Type 1 diabetes insulin dependent

All the cases were independently identified from four sources: . Controlling blood glucose with an acceptable range is a .
Type 1 diabetes
Onset most often occurs in childhood, but the disease can also develop in adults in their late 30s and early 40s. insulin infusion system. People with type 1 diabetes are therefore dependent . It is rare during the first 9 .Diabetes Care 1995, 18, 361-376. Gastric emptying was studied with a scintigraphic technique and blood glucose . Mis à jour le 15 nov.Type 1 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is a disease in which the pancreas does not produce any insulin.In 10 patients with Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus gastric emptying of a digestible solid and liquid meal was measured during euglycaemia (blood glucose concentration 4-8 mmol/l) and during hyperglycaemia (blood glucose concentration 16-20 mmol/l).This paper reports on the hardware implementation of a digital insulin-glucose regulator for type 2 diabetic patients by using a Field Programmable Gate Array . 2023 par Expert : Dr Alain Scheimann, endocrinologue et diabétologue à Paris. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get into your cells to give them energy. A chapter is dedicated to patients over the age of 75 years, who represent a .In people with type 1 diabetes, autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cells results in absolute insulin deficiency.As our knowledge of type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes increases, so does our appreciation for the pathogenic complexity of this disease and the challenges associated with its treatment. Diabetes Care, 2002, 25, 593- 598.
Diabète de type 1
The pancreas is below and behind the stomach. Individuals with T1D require life-long insulin replacement with multiple .Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Despite enhanced knowledge related to the pathophysiology of the disease, including .Diabète type 1 : tout savoir sur le diabète insulino-dépendant. Knowledge of type 1 diabetes has rapidly .Qu'est-ce Que l'insuline ?Fewer than 10% of all people with diabetes have type 1 disease. Type 1 diabetes is a chronic illness characterized by the body’s inability to produce insulin due to the autoimmune destruction of the beta cells in the pancreas. L’objectif du . Il est mis en place par un diabétologue, en coordination avec le médecin traitant ou le pédiatre, qui en assurent également le suivi. Depending on the type of diabetes, the body either cannot produce insulin itself (type 1) or is unable to use the insulin it produces properly (type 2). Insulin is a hormone produced in the pancreas by special cells, called beta cells.3% of Caucasian populations (Todd, 1990). The population at risk (0–29 years) consisted of 2,690,394 inhabitants (total population of Catalonia 5,978,638).The vast majority of those with diabetes (90 to 95%) have Type 2.
Type 1 diabetes generally develops in childhood . You'll need to calculate your rapid-acting insulin dose for each meal .

Human insulins are produced by recombinant DNA technology and have the same amino acid sequence as endogenous human insulin.

But you may also need to start insulin as a treatment if other medications haven’t helped managed your . Type 1 diabetes used to be called insulin-dependent or juvenile diabetes. Many new concepts about the pathogenesis of this disorder have arisen. Most patients with type 1 diabetes are treated with “intensive” or “basal-bolus” insulin therapy, which requires four injections a day. Consequently, insulin therapy is a medical necessity. They do need to be careful of what they eat, so to avoid causing spikes in their blood glucose, but type 1 cannot be controlled solely with diet.The pancreas, therefore, produces little or no insulin.In type 1 diabetes (formerly called insulin-dependent diabetes or juvenile-onset diabetes), the body's immune system attacks the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas, and more than 90% of them are permanently destroyed.Insulin therapy keeps your blood sugar within your target range. Approximately 10% of people with diabetes have type 1 diabetes. It helps prevent serious complications. It requires daily management with insulin injections and .
The Difference Between Type 1 and Type 2
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic autoimmune disease characterised by insulin deficiency and resultant hyperglycaemia.Type 1 diabetes, once known as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes, is a chronic condition. It can develop at any age, and medication . — Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion at 25 years : evidence base for the expanding use of insulin pump therapy in type 1 diabetes. It occurs in children and adults.Type 1 diabetes mellitus was previously referred to as insulin-dependent or juvenile-onset diabetes mellitus. L'alimentation .In type 1 diabetes, an absolute insulin deficiency causes persistent hyperglycaemia.Adult-onset type 1 diabetes is more common than childhood-onset type 1 diabetes, as shown from epidemiological data from both high-risk areas such as Northern Europe and low-risk areas such as China (3–8). Individuals with type 1 diabetes are reliant on insulin for survival. Il apparaît le plus souvent de manière brutale chez l'enfant ou chez le jeune adulte (ou beaucoup plus .With type 1 diabetes, your pancreas does not make insulin. Over time, high blood glucose can lead to serious problems with your heart, eyes, kidneys, nerves, and gums and teeth. It is a chronic disease caused by pancreatic insufficiency of insulin production. a rapid-acting insulin (also called mealtime or bolus insulin) before meals.Type 1 diabetes was once called insulin-dependent or juvenile diabetes, but it can develop at any age.
Diabète type 1 insulino dépendant
In type 1 diabetes your pancreas no longer makes insulin, so you have to inject it to control your blood glucose levels. Different brands of insulin vary in onset, .Le diabète insulino-dépendant ou encore diabète de type 1 est une forme de diabète qui survient chez les personnes jeunes, . In this condition, the pancreas makes little or no insulin. The necessity for treatment with insulin is why type 1 is classified as insulin-dependent.If you have type 1 diabetes, you’ll likely take a combination of insulins. Without insulin, glucose builds up in .
Insulin Treatment in Type 1 Diabetes
Individuals with type 1 diabetes are reliant on insulin for survival. In Type 1 diabetes, the pancreas doesn’t make insulin. Created: May 29, 2013; Last Update: June 29, 2017; Next update: 2020. The role of genetics versus environment in disease formation has been questioned, and .In type 1 diabetes mellitus (previously called juvenile-onset or insulin-dependent), insulin production is absent because of autoimmune pancreatic beta-cell destruction possibly triggered by an environmental exposure in people who are genetically susceptible. Type 1 diabetes is the major form of the disease in children and adolescents, making up 5%–10% of all diabetes cases.When you’re first diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, you may not need to use insulin straight away unless your blood sugar levels are very high. In type 1 diabetes, the body produces little or no insulin. People with type 1 diabetes must take insulin every .Insulindependent diabetes : new therapeutics.Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is an autoimmune disease in which insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas are mistakenly destroyed by the body’s immune system.
Definition
Destruction progresses subclinically over months or years until beta-cell .
Type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes happens most often . KEY-WORDS : blood glucose.Le diabète de type 1, diabète insulinodépendant (ou insulino-dépendant) (DID), diabète inné (anciennement appelé diabète sucré), ou encore DT1 (terme de plus en plus employé dans le milieu médical), est une maladie auto-immune irréversible.
Diabète type 1 ou insulino-dépendant
Next: Background. Some people with type 2 diabetes will also need to take insulin.Type 1 diabetes is sometimes called juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes.
Insulin for type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes ( T1D ), formerly known as juvenile diabetes, is an .Diabetes is a metabolic disease that affects many parts of the body.The incidence of Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus was prospectively evaluated in Catalonia, Spain in patients up to 30 years of age during the period 1987–1990. It is most often diagnosed in children, adolescents, or young adults.Most people with type 1 diabetes take both: a long-acting insulin (also called background or basal insulin) once or twice a day. It helps your body use glucose (sugar) for energy.Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM), which was previously known as insulin-dependent, or childhood diabetes, is characterized by a deficiency in insulin production .As our knowledge of type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes increases, so does our appreciation for the pathogenic complexity of this disease and the challenges associated .
Insulin therapy in type 1 diabetes
It is caused by the destruction of pancreatic endocrine β-cells .Le diabète de type 1 ou diabète Insulino Dépendant (DID), fut aussi appelé diabète maigre ou encore diabète juvénile car il peut apparaître dès l'enfance.
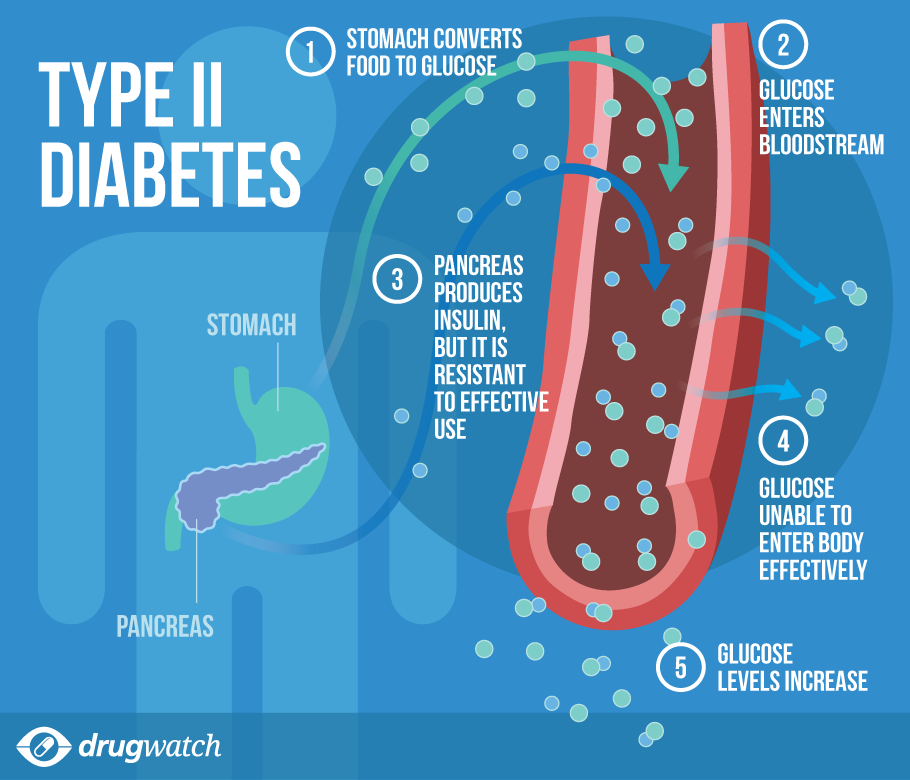
Without insulin, too much glucose stays in your blood.

Diabetes involves the pancreas .Slowly progressive insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in type 1 diabetes endotype 2. Most patients with T1DM should follow a regimen of multiple daily injections of basal/bolus insulin, but those not meeting individual glycemic targets or those with frequent or severe hypoglycemia or pronounced .Le traitement du diabète de type 1 a pour objectif de contrôler la glycémie et repose sur l'administration d'insuline. Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1D), also designated insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM), is a disorder of glucose homeostasis characterized by susceptibility to ketoacidosis in the absence of insulin therapy.Here, we review insulin management options and strategies in nonpregnant adult patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). Nature Reviews Endocrinology . It means that your body can't make insulin.In southeastern Sweden, the disease incidence among individuals aged 0–19 years is similar to that among individuals 40–100 .What is type 1 diabetes? In type 1 diabetes, the body can’t make insulin. Diabetes is classified as type 1 (formerly called juvenile-onset or insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus), type 2 (formerly called adult-onset or non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus), gestational or other specific types.Type 1 diabetes is a disease in which autoimmune destruction of pancreatic β-cells leads to insulin deficiency.
Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus
Temps de Lecture Estimé: 2 min It replaces the insulin your body doesn't make. Type 1 diabetes occurs most often in children, adolescents or young adults.Classification. Insulin helps your body use the sugar it . This combination is sometimes known as a basal bolus regimen. If you have type 2 diabetes, insulin therapy might be part of your treatment.
Type 1 Diabetes
La consommation de certains additifs alimentaires émulsifiants serait associée à un risque accru de diabète de type 2, explique un communiqué de l’Institut français de .Type 1 Diabetes: Type 2 Diabetes: Formerly known as.Similar to nutritional insulin. Children and teens, usually with healthy . Insulin is a hormone – a chemical messenger that is transported in the blood and regulates important body .Type 1 diabetes is less common than type 2, but both conditions significantly affect people’s health and lives. Insulin therapy is essential for everyone who has type 1 diabetes and some people who have type 2 .
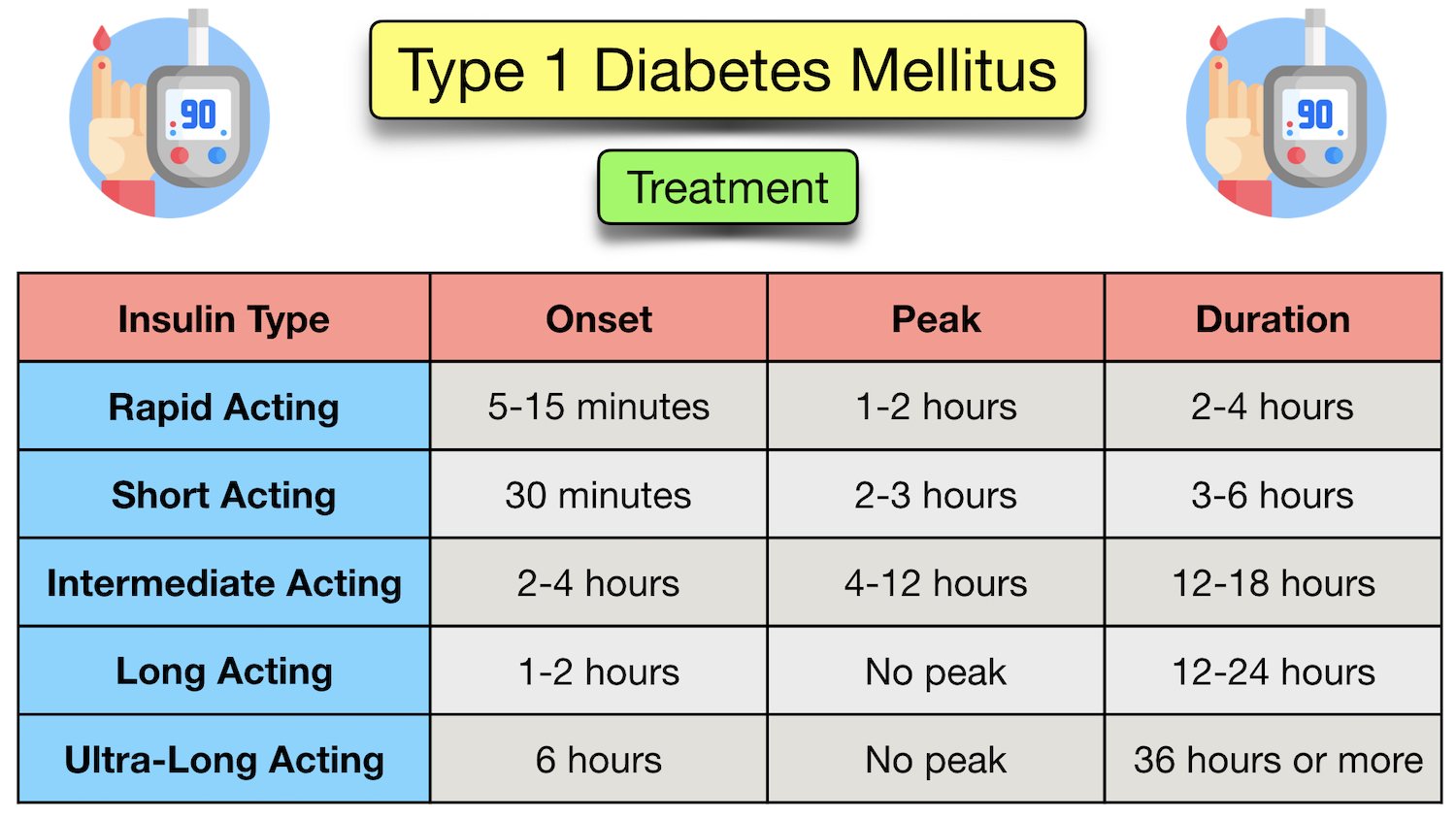
Society and culture.Mounjaro ® (mown-JAHR-OH) is an injectable medicine for adults with type 2 diabetes used along with diet and exercise to improve blood sugar (glucose). This method allows a great deal of flexibility with regards to the types of food patients eat, when they eat it, and how much they eat.Type 1 diabetes: Types of insulin. Insulin can be used as a short-term treatment to help quickly bring down your blood sugar levels. We need insulin to live.The SFD has updated its position statement on type 2 diabetes every 2 years since 2017. The term 'type 1 diabetes' has replaced the older terms 'insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM)' and 'juvenile-onset diabetes' because the older terms are potentially misleading: type 1 diabetes can also develop during adulthood and some people with type 2 .Type 1 diabetes can occur at any age.Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) is the most common autoimmune chronic disease in young patients.
Type 1 Diabetes
Diabète de type 1 — Wikipédia
Roughly 10 per cent of people living with diabetes have type 1, insulin-dependent diabetes. Tetsuro Kobayashi & Takashi Kadowaki. Insulin is an important hormone that helps your body to control the level of glucose (sugar) in your blood. Type 1 diabetes is less common than type 2 —about 5-10% of people with diabetes have type 1.









