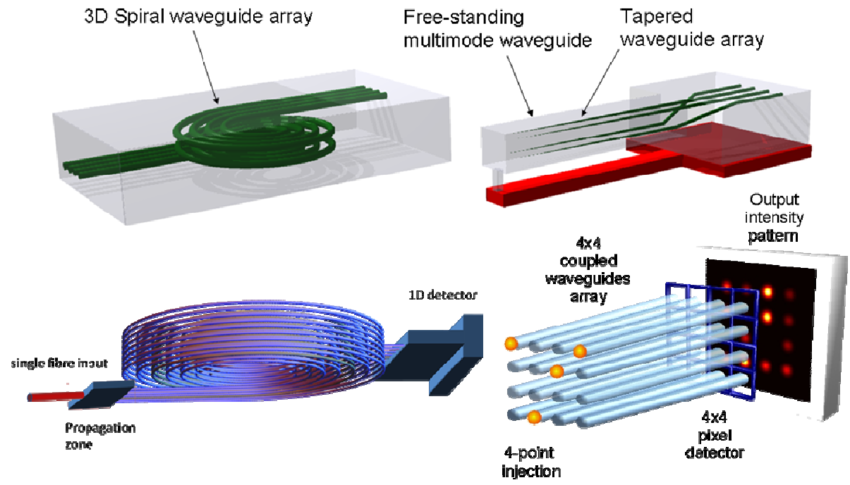
Types of optical waveguide

Fundamentals and Design Guides for Optical WaveguidesThe mode conversion in tapered submicron silicon ridge optical waveguides is investigated theoretically and experimentally. There are basically th...
Fundamentals and Design Guides for Optical Waveguides
The mode conversion in tapered submicron silicon ridge optical waveguides is investigated theoretically and experimentally. There are basically three pre-defined types of S-Bend waveguide shapes in OptiBPM layout. They can be defined in terms of their path, or by specifying the upper and .In the types of optical fibers mentioned above, light travels due to total internal reflection and refractive indices of the core and cladding.There are two types of optical interconnections: guided interconnections and free-space interconnections.
Designing Optical Waveguides: Myth and Reality
Three Types of Dispersion Optical waveguides display three types of dispersion: material dispersion, modal dispersion and waveguide dispersion.
Review on Optical Waveguides
The most important type of dielectric waveguides is optical fibers.The optical waveguide structure, used in the design of all Y-branch optical splitters, is a silica-on-silicon (SoS) buried rectangular channel, . This course focuses on dielectric .
Lecture 4: Optical waveguides
Metallic waveguides (coaxial cables, useful for microwaves).Optical MEMS and Waveguide Integrated Optics Photonic integrated circuit include optical MEMS and waveguide integrated optics Optical MEMS (can be free space or waveguide) Waveguide Integrated Optics (what’s known as integrated optics in earlier day) w. Planar or slab waveguides are one-dimensional waveguide structures which confine light (waves) only in one .
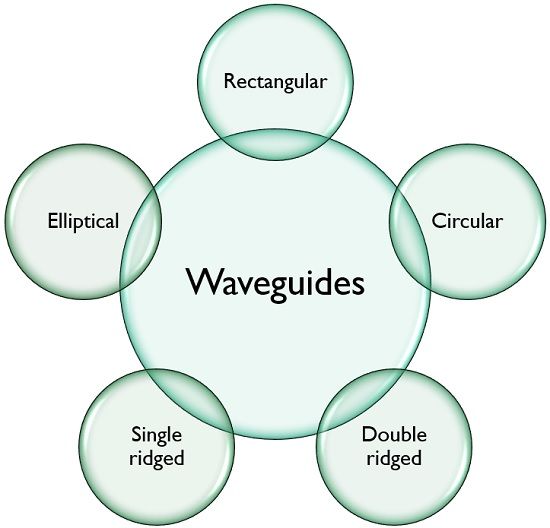
The refractive index of the core n1 is higher than that of the cladding n0.Types of Optical Fibres. One is a regular lateral taper for which the waveguide width varies while the etching depth is kept the same. Optical fibers (except for photonic crystal fibers) usually have a . Publisher Summary.In fact, there are many different wave-types, e.In radio-frequency engineering and communications engineering, waveguide is a hollow metal pipe used to carry radio waves. 2 – An image . This chapter discusses the basic concepts and equations of electromagnetic wave theory that are required for the comprehension of . Without a waveguide .Optical change in the proximity of the guiding surface resulting from the evanescent wave scattering is used as detection mechanism in optical waveguide biosensors.
Optical Waveguide Modes
Holographic waveguides using shallow etching of silicon-on-insulator waveguides makes designing integrated, preset optical vector matrix multiplication .A waveguide also has cladding modes, the intensity distributions of which essentially fill the whole cladding (and core) region.Optical sensors can be classified into two main types: Fiber optic sensors - Rely on optical fibers.There are two basic types of waveguides: In a nonplanar waveguide of two-dimensional transverse optical confinement, the core is surrounded by cladding in all transverse .We present a new scheme to create all-optical tunable and lossless waveguide using a controllable coherent Raman process in an atomic rubidium vapor in .Two types of optical waveguide tapers are considered in this paper.
Waveguide (radio frequency)
In the first type, light propagates inside a guiding region such . Physics, Engineering.A typical optical planar waveguide is illustrated in Fig. Common types of waveguides include acoustic waveguides which direct .There are mainly two types of optical sensor: optical fiber sensor and planar waveguide sensors. Optical waveguides, also known as “dielectric” waveguides, are the structures that are used to confine and guide the light in the .Optical fibers (even single-mode fibers) have a large number of cladding modes, which often exhibit substantial propagation losses at the outer interface of the cladding.Types of optical waveguides. However, unlike electrical current that flows through a metal strip according to Ohm’s law, optical waves travel in the waveguide in distinct .In this context, types of modes, dispersion, cutoff frequency, and effective thickness of the optical waveguides are discussed thoroughly.Auteur : Essam M. Full size image.
Fundamentals of Optical Waveguides
A typical optical waveguide biosensor is highly sensitive, flexible and high resolution optical waveguide biosensors have been recently developed [63], [64].
Waveguide: RF and Rectangular Types, Modes
Additionally, an analysis of planner waveguides based . Graded Index Fibres: The refractive index . This chapter discusses the basic concepts and equations of electromagnetic wave theory that are required for the comprehension of light wave .This chapter reviews optical waveguides and their classification on the basis of geometry (Non-Planar (Slab/Optical Fiber)/Planar (Buried . 3m–n, the incoming waveguide . When an optical waveguide comes from the previous track at these internal points, it can route in any of the five different paths (Fig.In this recorded webinar, learn all about modeling optical waveguides using COMSOL Multiphysics ® and the Wave Optics Module, an add-on product that expands the features and functionality for modeling optical applications. Two types of optical waveguide tapers are considered in this paper.
Electromagnetic Waveguide

Fiber optic and Waveguide Sensors Ocenan optics Fiber optic Sensors . Pros and Cons of Waveguide Technology.Herein, recent advances of optical waveguide based on 1D organic micro/nanocrystals with solid, flexible, hollow, uniformly doped, core-shell, multiblock and .
Auteur : Swagata Samanta, Pallab Banerji, Pranabendu Ganguly
Theory of Optical Waveguides
Optical waveguides can be classified according to their geometry (planar, strip, or fiber waveguides), mode structure (single-mode, multimode), refractive index . This type of waveguide is used as a transmission line mostly at microwave frequencies, for such purposes as connecting microwave transmitters and receivers to their antennas, in equipment such as microwave ovens, . However, as shown in Fig. Despite the many existing reviews focusing on the materials that these devices are made from, a systematic review that relates these devices to the various materials, fabrication . Obayya
Introduction to Waveguides
Here are some key characteristics and concepts associated with magnetic photonic crystal-based waveguides: photonic crystal structure, magnetic . The classification based on the refractive index is as follows: Step Index Fibres: It consists of a core surrounded by the cladding, which has a single uniform index of refraction.A waveguide is a structure that guides waves by restricting the transmission of energy to one direction.
Chapter 6 DISPERSION IN WAVEGUIDES
Wave propagation in a thick optical fiber at θ > θc.This type of waveguide is designed to take advantage of the unique properties of magnetic photonic crystals to control the propagation of light within a waveguide structure.
optical, sonic or electromagnetic, which can be guided, and each type requires a completely different waveguide structure.A simple method is presented for finding the modes on those optical waveguides with a cladding refractive index that differs only slightly from the refractive index of the core. Types of optical waveguides.Published 1988.Optical fibers are a type of waveguide more specifically we can say dielectric waveguide that operates at optical frequencies in order to transmit the optical (light) signal.
of optical waveguides 1
The waveguide functions are determined by the design, but the size of the waveguide and its optical properties are determined by the waveguide material.The integration of subwavelength-structured metasurfaces and metamaterials on the canonical building block of optical waveguides is gradually .Hence, the movement of an optical waveguide in the channel grid results in five different types of bends with an angle of \(\alpha\), \(\theta\) .Optical Waveguide: What It Is and How It Works When thinking about light waves, the quintessential waveguide is the Optical Waveguide. The usability of planar waveguide optical sensors is high. Employed chiefly in fibre-optic communications, these waveguides leverage the principle of total internal reflection to confine and guide light along their length. A guided optical wave propagates in the waveguide along its longitudinal direction.1 Fiber Optic (FO) Sensors and Classification We begin with a general introduction to the different types of optical waveguides, after which we provide a brief overview of the . Elkaramany, Mohamed Farhat O. They also exist in the form of wires, coaxial cables, parallel plates, or optical fibers. In contrast, the guides of interest to in tegrated optics are usually planar structures such as planar films or strips. These are Arc, Sine, and Cosine.Most waveguides exhibit two-dimensional guidance, thus restricting the extension of guided light in two dimensions and permitting propagation essentially only in one dimension.Optical waveguides, also known as “dielectric” waveguides, are the structures that are used to confine and guide the light in the guided-wave devices and circuits of integrated . It is not a completely new concept though, which works in the same way as optical fibers for communication network.Optical waveguides and integrated optical devices are promising solutions for many applications, such as medical diagnosis, health monitoring and light therapies. Dielectric waveguides (optical. The types of optical fibres depend on the refractive index, materials used, and mode of propagation of light.Optical fibers and optical waveguides comprise a core, in which light is confined, and a cladding, or substrate is surrounded by the core. The optical waveguide aims to guide the light from the . Volume scattering is caused by imperfectioils, such as voids, contaminant atoms and crystalline defects, within the volume of the waveguide. The other is a so-called “bi-level” taper, which includes . The only difference is the .There are two types of scattering loss in an optical waveguide: volume scattering and surface scattering. It has a high index lm surrounded by cladding and a substrate; both have a lower index of refraction. Our discussion will focus on these planar guides even though most of the fundamentals are applicable to all optical waveguide types. succeeded in producing magneto-optic switching inside bulk terbium-doped Faraday glass [50]. 59 Due to a heroic technological effort during three decades starting from the mid-1960s, the attenuation of such fibers has been decreased from the values of the order of 20 db/km (typical for a window glass) to . This has good research significance .Optical waveguides such as optical fibers typically trap and guide light within rectangular or cylindrical boundaries over useful distances. Therefore, the light beam that is coupled to the end face of the waveguide is confined in the core by total internal reflection.Moreover, microrings [152,153,154,155] and MZI-type optical waveguide sensors [156,157] have high sensitivity and selectivity, strong anti-interference ability, small size, and a wide application range. The optical waveguide technology was introduced most recently as a unique type of optical combiner as it generally carries no optical power. The technology to fabricate these waveguides is based on a cost-efficient replication method, employing .comSlab Waveguides Chapter - NTUAusers. The thickness of the substrate and cladding also extends to in nity in the x direction. In material dispersion, different wavelengths of light travel at different velocities within a given medium. The optical waveguide is a physical structure that can guide electromagnetic waves in the optical spectrum [69, 70], which consists of visible light in this specific case.Auteur : Shankar Kumar Selvaraja, Purnima Sethi
Introduction to Optical Waveguides
We introduce the concept of mechanically stretchable optical waveguides. Recently, optical waveguide sensors are preferred for different applications due to higher sensing region in its compact size in comparison with optical fiber sensors.A well-known optical waveguide is, of course, the optical fiber which usually has a circular cross-section. In microstructured optical fibers, the physical structure of the waveguide is used at a nano-scale level to manipulate light.