What are the two functions of bile
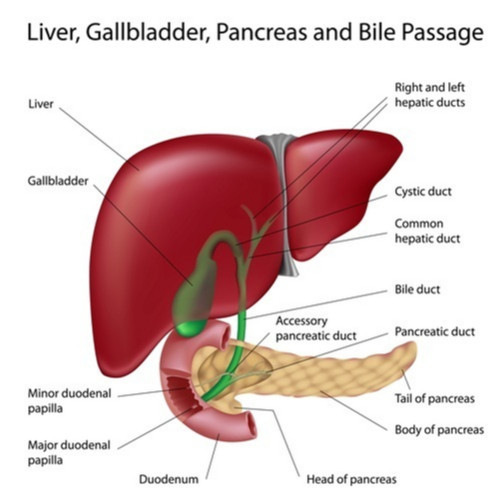
Your biliary tract plays an important role in your digestive system.
Bile acids (also called bile salts) Bilirubin (a breakdown product or red blood cells) It also contains:
Biliary System: Anatomy and Functions
What Bile Is Made of
Physiology, Bile
The alkaline properties of bile allow for this to occur.The biliary system refers to bile production, storage, and secretion via the liver, gallbladder, and bile ducts. The bile is composed of ~95% water, which has dissolved solid constituents such as bile salts (0. The presence of bile in the intestine helps the digestion and absorption of fats and the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E and K. They are necessary for the digestion and absorption of fats. Bile is made in the liver and stored in the gallbladder.
Functional, Diagnostic and Therapeutic Aspects of Bile
Bile is the greenish-yellow fluid (consisting of waste products, cholesterol, and bile salts) that is secreted by the liver cells to perform 2 primary functions: To carry away waste To break down fats during .
Gallbladder and Biliary Tract
Recycling of the bile. The gallbladder releases the bile into the duodenum, a part of .Fat Digestion: A key function of the liver in the digestion of fats. It acts to emulsify fats, breaking large fat globules into smaller ones. About 400 to 800 milliliters of bile is produced per day in the adult citizenry. This particular flow is known as the bile salt-dependent flow or BDSF. When these two pigments are mixed, they are liable for the brown color of feces. This is a detergent-like action of bile that helps the body to absorb the broken-down fat products in the gut.In sum, the three main functions of bile acids are to (1) emulsify fat, (2) excrete cholesterol, and (3) have an antimicrobial effect.51%) such as cholesterol, fatty acids and lecithin, inorganic salts, vitamins and environmental toxins. Working together with bile salt-independent flow (BSIF), these mechanisms enable .bile, greenish yellow secretion that is produced in the liver and passed to the gallbladder for concentration, storage, or transport into the first region of the small intestine, the duodenum.Biliary System Anatomy and Functions | Johns Hopkins .7%), bilirubin (0. Tiny canals called bile ducts connect your liver, gallbladder and pancreas to your duodenum, the top of your small intestine.Some of the more well-known functions include the following: Production of bile, which helps carry away waste and break down fats in the small intestine during digestion. Bile is essential for the .orgBiliary System Anatomy and Functions - Verywell Healthverywellhealth. Bile salts aid in digestion by making cholesterol, fats, and fat-soluble vitamins easier to absorb from the intestine.
What Bile Is, Where It's Made, and What It Does
The pathway initiated by CYP7A1 is referred to as the “classic” or “neutral” pathway of bile acid synthesis.
What Is Bile?

Bile salts, also called bile acids, are a major constituent of bile. Bile is formed initially in the hepatocyte (liver cell), and the rate of formation is dependent primarily on the rate at which bile acids are secreted into the bile channels, or canaliculi.
3 Major Functions of Bile
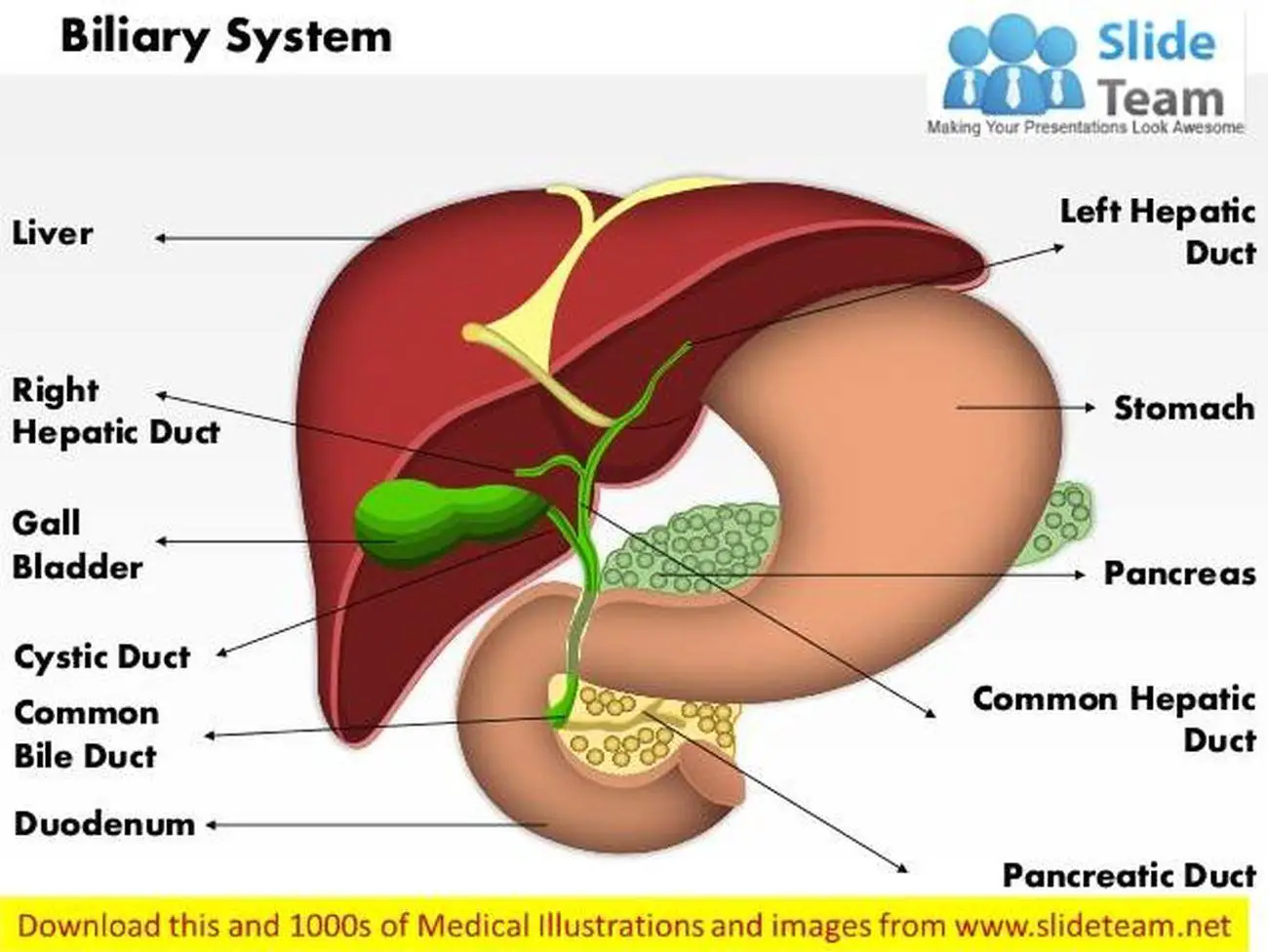
The biliary system, also called the biliary tract or biliary tree, is a system of ducts, organs, and associated structures that function to .Your biliary tract, or biliary system, is the network of organs and vessels that make, store and transfer bile through your body.
Bile: Role, Properties and Functions
It is produced in the liver and is stored in the gallbladder. Bile is formed initially in the hepatocyte (liver cell), and the .
Gallbladder: What Is It, Function, Location & Anatomy
Role of Bile in the Process of Digestion.
Biliary System Anatomy and Functions
Human digestive system - Bile, Enzymes, Absorption: The primary digestive function of bile is to aid in the dispersion and digestion of fat in the lumen of the small intestine.
Metabolism: The liver metabolizes carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the blood that are initially processed during digestion.
Bile: Anatomy, Function, and Associated Diseases
They have a mild purgative action. Bile, which is excreted from the body in the form of stool (feces . Action of bile salts in digestion. The pancreas produces biological catalysts called digestive enzymes which speed up the digestive. The liver secretes bile or gall that acts .Bile has two main roles: Neutralising the hydrochloric acid from the stomach. In connection with this, bile salts bind with lipids to form micelles. Miscellaneous pathways, in addition to these two, include those started . Bilirubin is a waste product that is formed . It delivers bile and pancreatic enzymes to your duodenum . Bile is a physiological aqueous solution produced and secreted by the liver. Intrahepatic bile ducts include the left and right hepatic ducts, which join to form the common hepatic duct (CHD), while extrahepatic bile ducts include the . Bile salts function not only as a lipid emulsifying agent but help to regulate the flow of bile from the liver into the bile capillaries (bile canaliculi) by way of osmosis. In the small intestine, bile helps in the emulsification of fats. Bile is a fluid your liver makes that helps digest your food.
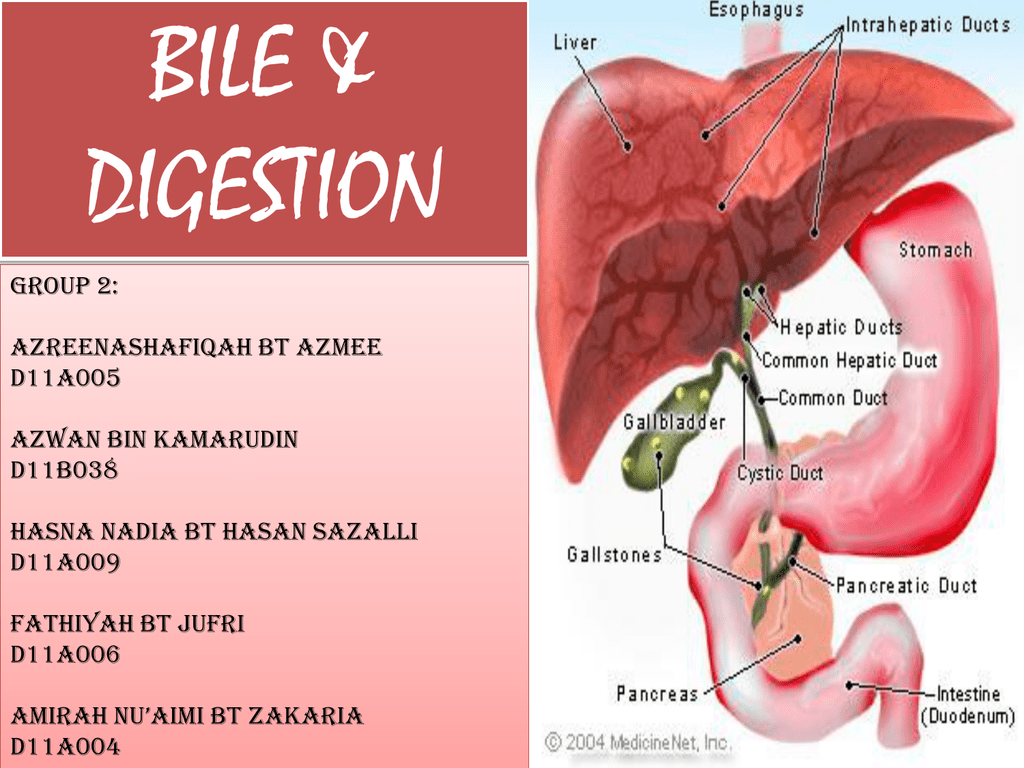
It makes up part of the long pathway that food takes through your body, called the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Expression of CYP7A1 occurs . They activate pancreatic lipase and help in emulsification of food fats and their absorption in the intestine. Functions of Bile: a.Bile Salts Function. Bile: Micrograph of bile (yellow material) in a liver biopsy. bile: A bitter, brownish-yellow or greenish-yellow .Its function is to aid in the digestion of fats in the duodenum. Bile ducts are categorized into intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts. It is stored in the gallbladder. They are made from cholesterol in the liver. This is then absorbed through the intestinal mucosa.The bile duct is a small channel (tube) through which bile from the liver is delivered into the duodenum.Other functions of bile acids include removing the body's cholesterol, powering bile flow to remove various metabolites . Bile or gall acts to some extent as a surfactant, helping to emulsify the lipids in food.Bile is a liquid that helps your body digest food and eliminate toxins.
The liver: Structure, function, and disease
comRecommandé pour vous en fonction de ce qui est populaire • Avis
Biliary System Anatomy and Functions
Temps de Lecture Estimé: 9 min
Physiology, Biliary
Its endocrine function involves the release of insulin and glucagon into the bloodstream, two important hormones . Bile is composed of bile acids and salts, phospholipids, cholesterol, pigments, water, and electrolyte . What is apart of the endocrine functions?Bile is a fluid that is made and released by the liver and stored in the gallbladder.The gallbladder's main function is to store bile, a fluid that helps with digestion.What are the two main functions of the pancreas? - secretes enzymes.The small intestine is part of your digestive system. Bile contains: Mostly cholesterol.Bile is made up of bile acids, cholesterol, phospholipids, bile pigments (such as bilirubin and biliverdin), electrolytes and water. The pancreas is a unique organ because it fulfills both exocrine and endocrine roles. To help in digestion with the controlled release of bile.Bile is a digestive product made by the liver.39 Cholesterol solubility in the bile depends on two variables: bile salt-lecithin ratio and the total lipid ((bile salts + lecithin + cholesterol) concentration in the bile. Below are the important functions of bile.Bile has two main functions: Bile. The hepatocytes secrete bile . It breaks down fats into fatty acids, which can be taken into the body by the digestive tract. Small intestine Where food is mixed with digestive enzymes and bile and digested food is absorbed into the blood.Bile is the greenish-yellow fluid (made of waste products, cholesterol, and bile salts) that is secreted by the liver cells to do these two main functions: Carry away waste.The liver produces bile, which helps the digestion of lipids (fats and oil). Where is the gallbladder located? - Exocrine functions (acinar cells) - Endocrine functions (islet of langerhan) What is 98% of the pancreas made of? - Acinar cells.Bile’s main job is to help your body digest the fats you eat. Synthesis of the two primary bile acids, cholic acid (CA) and chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA). Bile salt is the actual component that helps break down and absorb fats.Bile, which is alkaline, also has the function of neutralizing any excess stomach acid in the small intestine. The biliary ducts combine to form the left and right hepatic ducts, which in turn combine to form the common hepatic duct. Bile salts help to lower the surface tension of water and thus emulsify fats in the intestine and dissolve fatty acids and water-insoluble soaps.
What is the function of bile?
- makes insulin. Bile helps with digestion. It is transported into the duodenum section of the small intestine through the common bile duct. The lithogenic .
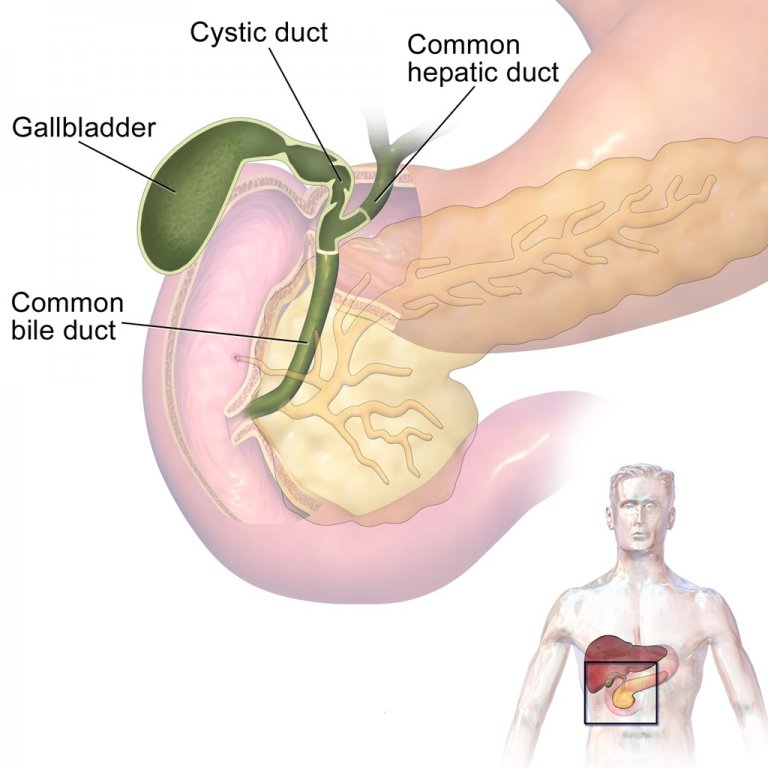
Read on to find out about its anatomy, function, and associated diseases. The reaction catalyzed by the 7α-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) is the rate limiting step in bile acid synthesis. They keep cholesterol in solution in the bile.Bile is an aqueous, alkaline, greenish-yellow liquid whose main function is to emulsify fats in the small intestine and to eliminate substances from the liver. Bile: The greenish-blue coloured fluid produced by the liver is called bile. Bile is composed of bile acids and salts, phospholipids, cholesterol, pigments, water, and electrolyte chemicals that . Break down fats during digestion.The bile is composed mainly of water and electrolytes and other substances which include bile salts, cholesterol, bilirubin, lecithin, amino acids, drugs, toxins, heavy metals, and vitamins. It sits just under your liver. Bile leaves the liver via biliary ducts continuously and is stored in the gall bladder until needed.The biliary system's main function includes the following: To drain waste products from the liver into the duodenum.hopkinsmedicine. most of the functions .Hepatocytes store glucose obtained from the . Functions of Bile.Bile becomes lithogenic when the bile gets supersaturated with cholesterol either due to hypersecretion of biliary cholesterol or decreased bile acid output.
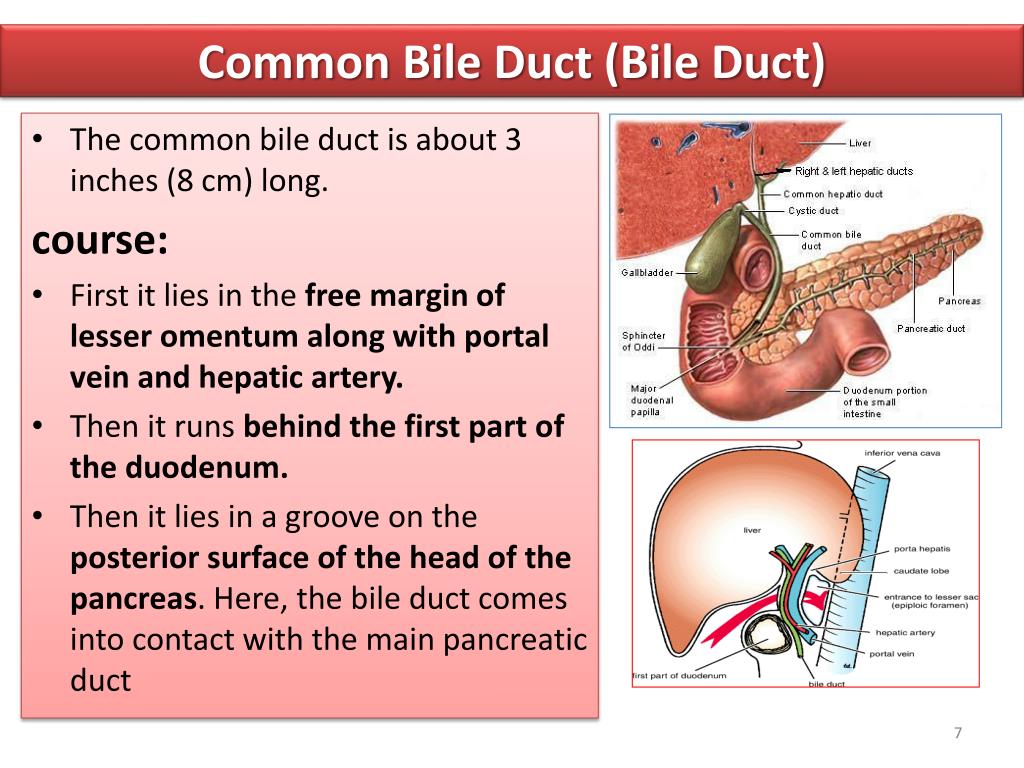
Its main function is to convert fats in food into fatty acids, which are absorbed in the gut. When food leaves your stomach, it enters the small intestine, also called the small bowel. The green and yellow colour of the bile is achieved from the two pigments biliverdin (oxidised form . Bile is the greenish-yellow fluid (made of waste products, cholesterol, and bile salts) that is secreted by the liver cells to do these two main functions: Carry away waste.
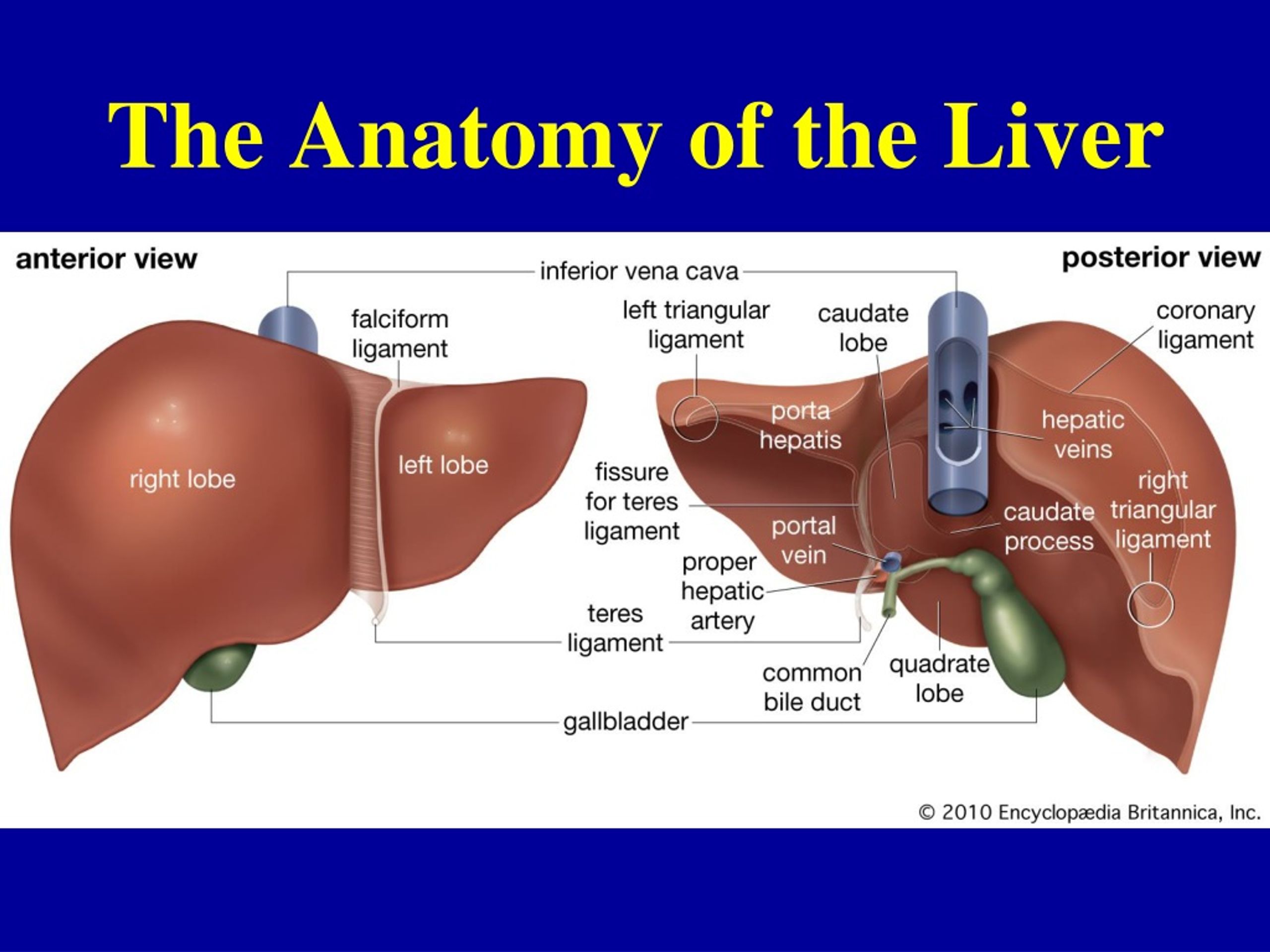
Conjugated bile salts are those that form amide bonds with amino acids.Explain the function of bile: Bile is a fluid made up of cholesterol, bile salts, bilirubin, water, and bicarbonate ions.The two main pigments of bile are bilirubin, which is orange-yellow, and its oxidized form is biliverdin, which is green in color. Its exocrine function includes the synthesis and release of digestive enzymes into the duodenum of the small intestine.The primary digestive function of bile is to aid in the dispersion and digestion of fat in the lumen of the small intestine. Eliminating certain waste products (mainly hemoglobin and excess cholesterol) from the body. When you start eating, the gallbladder contracts .The major functions of the liver include: Bile production: Bile helps the small intestine break down and absorb fats, cholesterol, and some vitamins. Bilirubin is the main pigment in bile.









