Vp shunt overdrainage

Patients with SVS may develop intracranial hypertension or hypotension in the setting of an under-functioning shunt or overdrainage from an overfunctioning shunt.Shunt overdrainage syndrome Shunt overdrainage is a condition with various clinical presentations, ranging from mild to very severe symptoms, often requiring multiple evaluations and admission in some cases.

Shunt overdrainage is a condition with various clinical presentations, ranging from mild to very severe symptoms, often requiring multiple evaluations and admission in some cases .Publiée : 2023/04/03Ventriculoperitoneal shunt complications in an adult population: A comparison of various shunt designs to prevent overdrainage - PMC. Current literature .Overdrainage of cerebrospinal fluid is one of the most notorious complications after ventriculoperitoneal shunt implantation.Critiques : 5,4K In this pathogenesis, shunt function is maintained. Various overdrainage-preventing devices have been invented to counteract the siphon effect. The clinical evaluation method disappeared or remained signs of overdrainage. Distended dural venous sinuses, which are of normal density.Case 3 had bilateral subdural hygromas and had insertion of shunt-assisted device (SAD) because of overdrainage syndrome 2 months prior to developing acute on chronic SDH. Q: Can hydrocephalus cause death? A: If left untreated, hydrocephalus can indeed lead to death.Complications including infection, shunt obstruction, overdrainage, cardiopulmonary events, renal dysfunction, and shunt revision were recorded. Modern gravitational valve technology from MIETHKE, which has proven its superiority in overdrainage prevention for VP-shunts, can now also be used for LP-shunts using the MIETHKE Valve Board (15, 20).Q: What are the symptoms of VP shunt overdrainage? A: Increased intracranial pressure, difficulty walking, decreases in appetite, incontinence, and headache are some of the symptoms of VP shunt overdrainage.The slit ventricle syndrome is intimately related with the entity of shunt over-drainage, although who's the definition of the former is implicated by a lack of universally accepted inclusion criteria.The interval to the appearance of overdrainage ranged from 0. The condition typically presents with postural headache as well as nausea, emesis, and irritability, exacerbated in an upright position and alleviated in a .The presence of a VP shunt expands the scope of differential diagnoses for periodic headaches and vomiting, even if the patient’s symptoms comply with the typical case definitions of CVS. Important problems exist relating to the real incidence of the entity, its definition, classification, and the pathophysiological theories behind the various treatment . Appearances suggest intracranial .The authors evaluated shunt surgery overdrainage complications in iNPH and their relationship to lumbar puncture opening pressure (LPOP).Sixty-four shunt-treated young hydrocephalus patients aged 1.

A ventriculoperitoneal shunt for hydrocephalus in patients with a skull defect may lead to excessive sinking at the craniectomy site as a result of the atmospheric pressure . Another point of controversy is related with the absence of widely accepted criteria that would be able to discriminate the existing differentiations .
Ventriculoperitoneal Shunts in the Emergency Department: A Review
overshunting-associated myelopathy.
Shunt Over-drainage, Slit Ventricle Syndrome, Programmable
Overdrainage (OD) is one of the most frequent complications related to drainage of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).A retrospective study in adult ventriculoperitoneal shunt patients with gravitational valves (GVs), Diesner et al analysed all available data, including the most recent computed tomography (CT) scans, to determine the best adjustments for alleviating any symptoms of overdrainage and underdrainage. What are the major . Also, contact the team if you have an abdominal infection including appendicitis, peritonitis, diverticulitis or other condition that requires emergency surgery or antibiotic treatment. This patient did not have a new CT scan following the addition of the SAD and prior to admission with the bleed.Recent reports have suggested that the evidence about overdrainage and its consequences is not so robust as presumed.intermittent ventricular isolation, in which one over drained ventricle collapses and occludes the shunt catheter resulting in under drainage of the contralateral ventricle.A complication of ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunting is overdrainage or overshunting of cerebrospinal fluid, which can cause formation of hygroma but in rare . HYDROCEPHALUS THERAPY LUMBOPERITONEAL SHUNT AS AN ALTERNATIVE. The first case of epidural hematoma after ventricular drainage was made in 1941 [ [6], [7], [8] ].Conclusions: The recent improvements in the quality of the LP shunt device and the proficiency of the procedure has made the LP shunt a safer procedure than the VP shunt.
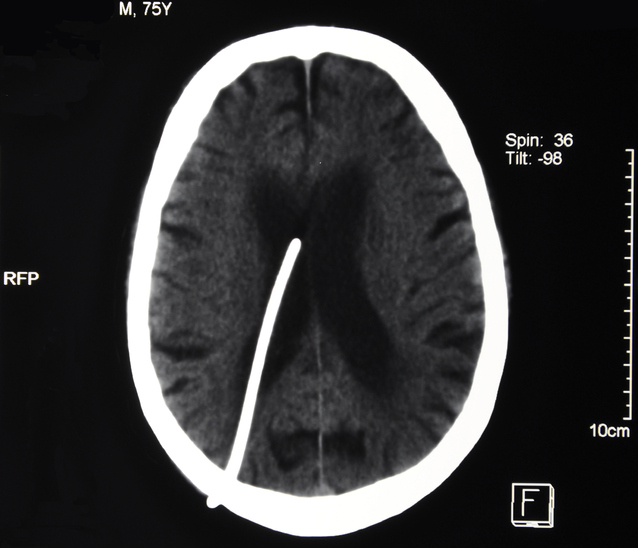
The shunt can also become blocked at the distal end if the shunt is pulled out of the abdominal cavity (in the case of VP shunts), or from similar protein buildup.This is due to early shunting through the VP shunt and overriding of the cranial sutures., programmable valves with fixed ASDs).5 to 8 years (mean 4.Surg Neurol 1991;35:200-12.VP shunt tapping is a controversial subject even within the neurosurgical literature due to concerns regarding infection and morbidity and mortality associated with it . The patients were treated with a diversity of procedures: revision of the CP drainage, replacement of the CP shunt, pressure upgrading of the existing valve, insertion of a programmable valve, and VP shunt or LP shunt insertion.5 years) suffering from clinical and/or radiological overdrainage underwent shunt revision surgery with the .Disccusion: The gravitational effect and the atmospheric pressure gradient effect are two factors associated in the ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt treatment of hydrocephalus for . Symptoms may also be subtle, change in behavior, change in school performance.
Hydrocephalus
In this paper, we review the indications, complications, and pitfalls associated with ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunts.
CSF overshunting and intracranial hypotension
[2, 4, 10, 14, 23, 25-27] Several studies have evaluated overdrainage rates with SC versus NSC in NPH patients with mixed results: some demonstrating increased overdrainage symptoms with no difference in SDH rates and others showing the opposite [2, 4, 9, 10, 16, 17, 25] The . trapped ventricle : after .VP-shunts (27). As most VP shunt problems initially .shunt overdrainage. The other seven cases had no evidence for subdural . The condition typically presents with postural headache as well as nausea, emesis, and irritability, exacerbated in an upright position . These occur sequen- tially at different age . The hydrostatic, gravitational force in the upright position can . Siphon effect plays a major role in the development of overdrainage.Other complications associated with VP shunts include surgery-related complications, shunt overdrainage and slit-ventricle syndrome, neoplastic metastasis, .We attempt to present an overview of this complex entity, emphasizing on the hydrodynamics of the cerebrospinal fluid circulation in conditions harboring a .In some cases, the shunt may result in overdrainage (low pressure) or underdrainage (high pressure) of CSF, causing a range of symptoms. Siphon effect plays a major . Slit-like 3 rd and lateral ventricles. In lumbo-peritoneal shunts this .Although shunt overdrainage is a well-known complication in hydrocephalus management, the problem has been underestimated.Selected literature review of the clinical course of patients with ventricular shunts for hydrocephalus shows that the effects of cerebrospinal fluid overdrainage are . With our procedural steps, the LP shunt can be used to decrease the .3% exposed shunt reservoir and 10% exposed distal catheter) followed by shunt obstruction .Special Considerations for Ventriculo-Peritoneal (VP) Shunt Notify your neurosurgery team before any abdominal surgery, so proper precautions can be discussed with your surgeon. Ever since, sporadic cases of . However, it's important to emphasize that these figures are estimates and can differ significantly depending on individual circumstances and the chosen healthcare . Consequently, the topic requires more .Background
Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt
intracranial peri-shunt fluid collection with edema 3.

A ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt is a cerebral shunt that drains excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) when there is an obstruction in .
Ventriculoperitoneal shunt
For further understanding on abdominal pain and VP shunts, consider watching our Ask .Subdural fluid collection in patients with internal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) shunts has generally been linked to overdrainage and more rarely to pus accumulation.Overdrainage after ventriculoperitoneal shunting in a patient with a wide depressed skull bone defect: The effect of atmospheric pressure gradient - PMC.Ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt in situ. Other causes of blockage are overdrainage and slit ventricle syndrome. Chronic shunt overdrainage may have a similar clinical presentation to CVS but is significantly underdiagnosed in patients with ventricular . The goal was to transform this fixed differential pressure valve into a valve with both a pressure-controlled and flow-regulated valve. No other treatment was associated with this technique.A shunt is said to have failed when any complication of the treatment of hydrocephalus requires surgery.On average, patients considering VP shunt surgery in Philippines might anticipate costs falling within the range of approximately $10,000 to $30,000 USD or potentially higher.In ventriculo-peritoneal shunts this gradient generates distal negative pressure caused by the fluid column in peritoneal drain. noncompliant ventricles due to periventricular gliosis (stiff ventricle), which is unable to adapt to shunt malfunction (underdrainage), leading to intraventricular .Shunt overdrainage in patients with hydrocephalus still represents a challenge for neurosurgeons, in part due to the lack of agreement or uniformity concerning the entity. This translates to a risk .
LUMBOPERITONEAL SHUNTS
Background: Overdrainage after cerebrospinal fluid diversion remains a significant morbidity. Asante, Bradley Danie.Epidural hematomas are an unusual complication of ventriculoperitoneal shunt in the treatment of chronic hydrocephalus and are much less common than post shunting subdural hematomas [ [5], [6], [7] ].
Surgical Neurology International

Ventriculoperitoneal shunt overdrainage
ventriculoperitoneal
Methods: The authors reviewed the charts of 164 consecutive patients with iNPH who underwent shunt surgery at their institution from 2005 to 2011. Though some of the devices are designed to reduce the . It is mostly associated with valve-bearing .curatively in case of overdrainage during a shunt revision.
Overdrainage Syndromes in Shunted Arachnoid Cysts
They noted age, sex, presenting symptoms, symptom .

Selected literature review of the clinical course of patients with ventricular shunts for hydrocephalus shows that the effects of cerebrospinal fluid overdrainage are subdural hematoma, craniosynostosis, slit ventricle syndrome, and low intracranial pressure syndrome.Literature overdrainage complication rates range from 3 to 50%.






-est-sorti-de-la-prison-de-mulhouse-hier-en-debut-de-soiree-accompagne-de-m-e-pierre-schultz-l-un-de-ses-avocats-photo-vincent-voegtlin-1599117670.jpg)