Vitreous haemorrhage definition

Overview
Hémorragie du vitré
Definition of acute massive haemorrhage varies. Vitreous haemorrhage is a common accompaniment to . If the blood leaks into the vitreous humor (the colorless, gel-like material located between the retina and .Authoring team. Learn more in the Cambridge English-Chinese traditional Dictionary.Hémorragie du vitré : Petits vaisseaux sanguins de la rétine qui saignent dans le vitré. A moderately dense vitreous hemorrhage caused by an acute PVD.Vitreous hemorrhage is associated with a myriad of conditions such as proliferative diabetic retinopathy, proliferative retinopathy following vascular occlusion and vasculitis, . Severe haemorrhage results in dangerous loss of circulating blood . The condition is common for older adults; over 75% of . This fluid is called the vitreous gel. A vitreous haemorrhage can have a variety of causes such as trauma, tumours or neovascular age .Management of Submacular Hemorrhage. Formation of a nuclear sclerotic cataract is a well‐known and .
Vitreous Haemorrhage.Vitreous hemorrhage can be caused by the pathologic mechanisms of disruption of normal retinal vessels, bleeding from diseased retinal vessels or abnormal . This condition may .Definition of FOVH was as follows: vitreous haemorrhage obscuring details of the posterior pole, including optic nerve and macula, and precluding visibility of the peripheral retina in ≥3 .8% of VH and retinal detachment accounted for 12.Vitreous haemorrhage is a bleed into the gel-like filling (vitreous humour) in the globe of the eye.Vitreous hemorrhage has an incidence of seven cases per 100,000, which makes it one of the most common causes of acutely or subacutely decreased vision.Vitreous Haemorrhage. Cela peut donner l'impression de voir des fils noirs, une toile d'araignée, des petites mouches et même voiler la vision de façon complète.Definition of Vitreous Hemorrhage.Timely surgical removal of the vitreous haemorrhage has the advantage of significant and immediate improvement of vision, and may also prevent complications of longstanding haemorrhage. Elle résulte toujours de la rupture d’un ou . A thorough examination of the fellow eye is recommended as it . It can be defined as a 50% blood loss within 3 hours or a rate >150ml/minute.L' hémorragie intra-vitréenne ou hémorragie du vitré est une extravasation de sang d'origine rétinienne dans l'espace vitréen 1. However, vitrectomy, despite being a routine procedure, also has numerous risks and side effects. Large amounts of blood can make the . treatment is dictated by finding the underlying . The gel is clear, so light passes through it to the retina.

Hyphema and vitreous hemorrhage are frequent presentations in ocular trauma.
Hémorragie intravitréenne — Wikipédia
It refers to the separation of the posterior hyaloid membrane from the retina anywhere posterior to the vitreous base (a 3–4 mm wide attachment to the ora serrata). An abnormal escape of blood from an artery, a vein, an arteriole, a venule or a capillary network. A vitreous hemorrhage can quickly escalate into a very serious situation. This finding is compatible with the results of previous reports.Patients with vitreous hemorrhage complain of sudden visual loss, abrupt onset of floaters that may progressively increase in severity, or occasionally, “bleeding within the eye.Retinal hemorrhage symptoms.Etiologi perdarahan vitreus dapat ditemukan saat pemeriksaan awal, setelah perdarahan terabsorpsi sebagian, atau saat operasi vitrektomi. Le sang dans le vitré obstrue la vision entraînant une perte graduelle de celle-ci. For one, vitreous hemorrhage due to a retinal tear .
vitreous haemorrhage definition
[2] Tata laksana perdarahan vitreus meliputi terapi konservatif, laser fotokoagulasi, cryotherapy, injeksi anti-VEGF ( anti-vascular endothelial growth factor ), atau pembedahan vitrektomi pars plana. Some causes of vitreous hemorrhage are injury and diabetic retinopathy. Who gets retinal hemorrhages? Anyone can experience a retinal hemorrhage. Internal haemorrhage often causes a HAEMATOMA. Treatment will vary .By definition, it is the presence of extravasated blood within a space lined by posterior lens capsule anteriorly, internal . : +33 3 83 96 21 76 - Fax : +33 3 83 97 24 56Vitreous hemorrhage is seen as blood floating in vitreous, occluding the view of retina variably.Publiée : 2023/07/31
Vitreous hemorrhage
Symptômes : Corps flottants, pluie de suie, baisse de vision brutale.Any blood in the vitreous cavity is known as vitreous hemorrhage (VH). one of the most common causes of sudden loss of vision (1) bleeding into the vitreous occurs whenever the sensory retina is torn. Of these, PCV is the condition most frequently associated with large . Abnormal vessels: Diabetic retinopathy – diabetes can damage the blood vessels supplying the retina, leading to growth of abnormal new and friable vessels that bleed .By definition, it is the presence of extravasated blood within a space lined by posterior lens capsule anteriorly, internal limiting membrane (ILM) .Vitreous hemorrhage refers to bleeding into the vitreous humor.
Vitreous Hemorrhage
This occurs when damage to the retinal blood vessels has occurred.
Haemorrhage
Vitreous hemorrhage is defined as the presence of extravasated blood in the vitreous cavity between the posterior lens .Vitreous hemorrhages happen when your retina bleeds into the vitreous cavity in your eye.A vitreous hemorrhage is bleeding into the thick fluid that fills the center of the eye. According to the American National Cancer Institute, the vitreous humour is the substance that fills the eyeball which is clear and jelly-like in texture. In our study, proliferative diabetic retinopathy accounted for 36.
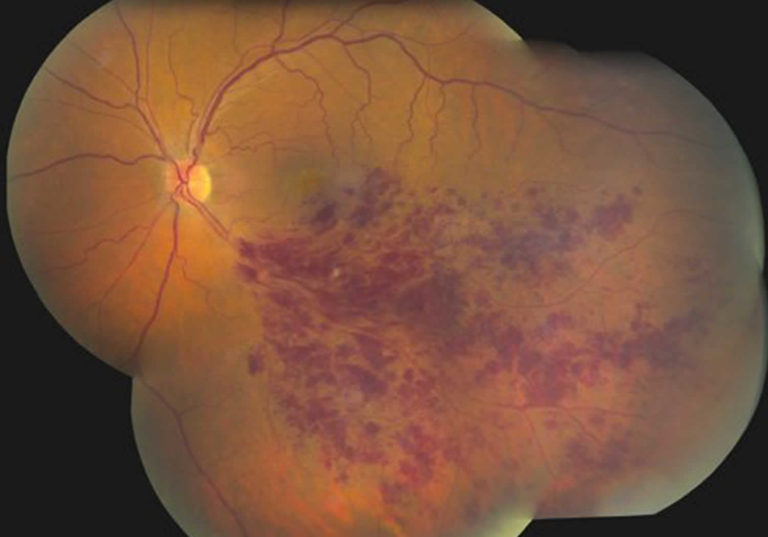
Clinical presentation.Vitreous hemorrhage is the presence of blood in the vitreous humor. Both eyes can be affected. The most common . : +33 3 83 96 21 76 - Fax : +33 3 83 97 24 56
Safety profile and surgical outcomes of early vitrectomy in
” Visual acuity ranges from 20/20 (6/6) to light perception. Contact an eye doctor immediately if you're experiencing a rapid onset of blurriness or loss of vision. However, complications such as increased intraocular . These can be grouped into causes relating to bleeding from abnormal or normal vessels. RDs and retinal tears are, arguably, the most concerning cause of spontaneous vitreous hemorrhage because of the increased risk of permanent visual loss if not treated appropriately and in a timely manner. Having blood in the vitreous gel can keep light from reaching your retina. First Online: 23 July 2021. Haemorrhage may occur into a body cavity or organ, into tissues such as muscles, or externally by way of a wound. A small amount causes blurring of the vision.Vitreous hemorrhage is the extravasation of blood into one of the several potential spaces formed within and around the vitreous body. Traction at its attachments at the ora serrata and optic disc can result in bleeding. vitreous haemorrhage. Because the retina is critical for vision, even small injuries and minor bleeding can lead to vision problems such as blurred vision, blind spots, or perceiving streaks and lines.Vitreous hemorrhage is defined as the presence of extravasated blood within the space outlined by the zonular fibers and posterior lens capsule anteriorly, the nonpigmented epithelium of the ciliary body laterally, and the internal limiting membrane of the retina (lamina limitans interna) posteriorly and posterolaterally. Often the blood vessels affected are .Causes of vitreous hemorrhage include retinal tear (with or without detachment), diabetic or sickle cell retinopathy, retinal vein occlusion, retinal vasculitis, neovascular age-related . This may result in obscuration of the fundus view in severe cases. By definition, it is the presence of extravasated blood within a space lined by posterior lens . Submacular hemorrhage (SMH) is an uncommon complication of choroidal or retinal vascular abnormalities, including choroidal neovascularization (CNV), polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy (PCV), and retinal macroaneurysm.Definition of major haemorrhage. L'humeur vitrée est le gel clair qui remplit .
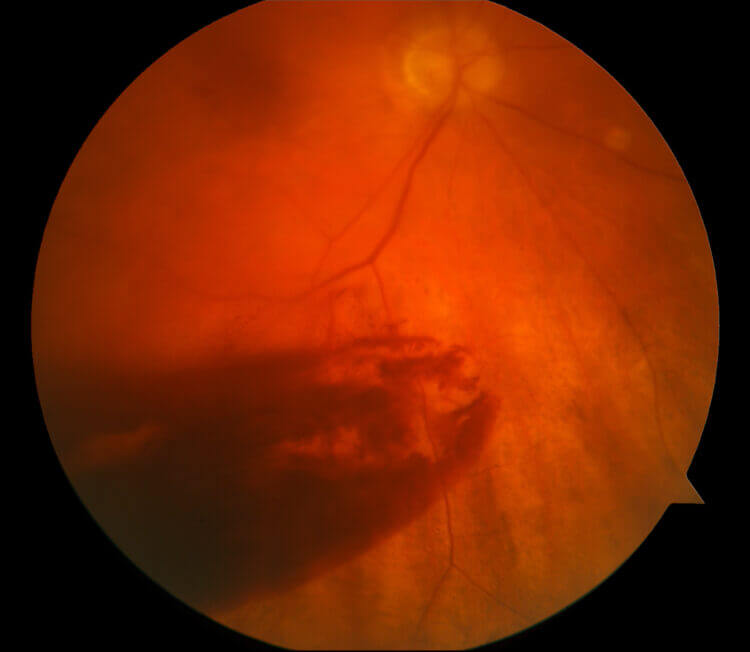
Vitreous hemorrhage has an incidence of approximately 7 in 100,000 1,2. The normal human blood volume in an adult is 65-70ml/kg; therefore a 70kg male has a blood volume of approximately 5000ml - a 50% loss is approximately 2500ml. It could occur either because of trauma or in association with systemic illness, or . Vitreous haemorrhaging refers to bleeding in the vitreous cavity.
GGC Medicines
Retinal vein occlusion (RVO) guideline: executive summary
The eye is not inflamed, red, or painful, and clues to diagnosis are inability to see fundus details or localized collection of blood in .
L'hémorragie intra-vitréenne
If vitreous haemorrhage precludes a view of the fundus, then transcleral diode therapy and retinal cryotherapy can be used. urgent investigation is required as there may be a retinal detachment requiring early surgery.Vitreous haemorrhage occurs as a result of vitreous traction on any pre-retinal neovascular proliferation. The typical boat shape of subhyaloid hemorrhage may be noted. Retinal vein occlusion (RVO) is an obstruction of the retinal venous system by thrombus formation and may involve the central, hemi-central or branch retinal vein. Neovascularization .
Hémorragie vitréenne : symptômes, causes et traitement
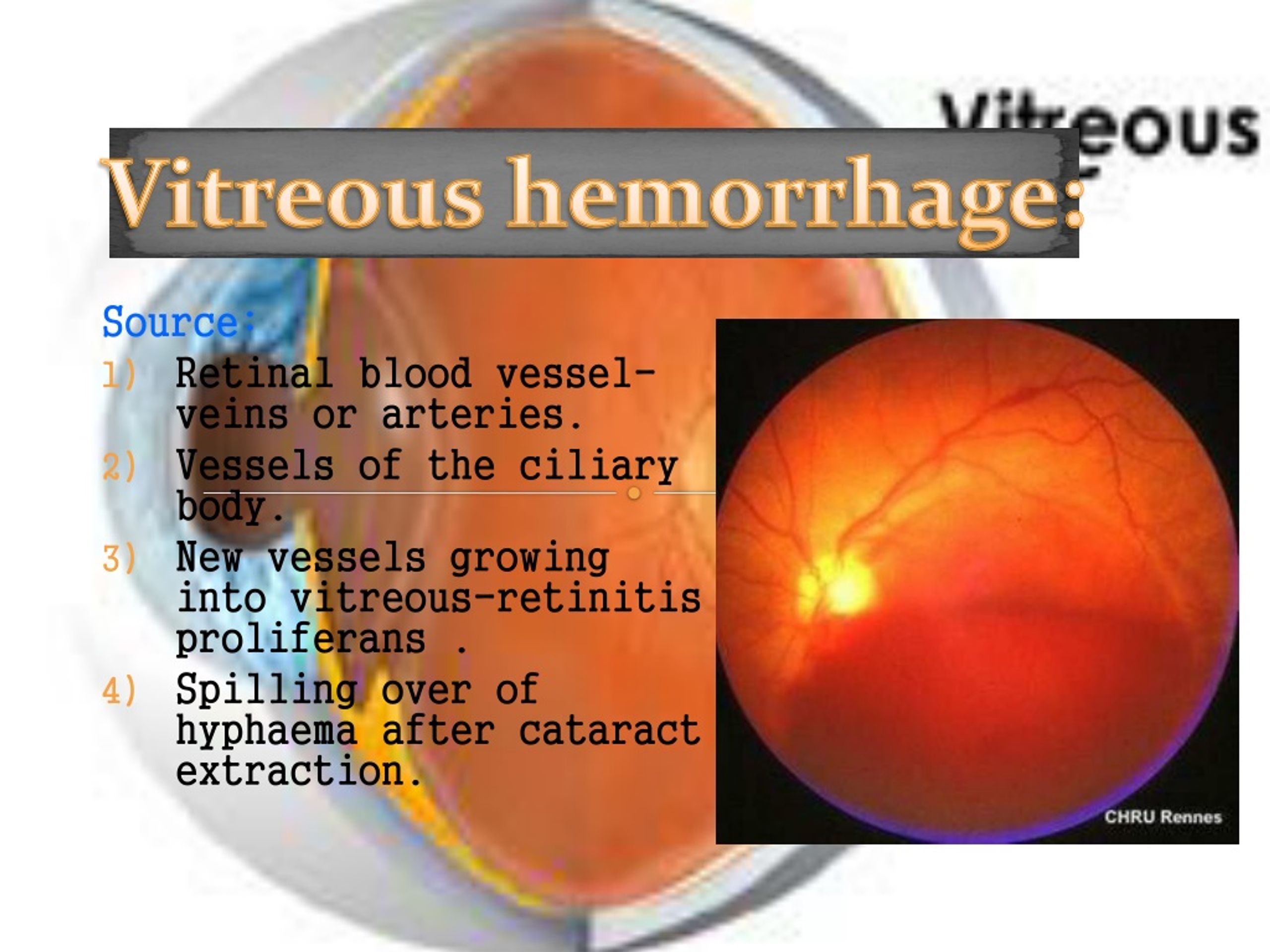
Bleeding can occur from any of the structures of the eye where there is a presence of vasculature.A posterior vitreous detachment (PVD) is a condition of the eye in which the vitreous membrane separates from the retina. Le sang dans le vitré obstrue la . They occur most commonly in young males [ 1 ].
Vitreous hemorrhage
Hémorragie du vitré.IJO_928_22
Hémorragie du vitré
When treated properly, they may not leave severe sequelae [ 2 ].