Types of platelet diseases
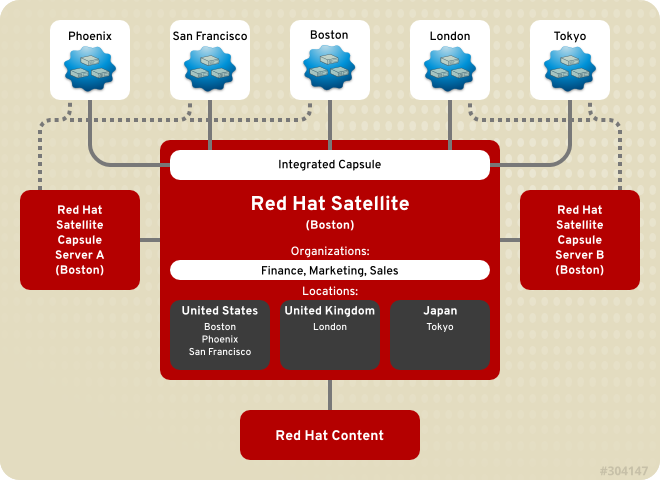
If the exact cause of this condition isn't known, it's called idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura.Thrombocytopenia is a condition that lowers the body’s platelet count, sometimes making it more difficult for the blood to clot after an injury. While platelets can act individually, they interact with vascular cells and leukocytes at .Thrombocytosis (throm-boe-sie-TOE-sis) is a disorder in which your body produces too many platelets. Dysfunction of the immune response is regarded as a prominent feature of neurological diseases, including neurodegenerative diseases, malignant tumors, acute neurotraumatic insult, and cerebral ischemic/hemorrhagic diseases. Platelet disorders are conditions that occur when the platelet count in your blood is too high or too low or your platelets do not work properly.Platelet-derived DDSs are novel approaches for drug delivery that utilize various forms of platelets as carriers of therapeutic agents.
Immuno-thrombosis of COVID-19 results in the activation of platelets and coagulopathy. Platelet hyperaggregation among the diabetic patients with CVD remains another striking area to explore.Abnormal bleeding can result from disorders of the coagulation system, of platelets, or of blood vessels.It is important to distinguish patients with IPD from those with acquired platelet disorders to avoid unnecessary or potentially harmful treatments.There are many causes, including acute infection, chronic inflammatory disorders (eg, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, tuberculosis, sarcoidosis), iron . Similar content being . This plug is called a blood clot.Inherited platelet disorders (IPDs), which manifest as primary hemostasis defects, often underlie abnormal bleeding and a family history of thrombocytopenia, bone .Exclusion criteria were the presence of heart disease, diabetes mellitus of either type, peripheral artery disease, a history of stroke, and the use of drugs which directly affect .
Inherited Platelet Disorders: An Updated Overview
Platelet disorder.Purpose of the review: The study of platelets in the context of neurodegenerative diseases is intensifying, and increasing evidence suggests that platelets may play an important role in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disorders.In this review we compare clinical, biological and genetic characteristics of inherited platelet disorders (IPD) with abnormal platelet function but a normal platelet . Their brief life span in circulation is strictly controlled by intrinsic apoptosis, where the .
Emerging roles for platelets as immune and inflammatory cells
Testing can help: Identify whether you’re at risk for further clotting.Inherited platelet disorders (IPDs), affecting either platelet count or platelet functions, comprise a heterogenous group of about sixty rare diseases caused by .Autoimmune diseases are . Currently, based on their different sources and assembly methods, platelet-derived DDSs can be divided into whole platelet drug delivery devices, platelet membrane-camouflaged drug delivery devices, PMP drug . 2 A blood smear is helpful for patients with myosin heavy chain 9 (MYH9)–related diseases (giant platelets and Döhle-like inclusion bodies within leukocytes) and Gray platelet syndrome (pale platelets); a .

If your platelet count is too low (thrombocytopenia), you won’t have enough platelets to clot a wound.49 lignesInherited platelet disorders (IPDs), affecting either platelet count or platelet functions, comprise a heterogenous group of about sixty rare diseases . Sometimes the white blood cell and . When you are injured, platelets stick together to form a plug that seals your wound. and reactive thrombocytosis.Among all the types of MPs in the blood of healthy individuals, platelet-derived microparticles (PMPs) are the most abundant [3,4]. This fact sheet describes the types, signs and symptoms, .Auteur : Verónica Palma-Barqueros, Nuria Revilla, Ana Sánchez, Ana Zamora Cánovas, Agustín Rodriguez-Alén, An. In the event of an injury, you may bleed too much and it could be difficult to stop. In ITP, your blood does not clot as it should, because you have a low platelet count. Your platelets . Originally published 14 Jan 2021 .
How is ITP treated? What health problems can ITP cause? What is ITP? Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) is a type of platelet disorder.In thrombocytopenia caused by platelet destruction, transfusions are reserved for life-threatening,central nervous system or ocular bleeding.Immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) are characterized by excessive and uncontrolled inflammation and thrombosis, both of which are responsible for organ damage, morbidity and death. Immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis are highly prevalent, for example affecting 3–8% of the population in high-income countries, and they remain a major cause of morbidity and death worldwide despite therapeutic advances 1. Cytopenia is the term used to refer to a lower-than-normal percentage of blood cells. What Are the Specific Types of Platelet Disorder? Some .Thrombocytopenia is a condition that occurs when the platelet count in your blood is too low.Platelets are important actors of cardiovascular diseases (CVD). Thus, thrombocytopenia, describes a lower than normal platelet count. The major causes of acquired coagulation disorders are. In this review, we will discuss platelet and platelet .Enhanced platelet activation and thrombosis are linked to various cardiovascular diseases (CVD). The inherited platelet disorders are a heterogeneous collection of rare diseases that are infrequently encountered in clinical practice.Heparin antibodies (in people who develop low platelet counts while exposed to heparin).There are many different kinds of platelet function disorders.
Frontiers
Your body makes too few platelets. Determine the right course and length of treatment to prevent future clots. Platelet hyperactivity in various diseases provokes adverse effects in some cases, especially in coronary artery disease where .Acquired disorder of platelet dysfunction is commonly due to diseases (e.Formyl peptide receptors (FPRs) are members of seven transmembrane G protein-coupled receptors superfamily that exhibit different responses based on the .Extracellular microparticles (MPs) provide a means of cell-to-cell communication and can promote information exchanges between adjacent or distant cells [1,2]. In ITP, your blood does .
This disorder is deadly; most dogs with the disease die from infections before 6 months of age.
What Are Platelet Disorders?
Inherited Platelet Disorders: An Updated Overview
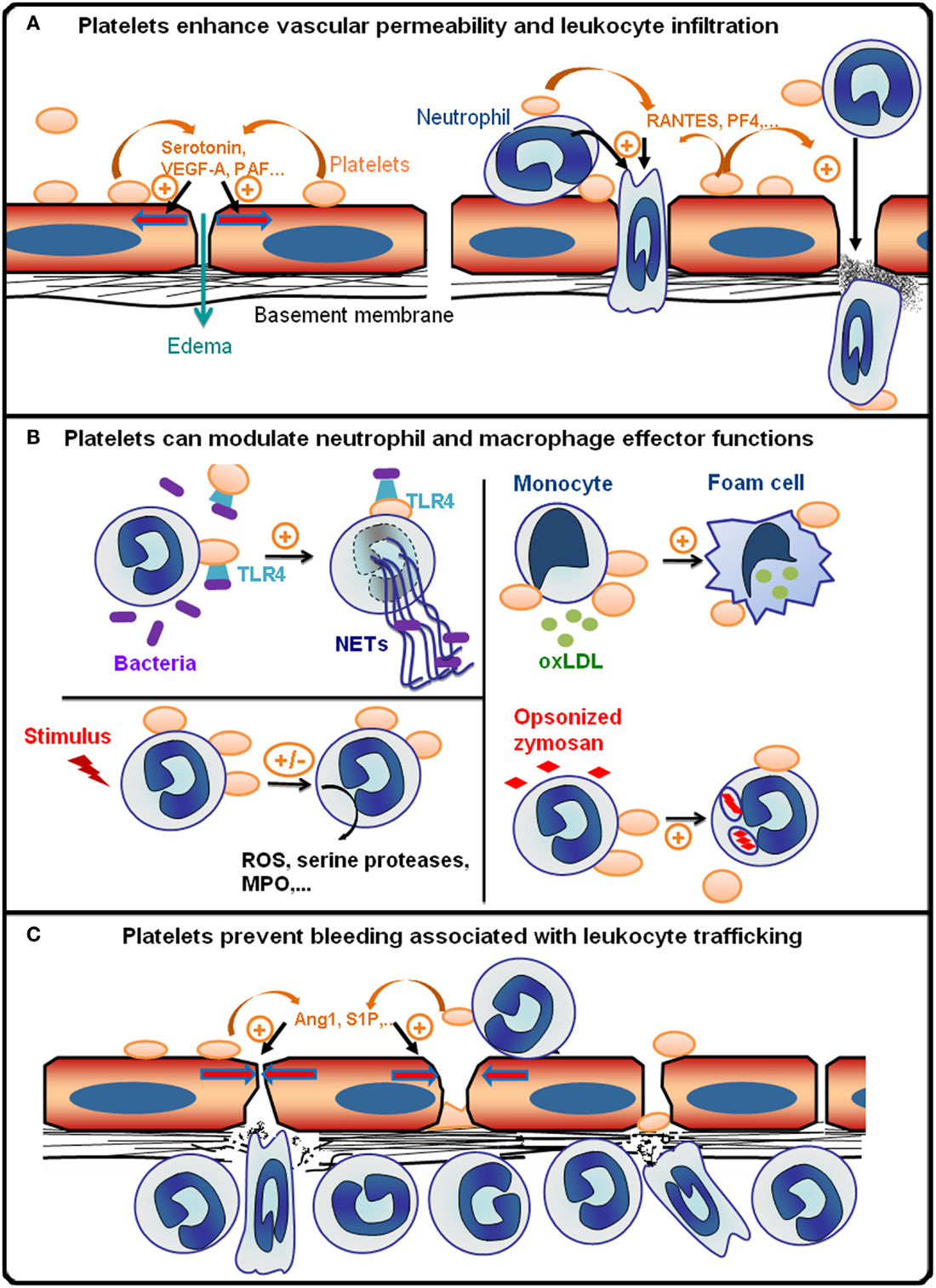
When you are injured, platelets stick together to form a plug to seal your wound. Altogether, the current knowledge of platelet biology indicates .Platelets — blood cells continuously produced from megakaryocytes mainly in the bone marrow — are implicated not only in haemostasis and arterial thrombosis, but . An abnormal increase in platelets (essential thrombocythemia and reactive thrombocytosis) A decrease in platelets (thrombocytopenia) Platelet . Here we summarize the evidence .IMIDs include .Platelet-activating factor (PAF) and its receptor (PAFr) have been implicated in a wide range of diseases and disorders that originate from the activation of inflammatory pathways.In recent years, platelet proteomics has seen progress not only in the cardiovascular field, but also in cancer and neurological disorders highlighting that the .Platelet disorders include. Mild to severe platelet shortages can be seen, and excessive bleeding is a potential complication. An abnormal increase in platelets ( essential thrombocythemia. The body's immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys platelets. Platelet disorders happen when: Your body makes too many platelets.Autoimmune diseases, such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, cause this type. In some contexts, platelet immune functions are protective, whereas in others platelets contribute to adverse inflammatory outcomes. It's called reactive thrombocytosis or secondary .These growth factors allow stem cell proliferation and angiogenesis, promote bone regeneration, improve the local microenvironment, and enhance tissue regeneration capacity and functional recovery. Bacteria in the blood. Platelets are tiny blood cells that are made in the bone marrow from larger cells. This type more often affects children.Platelets are linked to the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases such as atherosclerosis, malaria infection, transplant rejection, and rheumatoid arthritis. Platelets are also called thrombocytes, because a . Beyond those normal functions, . Having too many platelets can cause blood clots to .They have also recognised functions in thrombosis, immunity, antimicrobal defense, cancer growth and metastasis, tumour angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, inflammatory diseases, wound healing, liver regeneration and neurodegeneration.
Overview of Platelet Disorders
Application of platelet-rich plasma in spinal surgery
A higher-than-normal platelet count is called thrombocytosis or thrombocythemia.The most commonly used drug that inhibits platelet function is aspirin, which inhibits cyclooxygenase I (COX-1) conversion of arachidonic acid to thromboxane A 2, inhibiting platelet function by preventing the enhancement and propagation of agonist-induced platelet signaling.Moreover, recent reports demonstrate their ability to release mediators that can be recognized by other cell types, such as endothelial cells, macrophages, T lymphocytes, neutrophils, and mast cells, showing their potential role in pathologies such as allergy or infectious lung diseases. Current antiplatelet drugs that inhibit platelet aggregation have been shown to be effective in CVD treatment. Another name for platelets is thrombocytes.Platelet interaction and cardiovascular disease progression remain an unsolved riddle for many years . Understanding of the coagulation cascade and hemostatic . Low platelet count can lead to excessive blood loss, hemorrhaging and internal bleeding, which could be life-threatening.

Thrombocythemia.What Are the Types of Platelet Disorders?

Among other mechanisms, oxidative stress seems to play a pivotal role in platelet hyperactivity. Severe cases of bleeding inside of . Disorders of coagulation can be acquired or hereditary.This suggests that platelet-mediated adaptive immunity plays a role in the development of immune-related kidney diseases, and that this mechanism is likely applicable to many other immune-mediated inflammatory disorders, as IgG-containing immune complexes have been identified in various diseases, including systemic .1 Department of Endocrinology, Guang’anmen Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing, China; 2 Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, . Download chapter PDF.Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) is a type of platelet disorder. Therefore, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of the role of platelets and their diverse . In platelet function disorders, a person's blood platelets do
Platelets: When To Worry About Platelet Count
In patients with IMIDs, platelets are activated by disease-specific factors, and their activation often reflects disease activity. However, the management of bleeding complications is still an issue in vascular diseases. Indeed, upon stimulation by physiological agonists, human platelets generate and release several types of .There are many types of platelet disorders.

Overview of Platelet Disorders - Etiology, pathophysiology, symptoms, . Severe liver disease (eg, cirrhosis, fulminant hepatitis, acute fatty liver of pregnancy) may disturb hemostasis by impairing .
Inherited Platelet Disorders
IN THIS ARTICLE.