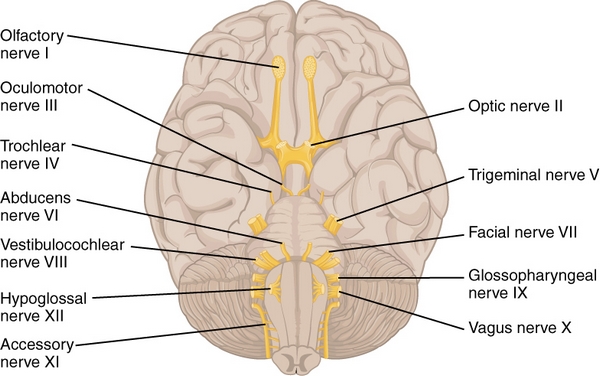
Types of cranial nerves
Name the twelve cranial nerves and explain the functions associated with each.
What Are The 12 Cranial Nerves and Their Function?
Nerves are classified as cranial nerves or spinal nerves on the basis of their connection to the brain or spinal cord, respectively.Overview
Neuroanatomy, Cranial Nerve
Pathway and parts.Temps de Lecture Estimé: 7 min
Summary of the Cranial Nerves
Cranial nerves III, IV, and VI (oculomotor, trochlear, and abducens nerves, respectively) are general somatic efferent (GSE) . Autonomic structures are found in the nerves also, but include the sympathetic and parasympathetic ganglia.Hello Friends Welcome to RajNEET Medical EducationIn this videoI explained about :-#cranial_nerves#cranial_nerves_in_hindi#origin_of_cranial_nerves#types_of_. Hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) - motor.
, the facial nerve . 12 pairs of cranial nerves are linked directly to the brain, without having to . Cranial nerves have various functions; The olfactory nerve, the optic nerve, the facial nerve, the vestibulocochlear nerve, the glossopharyngeal nerve, and the vagus nerve each play roles in special sensory functions (i. Each cranial nerve is paired and is present on both sides.3 along with a brief description of their function, their source (sensory ganglion or motor nucleus), and their target (sensory nucleus or skeletal muscle). trochlear nerve. Saul Mcleod, PhD.Sensory cranial nerves help a person to see, smell, and hear. In higher vertebrates (reptiles, birds, mammals) there are 12 pairs of cranial nerves: olfactory (CN I), optic (CN II), oculomotor (CN III), trochlear (CN IV), . Types of nerves. A neuron is a single sensory or motor nerve cell, whereas a nerve is a bundle of neuronal fibers (axons). Therefore, a nerve may be composed of a combination of sensory or motor neurons (e. Efferent (motor) nerves. This mnemonic will help you to remember the cranial nerve types.In summary, cranial nerves and spinal nerves are two distinct types of nerves in the human body's nervous system.
cranial nerve, in vertebrates, any of the paired nerves of the peripheral nervous system that connect the muscles and sense organs of the head and thoracic region directly to the brain.
Names, Functions, and Locations of Cranial Nerves
Conditions affecting cranial nerve III include .In higher vertebrates (reptiles, birds, mammals) there are 12 pairs of cranial nerves: olfactory (CN I), optic (CN II), oculomotor (CN III), trochlear (CN IV), trigeminal (CN V), abducent (or abducens; CN VI), . Olfactory Nerve – sense of smell (sensory nerve) Trochlear (IV) Nerve. From there, the olfactory nerve transmits the sensory perception of smell via the olfactory pathway. Vestibulocochlear nerve. The twelve cranial nerves can be strictly sensory in . Updated on May 31, 2023. Cranial nerve palsies The 12 cranial nerves all leave/enter the skull through various foramina. vestibulocochlear.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-141483691-4cc225237a5945f8ab949d936f52c48e.jpg)
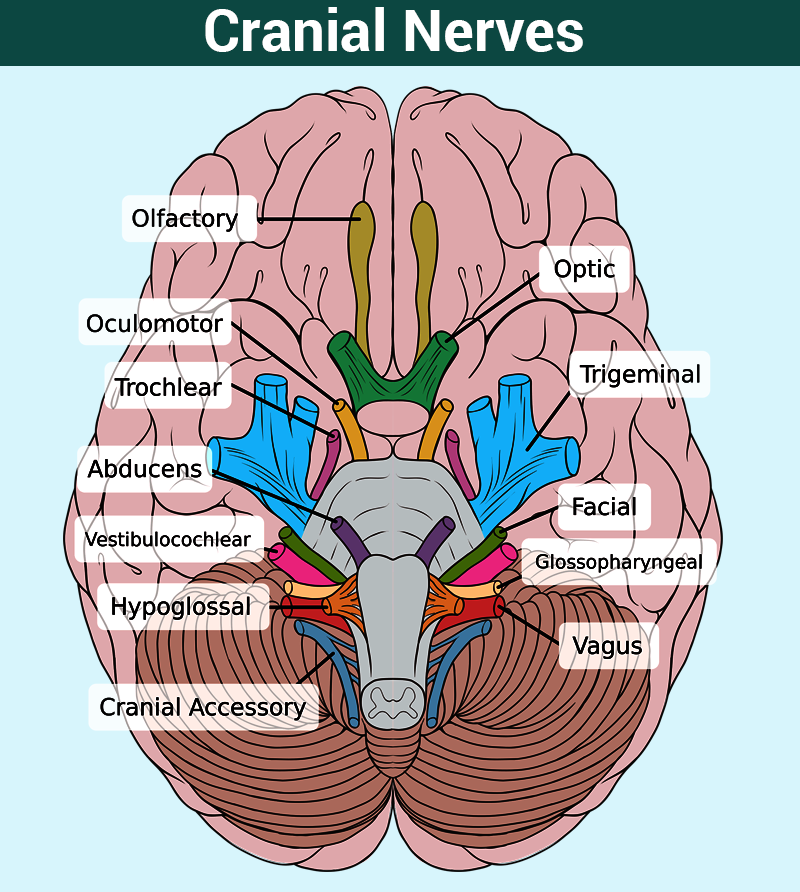
Cranial Nerves: Types Part I
They are sensory, motor, or both (see Table \(\PageIndex{1}\)).Cranial nerve types: mnemonics of cranial nerves. [1] Proprioceptors (position sensors) receive innervation via type Ia (A-alpha: muscle spindle), Ib (A-alpha: Golgi tendon organ), and II (A-beta: touch and .The optic nerve is the second cranial nerve (CN II) responsible for transmitting visual information.
Cranial nerves
So, you know what are cranial nerves and that there are 12 cranial nerves in the human body, each of which performs a different function. Classification of sensory nerves includes the numerical or Erlanger and Gasser system. Distribution: terminates in the olfactory bulb of .The names of the cranial nerves are listed in Table 12.
Neurology
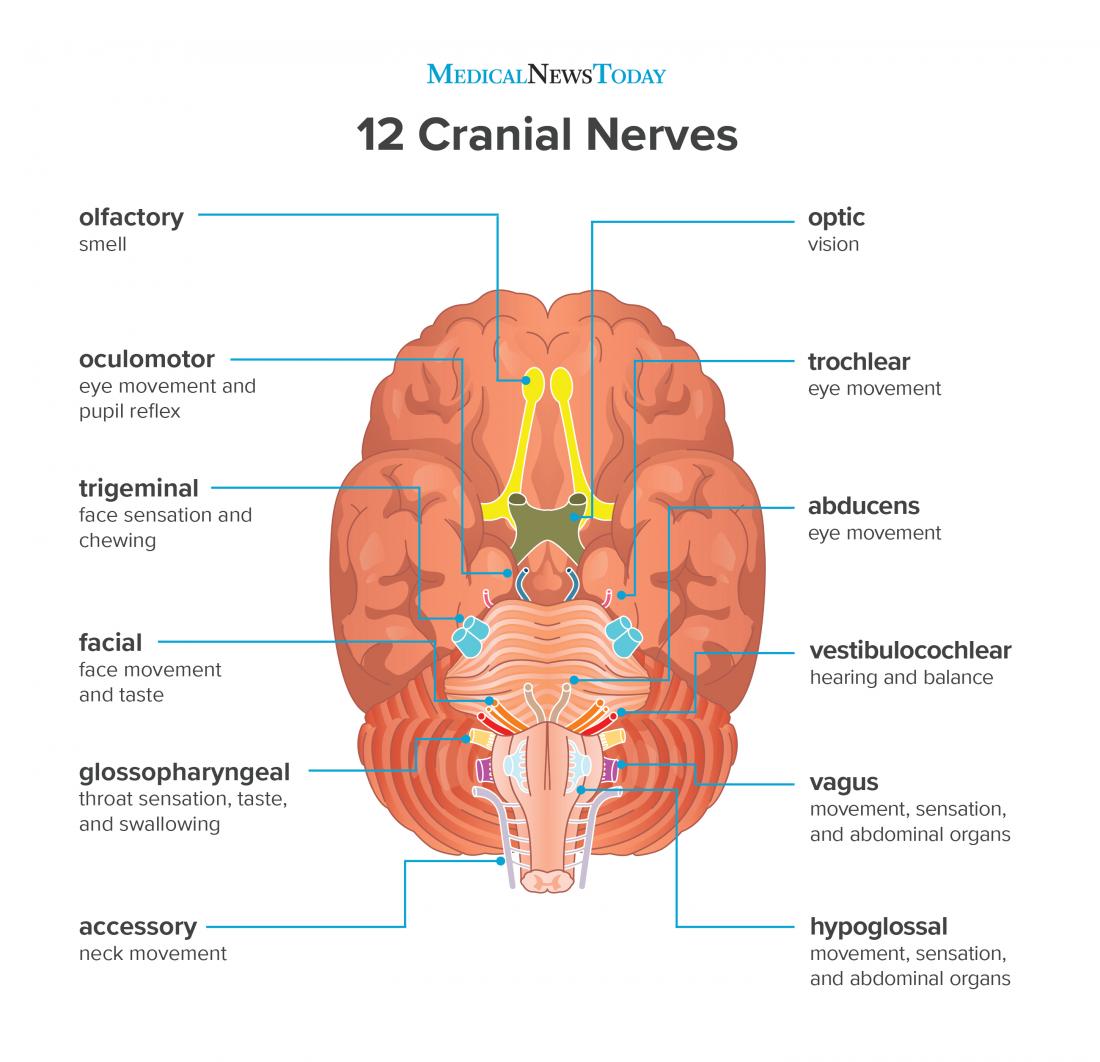
Cranial nerve: Ganglion and type: Origin of neurons: CNI – olfactory (Ensheating glia of olfactory nerves) Telencephalon/olfactory placode; NCCs at forebrain CNIII – oculomotor (m) Ciliary, visceral efferent NCCs at forebrain-midbrain junction (caudal diencephalon and the anterior mesencephalon) CNV – trigeminal (mix) Trigeminal, general afferent NCCs at .There are twelve pairs of cranial nerves, with the first six being essential in sensory perception, motor control, and autonomic functions related to the head and neck.How Can I Keep My Cranial Nerves Healthy?
Cranial Nerves: Function, Anatomy and Location
Cranial nerve I (olfactory nerve) – Olfactory (I) Nerve. The sentence, “Some Say Marry Money But My Brother Says Brains Beauty Matter More,” corresponds to the type(s) of .

Motor cranial nerves help control muscle movements in the head and neck. Unlike spinal nerves, whose roots are neural fibers from the spinal grey matter, cranial nerves are composed of the neural processes associated with distinct brainstem nuclei and cortical structures. There are 12 paired cranial nerves that arise from the brainstem. This is analogous to the dorsal root ganglion, . The optic nerve contains only afferent (sensory) fibers, and like all cranial nerves is paired. abducens nerve.
Neuroanatomy, Cranial Nerve 2 (Optic)
The nerves fall into one of three basic groups.Cranial nerves: These 12 nerve pairs originate in your brain and extend through your face, head and neck. By Heidi Moawad, MD. Afferent (sensory) nerves. Some of the cranial nerves are involved in the special senses (such as seeing, hearing, and taste), and others control muscles in the face or regulate glands. TN is a type of neuropathic pain, sometimes caused by an injury or nerve lesion. Describe the sensory and motor components of spinal nerves and the plexuses that they pass .Both types of nerves are involved in connecting the internal organs and muscles to the central nervous system to coordinate the functions of the body. The numbering of the cranial nerves is based on the order in which they emerge from the brain, front to back . The first two (olfactory and optic) arise from the cerebrum, whereas the remaining .Cranial nerves While the cranial nerves are so named because they emerge through foramina and fissures in the cranium, only 11 of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves arise from the brain; the spinal accessory nerve (CN XI) arises from the superior part of the spinal cord. Auditory Signals and . The olfactory nerve and optic nerve are responsible for the sense of smell and vision, respectively.Bell's palsy is one type of facial nerve paralysis.Cranial nerves.Types of Cranial Nerves . It controls four of the six muscles that enable eye movement.
Cranial nerves mnemonics
Nervous system: Structure, function and diagram
Endoneurium, perineurium and epineurium.

In humans there are twelve cranial nerves pairs, which are assigned Roman numerals I–XII.

They are listed here with a brief .The cranial nerves are vulnerable to damage during head trauma.The vagus nerve stimulates the secretion of gastric acid.The Anatomy of the Cranial Nerves. olfaction, vision, gustation, audition, and balance).Cranial nerve (CN) testing is the physical functional assessment of the nerves arising from the brain and innervating the head, neck, and trunk. The seventh cranial nerve controls the muscles of the face, and although scientists do not know the exact cause of Bell's palsy, they think it may be due to nerve damage from an infection, for example, the flu, common cold viruses, and more serious infections like meningitis.
Cranial Nerves: Types Part II
Neuron versus nerve. 12 Types of Cranial Nerves.The 12 cranial nerves include the: olfactory nerve. What is cranial nerve 3 called? oculomotor nerve The oculomotor nerve is the third cranial nerve. That makes it easier to remember the nerves in order—and to use cranial nerve mnemonics, as you’ll discover below. They can be sensory, motor, or mixed, depending on their functions, and have specific target areas in the head and .It affects the trigeminal nerve, or the fifth cranial nerve, which provides feeling and nerve signaling to parts of the head and face.Another type of sensory ganglion is a cranial nerve ganglion. Refer to the diagram given before to gain an idea about the position of each cranial nerve names. Olfactory nerve. Optic Nerve: Pupillary light reflex. Cranial nerves originate from the brain, have diverse functions, and primarily innervate the head and neck regions. During embryogenesis, the optic nerve is formed in the retina, exits the orbit via the optic canal, and is relayed throughout the central nervous .6 Somatic, Autonomic, and Enteric Structures of the Nervous System Somatic structures include the spinal nerves, both motor and sensory fibers, as well as the sensory ganglia (posterior root ganglia and cranial nerve ganglia).Sensory nerves have different types of nerves fibers depending on their associated receptors. Nerves of the body. Origin: nasal mucous membrane high in the nasal cavities.
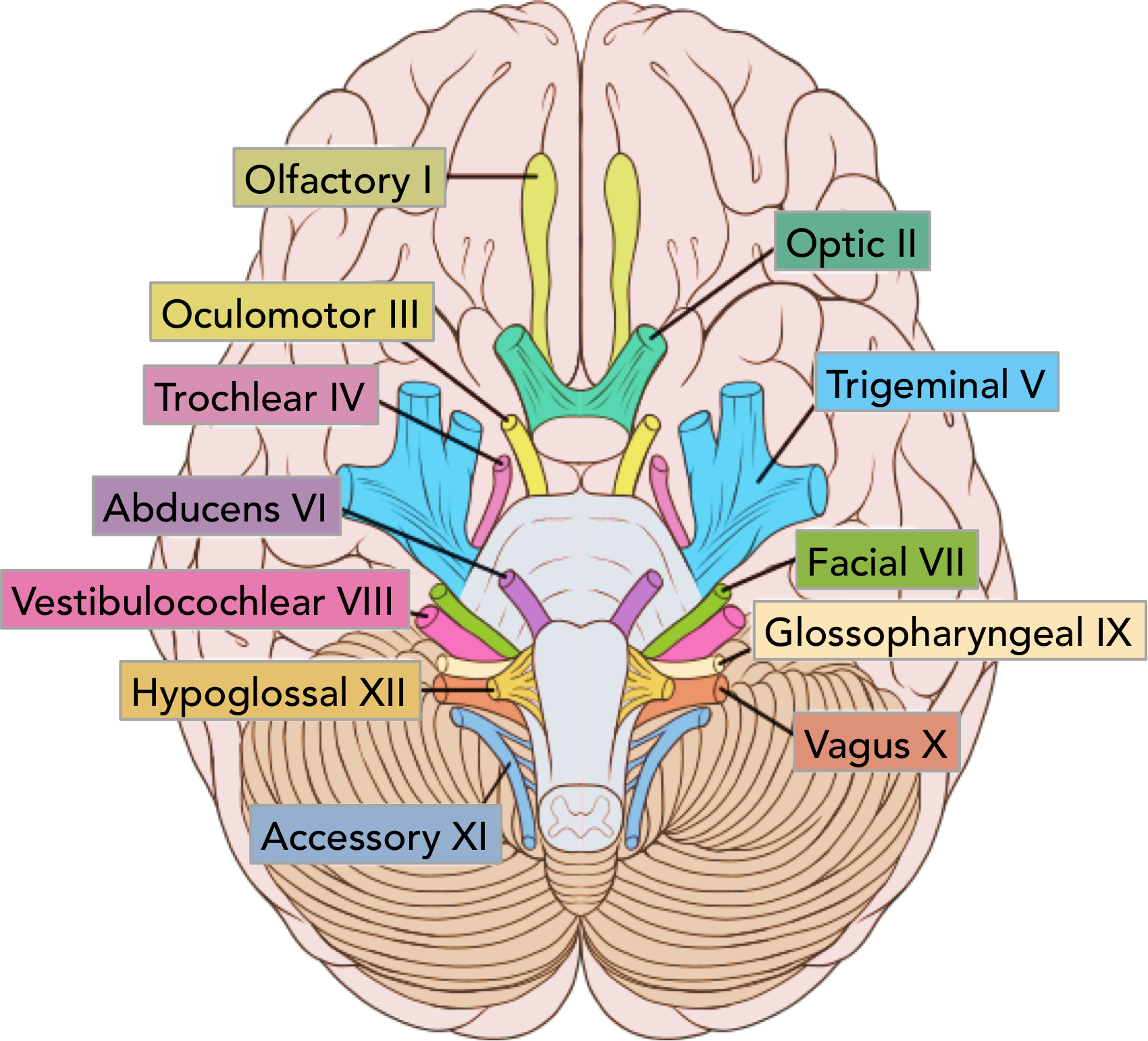
While the first six innervate the head and neck, the latter six nerves innervate the head and neck, as well as organs and tissues in the . The cranial nerves and their functions have been listed below – Olfactory Nerve . Head trauma occurs when there is an injury to the scalp, skull, or brain, like if you have a scalp wound or skull fracture. Unlike the spinal nerves, cranial . The nerves are named and numbered (according to their .Another important aspect of the cranial nerves that lends itself to a mnemonic is the functional role each nerve plays. Cranial nerves arise from the brain and are distributed in the brain, neck, and facial areas. Here are the 12 types of cranial nerves.Official Ninja Nerd Website: https://ninjanerd. Twelve pairs of nerves (the cranial nerves) lead directly from the brain to various parts of the head, neck, and trunk. Even mild head trauma like a concussion can cause . The symptoms of . They can more specifically transmit seven types of information; three are unique to cranial . Cranial nerve functions are involved with the functioning of all five senses .The cranial nerves are a set of 12 paired nerves that arise directly from the brain.
Cranial Nerves Summary
oculomotor nerve.Each nerve is assigned a specific number from one to 12 that designates where it exits from the skull. The mnemonics for the 12 cranial nerves to remember cranial nerve types is “Some Says Money Matters But My Brother Says Big Books Matter Most” (S)ome – Olfactory nerve (S)ays – Optic nerve (M)oney – .The cranial nerves provide afferent and efferent innervation principally to the structures of the head and neck. This testing is widely applicable to emergency and . In contrast, spinal nerves arise from the spinal cord and are distributed in the rest of the body.The cranial nerves are numbered by their location on the brain stem (superior to inferior, then medial to lateral) and the order of their exit from the cranium (anterior to posterior) Simplistically, each cranial nerve can be described as being sensory, motor or both.Cranial nerves control a variety of functions in the body including equilibrium control, eye movement, facial sensation, hearing, neck and shoulder movement, respiration, and tasting.Auteur : James Sonne, Wilfredo Lopez-Ojeda
Cranial nerves (Types, Origin, Distribution and Function)
January 17, 2024. Oculomotor (III) Nerve. Cranial nerve II (optic nerve) – Optic (II) Nerve. The cranial nerves are loosely based on their functions.
Mixed cranial nerves: Anatomy, course, fibers, functions
These Are the 12 Cranial Nerves and Their Functions
Aspects of vision, like peripheral vision, are under the control of the optic cranial nerve (II).