West syndrome prognosis

West syndrome: a comprehensive review
Dans la majorité des cas . Infantile spasms .4% of the epileptic syndromes in pediatric age.West syndrome is a rare neurological syndrome that can affect males and females.Purpose: Nearly half of all patients with seizure onset in the first year of life suffer from West syndrome (WS).Long-term prognosis of 150 cases of West syndrome Long-term prognosis of 150 cases of West syndrome Long-term prognosis of 150 cases of West syndrome Epilepsia. Social Support* Spasms, Infantile / psychology* Spasms, Infantile / therapy* West syndrome (WS) is commonly associated with a poor long-term outcome including a . 12 have reported that the prognosis of idiopathic West syndrome is better as compared with symptomatic infantile spasms, whereas Matsuo et al. We report a girl with West syndrome associated with Down syndrome revealed at 8 months of age for repetitive .3 per 1,000 patient‐years. The present case was diagnosed as a symptomatic form of West syndrome as a history of maternal . The prognostic consequences of WS have been related to various parameters, such as eti-ology, premorbid . West syndrome is generally not life-threatening but it occurs more often in children with life-threatening conditions.
Evaluation of the outcome of West syndrome (WS) highlights two important clinical features; seizure and developmental outcome [1–4].
West Syndrome and the new classification of epilepsy
West syndrome is a multi-etiological condition.Many studies have addressed the natural history and prognosis of West syndrome, but outcome figures differ widely among them [79].Infantile spasms, or West syndrome, is a rare condition marked by subtle seizures in a baby, usually within their first year of life.
Infantile Spasms (West Syndrome)
WS was first described by occursDr.

Infantile epileptic spasms syndrome (IESS) has been reclassified to include patients who do not meet the full West syndrome criteria. Les spasmes tendent à .An additional, and fourth search included the MeSH terms “West syndrome” OR “infantile spasm syndrome” AND “therapy/treatment” (8169–9487; 1022–1180 .Keywords Infantile spasm West syndrome Prognosis Seizure Development Etiology Introduction Evaluation of the outcome of West syndrome (WS) high-lights two important clinical features; seizure and devel-opmental outcome [1–4]. The seizures occurred in clusters of up to 20 spasms in 3 min, .
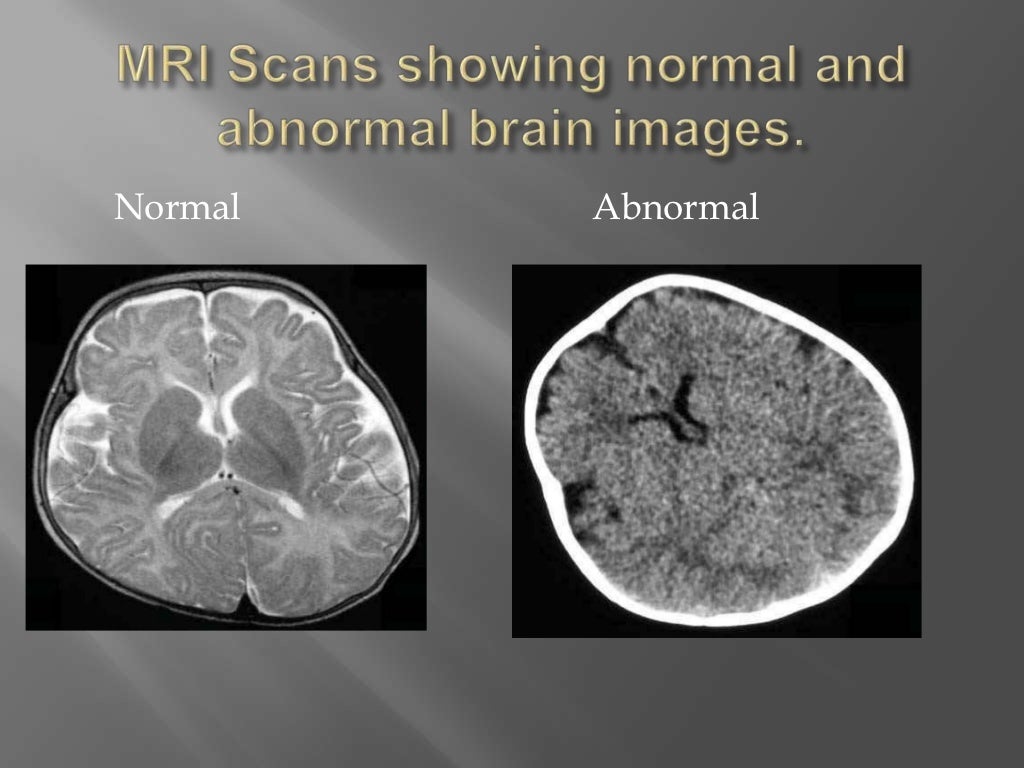
Auteur : Betül Tekin Güveli, Özlem Çokar, Nimet Dörtcan, Gülçin Benbir, Veysi Demirbilek, Ayşın Dervent
Le syndrome de West
The mean overall annual mortality rate was 15., the human chromosomes 1-22) in which a trait manifests in individuals with two pathogenic alleles, either homozygotes (two copies of the same mutant allele) or compound heterozygotes (whereby each copy of a gene has a .Whereas children with uncomplicated epilepsy are not at higher risk of death than the general population, the mortality risk is many‐fold higher in complicated epilepsy.Among the epilepsy syndromes, West syndrome (WS), a malignant epilepsy syndrome defined on the basis of infantile spasms and hypsarrhythmia on the EEG [1], [2] (with or without accompanying developmental delay), is recognised to have a very poor long-term prognosis in terms of spasm control, freedom from other seizure types, .
Manquant :
prognosisLong‐term mortality of patients with West syndrome
West syndrome is often associated with poor long-term prognosis in most of children. It had perinatal aetiology in 76.Although West syndrome is regarded as one of intractable epilepsies, the prognosis differs widely according to etiology. 1973 Jun;14(2):153-64.
West Syndrome (Infantile Spasms)
Keywords: syndrome, spasms, infantile, epileptic encephalopathy, etiology, prognosis INTRODUCTION West syndrome Such(WS) is the most severe, devastating and/or catastrophic epileptic encephalopathy during the lactation period. Changes in sleep patterns, such as sleeping more . As clinical, electroencephalographic and therapeutic aspects of this syndrome have recently been reviewed 2, 3, this article deals with its etiological and prognostic aspects. From a general standpoint, idiopathic forms have a better seizure control and developmental outcome than cryptogenic or symptomatic subtypes. Around 70% of children with West syndrome will have their spasms fully controlled through the use of AEDs or other treatments.During follow‐up, 102 (49%) of 207 patients had died at the mean age of 19 years. Characteristics include: Epileptic spasms. Explore all metrics.The West syndrome is an epileptic encephalopathy in the child's first year of life, corresponding to 1.West syndrome (WS) is commonly associated with a poor long-term outcome including a small but significant mortality, infantile spasms that are resistant to treatment, . Children with West syndrome may have other symptoms such as: Crankiness.Clinical characteristics and prognosis of pulmonary renal syndrome in West China. It affects both sexes, with a higher . The prognosis of epilepsy and psychosocial outcomes in .Le syndrome de West touche plus fréquemment les garçons que les filles.[2] The syndrome is aptly named .Infantile spasms, also known as West Syndrome, is a severe infantile epilepsy syndrome with a characteristic age of onset (2-14 months), pattern of seizures and .Sometimes, they don’t happen in clusters at first. Sign in | Create an account.The prognosis of West syndrome depends on the underlying etiology, and possibly on the rapidity of response to treatment. PMID: 4515986 . l A quoi est-il dû ? Les causes du syndrome de West peuvent être diverses. Lennox from Boston, United States, described the characteristic electroencephalogram (EEG) features of this condition.
Manquant :
prognosis Published in Epilepsia 1 June 1973. Hongwen Zhao 2 Show authors.Infantile Spasms (West Syndrome): Symptoms, Causes, & More
The X-linked form of West syndrome affects males more often than females.West syndrome is a devastating disorder characterized by a triad of epileptic spasms, abnormal electroencephalography (EEG), and developmental arrest or .Long‐term Prognosis of 150 Cases of “West Syndrome”.Le pronostic est très variable et dépend des causes sous-jacentes des spasmes, qui peuvent être multiples. West syndrome may follow other epileptic encephalopathies of earlier onset, such .Ten prognostic factors possibly affecting the outcome of West syndrome including (1) gender, (2) age at the onset (3) presence of seizures prior to spasms, (4) presence of asymmetric spasm, (5) presence of abnormal neurological signs, (6) treatment lag, (7) etiology, (8) drug chosen as the initial treatment, (9) response to initial treatment . As clinical, electroencephalographic and .

This study was performed to examine the factors influencing the outcome of this patient population.
Infantile Epileptic Spasms Syndrome (West Syndrome)
West syndrome is a severe epilepsy syndrome composed of the triad of infantile spasms, an interictal electroencephalogram (EEG) pattern termed .5% of the patients, prenatal in 21%, and postnatal in 2. The West's syndrome was idiopathic in four children and symptomatic in 38 children (90. A mode of inheritance that is observed for traits related to a gene encoded on one of the autosomes (i.Nearly half of all patients with seizure onset in the first year of life suffer from West syndrome (WS). Complete seizure control was achieved . He reported the first . It is characterized by the triad: 1) epileptic spasms, 2) hypsarrhythmic tracing on the electroencephalogram (EEG) and 3) neurodevelopment regression.
Infantile Spasms Syndrome (West Syndrome)
West syndrome: Long-term prognosis and social aspects
According to the literature, 2, 3 the mortality varied widely between 3% and .West's syndrome--etiology, treatment and prognosis.

Differences in prognosis may be due to variation among studies in the length of follow-up, the relative proportion of different etiological groups, treatment status, and in criteria used to define normality or . The International League Against Epilepsy commission classifies the aetiologies of WS into genetic, structural, metabolic . Il peut entraîner de graves séquelles motrices et intellectuelles et .Auteur : Richard E Appleton
West Syndrome: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Life Expectancy
Authors P M Jeavons, B D Bower, M Dimitrakoudi. Thirty‐three children had died, nearly all of the rest were 5 yr old or more. Furthermore, the treatments used . Infantile spasms is a seizure .Le pronostic est lié à l’étiologie et à la rapidité de mise en route du traitement. West syndrome (WS), also known as infantile . Henri Gastaut in Marseille, France in 1966. Spasms, neurodevelopmental regression and hypsarrhythmia on electroencephalogram (EEG) basically define WS.Infantile spasms has been known by many names over the years, including salaam attacks, salaam convulsions, generalized flexion epilepsy syndrome, Blitz-Nick-Salaam-Krämpfe, eclampsia nutans, flexion spasm, infantile spastic epilepsy, jackknife convulsion syndrome, jackknife spasm, massive myoclonia syndrome, and nodding spasms .Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (LGS) is a rare but severe form of childhood epilepsy that was first described by Dr.
West syndrome: long-term prognosis and social aspects
Since its first clinical description (on his son) by William James West (1793–1848) in 1841, and the definition of the classical triad of (1) infantile spasms; (2) hypsarrhythmia, and . Recent progress in perinatal medicine and the recent development of new neuroimaging techniques may have changed the etiological panorama of West syndrome.West syndrome (WS), also known as infantile spasms, occurs in infancy with a peak between 4 and 7 months. Children with infantile spasms, 104 boys and 46 girls, were followed up; 105 received steroids. Despite the heterogeneous nature of causes of infantile spasms, a careful diagnostic evaluation can lead to diagnosis in many patients and may guide treatment choices. While the seizures may be subtle, they can have serious . A Letter to the Editor to this article was published on 19 March 2018.The prognostic consequences of WS have been related to various parameters, such as etiology, premorbid neurological status, gender, age at onset of WS, type of spasm, treatment lag, type of treatment and .

The prognosis of epilepsy and psychosocial outcomes in children with WS are variable.West syndrome, or infantile spasms syndrome is a frequently catastrophic infantile epileptic encephalopathy with a variety of etiologies.

Loss of appetite.An epileptic spasm is a specific type of seizure seen in an epilepsy syndrome of infancy and childhood often called West Syndrome.












