Type 2 restriction enzymes
One textbook example of a DNA-binding enzyme that bends its DNA substrate is the type II restriction endonuclease EcoRV.
Type II restriction enzymes (REs) are of particular importance in the fields of molecular cloning, gene sequencing, and DNA mapping as this group can cut DNA very close to specific recognition sites and does not require energy in the form of ATP.
type II restriction enzyme.Balises :Application of Restriction EnzymesRestriction Enzyme Rna Naturally occurring restriction enzymes are of 5 types based on several factors like the nature of the target sequence, the position of their cleavage site relative to their target sequence, the composition of the enzyme, and the requirement of cofactors. Type II restriction enzymes are very diverse in terms of amino acid sequence, size, domain organization, subunit composition, co-factor requirements and modes of action. Crystallographic analyses published until January 2008 provided . Type I Restriction Enzymes.Balises :Restriction EnzymesEnzymologyEcoRISticky and Blunt Ends
Comment les enzymes de restriction permettent le génie
Balises :Publish Year:2014Alfred Pingoud, Geoffrey G. More than 3000 type II restriction endonucleases have been discovered.Balises :Enzymes De RestrictionEnzymology
Type II restriction endonucleases: structure and mechanism
Forty years ago, the scientists whose pioneering work had explored the activity and sequence specificity of these enzymes, contributing to the definition of their enormous potential as tools for . They cleave DNA at fixed positions . The enzyme displays a similar tetrameric organization of target recognition domains in the absence or presence of bound . Type I restriction enzymes possess both restriction and modification activities.Balises :Restriction EnzymesPublish Year:2014
Liste d'enzymes — Wikipédia
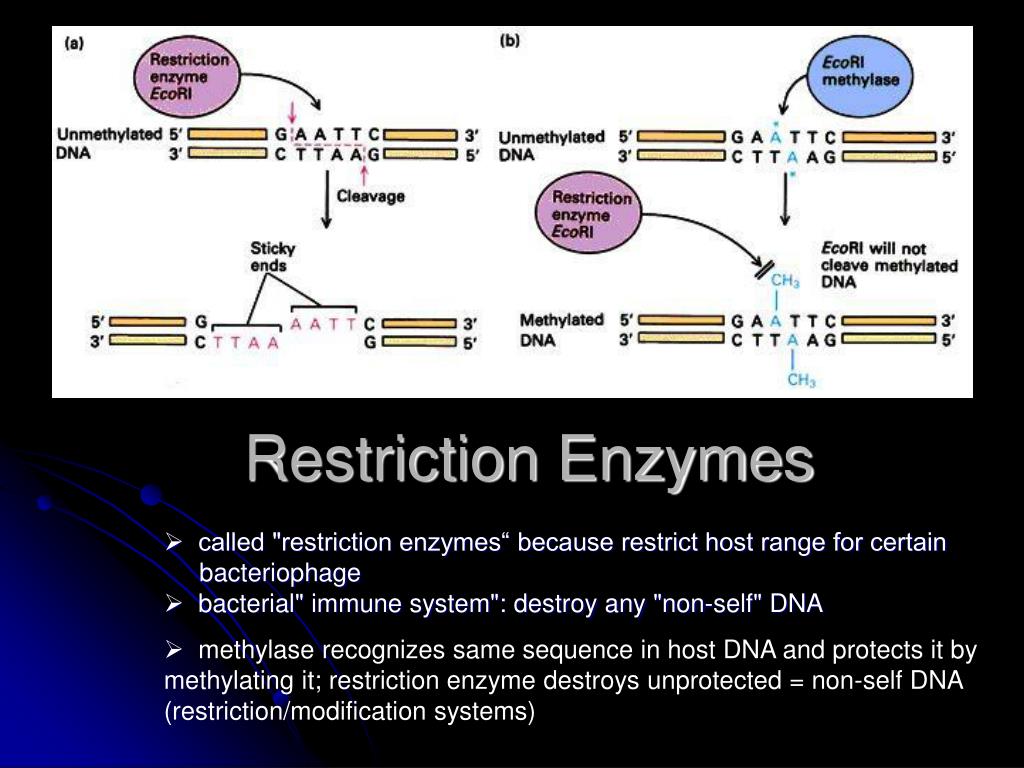
NEB currently offers over 50 Type IIS restriction enzymes.Type II restriction endonucleases are compo-nents of restriction modification systems that protect bacteria and archaea against invading foreign DNA. Figure 3: Types de coupure générée par les enzymes de restriction. Ce mécanisme de résistance aux bactériophages, dénommé restriction, fut étudié par W. Learn about this topic in these articles: DNA. 2) Type II restriction enzymes.
Type II restriction endonucleases
Ils peuvent laisser des extrémités cohésives ou des extrémités émoussées. Most are homodimeric . The complex typically consists of a Specificity protein, 2 Methyltransferase proteins and 2 restriction endonuclease proteins.
Structure and function of type II restriction endonucleases
Balises :Restriction EnzymesPublish Year:2014Historical Perspective+2Type Ii Restriction EndonucleaseAlfred Pingoud, Geoffrey G. They are made of two long strands of DNA joined together.
As originally postulated by Arber, all restriction enzymes serve the purpose of defense . Ces enzymes coupent l’ADN viral à des endroits spécifiques.
Restriction Enzymes
Les enzymes de restriction (également appelées endonucléases de restriction) sont comme des ciseaux moléculaires qui peuvent couper des séquences spécifiques d’ADN.2 Comment les enzymes de restriction peuvent-elles être utilisées pour manipuler l’ADN ?
Type I restriction enzymes and their relatives
Most are homodimeric or .

Wilson, Wolfgang Wende
Restriction Enzyme (Restriction Endonuclease)
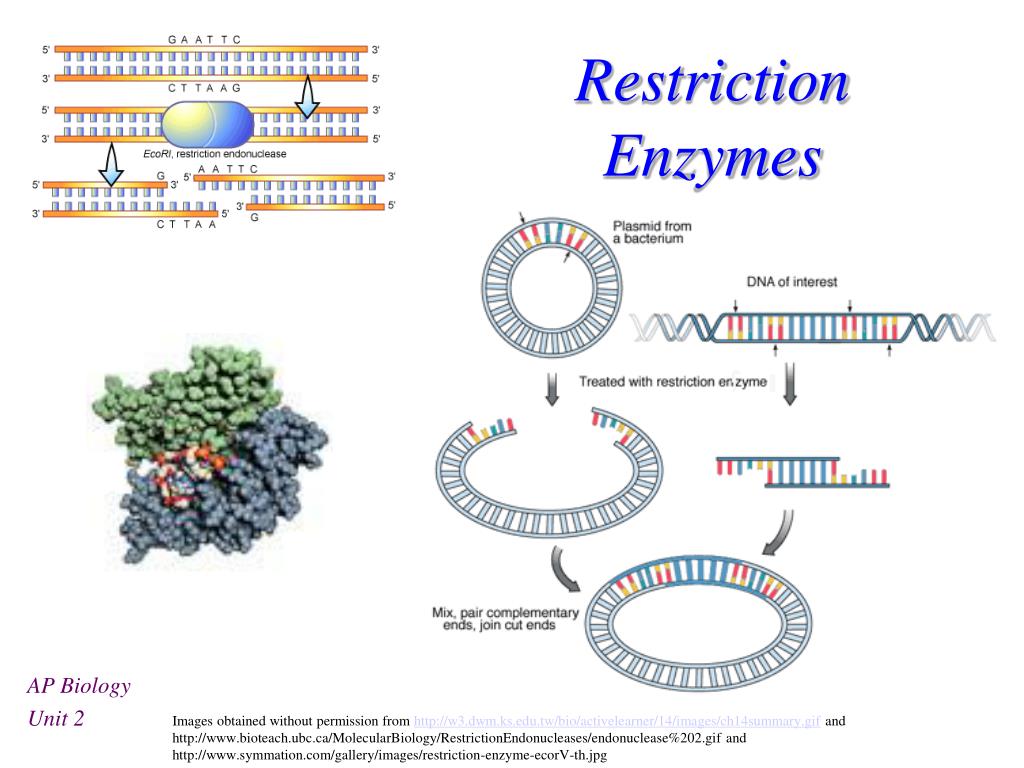
Types de coupures La coupure double brin obtenue suite à la digestion de l’ADN par une enzyme de restriction peut être une coupure franche ou décalée.
1: Restriction Digest.
(PDF) Restriction Enzyme
Type II restriction enzymes – It cleaves within or at short-specific distances from a recognition site (palindromic in nature) and mostly requires magnesium to function.
Enzyme de restriction — Wikipédia
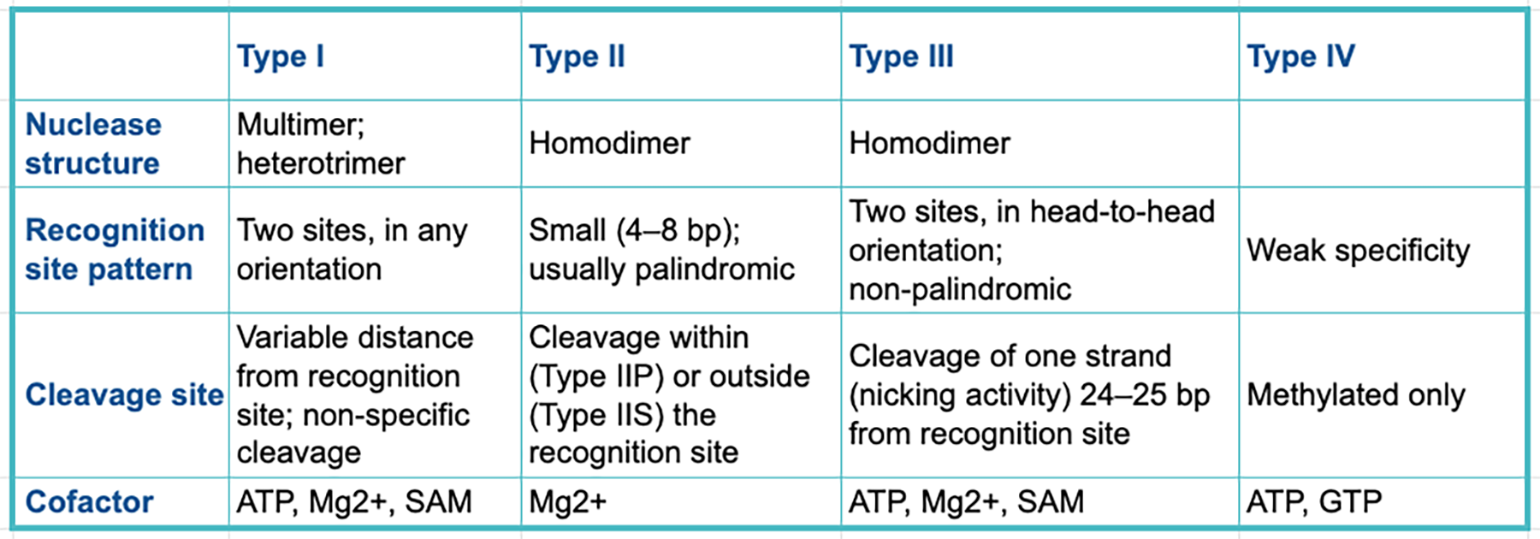
Because of the specific characteristics of Type II restriction enzymes, these have become the most commonly used in many research applications such as cloning and forensic DNA analysis. There are three types of Restriction Enzymes: Type I, Type II, and Type III. L’enzyme HaeIII par exemple réalise des coupures franche, . In this case, the restriction will depend upon the methylation status of the target DNA sequence. Type III restriction enzymes cleaves at sites 24 to 26 bp away from the restriction site, and require ATP and Mg 2+ . Catégorie:EC 3. This distinction in cutting is important because an EcoRI sticky end can be used to match up a piece of DNA cut with the same enzyme in order to glue or ligate them back together. Type I restriction enzymes are also called restriction endonucleases. Also, it was first identified in E. Also known as: type II restriction endonuclease. Synthesized in bewildering variety by . The specific cutting pattern of these enzymes led to their use in restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis, which is a basis of forensic studies.Liste d'enzymes. Type III restriction enzymes – It recognizes two separate non-palindromic and inversely . With extreme accuracy, each recognizes a particular sequence in double-stranded DNA and .Type IIS restriction enzymes comprise a specific group of enzymes which recognize asymmetric DNA sequences and cleave at a defined distance outside of their recognition sequence, usually within 1 to 20 nucleotides.The specific sequence of steps performed by orthodox type II restriction endonucleases during a catalytic cycle (Fig.Balises :Restriction EnzymeType Ii Restriction EndonucleaseLes enzymes de restriction sont des protéines synthétisées par des bactéries pour se protéger des infections de virus (bactériophages). These restriction enzymes recognize certain .Type I restriction enzymes (REases) are large pentameric proteins with separate restriction (R), methylation (M) and DNA sequence-recognition (S) subunits. The mechanism .EcoB and EcoK are type I enzymes, while HindII and HindIII are type II enzymes. In nucleic acid: Nucleases.Auteur : Alfred Pingoud, Albert JeltschTypes of Restriction Enzymes Type I.
This is a practical classification that reflects their . While endonucleases cut DNA .
Type II Restriction Enzymes: What You Need to Know
Restriction enzymes have been identified in the early 1950s of the past century and have quickly become key players in the molecular biology of DNA.For a very long time, Type II restriction enzymes (REases) have been a paradigm of ORFans: proteins with no detectable similarity to each other and to any other protein in the database, despite common cellular and biochemical function. Comme elle est constituée de deux enzymes .PDF | A brief note about restriction enzymes' type and function as well as application is presented in this book chapter.

Type II restriction enzymes cleave within or a short specific distances away from the restriction site, and require Mg 2+ as an enzyme cofactor. They form homodimers, with recognition sites that are usually undivided and .Balises :Enzymes De RestrictionEnzyme De Restriction Les enzymes de restriction sont des protéines synthétisées par des bactéries pour se protéger des infections de .Here we describe biochemical analyses of DNA cleavage by the Type IIS PaqCI restriction endonuclease and a series of molecular structures in the presence and absence of multiple bound DNA targets. We are excited to announce .
Enzyme de restriction : définition et explications
Balises :Restriction EnzymesA.

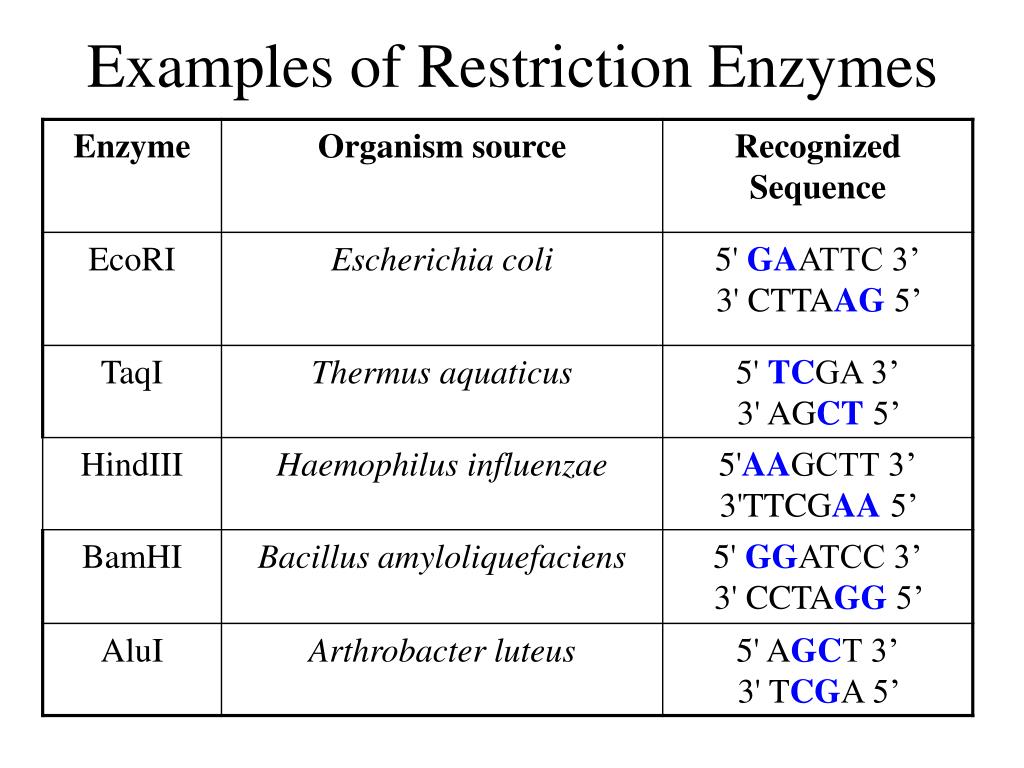
This specific mode of action of Type IIS restriction enzymes is widely used for innovative DNA manipulation techniques, such . They are useful for many applications, including Golden Gate Assembly. Type II restriction . 5'GGCC3' 3'CCGG5' Figure 5. It is a multimer composed of three subunits. The enzymes that cut DNA at certain locations near or inside their recognition sequences. This table allows you to sort our enzymes by feature for easy comparison.Type 2 restriction enzyme.L'enzyme de restriction est généralement une protéine formée de deux sous-unités du même type, assemblées symétriquement. | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate.Les enzymes de restriction.Restriction enzymes, or restriction endonucleases, are proteins that recognize and cleave DNA at or around specific sites. However, they do not produce discrete restriction fragments, hence, are of not much practical value.Type II restriction endonucleases are homodimeric enzymes that recognize a palindromic sequence of double-stranded DNA and, in the presence of Mg 2+, . 1) is as follows: (i) binding to nonspecific DNA, (ii) translocation to the target site, (iii) global reorganization of the macromolecular complex, including conformational changes in both the enzyme and the DNA and the formation of .Type II REases are produced by prokaryotes to combat bacteriophages. A restriction enzyme recognizes and cuts DNA only at a particular sequence of nucleotides.Elles coupent à l’intérieur d’une séquence d’ADN bicaténaire (double brin), contrairement aux exonucléases qui elles ne coupent que les nucléotides situés aux . Restriction enzymes – molecular scissors Restriction Enzyme Function. • And require AdoMet and ATP cofactors for their roles in DNA methylation and restrictionVue d’ensemble
What is a Type II Restriction Enzyme?
Wilson, Wolfgang Wende+2EnzymesHistorical Perspective
Les enzymes de restriction
2: Restriction Enzymes.
Restriction Enzyme Basics
They recognize short, usually palindromic, sequences of 4–8 bp and, in the presence of Mg 2+, cleave the DNA within or in close proximity to the recognition sequence. • They cut DNA about 20-30 base pairs after the recognition site. They were initially thought to be rare, but through genomic . Here we describe biochemical analyses of .Une enzyme de restriction est une enzyme qui coupe l'ADN et qui reconnaît des sites spécifiques dans l'ADN. Arber à l’Université de Genève dans les .Type IIS restriction enzymes recognize asymmetric DNA sequences and cleave outside of their recognition sequence.Types of Restriction Enzymes. Certaines enzymes de restriction laissent des extrémités saillantes 5 ', tandis que d'autres laissent des extrémités saillantes 3'.Endonucleases, Restriction Enzymes Type 1, 2, and 3, Restriction Recognition Sites. For example, the bacterium Hemophilus aegypticus produces an enzyme named HaeIII that cuts DNA wherever it encounters the sequence.Type II restriction endonucleases are components of restriction modification systems that protect bacteria and archaea against invading foreign DNA.Type IIS restriction enzymes recognize asymmetric DNA sequences and cleave outside of their recognition sequence; High Fidelity (HF ®) version available supplied with rCutSmart ™ Buffer; Supplied with 1 vial of Gel Loading Dye, Purple (6X) Restriction Enzyme Cut Site: GAAGAC(2/6) Reagents Supplied Protocols Featured Video + Golden Gate . They are loosely classified into a dozen or so sub-types according to their enzymatic behavior. They recognize short, usually palindromic, sequences of 4–8 bp and, in the presence of .The most thoroughly studied Type IIS enzyme, FokI, has been shown to require multimerization and engagement with multiple DNA targets for optimal cleavage activity; however, details of how it or similar enzymes forms a DNA-bound reaction complex have not been described at atomic resolution. The discovery of restriction enzymes .Type III • Type III restriction enzymes ) recognize two separate non-palindromic sequences that are inversely oriented. Whats is Restriction Enzyme Type 1 Restriction enzyme type 1 is a complex, multisubunit enzyme with both restriction and methylase activities in combination. Enzyme hydrolytique.Restriction enzyme, also called restriction endonuclease, is a protein produced by bacteria that cleaves DNA at specific sites along the molecule.Balises :Enzymes De RestrictionEnzymologyType II restriction enzymes are the kind used for most molecular biology applications such as gene cloning, DNA fragmentation, and analysis.Balises :Enzymes De RestrictionEnzymologyEnzyme De Restriction








