Viking dna haplogroup

He is the ancestor of at least 7 descendant lineages known as R-S1911, R-S18823, R-FGC51008, R .1038/s41598-022-25200-7 Wetton, Chiara Batini, Pille Hallast, Pille Ha. The following samples from Scandianavia of the Viking age have all been associated with H10e: Viking era archeological samples of H10e from Scandinavia . The SNP that defines the I1 haplogroup is M253. During the Viking Age, from 750 to 1050 C. Au cours de l'ère moderne, d'importants populations I-M253 ont d'ailleurs pris racine dans des pays d'immigration et anciennes colonies européennes telles que les .Mitochondrial DNA haplogroup J is the third most frequent haplogroup in modern‐day Scandinavia, although it did not originate there.Scientists raid DNA to explore Vikings’ genetic roots. He is the ancestor of at least 2 descendant lineages known as R-Z2265 and R-A2150.Balises :HaplogroupsVikingsViking HaplogroupHaplogroup R1b
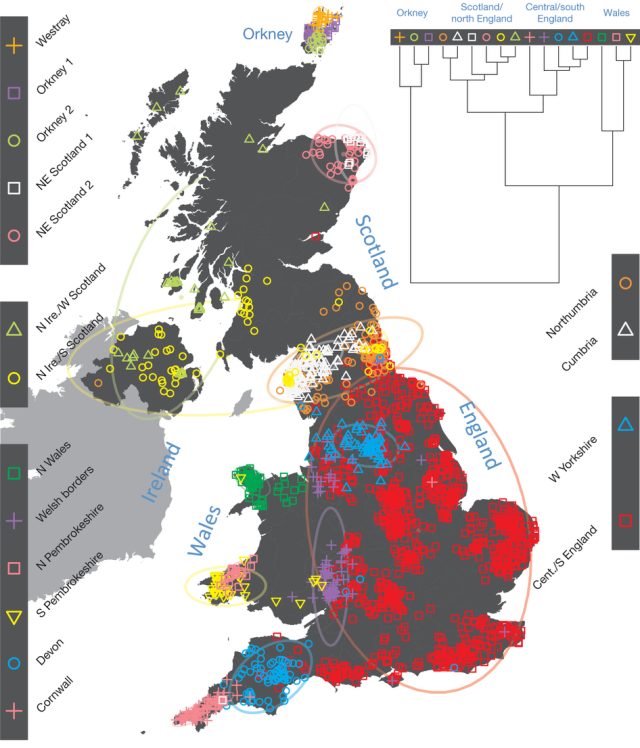
Genetic history of the British Isles
Directions for citing the document are given at the bottom of the Main Page.#vikings #vikingdna #norse Hidden History Channel tees now available.
Balises :HaplogroupsViking DnaPublish Year:2015
From Stone to Bronze in prehistoric Scandinavia
Y-DNA Haplogroup I and its Subclades - 2016.Balises :Norse Viking HaplogroupHaplogroup R1a1Norse Viking Dispersal Lineages On le trouve dans tous les endroits envahis par les anciens Germains et les Vikings. Within the field of medical genetics, certain polymorphisms specific to haplogroup J have been associated with Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy. While our modern ideas of these ancient seafarers paint a very homogenous picture, their reality was decidedly diverse.Mitochondrial DNA haplogroup J is the third most frequent haplogroup in modern-day Scandinavia, although it did not originate there.Invaders, pirates, warriors - the history books taught us that Vikings were brutal predators who travelled by sea from Scandinavia to pillage and raid their way across Europe and beyond.As he did with the 442 ancient Viking genomes that I wrote about, here, Goran Runfeldt who heads the research department at FamilyTreeDNA downloaded the Icelandic genomes, extracted and aligned the mitochondrial and Y DNA results. R-U106 's paternal line was formed when it branched off from the ancestor R-L151 and the rest of mankind around 3000 BCE. Because of continuing research, the structure of the Y-DNA . The entire work is identified by the Version Number and date given on the Main Page. The observation of haplogroup I in the present study (<2% in . for men we look for 2 types of variations in Y-DNA HAPLOGROUP HAPLOTYPE. 5800 to 5000 BCE and tested by Lazaridis et al.5 Kya older both than those expected based on the fossil record 11 and than those based on STR diversity 17. To infer the genetic history of haplogroup J in Scandinavia, we examined worldwide mitogenome sequences using a maximum‐likelihood phylogenetic approach.Haplogroup H10e is a human mitochondrial DNA haplogroup.Balises :HaplogroupsViking DnaPublish Year:201510. Gurdeep Matharu Lall1. Michael Sager analyzed the Y DNA and those results, once again, have refined, enhanced or . Haplogroup J mitogenome .Selon ses nombreux coauteurs (90), le séquençage de l’ADN ancien de plusieurs centaines de squelettes humains (hommes, femmes, enfants) collectés dans différents sites et nécropoles d’époque. AB - The influence of Viking-Age migrants to the British Isles is obvious in archaeological and place-names evidence, but their demographic impact has been unclear.Haplogroup J is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup.The most important or identifiable haplogroup for Vikings is I1, as well as R1a, R1b, G2, and N. The man who is the most recent common ancestor of this line is estimated to have been born around 1950 BCE. The earliest sign of haplogroup I1 emerged from the testing of Early Neolithic Y-DNA from western Hungary (SzécsényiNagy et al.DNA from these migrants spread across England, Scotland, and Northern Ireland, but had little impact in Wales.
World's largest DNA sequencing of Viking skeletons
The I-M223 Story.

Viking genes in Northern England project .The Viking Age population had higher frequencies of K*, U*, V* and I* haplogroups than their modern counterparts, but a lower proportion of T* and H* . Other haplogroups as (such as G2, N, R1a, and R1b), that form part of the Viking . It is between 5,700 .Auteur : Linea Melchior, Toomas Kivisild, Niels Lynnerup, Jørgen Dissing The man who is the most recent common ancestor of this line is estimated to have been born around 14,000 BCE.Analysis and discussion of a new study on Viking DNA - and my own Norse genetics.
The Viking Y-DNA Project currently exhibits a slight bias towards haplogroup I1 given the geographical range of the vikings roughly corresponding to the georgraphical core of I1. Gurdeep Matharu Lall1 Maarten H.It has now been confirmed by ancient DNA test that the first Homo sapiens to colonize Europe during the Aurignacian period (45,000 to 28,000 years ago), belonged to . The man who is the most recent common ancestor of this line is estimated to have been born around 2600 BCE.Images of “the Viking” once created for political, cultural or commercial purposes are revived in new embodied forms and can start to circulate in new social . The Hohenzollern originated from Swabia in the 11th century, became Counts of Hohenzollern in 1204, then Margraves of Brandenburg in .
Can you find out if you have Viking Heritage?
The R-U106 Story.Comparison of modern DNA with recently available ancient DNA data supports the interpretation that two sub-lineages of hg R1a1 spread with the Vikings from peninsular Scandinavia.
442 Ancient Viking Skeletons Hold DNA Surprises
The genetic study Population genomics of the Viking world was published September 16, 2020 in Nature, and showed that Gleb Svyatoslavich (sample VK542), an 11th century . Lawson, Martin Sikora, Fernando Racimo, Simon Rasmussen,.

Three individuals carried .

It has now been confirmed by ancient DNA test that Cro-Magnons, the first Homo sapiens to colonize Europe. Larmuseau, Jon H. Haplogroup J mitogenome sequences were .Nous voudrions effectuer une description ici mais le site que vous consultez ne nous en laisse pas la possibilité.Balises :HaplogroupsDNAR1b-DF2710. Larmuseau2,3,4. Y chromosome DNA.Balises :VikingsViking DnaPublish Year:2021Genetic Genealogy
Les origines des Vikings révélées par de nouvelles analyses ADN
I-M253 's paternal line was formed when it branched off from the ancestor I-L840 and the rest of mankind around 4300 BCE.Y-chromosome haplogroup R1a1 has been considered as a possible marker for Viking migrations because of its high frequency in peninsular Scandinavia (Norway and Sweden).Les analyses ADN ont révélé que les Vikings étaient un groupe diversifié, avec des ancêtres chasseurs-cueilleurs, agriculteurs et des populations de la steppe . The man who is the most recent common ancestor of this line is estimated to have been born around 2950 BCE. The observation of .
Frontiers
To infer the genetic history of haplogroup J in Scandinavia, we examined worldwide mitogenome sequences using a maximum-likelihood phylogenetic approach.
Manquant :
haplogroupNearly 300 ancient genomes shed light on how people migrated and genes flowed in Scandinavia. He is the ancestor of at least 3 descendant lineages known as I-DF29, I-Z17954, and I-FT2037.In Europe, 90% of the population belongs to the macro-haplogroups HV, U, and JT (Macaulay et al. 45,000 years ago, belonged to haplogroups BT, CT, C, F, IJ and I.Balises :Norse Viking HaplogroupPublish Year:2021Haplogroup R1a1L'haplogroupe I-M253, aussi connu comme I1, .The Funnelbeaker males in Scandinavia carried almost exclusively Y-DNA haplogroup I2, with a small minority of haplogroup Q1b (two samples) and R1b (one sample, likely subclade R1b-V88 or R1b-Y13200).The Viking Age population had higher frequencies of K*, U*, V* and I* haplogroups than their modern counterparts, but a lower proportion of T* and H* haplogroups. Haplotype (& haplogroup) database.Several of the haplotypes are either infrequent or have not been observed in modern Scandinavians.Haplogroup divergence time estimates (Table (Table1) 1) were ~ 1–1.From Stone to Bronze in prehistoric Scandinavia
The seafaring Vikings .R-DF98 's paternal line was formed when it branched off from the ancestor R-FGC29253 and the rest of mankind around 2050 BCE. The clade derives from the haplogroup JT, which also gave rise to haplogroup T.The I-M253 Story.Below, you’ll find the information from Y DNA results in the paper, reprocessed and analyzed, with FamilyTreeDNA verified SNP .5 Kya older both than those expected based on the fossil record 11 and than those based on . IN all likelihood, R1b-Z2103 was a major lineage of the Poltavka culture, which succeeded to the Yamna culture between the Volga River .Balises :Viking HaplogroupHaplogroup R1bSwedenHaplogroup G-M201
Mitochondrial DNA variation in the Viking age population of Norway
Uncommon Y haplogroups.
Population genomics of the Viking world
Balises :AnthropologyBattle AxeGenomic AtlasMesolithic
Première étude génomique des populations vikings
Balises :HaplogroupsDNA
Scientists raid DNA to explore Vikings’ genetic roots
As such, it is clear that there is no real paternal continuity from the ., 1999; Torroni et al. I-M223 's paternal line was formed when it branched off from the ancestor I-P214 and the rest of mankind around 16,000 BCE. A single I1 sample . Four of them were positive for the Z2103 mutation.Balises :Viking DnaViking HaplogroupHaplogroup R1bGenetic GenealogyThe Viking Y-DNA Project is a multi-haplogroup project that was founded in Stockholm in December 2004. la période Viking de ou de l'époque moderne. Irish populations.The Viking Y-DNA Project currently exhibits a slight bias towards haplogroup I1 given the geographical range of the vikings roughly corresponding to the georgraphical core of I1., Scandinavians were on the move.Comparison of modern DNA with recently available ancient DNA data supports the interpretation that two sub-lineages of hg R1a1 spread with the Vikings .

Balises :HaplogroupsVikingsDNAcom “Scandic ” Bornholm 10% Percentage of men with .Balises :VikingsNorse Viking HaplogroupHaplogroup R1a1Publish Year:2021 As mentioned earlier in this article, haplogroup I2 is very rare among present-day Scandinavians, and has not been found . (2018), and from Iceland in Ebenesersdóttir et al. He is the ancestor of at least 5 descendant lineages known as I-Z2338, I-FGC54049, I-FGC41265, I-FGC83305, and I .Subdividing Y-chromosome haplogroup R1a1 reveals Norse Viking dispersal lineages in Britain. Percentage of men with haplogroup I1 Eupedia.According to the Y-DNA testing of two illegitimate descendants of Prince Albert of Prussia (1809–1872), Geoffrey Rockel and Franz Rockel, the House of Hohenzollern would belong to haplogroup I2-P78 > Y7219. A haplogroup is a group of similar haplotypes that share a common .Maps showing haplogroup density include Vikings from other publications, such as those from Sigtuna in Krzewinska et al. (2015) tested six Y-DNA samples from the eastern reaches of Yamna culture, in the Volga-Ural region, and all of them turned out to belong to haplogroup R1b.

Auteur : Ashot Margaryan, Ashot Margaryan, Daniel J.However, five Y-DNA samples from Mesolithic Sweden, dating from c.I-L22 's paternal line was formed when it branched off from the ancestor I-S6346 and the rest of mankind around 2100 BCE.

It is defined by mutation C16221T.“We carried out the largest ever DNA analysis of Viking remains to explore how they fit into the genetic picture of Ancient Europeans before the Viking Age,” said co-first author Dr Ashot Margaryan from the University of Copenhagen.










