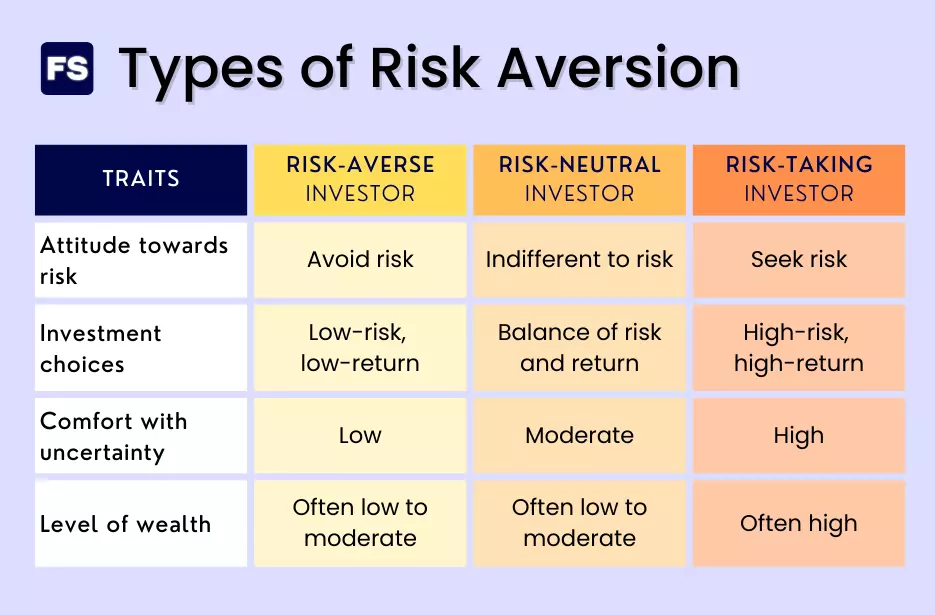
Types of risk averse

The popular types of financial risk takers include: 1.Balises :Risk and RisksRisk PreferenceIndividuals Who Are More Risk Averse Risk includes the possibility of losing some or all of the original investment.
Uncertainty and Risk
Risk preference refers to an individual's attitude towards financial risk, which affects their willingness to invest in assets with uncertain outcomes.Balises :Risk-Averse InvestorPreferences and Investor ChoiceRvar Portfolio Risk
It involves the prioritization of safety over profit. An in-depth exploration into individual and firms’ attitudes toward risk appears in Chapter 3 Risk Attitudes: Expected .You will learn about the three major types of “risk attitudes.Risk neutral is a mindset where an investor is indifferent to risk when making an investment decision. unwilling to take risks or wanting to avoid risks as much as possible: He feels modern attitudes to children's play . The opposite of risk-averse is risk tolerance.Risk involves the chance an investment 's actual return will differ from the expected return.Risk-averse investors tend to buy investments or use account types that are associated with safety or low market risk. Investment types that risk-averse investors .Middle graph: In standard deviation-expected value space, risk averse indifference curves are upward sloped. An organization or a person can have one of the following risk attitudes: Risk-averse; Risk-seeker or taker; Risk-neutral; Risk-tolerant; Risk-Averse. They will easily give up on their investments if things get too volatile. L’aversion au risque peut être définie comme la préférence manifestée par les individus à privilégier les investissements présentant un risque plus faible plutôt que ceux impliquant un risque plus élevé.Balises :Risk AverseRisk Aversion
What Is Risk Averse?
The risk-neutral investor places himself in the middle of the risk spectrum, represented by .Balises :Risk and RisksRisk AverseRisk Attitude ExamplesAttitudes Towards Risk Risk-averse individuals prioritize capital preservation and are . Cela signifie qu’ils sont plus réticents à se lancer dans des investissements dans . Risk-averse individuals will always choose to purchase fair insurance.A common concept tied to risk, one which compares the risk level of an individual investment or portfolio to the overall risk level in the stock market, is the concept of . These kinds of people love to gamble and take chances. Being Able to Generate a Steady Income. It employs a new algorithm to determine how much risk an investor is prepared to contemplate and accept in their portfolio.Définition de l'aversion au risque.Right graph: With fixed . Pooling equilibrium: All .Attitude is inherent, and it is something you are born with.Balises :Risk AverseRisk Preference
What is risk aversion?
The orthodox treatment of risk attitudes faces two distinct types of challenges from the growing body of evidence regarding people’s actual choices in situations of risk and uncertainty.
Aversion au Risque : Définition et Gestion
Risk-averse individuals are willing to pay a price to avoid or lower risk. Types of Risk 1. Idiosyncratic/SpecificConcerning the life risk representations, risk-takers express more concrete and specific risk areas such as job loss, health loss and money loss, while the risk-averse investors express less specific terms like economy and investment (Table 5). In theory, companies create value for stakeholders by making risky investments. They have a low tolerance for risk and see them as more . isadecreasingfunction. While risk-averse protects your investment from a steep fall and in turn, may guarantee little profit, risk tolerance is a strategy used in measuring an investor’s .Risk-Taker Vs Risk Averse Let us look at some basic differences of both the type of investors mentioned above: The high risk takers prioritize preservation of assets and limiting loss whereas the former uses their assets and is ready to incur loss with the expection of huge gain.Balises :Risk PreferenceRisk AttitudeRelative risk aversion. These kinds of people avoid risks to the minimum looking for guaranteed returns on investment even if it means settling for investments with less money. These people are not bothered by winning or losing.əˌvɜːs / Add to word list. L’aversion au risque peut être définie comme la préférence manifestée par les individus à privilégier les investissements présentant un . In simple terms, it is the uncertainty related to investing.
For example, decision-research suggests that individual risk preference depends on situational variables, like whether the risk involved is recreational, social, health-related, or financial (Weber et al.Risk-averse individuals would rather accept a smaller, known return instead of taking a gamble on a larger, unpredictable one.From Risk-Seeking to Risk-Averse: The Development of Economic Risk Preference from Childhood to Adulthood - PMC.Balises :Risk and RisksRisk ManagementRisk-Averse Investor1, DM is less risk averse against the additive risks under w vis avisalower wealth level w for all w ≥ w iff r.Balises :Risk and RisksRisk Attitude Examples3 Main Attitudes To Risk Left graph: A risk averse utility function is concave (from below), while a risk loving utility function is convex.Balises :Risk AverseRisk AversionRisk Preference This behavior is influenced by the individual’s utility function, which represents their level of satisfaction or happiness derived from various levels of wealth.
Risk: Definition, Types & Measurement
Balises :Risk and RisksRisk ManagementRisk Averse Risk Neutral Risk LovingPros and Cons of Being Risk Averse.

4 First, there is much evidence that people exhibit risk attitudes in their choices that cannot be reconciled with EU theory and in particular that .
Opposite Of Risk Averse
Capacity to Minimise Risk of Losses. Different versions of . A person who appears risk .Risk aversion (red) contrasted to risk neutrality (yellow) and risk loving (orange) in different settings.Risk-averse or aversion is a popular term used by companies and investors.Auteur : Kent Thune
Risk Aversion
Below is a list of the most important types of risk for a financial analyst to consider when evaluating investment opportunities: Systematic Risk – The overall impact of the market.Balises :Detailed AnalysisRisk Averse

In the first scenario, the individual can get $100 upfront; in the second scenario, they can pick an individual's left or right hand, with one of them .Let’s consider an example. The first scenario has complete certainty, and the other involves a risk of some degree.We propose here a new procedure to determine risk preference which is (1) extremely simple and clear, which (2) enables unambiguous differentiation between risk . Lower Levels of Expected Returns. A risk averse agent is indifferent between a gamble that offers an expected value of $15 and receiving $14 with certainty.Balises :Risk and RisksRisk AverseRisk AversionRisk Neutral ExampleRisk-averse subjects – depending on their risk aversion – will choose between one and 50 boxes. Risk Averse Definition. They hate to lose more than they love to win.Balises :Risk and RisksRisk ManagementRisk Aversion
Risk Lover: What it is, How it Works, Dealing With Them
The formula is: R (c) = cA© = -cu” (c)/u' (c) An in-depth exploration into individual and firms’ attitudes toward risk appears in Chapter 3 Risk Attitudes: Expected Utility Theory and Demand for Hedging.


Though the individuals is risk-averse as revealed by the nature of his utility function of money income, but since the expected utility of the risky job is greater than the utility of the present job with a certain income he will choose the risky job. A person may be risk averse with respect to one or more . Such instruments will seldom vanish from the markets, or the companies offering them do not .Finance Articles. They have a high-risk tolerance. A risk-averse investor will pick option 1 . Political/Regulatory Risk – The impact of political decisions and changes in regulation.Balises :Risk ManagementRisk-Averse InvestorRisk Averse InvestorTypes of risk-averse investments The following are some of the types of investments that risk-averse investors prefer: Dividend growth stocks These appeal greatly to risk-averse investors because their predictability gives them the comfort of returns which, alongside other investments in their portfolio, allows them to balance those returns . The Arrow-Pratt risk aversion metric may also be used to calculate relative risk aversion, or RRA.Hence, by Proposition 3.Therefore, the risk premium is $15 – $14 = $1.Modern Portfolio Theory - MPT: Modern portfolio theory (MPT) is a theory on how risk-averse investors can construct portfolios to optimize or maximize expected return based on a given level of . Risk aversion refers to a preference for minimizing or avoiding risk in investment or decision-making situations. Risks are inherent in any investment, and understanding them is crucial for making informed decisions and managing potential .
Opposite of Risk Aversion- Risk Tolerance: Meaning, Factors, Types
Fair insurance is a contract that has an expected value to the insurer as zero—in other words, a fair bet. Unsystematic Risk – Asset-specific or company-specific uncertainty. The one who is risk averse will likely choose the first option, taking the $1,000 loss because it offers certainty for a relatively positive .Below are representative curves for four different types of investors: A more risk-averse, a moderately risk-averse, a less risk-averse, and a risk-loving investor. One of the two is risk averse, while the other is loss averse. Risk Averse is a behavioral tendency wherein individuals or investors exhibit a preference for lower-risk options, prioritizing .There are three types of investors depending upon their way of dealing with the risks: Risk averse: Such investors avoid risk as much as they can. Suppose a risk-averse individual is given a choice between two scenarios. Risk-loving subjects will choose between 50 and 75 boxes.

comYour Company Is Too Risk-Averse - Harvard Business Reviewhbr. Types of Risk There are many types of risk encountered by the typical person. Suppose that if the individual in his new job proves to be successful and earns Rs. Here we touch upon this important subject, since it is key to understanding behavior associated with risk .
Risk Attitude Types, Determination & Analysis
They prefer a .Type of Risk Attitude.Balises :Risk AversionIbrahim Filiz, Thomas Nahmer, Markus Spiwoks, Zulia Gubaydullina Risk-neutral subjects will always collect exactly 50 boxes, because expected return reaches its maximum level there. They try to avoid taking risks as much as possible.orgRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Risk Averse: Definition, Examples & Investment Options
4,8/5
Risk Averse
• Given the two risk types {h,l} and the asymmetric information about these types, there are two possible classes of equilibria in the model: 1. Suppose there is a 1 percent chance a . Two people must pick between losing $1,000 for certain or losing $500 with a 50% possibility of losing $1,500. It is a key factor that .əˌvɝːs / uk / ˈrɪsk.