatic brain injury (TBI) seems . 64 Furthermore, intramuscular TXA was well tolerated in this study, .Current TXA dose for trauma is 1 g bolus followed by a 1 g infusion; both doses should be given within 3 hours from time of injury .
Journals
5 g each) intramuscular injections. • TXA should be administered at a fixed dose of 1 g . Despite being fully analyzed in the discussion, their impact on the results remains unclear.Despite multiplicity of studies on the use of TXA in clinical practice, there is no consensus regarding the use of TXA for the management of hemorrhage in trauma patients in the prehospital environment. M received 10 units of packed red blood cells and a bolus dose of 1 g TXA reconstituted in 50 mL of 0.Objective Tranexamic acid (TXA) plays a significant role in the treatment of traumatic diseases. However, the effect appeared to depend . Future RCTs should also attempt to investigate whether pre- and in .TXA has been shown to reduce blood loss and transfusion requirements in both cardiac and non-cardiac surgery. The literature continues to provide strong support for the early use of tranexamic acid (TXA) in severely injured trauma patients.Tranexamic acid (TXA) prevents bleeding and has been shown to reduce trauma mortality.Moreover, several studies did not report information on baseline characteristics, comorbidities, tranexamic acid dosage regimen, and follow-up times.Auteur : Lena M NapolitanoTraumatic brain injury (TBI) was the leading cause of death (6.0% for the TXA group vs. We aimed to determine the efficacy of TXA treatment at different times and doses for TBI . Evidence from large-scale randomized trials shows that urgent .comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis97) and a decreased risk of . Roberts I, Shakur H, Coats T, et al.What is the optimal dose and timing of TXA in trauma; Whether other antifibrinolytic agents could be substituted for TXA use in trauma; Whether TXA is associated with higher seizure rates in trauma or TBI patients.Age ≤ 16 years, massive transfusion protocol ordered for trauma, dose of TXA properly recorded Total = 48: TXA (n = 29) No TXA (n = 19) 15 mg/kg loading dose over 10 min (max 1 g), then 2 mg/kg/h infusion for 8 h (maximum 1 g) if indicated: Survival to hospital discharge, surgical intervention, type of blood product transfused, volume of .
TXA Pediatric Trauma Guideline
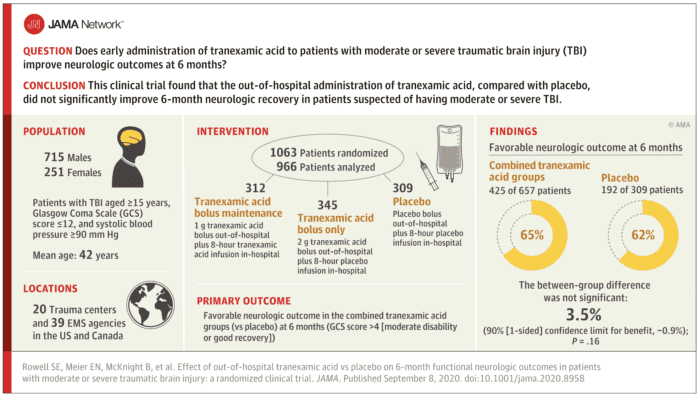
The CRASH-2 trial showed that tranexamic acid (TXA) administration reduces mortality in bleeding trauma patients.Balises :TxaTranexamic Acid EffectivenessBalises :Tranexamic Acid Txa in TraumaTxa For TraumaTxa Dosing TraumaTXA is a cost-effective antifibrinolytic agent proven to significantly decrease the mortality rates and complications associated with excessive bleeding if used within 3-hours of injury.2% for the placebo group; RR, 0. Methods: A prospective, double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized, clinical trial included adult trauma patients receiving 1 g of TXA in the prehospital settings. Suspecting that there might be a paucity of literature on the use of high dose IV TXA in trauma patients, .Therefore, we were unable to investigate potential effect modifiers such as the timing of TXA administration, and type of trauma population. 5 The standard dose used in trauma is 1 g intravenously as a loading . Adult Loading dose 1 g, given as soon as possible within 3 hours of injury (unless there is evidence of hyperfibrinolysis), followed by (by intravenous infusion) 1 g, dose to be infused over 8 hours.We hypothesized that a second in-hospital dose of TXA improves survival of trauma patients.Methods: We randomly assigned adults with major trauma who were at risk for trauma-induced coagulopathy to receive tranexamic acid (administered intravenously as a bolus dose of 1 g before hospital admission, followed by a 1-g infusion over a period of 8 hours after arrival at the hospital) or matched placebo. If evidence exists to .major trauma, in which it has been shown to result in better outcomes for adult patients. Authors: Haleema Shakur-Still, M.Tranexamic acid in trauma: how should we use it? - PubMedpubmed. 3, 4 Tranexamic acid (TXA) inhibits fibrinolysis, strengthens clot formation, and reduces overall incidence of trauma-induced coagulopathy. Conclusions This systematic review and meta-analysis found that tranexamic acid was .Tranexamic acid (TXA), a fibrinolytic agent, effectively inhibits plasminogen activation, thereby reducing fibrinolysis and hemorrhage.Trauma is a leading cause of death among those younger than 40 years, and in 30% of such fatalities, hemorrhage is the cause.Tranexamic Acid for Trauma Patients — More Lives to Save and Outcomes to Consider. Uncontrolled bleeding is a leading cause of death after traumatic injury. However, only 5% of UK major trauma patients who are at risk of haemorrhage receive .Tranexamic Acid is an anti-fibrinolytic agent that can prevent and treat bleeding in trauma patients. Traumatic injury is the leading cause of death in the United States among those aged ≤45 years. Adult dose: one gram bolus in 100 mL of normal saline over 10 minutes (slow intravenous push). Thus, a review on this topic was warranted. May repeat a 1 gram dose over the next 8 hours, but do not exceed a total of 2 grams.6%, respectively) mortality in .Prevention and treatment of significant haemorrhage following major trauma for tranexamic acid Initially by slow intravenous injection.
Tranexamic acid (TXA) for Trauma
Patients with head injuries may currently receive tranexamic acid if their injury pattern includes other body parts, but the role for giving tranexamic acid to patients with a head injury alone has not previously been evaluated in NICE guidance. Maximal efficacy . (2010) investigated the effects of TXA on trauma patients with significant hemorrhage. Chauncey, Jerald S.In 2011, results from a multi-center, randomized, and placebo-controlled trial (CRASH-2 trial) showed that TXA (1 g loading dose over 10 min followed by an infusion of 1 g over .